Coming in the Air: Hypoxia Meets Epigenetics in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hypoxia in Cancer
3. HIF Transcription Factor Family—The Key Players in Response to Hypoxia
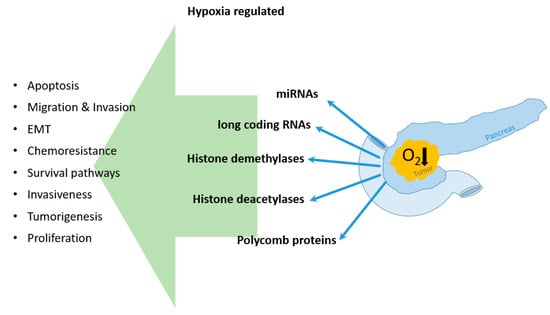
4. Hypoxia Influenced Epigenetic Regulation of Pancreatic Cancer
4.1. Hypoxic Regulation of miRNAs in PDAC Cells
4.2. Long Coding RNAs and Hypoxia in PDAC
4.3. Hypoxia and Its Impact on DNA Modifying Enzymes
4.3.1. Histone Demethylase
4.3.2. Histone Deacetylases
4.3.3. Polycomb Protein
5. Final Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGuigan, A.; Kelly, P.; Turkington, R.C.; Jones, C.; Coleman, H.G.; McCain, R.S. Pancreatic cancer: A review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4846–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goess, R.; Friess, H. A look at the progress of treating pancreatic cancer over the past 20 years. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2018, 18, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, B.; Shi, S.; Yu, X.; Liang, C. Hypoxia: A barricade to conquer the pancreatic cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 3077–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Hockel, M.; Mayer, A. Detection and characterization of tumor hypoxia using pO2 histography. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koong, A.C.; Mehta, V.K.; Le, Q.T.; Fisher, G.A.; Terris, D.J.; Brown, J.M.; Bastidas, A.J.; Vierra, M. Pancreatic tumors show high levels of hypoxia. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 48, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S.K.; Sullivan, K.M.; Labadie, K.P.; Pillarisetty, V.G. Hypoxia as a barrier to immunotherapy in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia (Auckl) 2015, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wigerup, C.; Pahlman, S.; Bexell, D. Therapeutic targeting of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 164, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Ji, S.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Qin, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, X. Role of angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer biology and therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eales, K.L.; Hollinshead, K.E.; Tennant, D.A. Hypoxia and metabolic adaptation of cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhandari, V.; Hoey, C.; Liu, L.Y.; Lalonde, E.; Ray, J.; Livingstone, J.; Lesurf, R.; Shiah, Y.J.; Vujcic, T.; Huang, X.; et al. Molecular landmarks of tumor hypoxia across cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Yang, F.; Shao, C.; Wei, K.; Xie, M.; Shen, H.; Shu, Y. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuen, A.; Diaz, B. The impact of hypoxia in pancreatic cancer invasion and metastasis. Hypoxia (Auckl) 2014, 2, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillaumond, F.; Leca, J.; Olivares, O.; Lavaut, M.N.; Vidal, N.; Berthezene, P.; Dusetti, N.J.; Loncle, C.; Calvo, E.; Turrini, O.; et al. Strengthened glycolysis under hypoxia supports tumor symbiosis and hexosamine biosynthesis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3919–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuentes, N.R.; Phan, J.; Huang, Y.; Lin, D.; Taniguchi, C.M. Resolving the HIF paradox in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 489, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Salnikov, A.V.; Bauer, N.; Aleksandrowicz, E.; Labsch, S.; Nwaeburu, C.; Mattern, J.; Gladkich, J.; Schemmer, P.; Werner, J.; et al. Triptolide reverses hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem-like features in pancreatic cancer by NF-kappaB downregulation. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 2489–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.H.; Huang, C.; Feng, Z.Z.; Lv, X.H.; Qiu, Z.J. Hypoxia-induced snail expression through transcriptional regulation by HIF-1alpha in pancreatic cancer cells. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 3503–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, I.B.; Koti, M.; Siemens, D.R.; Graham, C.H. Mechanisms of hypoxia-mediated immune escape in cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7185–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pergamo, M.; Miller, G. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells and their role in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Dai, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. Implications of HIF-1alpha in the tumorigenesis and progression of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.P.; Wu, K.J. Epigenetic regulation of hypoxia-responsive gene expression: Focusing on chromatin and DNA modifications. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, M.A.; Evans, A.J.; Hosomi, T.; Hara, S.; Jewett, M.A.; Ohh, M. Human HIF-3alpha4 is a dominant-negative regulator of HIF-1 and is down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkila, M.; Pasanen, A.; Kivirikko, K.I.; Myllyharju, J. Roles of the human hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-3alpha variants in the hypoxia response. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 3885–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, X.; Chen, M.; Xie, C.; Jiang, J. HIF-3alpha Promotes Metastatic Phenotypes in Pancreatic Cancer by Transcriptional Regulation of the RhoC-ROCK1 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, J.A.; Watson, C.J.; McCann, A.; Baugh, J. Epigenetics, the epicenter of the hypoxic response. Epigenetics 2010, 5, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camuzi, D.; de Amorim, I.S.S.; Ribeiro Pinto, L.F.; Oliveira Trivilin, L.; Mencalha, A.L.; Soares Lima, S.C. Regulation Is in the Air: The Relationship between Hypoxia and Epigenetics in Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prickaerts, P.; Adriaens, M.E.; Beucken, T.V.D.; Koch, E.; Dubois, L.; Dahlmans, V.E.H.; Gits, C.; Evelo, C.T.A.; Chan-Seng-Yue, M.; Wouters, B.G.; et al. Hypoxia increases genome-wide bivalent epigenetic marking by specific gain of H3K27me3. Epigenet. Chromatin 2016, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Ding, L.; Bennewith, K.L.; Tong, R.T.; Welford, S.M.; Ang, K.K.; Story, M.; Le, Q.T.; Giaccia, A.J. Hypoxia-inducible mir-210 regulates normoxic gene expression involved in tumor initiation. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsen, T.W. Mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation in animal cells. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; He, C.; Deng, S.; Li, X.; Cui, S.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhao, S.; Chen, J.; Jin, Y.; et al. MiR-548an, Transcriptionally Downregulated by HIF1alpha/HDAC1, Suppresses Tumorigenesis of Pancreatic Cancer by Targeting Vimentin Expression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Calin, G.A.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. miRNA Deregulation in Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, S.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M.; Coukos, G.; Zhang, L. Mechanisms of microRNA deregulation in human cancer. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2643–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.Y.; Liu, W.J.; Zhao, Y.P.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.P.; Chen, G.; Shu, H. Induction, modulation and potential targets of miR-210 in pancreatic cancer cells. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2012, 11, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirlwell, C.; Schulz, L.; Dibra, H.; Beck, S. Suffocating cancer: Hypoxia-associated epimutations as targets for cancer therapy. Clin. Epigenet. 2011, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takikawa, T.; Masamune, A.; Hamada, S.; Nakano, E.; Yoshida, N.; Shimosegawa, T. miR-210 regulates the interaction between pancreatic cancer cells and stellate cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 437, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhou, S.; Yuan, W.; Cen, F.; Yan, Q. Mechanism of miR-210 involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells under hypoxia. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2019, 39, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasanaro, P.; Romani, S.; Voellenkle, C.; Maimone, B.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Martelli, F. ROD1 is a seedless target gene of hypoxia-induced miR-210. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Weng, L.; Jia, Y.; Liu, B.; Wu, S.; Xue, L.; Yin, X.; Mao, A.; Wang, Z.; Shang, M. PTBP3 promotes malignancy and hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells by ATG12 up-regulation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 2917–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaconstantinou, I.G.; Manta, A.; Gazouli, M.; Lyberopoulou, A.; Lykoudis, P.M.; Polymeneas, G.; Voros, D. Expression of microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer and its prognostic significance. Pancreas 2013, 42, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mace, T.A.; Collins, A.L.; Wojcik, S.E.; Croce, C.M.; Lesinski, G.B.; Bloomston, M. Hypoxia induces the overexpression of microRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 184, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriyama, T.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Yu, J.; Sato, N.; Nabae, T.; Takahata, S.; Toma, H.; Nagai, E.; Tanaka, M. MicroRNA-21 modulates biological functions of pancreatic cancer cells including their proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumarswamy, R.; Volkmann, I.; Thum, T. Regulation and function of miRNA-21 in health and disease. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nong, K.; Zhang, D.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Cai, H. MicroRNA-519 inhibits hypoxia-induced tumorigenesis of pancreatic cancer by regulating immune checkpoint PD-L1. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ji, N.; Wei, W.; Sun, W.; Gong, X.; Wang, X. MiR-142 modulates human pancreatic cancer proliferation and invasion by targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1alpha) in the tumor microenvironments. Biol. Open 2017, 6, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, P.; Deng, Z.; Wan, M.; Huang, W.; Cramer, S.D.; Xu, J.; Lei, M.; Sui, G. MicroRNA-101 negatively regulates Ezh2 and its expression is modulated by androgen receptor and HIF-1alpha/HIF-1beta. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Deng, S.C.; Deng, S.J.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; He, C.; Liu, M.L.; Zeng, Z.; et al. MiRNA-646-mediated reciprocal repression between HIF-1alpha and MIIP contributes to tumorigenesis of pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1743–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.J.; Chen, H.Y.; Ye, Z.; Deng, S.C.; Zhu, S.; Zeng, Z.; He, C.; Liu, M.L.; Huang, K.; Zhong, J.X.; et al. Hypoxia-induced LncRNA-BX111 promotes metastasis and progression of pancreatic cancer through regulating ZEB1 transcription. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5811–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, S.J.; Zhu, S.; Jin, Y.; Cui, S.P.; Chen, J.Y.; Xiang, C.; Li, Q.Y.; He, C.; Zhao, S.F.; et al. Hypoxia-induced lncRNA-NUTF2P3-001 contributes to tumorigenesis of pancreatic cancer by derepressing the miR-3923/KRAS pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6000–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Zhong, J.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, K.; Ye, Z.; Deng, S.; Chen, H.; Xu, F.; Li, Q.; Zhao, G. Hypoxia-induced feedback of HIF-1alpha and lncRNA-CF129 contributes to pancreatic cancer progression through stabilization of p53 protein. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4795–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Z.L.; Zhang, M.; Ji, L.D.; Luo, Z.; Han, T.; Lu, Y.B.; Li, Y.X. Long noncoding RNA FEZF1-AS1 predicts poor prognosis and modulates pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and invasion through miR-142/HIF-1alpha and miR-133a/EGFR upon hypoxia/normoxia. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 15407–15419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wen, C.; Huo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhan, Q.; Cheng, D.; Chen, H.; Deng, X.; Peng, C.; et al. Long noncoding RNA NORAD, a novel competing endogenous RNA, enhances the hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingenito, F.; Roscigno, G.; Affinito, A.; Nuzzo, S.; Scognamiglio, I.; Quintavalle, C.; Condorelli, G. The Role of Exo-miRNAs in Cancer: A Focus on Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patton, M.C.; Zubair, H.; Khan, M.A.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.P. Hypoxia alters the release and size distribution of extracellular vesicles in pancreatic cancer cells to support their adaptive survival. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonohara, F.; Yamada, S.; Takeda, S.; Hayashi, M.; Suenaga, M.; Sunagawa, Y.; Tashiro, M.; Takami, H.; Kanda, M.; Tanaka, C.; et al. Exploration of Exosomal Micro RNA Biomarkers Related to Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Pancreatic Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, G.; Zhang, K.; Cao, J.; Huang, C.; Jiang, T.; Liu, B.; Su, L.; Qiu, Z. Hypoxic Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-301a Mediates M2 Macrophage Polarization via PTEN/PI3Kgamma to Promote Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4586–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mambo, E.; Szafranska-Schwarzbach, A.E.; Latham, G.; Adai, A.; Schlageter, A.; Andruss, B. Chapter 5-microRNA Biomarkers as Potential Diagnostic Markers for Cancer. In Genomic Biomarkers for Pharmaceutical Development; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 95–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Chang, P.; LeBlanc, A.; Li, D.; Abbruzzesse, J.L.; Frazier, M.L.; Killary, A.M.; Sen, S. MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2009, 2, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Z.; Ren, H.; Gao, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Hao, J. The clinical significance and regulation mechanism of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and miR-191 expression in pancreatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 11319–11328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Shinjo, K.; Katsushima, K. Long non-coding RNAs as an epigenetic regulator in human cancers. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olgun, G.; Sahin, O.; Tastan, O. Discovering lncRNA mediated sponge interactions in breast cancer molecular subtypes. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Lu, X.; Yuan, L. LncRNA: A link between RNA and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Park, J.W. Hypoxia-driven epigenetic regulation in cancer progression: A focus on histone methylation and its modifying enzymes. Cancer Lett. 2020, 489, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.B.; Denko, N.; Barton, M.C. Hypoxia induces a novel signature of chromatin modifications and global repression of transcription. Mutat. Res. 2008, 640, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batie, M.; Frost, J.; Frost, M.; Wilson, J.W.; Schofield, P.; Rocha, S. Hypoxia induces rapid changes to histone methylation and reprograms chromatin. Science 2019, 363, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.A.; Laukka, T.; Myllykoski, M.; Ringel, A.E.; Booker, M.A.; Tolstorukov, M.Y.; Meng, Y.J.; Meier, S.R.; Jennings, R.B.; Creech, A.L.; et al. Histone demethylase KDM6A directly senses oxygen to control chromatin and cell fate. Science 2019, 363, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dandawate, P.; Ghosh, C.; Palaniyandi, K.; Paul, S.; Rawal, S.; Pradhan, R.; Sayed, A.A.A.; Choudhury, S.; Standing, D.; Subramaniam, D.; et al. The Histone Demethylase KDM3A, Increased in Human Pancreatic Tumors, Regulates Expression of DCLK1 and Promotes Tumorigenesis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1646–1659.e1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andricovich, J.; Perkail, S.; Kai, Y.; Casasanta, N.; Peng, W.; Tzatsos, A. Loss of KDM6A Activates Super-Enhancers to Induce Gender-Specific Squamous-like Pancreatic Cancer and Confers Sensitivity to BET Inhibitors. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 512–526.e518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassell, K.N. Histone Deacetylases and their Inhibitors in Cancer Epigenetics. Diseases 2019, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mie Lee, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jin Son, M.; Nakajima, H.; Jeong Kwon, H.; Kim, K.W. Inhibition of hypoxia-induced angiogenesis by FK228, a specific histone deacetylase inhibitor, via suppression of HIF-1alpha activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 300, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.Z.; Kachhap, S.K.; Collis, S.J.; Verheul, H.M.; Carducci, M.A.; Atadja, P.; Pili, R. Class II histone deacetylases are associated with VHL-independent regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8814–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Sang, N. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: The epigenetic therapeutics that repress hypoxia-inducible factors. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 197946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.; Lin, Z.; Liang, D.; Fath, D.; Sang, N.; Caro, J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce VHL and ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fath, D.M.; Kong, X.; Liang, D.; Lin, Z.; Chou, A.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, J.; Caro, J.; Sang, N. Histone deacetylase inhibitors repress the transactivation potential of hypoxia-inducible factors independently of direct acetylation of HIF-alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 13612–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klieser, E.; Swierczynski, S.; Mayr, C.; Schmidt, J.; Neureiter, D.; Kiesslich, T.; Illig, R. Role of histone deacetylases in pancreas: Implications for pathogenesis and therapy. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 7, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, K.; Yoshizumi, T.; Imura, S.; Sugimoto, K.; Batmunkh, E.; Kanemura, H.; Morine, Y.; Shimada, M. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, histone deacetylase 1, and metastasis-associated protein 1 in pancreatic carcinoma: Correlation with poor prognosis with possible regulation. Pancreas 2008, 36, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Chen, J.Z.; Zhang, J.Q.; Chen, H.X.; Yan, M.L.; Huang, L.; Tian, Y.F.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, Y.D. Hypoxia induces TWIST-activated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in nude mice. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Hu, K.; Lin, F.; Li, X.; Feng, T.; Wang, Z.M. Hypoxia-induced NIPP1 activation enhances metastatic potential and predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 14903–14914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, M.; Ferretti, E.; Battaglia, G.; Bellavia, D.; Mai, A.; Tafani, M. EZH2, HIF-1, and Their Inhibitors: An Overview on Pediatric Cancers. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| miRNA | Target | Affected Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA-21 ↑ | proliferation, apoptosis, cell survival | [42] | |
| miRNA-210 ↑ | HOXA9 | EMT, migration, invasiveness, NF-κB signalling | [38] |
| mRNA-101 ↓ | EZH2 | Invasion and metastasis | [47] |
| miRNA-548an ↓ | Vimentin | EMT, proliferation, Invasion | [32] |
| miRNA-519 ↓ | PD-L1 | Invasiveness, apoptosis, tumorigenesis | [45] |
| miRNA-646 ↑ | MIIP | Proliferation, invasion, HIF-1a degradation | [48] |
| miRNA-142 ↓ | HIF-1α | Proliferation, invasion | [46] |
| lncRNA-BX111887 ↑ | ZEB1 | Proliferation, invasion, migration, EMT | [49] |
| lncRNA NUTF2P3-001 ↑ | miRNA-3923 | Cell viability, proliferation, invasion | [50] |
| lncRNA-CF129 ↓ | FOXC2 | Cancer progression | [51] |
| lncRNA-FEZF1-AS1 ↑ | miRNA-142 | Proliferation | [52] |
| lncRNA-NORAD ↑ | miRNA-125a3p | EMT | [53] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geismann, C.; Arlt, A. Coming in the Air: Hypoxia Meets Epigenetics in Pancreatic Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 2353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112353
Geismann C, Arlt A. Coming in the Air: Hypoxia Meets Epigenetics in Pancreatic Cancer. Cells. 2020; 9(11):2353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112353
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeismann, Claudia, and Alexander Arlt. 2020. "Coming in the Air: Hypoxia Meets Epigenetics in Pancreatic Cancer" Cells 9, no. 11: 2353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112353
APA StyleGeismann, C., & Arlt, A. (2020). Coming in the Air: Hypoxia Meets Epigenetics in Pancreatic Cancer. Cells, 9(11), 2353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112353