Allergen-Induced C5a/C5aR1 Axis Activation in Pulmonary CD11b+ cDCs Promotes Pulmonary Tolerance through Downregulation of CD40
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Model of Combined HDM/OVA-Mediated Allergen Exposure
2.3. Pulmonary Cell Isolation
2.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis and Antibodies
2.5. Isolation and CFSE-Labelling of OVA-Specific T Cell Receptor Transgenic CD4+ T Cells
2.6. Co-Culture of Sorted cDCs with Naïve CD4+ T Cells from DO11.10 RAG2−/− Mice
2.7. Determination of Cytokine Production and Foxp3 Expression in OVA-Specific TCR tg CD4+ Cells
2.8. Saponin-Based Permeabilization Approach
2.9. Laser Scanning Microscopy to Assess Dendritic Cell T Cell Interactions
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pulmonary CD11b+cDCs Are a Heterogeneous DC Population
3.2. Impact of C5aR1+ and C5aR1− cDCs on the Proliferation and Differentiation of OVA-Specific TCR tg CD4+ T Cells
3.3. C5aR1+ cDCs Express Significantly Lower Levels of MHC-II and CD40 than C5aR1- cDCs after HDM/OVA Exposure
3.4. C5aR1+ cDCs Interact Less Frequently with OVA-specific TCR tg CD4+ T Cells than C5aR1− cDCs
3.5. C5aR1+cDCs Express Significantly Lower Levels of CCR7 in Comparison to C5aR1− cDCs
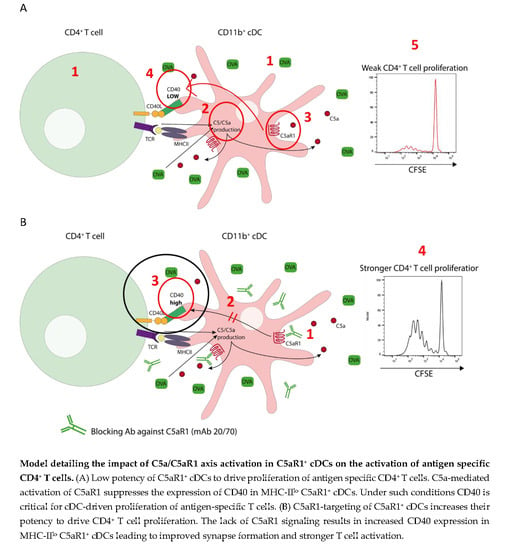
3.6. In Vitro Targeting of C5aR1 Increases the Potency of C5aR1+ cDCs to Induce CD4+ T Cell Proliferation through Regulation of CD40 Expression
3.7. CD40-CD40L Interaction Controls the Proliferation of CD4+ T Cells When the Availability of the Antigen Peptide Is Limited on C5aR1+ cDCs
3.8. CD40-CD40L Interaction Controls CD4+ T Cell Proliferation in C5aR1− cDCs When the Number of Antigen Peptide-Loaded MHC-II Molecules Is Low
3.9. Allergen Stimulation of C5aR1+ and C5aR1− cDCs Induces the Production of C5 and Cleavage into C5a
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H. The immunology of asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sertl, K.; Takemura, T.; Tschachler, E.; Ferrans, V.J.; Kaliner, M.A.; Shevach, E.M. Dendritic cells with antigen-presenting capability reside in airway epithelium, lung parenchyma, and visceral pleura. J. Exp. Med. 1986, 163, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guilliams, M.; Ginhoux, F.; Jakubzick, C.; Naik, S.H.; Onai, N.; Schraml, B.U.; Segura, E.; Tussiwand, R.; Yona, S. Dendritic cells, monocytes and macrophages: A unified nomenclature based on ontogeny. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantinga, M.; Guilliams, M.; Vanheerswynghels, M.; Deswarte, K.; Branco-Madeira, F.; Toussaint, W.; Vanhoutte, L.; Neyt, K.; Killeen, N.; Malissen, B.; et al. Conventional and monocyte-derived CD11b(+) dendritic cells initiate and maintain T helper 2 cell-mediated immunity to house dust mite allergen. Immunity 2013, 38, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furuhashi, K.; Suda, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Hashimoto, D.; Enomoto, N.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Inui, N.; Shibata, K.; et al. Mouse lung CD103+ and CD11bhigh dendritic cells preferentially induce distinct CD4+ T-cell responses. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clatworthy, M.R.; Aronin, C.E.; Mathews, R.J.; Morgan, N.Y.; Smith, K.G.; Germain, R.N. Immune complexes stimulate CCR7-dependent dendritic cell migration to lymph nodes. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krug, N.; Tschernig, T.; Erpenbeck, V.J.; Hohlfeld, J.M.; Köhl, J. Complement factors C3a and C5a are increased in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid after segmental allergen provocation in subjects with asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1841–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, M.M.; Korosec, P.; Kosnik, M.; Kern, I.; Flezar, M.; Suskovic, S.; Sorli, J. Complement factors c3a, c4a, and c5a in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruo, K.; Akaike, T.; Ono, T.; Okamoto, T.; Maeda, H. Generation of anaphylatoxins through proteolytic processing of C3 and C5 by house dust mite protease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 100, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber-Lang, M.; Younkin, E.M.; Sarma, J.V.; Riedemann, N.; McGuire, S.R.; Lu, K.T.; Kunkel, R.; Younger, J.G.; Zetoune, F.S.; Ward, P.A. Generation of C5a by phagocytic cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhl, J.; Baelder, R.; Lewkowich, I.P.; Pandey, M.K.; Hawlisch, H.; Wang, L.; Best, J.; Herman, N.S.; Sproles, A.A.; Zwirner, J.; et al. A regulatory role for the C5a anaphylatoxin in type 2 immunity in asthma. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewkowich, I.P.; Herman, N.S.; Schleifer, K.W.; Dance, M.P.; Chen, B.L.; Dienger, K.M.; Sproles, A.A.; Shah, J.S.; Köhl, J.; Belkaid, Y.; et al. CD4+CD25+ T cells protect against experimentally induced asthma and alter pulmonary dendritic cell phenotype and function. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1549–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lewkowich, I.P.; Kohl, G.; Clark, J.R.; Wills-Karp, M.; Köhl, J. A protective role for C5a in the development of allergic asthma associated with altered levels of B7-H1 and B7-DC on plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5123–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmudde, I.; Strover, H.A.; Vollbrandt, T.; Konig, P.; Karsten, C.M.; Laumonnier, Y.; Köhl, J. C5a receptor signalling in dendritic cells controls the development of maladaptive Th2 and Th17 immunity in experimental allergic asthma. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baelder, R.; Fuchs, B.; Bautsch, W.; Zwirner, J.; Köhl, J.; Hoymann, H.G.; Glaab, T.; Erpenbeck, V.; Krug, N.; Braun, A. Pharmacological targeting of anaphylatoxin receptors during the effector phase of allergic asthma suppresses airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lajoie, S.; Lewkowich, I.P.; Suzuki, Y.; Clark, J.R.; Sproles, A.A.; Dienger, K.; Budelsky, A.L.; Wills-Karp, M. Complement-mediated regulation of the IL-17A axis is a central genetic determinant of the severity of experimental allergic asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karp, C.L.; Grupe, A.; Schadt, E.; Ewart, S.L.; Keane-Moore, M.; Cuomo, P.J.; Köhl, J.; Wahl, L.; Kuperman, D.; Germer, S.; et al. Identification of complement factor 5 as a susceptibility locus for experimental allergic asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, S.M.; Sinha, M.; Sfyroera, G.; Lambris, J.D.; Wetsel, R.A. A protective role for the fifth complement component (c5) in allergic airway disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKinley, L.; Kim, J.; Bolgos, G.L.; Siddiqui, J.; Remick, D.G. Allergens induce enhanced bronchoconstriction and leukotriene production in C5 deficient mice. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiese, A.V.; Ender, F.; Quell, K.M.; Antoniou, K.; Vollbrandt, T.; König, P.; Köhl, J.; Laumonnier, Y. The C5a/C5aR1 axis controls the development of experimental allergic asthma independent of LysM-expressing pulmonary immune cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ender, F.; Wiese, A.V.; Schmudde, I.; Sun, J.; Vollbrandt, T.; Konig, P.; Laumonnier, Y.; Köhl, J. Differential regulation of C5a receptor 1 in innate immune cells during the allergic asthma effector phase. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsten, C.M.; Laumonnier, Y.; Eurich, B.; Ender, F.; Broker, K.; Roy, S.; Czabanska, A.; Vollbrandt, T.; Figge, J.; Köhl, J. Monitoring and cell-specific deletion of C5aR1 using a novel floxed GFP-C5aR1 reporter knock-in mouse. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1841–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engelke, C.; Wiese, A.V.; Schmudde, I.; Ender, F.; Strover, H.A.; Vollbrandt, T.; Konig, P.; Laumonnier, Y.; Köhl, J. Distinct roles of the anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a in dendritic cell-mediated allergic asthma. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5387–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.S.; Gorski, S.A.; Hahn, S.; Murphy, K.M.; Braciale, T.J. Distinct dendritic cell subsets dictate the fate decision between effector and memory CD8(+) T cell differentiation by a CD24-dependent mechanism. Immunity 2014, 40, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denda-Nagai, K.; Aida, S.; Saba, K.; Suzuki, K.; Moriyama, S.; Oo-Puthinan, S.; Tsuiji, M.; Morikawa, A.; Kumamoto, Y.; Sugiura, D.; et al. Distribution and function of macrophage galactose-type C-type lectin 2 (MGL2/CD301b): Efficient uptake and presentation of glycosylated antigens by dendritic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 19193–19204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheong, C.; Matos, I.; Choi, J.H.; Dandamudi, D.B.; Shrestha, E.; Longhi, M.P.; Jeffrey, K.L.; Anthony, R.M.; Kluger, C.; Nchinda, G.; et al. Microbial stimulation fully differentiates monocytes to DC-SIGN/CD209(+) dendritic cells for immune T cell areas. Cell 2010, 143, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satpathy, A.T.; Kc, W.; Albring, J.C.; Edelson, B.T.; Kretzer, N.M.; Bhattacharya, D.; Murphy, T.L.; Murphy, K.M. Zbtb46 expression distinguishes classical dendritic cells and their committed progenitors from other immune lineages. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1135–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satpathy, A.T.; Wu, X.; Albring, J.C.; Murphy, K.M. Re(de)fining the dendritic cell lineage. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlitzer, A.; Ginhoux, F. Organization of the mouse and human DC network. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlitzer, A.; McGovern, N.; Teo, P.; Zelante, T.; Atarashi, K.; Low, D.; Ho, A.W.; See, P.; Shin, A.; Wasan, P.S.; et al. IRF4 transcription factor-dependent CD11b+ dendritic cells in human and mouse control mucosal IL-17 cytokine responses. Immunity 2013, 38, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monks, C.R.; Freiberg, B.A.; Kupfer, H.; Sciaky, N.; Kupfer, A. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature 1998, 395, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiberg, B.A.; Kupfer, H.; Maslanik, W.; Delli, J.; Kappler, J.; Zaller, D.M.; Kupfer, A. Staging and resetting T cell activation in SMACs. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laman, J.D.; Claassen, E.; Noelle, R.J. Functions of CD40 and Its Ligand, gp39 (CD40L). Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 37, 371–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Ichim, T.E.; Sun, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Inagaki, A.; Beduhn, M.; Shunnar, A.; et al. A novel allergen-specific therapy for allergy using CD40-silenced dendritic cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 737–743, 743 e731–743 e736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, R.M.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Dendritic cells: Features and functions. Immunol. Rev. 1980, 53, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothoeft, T.; Balkow, S.; Krummen, M.; Beissert, S.; Varga, G.; Loser, K.; Oberbanscheidt, P.; van den Boom, F.; Grabbe, S. Structure and duration of contact between dendritic cells and T cells are controlled by T cell activation state. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 3105–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisvert, J.; Edmondson, S.; Krummel, M.F. Immunological synapse formation licenses CD40-CD40L accumulations at T-APC contact sites. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3647–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wetzel, S.A.; McKeithan, T.W.; Parker, D.C. Live-cell dynamics and the role of costimulation in immunological synapse formation. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6092–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benvenuti, F.; Lagaudriere-Gesbert, C.; Grandjean, I.; Jancic, C.; Hivroz, C.; Trautmann, A.; Lantz, O.; Amigorena, S. Dendritic cell maturation controls adhesion, synapse formation, and the duration of the interactions with naive T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinman, R.M.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Avoiding horror autotoxicus: The importance of dendritic cells in peripheral T cell tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawiger, D.; Inaba, K.; Dorsett, Y.; Guo, M.; Mahnke, K.; Rivera, M.; Ravetch, J.V.; Steinman, R.M.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Dendritic cells induce peripheral T cell unresponsiveness under steady state conditions in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonifaz, L.; Bonnyay, D.; Mahnke, K.; Rivera, M.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Steinman, R.M. Efficient targeting of protein antigen to the dendritic cell receptor DEC-205 in the steady state leads to antigen presentation on major histocompatibility complex class I products and peripheral CD8+ T cell tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, D.J., Jr.; Reis, E.S.; Pandey, M.K.; Köhl, G.; Harris, N.; Gerard, C.; Köhl, J. C5a receptor-deficient dendritic cells promote induction of Treg and Th17 cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grassme, H.; Bock, J.; Kun, J.; Gulbins, E. Clustering of CD40 ligand is required to form a functional contact with CD40. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30289–30299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strainic, M.G.; Liu, J.; Huang, D.; An, F.; Lalli, P.N.; Muqim, N.; Shapiro, V.S.; Dubyak, G.R.; Heeger, P.S.; Medof, M.E. Locally produced complement fragments C5a and C3a provide both costimulatory and survival signals to naive CD4+ T cells. Immunity 2008, 28, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arbore, G.; West, E.E.; Spolski, R.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Klos, A.; Rheinheimer, C.; Dutow, P.; Woodruff, T.M.; Yu, Z.X.; O’Neill, L.A.; et al. T helper 1 immunity requires complement-driven NLRP3 inflammasome activity in CD4(+) T cells. Science 2016, 352, aad1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bröker, K.; Figge, J.; Magnusen, A.F.; Manz, R.A.; Köhl, J.; Karsten, C.M. A Novel Role for C5a in B-1 Cell Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antoniou, K.; Ender, F.; Vollbrandt, T.; Laumonnier, Y.; Rathmann, F.; Pasare, C.; Singh, H.; Köhl, J. Allergen-Induced C5a/C5aR1 Axis Activation in Pulmonary CD11b+ cDCs Promotes Pulmonary Tolerance through Downregulation of CD40. Cells 2020, 9, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020300
Antoniou K, Ender F, Vollbrandt T, Laumonnier Y, Rathmann F, Pasare C, Singh H, Köhl J. Allergen-Induced C5a/C5aR1 Axis Activation in Pulmonary CD11b+ cDCs Promotes Pulmonary Tolerance through Downregulation of CD40. Cells. 2020; 9(2):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020300
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntoniou, Konstantina, Fanny Ender, Tillman Vollbrandt, Yves Laumonnier, Franziska Rathmann, Chandrashekhar Pasare, Harinder Singh, and Jörg Köhl. 2020. "Allergen-Induced C5a/C5aR1 Axis Activation in Pulmonary CD11b+ cDCs Promotes Pulmonary Tolerance through Downregulation of CD40" Cells 9, no. 2: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020300
APA StyleAntoniou, K., Ender, F., Vollbrandt, T., Laumonnier, Y., Rathmann, F., Pasare, C., Singh, H., & Köhl, J. (2020). Allergen-Induced C5a/C5aR1 Axis Activation in Pulmonary CD11b+ cDCs Promotes Pulmonary Tolerance through Downregulation of CD40. Cells, 9(2), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020300