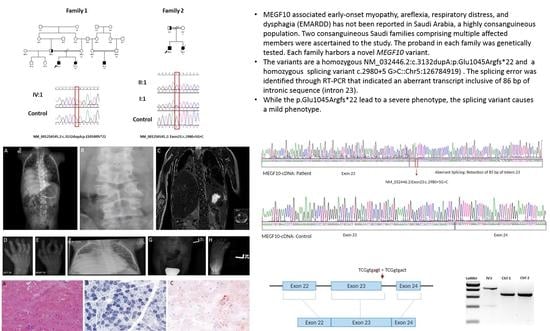
Phenotypic Variability of MEGF10 Variants Causing Congenital Myopathy: Report of Two Unrelated Patients from a Highly Consanguineous Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Ethics
| Patients | Patient 1 | Patient 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle Biopsy | Unremarkable. | Not done |
| Clinical Features | Plagiocephaly, forehead ridge and hirsutism, down slanting eyes, epicanthal folds, mild bilateral ptosis, symmetric facial weakness, low set ears with backward rotation, high arched palate, long fingers, camptodactyly of ring and middle fingers, pectus excavatus, low hair line, sacral dimple in the lower back and scoliosis, areflexia | Plagiocephaly, symmetric myopathic facies, high arched palate, low set ears, scoliosis, generalized hypotonia, areflexia |
| Outcome | Death due to respiratory infection. | Survival (patient is currently alive, last visit was at age of 9 years old) |
| Brain MRI | Mild bilateral frontalatrophic changes | Not done |
| EMG | Myopathic changes in tibialis anterior and vastus lateralis muscles | Neurogenic changes |
| Genotype | MEGF10:c.3132dupA:p.Glu1045Argfs*22:homozygous | NM-032446.2:c.2980+5 G>C:Splice site variant, homozygous |
| O2 req. | NC., 1-2L | None |
| Dysphagia | Gastronomy tube feeding (Severe dysphagia) | Oral (Mild oral dysphagia) |
| Best motor ability | Non-sitting | Ambulant |
| Onset of Symptoms | Since birth | Since birth |

2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Gene Panel Screening, Variant Detection, and Sanger Sequencing
2.4. RT-PCR
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Findings
3.1.1. Patient 1 (Family 1)
3.1.2. Patient 2 (Family 2)
3.2. Genetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- North, K.N.; Wang, C.H.; Clarke, N.; Jungbluth, H.; Vainzof, M.; Dowling, J.J.; Amburgey, K.; Quijano-Roy, S.; Beggs, A.H.; Sewry, C.; et al. Approach to the diagnosis of congenital myopathies. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2014, 24, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, J.C. The 2012 version of the gene table of monogenic neuromuscular disorders. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2011, 21, 833–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravenscroft, G.; Laing, N.G.; Bonnemann, C.G. Pathophysiological concepts in the congenital myopathies: Blurring the boundaries, sharpening the focus. Brain 2015, 138, 246–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cassandrini, D.; Trovato, R.; Rubegni, A.; Lenzi, S.; Fiorillo, C.; Baldacci, J.; Minetti, C.; Astrea, G.; Bruno, C.; Santorelli, F.M.; et al. Congenital myopathies: Clinical phenotypes and new diagnostic tools. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2017, 43, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mah, J.K.; Joseph, J.T. An Overview of Congenital Myopathies. Continuum 2016, 22, 1932–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jungbluth, H.; Treves, S.; Zorzato, F.; Sarkozy, A.; Ochala, J.; Sewry, C.; Phadke, R.; Gautel, M.; Muntoni, F. Congenital myopathies: Disorders of excitation–contraction coupling and muscle contraction. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holterman, C.E.; Le Grand, F.; Kuang, S.; Seale, P.; Rudnicki, M.A. Megf10 regulates the progression of the satellite cell myogenic program. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, C.V.; Lucke, B.; Pottinger, C.; Abdelhamed, Z.A.; Parry, D.A.; Szymanska, K.; Diggle, C.P.; van Riesen, A.; Morgan, J.E.; Markham, G.; et al. Mutations in MEGF10, a regulator of satellite cell myogenesis, cause early onset myopathy, areflexia, respiratory distress and dysphagia (EMARDD). Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyden, S.E.; Mahoney, L.J.; Kawahara, G.; Myers, J.A.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Estrella, E.A.; Duncan, A.R.; Dey, F.; DeChene, E.T.; Blasko-Goehringer, J.M.; et al. Mutations in the satellite cell gene MEGF10 cause a recessive congenital myopathy with minicores. Neurogenetics 2012, 13, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonorazky, H.D.; Bonnemann, C.G.; Dowling, J.J. The genetics of congenital myopathies. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 148, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmouri, G.O.; Nair, P.; Obeid, T.; Al Ali, M.T.; Al Khaja, N.; Hamamy, H.A. Consanguinity and reproductive health among Arabs. Reprod. Health 2009, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liewluck, T.; Milone, M.; Tian, X.; Engel, A.G.; Staff, N.P.; Wong, L.J. Adult-onset respiratory insufficiency, scoliosis, and distal joint hyperlaxity in patients with multiminicore disease due to novel Megf10 mutations. Muscle Nerve 2016, 53, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, K.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Shin, J.Y.; Tanaka, R.; Fujii, T.; Tsuburaya, R.; Mukaida, S.; Noguchi, S.; Nonaka, I.; Nishino, I. Japanese multiple epidermal growth factor 10 (MEGF10) myopathy with novel mutations: A phenotype-genotype correlation. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2016, 26, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, E.; Marini-Bettolo, C.; Topf, A.; Barresi, R.; Polvikoski, T.; Bailey, G.; Charlton, R.; Tellez, J.; MacArthur, D.; Guglieri, M.; et al. MEGF10 related myopathies: A new case with adult onset disease with prominent respiratory failure and review of reported phenotypes. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2018, 28, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.; Topf, A.; Barresi, R.; Hudson, J.; Powell, H.; Tellez, J.; Hicks, D.; Porter, A.; Bertoli, M.; Evangelista, T.; et al. Exome sequences versus sequential gene testing in the UK highly specialised Service for Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Brady, L.; Shoffner, J.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. Next-generation sequencing to diagnose muscular dystrophy, rhabdomyolysis, and hyperCKemia. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 45, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, A.C.; Bonaldi, A.; Fonseca, S.A.; Otto, P.A.; Kok, F.; Bak, M.; Tommerup, N.; Vianna-Morgante, A.M. The segregation of different submicroscopic imbalances underlying the clinical variability associated with a familial karyotypically balanced translocation. Mol. Cytogenet. 2015, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitsuhashi, S.; Mitsuhashi, H.; Alexander, M.S.; Sugimoto, H.; Kang, P.B. Cysteine mutations cause defective tyrosine phosphorylation in MEGF10 myopathy. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 2952–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, M.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Jones, M.D.; Manko, K.; Reddy, H.M.; Bruels, C.C.; Cho, K.A.; Pacak, C.A.; Draper, I.; Kang, P.B. Consequences of MEGF10 deficiency on myoblast function and Notch1 interactions. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2984–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, T.M.; Markello, T.; Accardi, J.; Wolfe, L.; Adams, D.; Sincan, M.; Tarazi, N.M.; Fajardo, K.F.; Cherukuri, P.F.; Bajraktari, I.; et al. Novel SNP array analysis and exome sequencing detect a homozygous exon 7 deletion of MEGF10 causing early onset myopathy, areflexia, respiratory distress and dysphagia (EMARDD). Neuromuscul. Disord. 2013, 23, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takayama, K.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Noguchi, S.; Hayashi, Y.; Nonaka, I.; Nishino, I. GP 155: A first Asian MEGF10 myopathy due to novel homozygous mutation. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2014, 24, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posey, J.E.; Harel, T.; Liu, P.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; James, R.A.; Coban Akdemir, Z.H.; Walkiewicz, M.; Bi, W.; Xiao, R.; Ding, Y.; et al. Resolution of Disease Phenotypes Resulting from Multilocus Genomic Variation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdullatif, M.A.; Al Dhaibani, M.A.; Khassawneh, M.Y.; El-Hattab, A.W. Chromosomal microarray in a highly consanguineous population: Diagnostic yield, utility of regions of homozygosity, and novel mutations. Clin. Genet. 2017, 91, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Rizzo, S.A.; Ramanathan, M.; Hightower, R.M.; Santostefano, K.E.; Terada, N.; Finkel, R.S.; Berg, J.S.; Chahin, N.; Pacak, C.A.; et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors ameliorate MEGF10 myopathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 2365–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saladini, M.; Nizzardo, M.; Govoni, A.; Taiana, M.; Bresolin, N.; Comi, G.P.; Corti, S. Spinal muscular atrophy with respiratory distress type 1: Clinical phenotypes, molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic insights. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breivik, N.; Fiskerstrand, T.; Sand, T.; Vogt, C. Three siblings with progressive respiratory distress as infants. Tidsskr. Nor. Laegeforen. 2013, 133, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arts, W.F.; de Groot, C.J. Congenital nemaline myopathy: Two patients with consanguineous parents, one with a progressive course. J. Neurol. 1983, 230, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Variant Name (cDNA) | Variant Type | Variant Name (Amino Acid) | Phenotypic Details | Ethnicity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | c.211C>T | Missense | p.R71W | Minicore myopathy | Portuguese | Boyden (2012) Neurogenetics 13, 115 [9] |
| 2 | c.230G>A | Missense | p.R77Q | Minicore myopathy | French-F/German-M | Liewluck (2016) Muscle Nerve 53, 984 [12] |
| 3 | c.352T>C | Missense | p.C118R | Muscular dystrophy, limb girdle | Unknown | Harris (2017) Orphanet J Rare Dis 12, 151 [15] |
| 4 | c.352T>C | Missense | p.C118R | Muscular dystrophy, limb girdle | Unknown | Harris (2018) Neuromuscul Disord 28: 48 [14] |
| 5 | c.976T>C | Missense | p.C326R | Minicore myopathy | Mixed European Origin | Boyden (2012) Neurogenetics 13, 115 [9] |
| 6 | c.1559G>A | Nonsense | p.W520* | EMARDD | Sri Lankan | Logan (2011) Nat Genet 43, 1189 [8] |
| 7 | c.1833T>G | Missense | p.C611W | Minicore myopathy | French-F/German-M | Liewluck (2016) Muscle Nerve 53, 984 [12] |
| 8 | c.2211G>A | Nonsense | p.W737* | Muscle weakness | Canadian/Not Specified | Wu (2018) Can J Neurol Sci epub, epub [16] |
| 9 | c.2301C>A | Nonsense | p.C767* | EMARDD | Qatari | Logan (2011) Nat Genet 43, 1189 [8] |
| 10 | c.2320T>C | Missense | p.C774R | EMARDD | English | Logan (2011) Nat Genet 43, 1189 [8] |
| 11 | c.2320T>C | Missense | p.C774R | EMARDD | Mixed European ancestry | Boyden (2012) Neurogenetics 13: 115 [9] |
| 12 | c.2429G>A | Missense | p.C810Y | Minicore myopathy | Japanese | Takayama (2016) Neuromuscul Disord 26, 604 [13] |
| 13 | c.3144T>G | Nonsense | p.Y1048* | EMARDD | Turkish | Logan (2011) Nat Genet 43, 1189 [8] |
| 14 | c.1426+1G>T | Splicing error | — | Muscular dystrophy, limb girdle | Unknown | Harris (2017) Orphanet J Rare Dis 12, 151 [15] |
| 15 | c.1426+1G>T | Splicing error | — | Muscular dystrophy, limb girdle | Unknown | Harris (2018) Neuromuscul Disord 28: 48 [14] |
| 16 | c.2981-2A>G | Splicing error | — | Minicore myopathy | Japanese | Takayama (2016) Neuromuscul Disord 26, 604 [13] |
| 17 | c.2980+5G>C | Splicing error | — | EMARDD | Saudi | THIS STUDY |
| 18 | c.131_132delTG | Small deletion | — | EMARDD | Japanese | Takayama (2014) Neuromuscul Disord 24 848 [21] |
| 19 | c.131_132delTG | Small deletion | — | EMARDD | Japanese | Takayama (2016) Neuromuscul Disord 26: 604 [13] |
| 20 | c.1325delC | Small deletion | p.Pro442Hfs*9 | EMARDD | English | Logan (2011) Nat Genet 43, 1189 [8] |
| 21 | c.1557delA | Small deletion | p.Trp520fs* | Myopathy, areflexia, respiratory distress, and dysphagia | Unkown (M+P) | Posey (2017) N Engl J Med 376, 21 [22] |
| 22 | c.1557delA | Small deletion | p.Trp520fs* | Myopathy, areflexia, respiratory distress, and dysphagia | Emarati | Alabdullatif (2017) Clin Genet 91: 616 [23] |
| 23 | c.2288_2297dup10 | Small insertion | p.Asp766EfsX4 | EMARDD | Pakistani | Logan (2011) Nat Genet 43, 1189 [23] |
| 24 | c.3132dupA | Small insertion | — | EMARDD | Saudi | THIS STUDY |
| 25 | N/A | Large deletion (757 bp in exon 7) | — | EMARDD | Arab | Pierson (2013) Neuromuscul Disord 23, 483 [20] |
| 26 | c.2320T>C | Missense | p.C774R | EMARDD | Unknown | Saha et al, Hum Mol Genet 2019 [24] |
| 27 | c.918-2A>G | Splicing error | — | EMARDD | Unknown | Saha et al, Hum Mol Genet 2019 [24] |
| 28 | c.976T>C | Missense | p.C326R | EMARDD | Unknown | Saha et al, Hum Mol Genet 2019 [24] |
| 29 | c.211C>T | Missense | p.T1030C | MEGF10 myopathy, adult onset | Unknown | Saha et al, Hum Mol Genet 2019 [24] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlMuhaizea, M.; Dabbagh, O.; AlQudairy, H.; AlHargan, A.; Alotaibi, W.; Sami, R.; AlOtaibi, R.; Ali, M.M.; AlHindi, H.; Colak, D.; et al. Phenotypic Variability of MEGF10 Variants Causing Congenital Myopathy: Report of Two Unrelated Patients from a Highly Consanguineous Population. Genes 2021, 12, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111783
AlMuhaizea M, Dabbagh O, AlQudairy H, AlHargan A, Alotaibi W, Sami R, AlOtaibi R, Ali MM, AlHindi H, Colak D, et al. Phenotypic Variability of MEGF10 Variants Causing Congenital Myopathy: Report of Two Unrelated Patients from a Highly Consanguineous Population. Genes. 2021; 12(11):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111783
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlMuhaizea, Mohammad, Omar Dabbagh, Hanan AlQudairy, Aljouhra AlHargan, Wafa Alotaibi, Ruba Sami, Rahaf AlOtaibi, Mariam Mahmoud Ali, Hindi AlHindi, Dilek Colak, and et al. 2021. "Phenotypic Variability of MEGF10 Variants Causing Congenital Myopathy: Report of Two Unrelated Patients from a Highly Consanguineous Population" Genes 12, no. 11: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111783
APA StyleAlMuhaizea, M., Dabbagh, O., AlQudairy, H., AlHargan, A., Alotaibi, W., Sami, R., AlOtaibi, R., Ali, M. M., AlHindi, H., Colak, D., & Kaya, N. (2021). Phenotypic Variability of MEGF10 Variants Causing Congenital Myopathy: Report of Two Unrelated Patients from a Highly Consanguineous Population. Genes, 12(11), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111783