Competitive sgRNA Screen Identifies p38 MAPK as a Druggable Target to Improve HSPC Engraftment
Abstract
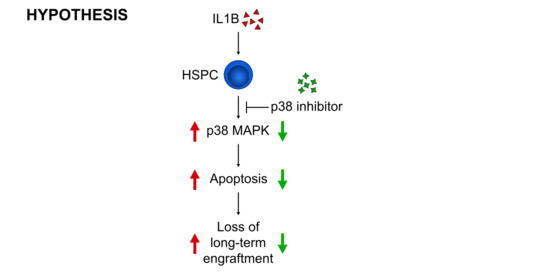
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Lentiviral Vectors and Vector Production
2.3. Bone Marrow Transplantation
2.4. Next Generation Sequencing
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Colony-Forming Unit (CFU) Assay
2.8. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Targeted Competitive sgRNA Screen Identifies Candidate Genes That Increase the Repopulating Capacity of HSPCs
3.2. p38 Knockout HSPCs Significantly Outcompete Their Competitor Cells in a Bone Marrow Transplantation Assay
3.3. p38 Is a Druggable Target That Improves the Engraftment of HSPCs from IL1B-Challenged Donor Mice
3.4. Inhibition of p38 Increases the Engraftment of HSPCs Derived from the X-CGD Mouse Model
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, E.; Jaishankar, G.B.; Saleh, H.; Jithpratuck, W.; Sahni, R.; Krishnaswamy, G. Chronic granulomatous disease: A review of the infectious and inflammatory complications. Clin. Mol. Allergy CMA 2011, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van den Berg, J.M.; van Koppen, E.; Ahlin, A.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Bernatowska, E.; Corbeel, L.; Espanol, T.; Fischer, A.; Kurenko-Deptuch, M.; Mouy, R.; et al. Chronic granulomatous disease: The European experience. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babior, B.M. NADPH oxidase: An update. Blood 1999, 93, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, E.P.; Lu, H.; Jacobs, H.L.; Messina, C.G.; Bolsover, S.; Gabella, G.; Potma, E.O.; Warley, A.; Roes, J.; Segal, A.W. Killing activity of neutrophils is mediated through activation of proteases by K+ flux. Nature 2002, 416, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, D. The genetic basis of chronic granulomatous disease. Immunol. Rev. 1994, 138, 121–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güngör, T.; Chiesa, R. Cellular Therapies in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, C.A.; Shah, S.; Shearer, W.T.; Rosenblatt, H.M.; Paul, M.E.; Chinen, J.; Leung, K.S.; Kennedy-Nasser, A.; Brenner, M.K.; Heslop, H.E.; et al. Excellent survival after sibling or unrelated donor stem cell transplantation for chronic granulomatous disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soncini, E.; Slatter, M.A.; Jones, L.B.; Hughes, S.; Hodges, S.; Flood, T.J.; Barge, D.; Spickett, G.P.; Jackson, G.H.; Collin, M.P.; et al. Unrelated donor and HLA-identical sibling haematopoietic stem cell transplantation cure chronic granulomatous disease with good long-term outcome and growth. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, D.B.; Booth, C.; Kang, E.M.; Pai, S.-Y.; Shaw, K.L.; Santilli, G.; Armant, M.; Buckland, K.F.; Choi, U.; De Ravin, S.S.; et al. Lentiviral gene therapy for X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.; Ott, M.G.; Schultze-Strasser, S.; Jauch, A.; Burwinkel, B.; Kinner, A.; Schmidt, M.; Krämer, A.; Schwäble, J.; Glimm, H.; et al. Genomic instability and myelodysplasia with monosomy 7 consequent to EVI1 activation after gene therapy for chronic granulomatous disease. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ott, M.G.; Schmidt, M.; Schwarzwaelder, K.; Stein, S.; Siler, U.; Koehl, U.; Glimm, H.; Kühlcke, K.; Schilz, A.; Kunkel, H.; et al. Correction of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease by gene therapy, augmented by insertional activation of MDS1-EVI1, PRDM16 or SETBP1. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, M.; Hakkim, A.; Brinkmann, V.; Siler, U.; Seger, R.A.; Zychlinsky, A.; Reichenbach, J. Restoration of NET formation by gene therapy in CGD controls aspergillosis. Blood 2009, 114, 2619–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grez, M.; Reichenbach, J.; Schwäble, J.; Seger, R.; Dinauer, M.C.; Thrasher, A.J. Gene therapy of chronic granulomatous disease: The engraftment dilemma. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2011, 19, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.A.; Gray, D.; Lomova, A.; Kohn, D.B. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Gene Therapy: Progress and Lessons Learned. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 574–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weisser, M.; Demel, U.M.; Stein, S.; Chen-Wichmann, L.; Touzot, F.; Santilli, G.; Sujer, S.; Brendel, C.; Siler, U.; Cavazzana, M.; et al. Hyperinflammation in patients with chronic granulomatous disease leads to impairment of hematopoietic stem cell functions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 219–228.e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, L.; Lin, K.K.; Boles, N.C.; Yang, L.; King, K.Y.; Jeong, M.; Mayle, A.; Goodell, M.A. Less is more: Unveiling the functional core of hematopoietic stem cells through knockout mice. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 11, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, H.J.; Christensen, J.; Fong, S.; Hu, Y.L.; Weissman, I.; Sauvageau, G.; Humphries, R.K.; Largman, C. Loss of expression of the Hoxa-9 homeobox gene impairs the proliferation and repopulating ability of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 2005, 106, 3988–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, T.; Rodrigues, N.; Dombkowski, D.; Stier, S.; Scadden, D.T. Stem cell repopulation efficiency but not pool size is governed by p27(kip1). Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takubo, K.; Goda, N.; Yamada, W.; Iriuchishima, H.; Ikeda, E.; Kubota, Y.; Shima, H.; Johnson, R.S.; Hirao, A.; Suematsu, M.; et al. Regulation of the HIF-1alpha level is essential for hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rathinam, C.; Thien, C.B.; Langdon, W.Y.; Gu, H.; Flavell, R.A. The E3 ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl restricts development and functions of hematopoietic stem cells. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seita, J.; Ema, H.; Ooehara, J.; Yamazaki, S.; Tadokoro, Y.; Yamasaki, A.; Eto, K.; Takaki, S.; Takatsu, K.; Nakauchi, H. Lnk negatively regulates self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells by modifying thrombopoietin-mediated signal transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Platt, R.J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yim, M.J.; Swiech, L.; Kempton, H.R.; Dahlman, J.E.; Parnas, O.; Eisenhaure, T.M.; Jovanovic, M.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9 knockin mice for genome editing and cancer modeling. Cell 2014, 159, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schambach, A.; Bohne, J.; Chandra, S.; Will, E.; Margison, G.P.; Williams, D.A.; Baum, C. Equal potency of gammaretroviral and lentiviral SIN vectors for expression of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase in hematopoietic cells. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, J.K.; Miyanohara, A.; LaPorte, P.; Bouic, K.; Burns, J.C.; Friedmann, T. A general method for the generation of high-titer, pantropic retroviral vectors: Highly efficient infection of primary hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9564–9568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maetzig, T.; Kuehle, J.; Schwarzer, A.; Turan, S.; Rothe, M.; Chaturvedi, A.; Morgan, M.; Ha, T.C.; Heuser, M.; Hammerschmidt, W.; et al. All-in-One inducible lentiviral vector systems based on drug controlled FLP recombinase. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4345–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, J.D.; Williams, D.A.; Gifford, M.A.; Li, L.L.; Du, X.; Fisherman, J.; Orkin, S.H.; Doerschuk, C.M.; Dinauer, M.C. Mouse model of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease, an inherited defect in phagocyte superoxide production. Nat. Genet. 1995, 9, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selich, A.; Daudert, J.; Hass, R.; Philipp, F.; von Kaisenberg, C.; Paul, G.; Cornils, K.; Fehse, B.; Rittinghausen, S.; Schambach, A.; et al. Massive Clonal Selection and Transiently Contributing Clones during Expansion of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Cultures Revealed by Lentiviral RGB-Barcode Technology. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takaki, S.; Morita, H.; Tezuka, Y.; Takatsu, K. Enhanced hematopoiesis by hematopoietic progenitor cells lacking intracellular adaptor protein, Lnk. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takaki, S.; Watts, J.D.; Forbush, K.A.; Nguyen, N.T.; Hayashi, J.; Alberola-Ila, J.; Aebersold, R.; Perlmutter, R.M. Characterization of Lnk. An adaptor protein expressed in lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 14562–14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, H.; Cheng, T. Hematopoietic stem cell exhaustion impacted by p18 INK4C and p21 Cip1/Waf1 in opposite manners. Blood 2006, 107, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Shen, H.; Franklin, D.S.; Scadden, D.T.; Cheng, T. In vivo self-renewing divisions of haematopoietic stem cells are increased in the absence of the early G1-phase inhibitor, p18INK4C. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kellner, J.; Liu, L.; Zhou, D. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase promotes ex vivo hematopoietic stem cell expansion. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, I.M.; Pietramaggiori, G.; Kim, F.S.; Passegué, E.; Stevenson, K.E.; Wagers, A.J. The transcription factor EGR1 controls both the proliferation and localization of hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr.; Friedman, A.D.; Paz-Priel, I. Loss of IKKβ but Not NF-κB p65 Skews Differentiation towards Myeloid over Erythroid Commitment and Increases Myeloid Progenitor Self-Renewal and Functional Long-Term Hematopoietic Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Eleswarapu, S.; Geiger, H.; Szczur, K.; Daria, D.; Zheng, Y.; Settleman, J.; Srour, E.F.; Williams, D.A.; Filippi, M.D. Loss of the Rho GTPase activating protein p190-B enhances hematopoietic stem cell engraftment potential. Blood 2009, 114, 3557–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaghy, R.; Han, X.; Rozenova, K.; Lv, K.; Jiang, Q.; Doepner, M.; Greenberg, R.A.; Tong, W. The BRISC deubiquitinating enzyme complex limits hematopoietic stem cell expansion by regulating JAK2 K63-ubiquitination. Blood 2019, 133, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Kim, J.A.; Castillo, A.; Huang, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, B. NBA1/MERIT40 and BRE interaction is required for the integrity of two distinct deubiquitinating enzyme BRCC36-containing complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 11734–11745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozenova, K.; Jiang, J.; Donaghy, R.; Aressy, B.; Greenberg, R.A.; Tong, W. MERIT40 deficiency expands hematopoietic stem cell pools by regulating thrombopoietin receptor signaling. Blood 2015, 125, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merchant, A.; Joseph, G.; Wang, Q.; Brennan, S.; Matsui, W. Gli1 regulates the proliferation and differentiation of HSCs and myeloid progenitors. Blood 2010, 115, 2391–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carnevalli, L.S.; Scognamiglio, R.; Cabezas-Wallscheid, N.; Rahmig, S.; Laurenti, E.; Masuda, K.; Jöckel, L.; Kuck, A.; Sujer, S.; Polykratis, A.; et al. Improved HSC reconstitution and protection from inflammatory stress and chemotherapy in mice lacking granzyme B. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oguro, H.; Ding, L.; Morrison, S.J. SLAM family markers resolve functionally distinct subpopulations of hematopoietic stem cells and multipotent progenitors. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 13, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, M.; Afrin, F.; Satija, N.; Tripathi, R.P.; Gangenahalli, G.U. Stromal-derived factor-1/CXCR4 signaling: Indispensable role in homing and engraftment of hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadrado, A.; Nebreda, A.R. Mechanisms and functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cicenas, J.; Zalyte, E.; Rimkus, A.; Dapkus, D.; Noreika, R.; Urbonavicius, S. JNK, p38, ERK, and SGK1 Inhibitors in Cancer. Cancers 2017, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hommes, D.; van den Blink, B.; Plasse, T.; Bartelsman, J.; Xu, C.; Macpherson, B.; Tytgat, G.; Peppelenbosch, M.; Van Deventer, S. Inhibition of stress-activated MAP kinases induces clinical improvement in moderate to severe Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslah, N.; Cassinat, B.; Verger, E.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Velazquez, L. The role of LNK/SH2B3 genetic alterations in myeloproliferative neoplasms and other hematological disorders. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyle, C.L.; Belghasem, M.; Chitalia, V.C. c-Cbl: An Important Regulator and a Target in Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis. Cells 2019, 8, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jehn, B.M.; Dittert, I.; Beyer, S.; von der Mark, K.; Bielke, W. c-Cbl binding and ubiquitin-dependent lysosomal degradation of membrane-associated Notch1. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8033–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, S.; Xu, Z.; Lipkowitz, S.; Longley, J.B. Regulation of stem cell factor receptor signaling by Cbl family proteins (Cbl-b/c-Cbl). Blood 2005, 105, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, J.; Zou, P.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Liu, L. Inhibition of p38 MAPK activity promotes ex vivo expansion of human cord blood hematopoietic stem cells. Ann. Hematol. 2012, 91, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bearman, S.I.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Buckner, C.D.; Petersen, F.B.; Fisher, L.D.; Clift, R.A.; Thomas, E.D. Regimen-related toxicity in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1988, 6, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthes-Martin, S.; Lamche, M.; Ladenstein, R.; Emminger, W.; Felsberger, C.; Topf, R.; Gadner, H.; Peters, C. Organ toxicity and quality of life after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in pediatric patients: A single centre retrospective analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 1999, 23, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolfien, M.; Klatt, D.; Salybekov, A.A.; Ii, M.; Komatsu-Horii, M.; Gaebel, R.; Philippou-Massier, J.; Schrinner, E.; Akimaru, H.; Akimaru, E.; et al. Hematopoietic stem-cell senescence and myocardial repair—Coronary artery disease genotype/phenotype anaysis of post-MI myocardial regeneration response induced by CABG/CD133+ bone marrow hematopoietic stem cell treatment in RCT PERFECT Phase 3. EBioMedicine 2020, 57, 102862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klatt, D.; Ha, T.-C.; Schinke, M.; Selich, A.; Lieske, A.; Dahlke, J.; Morgan, M.; Maetzig, T.; Schambach, A. Competitive sgRNA Screen Identifies p38 MAPK as a Druggable Target to Improve HSPC Engraftment. Cells 2020, 9, 2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102194
Klatt D, Ha T-C, Schinke M, Selich A, Lieske A, Dahlke J, Morgan M, Maetzig T, Schambach A. Competitive sgRNA Screen Identifies p38 MAPK as a Druggable Target to Improve HSPC Engraftment. Cells. 2020; 9(10):2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102194
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlatt, Denise, Teng-Cheong Ha, Maximilian Schinke, Anton Selich, Anna Lieske, Julia Dahlke, Michael Morgan, Tobias Maetzig, and Axel Schambach. 2020. "Competitive sgRNA Screen Identifies p38 MAPK as a Druggable Target to Improve HSPC Engraftment" Cells 9, no. 10: 2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102194
APA StyleKlatt, D., Ha, T. -C., Schinke, M., Selich, A., Lieske, A., Dahlke, J., Morgan, M., Maetzig, T., & Schambach, A. (2020). Competitive sgRNA Screen Identifies p38 MAPK as a Druggable Target to Improve HSPC Engraftment. Cells, 9(10), 2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102194