Tracing the Source of the Errors in Hourly IMERG Using a Decomposition Evaluation Scheme
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Rain Gauge Data
2.2.2. IMERG Satellite Precipitation Dataset
2.3. Method
- (1)
- The rain gauge measurements and IMERG are pre-processed. First, the precipitationUncal and precipitationCal are summed up from half-hour to hourly scale. Second, the rain gauge measurements, precipitationUncal, and precipitationCal at same location and time are matched together.
- (2)
- The total biases of the precipitationUncal and precipitationCal are calculated according to the Equation (1):where Ik is the precipitation estimated by IMERG; Ok is the observation of rain gauge;
- (3)
- The bias calculated by Equation (1) is decomposed into three independent components including missed bias (rain areas which are incorrectly determined as no-rain areas by IMERG, termed as MB), false bias (no-rain areas which are incorrectly determined as rain areas by IMERG, termed as FB), and hit bias (the rain areas correctly determined by IMERG, but the precipitation intensity is inaccurately estimated, termed as HB) by Equations (2)–(4), respectively. It is obvious that the sum of the FB, MB, and HB is equal to the bias, but the magnitude of some components could exceed the total bias because the three components could cancel each other.where FB, HB, and MB are the false bias, hit bias, and missed bias, and F, H, and M are the number of false alarmed grids, hit grids, and missed detected grids, respectively. Oh, and Om are the rain gauge observation at hit grids and missed detected grids, respectively. In contrast, If, and Im are the precipitation estimated by IMERG at false alarmed grids and missed detected grids, respectively. Ok is the observation measured by rain gauge k, and n is the number of all grids over the study area.
- (4)
- The HB of IMERG is further decomposed according to the precipitation intensity of the rain gauge measurements, with the aim of investigating whether any quantitative or qualitative relationships exist between them. To perform this analysis, all samples of hit bias are separated into 49 groups using the following thresholds: first, the samples with Rain gauge measurements values above 0 and no more than 3 mm/hour are separated into 30 groups with 0.1 mm/hour per step. Second, the samples with rain gauge measurements between 3 mm/hour and 10 mm/hour are separated into 14 groups for each 0.5 mm/hour step. Third, the samples with IMERG between 10 mm/hour and 15 mm/hour are separated into 5 groups at each 1 mm/hour step. Then the bias of each group is calculated according to the Equation (1).
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Pattern of the IMERG
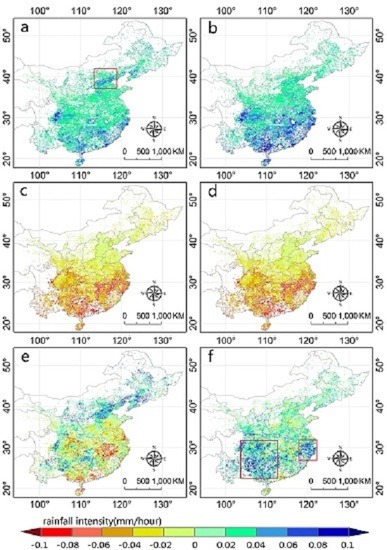
3.2. Bias Decomposition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Both precipitationUncal and precipitationCal could capture the spatial pattern of the precipitation over the study, but the former could better estimate the precipitation volume than the latter.
- (2)
- The calibration algorithm used by IMERG could significantly reduce the hit bias over the south regions, but it exaggerated the false bias over the south part. Additionally, this algorithm could not alleviate the missed bias of IMERG, which is largely responsible for the bias over the south part of the IMERG.
- (3)
- The false bias and hit bias were responsible for a large part of the total bias of both precipitationUncal and precipitationCal. Therefore, considerations concerning how to retrieve more accurate rain areas delineation using satellite observations deserve more attention in order to better apply and improve the application of IMERG in future work.
- (4)
- There was a strong non-linear relationship between the hit bias of IMERG and the rainfall intensity measured by rain gauges, which could be beneficial for the further correction of this new satellite precipitation dataset.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yong, B.; Liu, D.; Gourley, J.J.; Tian, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y. Global view of real-time TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis: Implications for its successor global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-G.; Niu, Z.; Shen, Y. Understanding the dependence of the uncertainty in a satellite precipitation data set on the underlying surface and a correction method based on geographically weighted regression. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6508–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Henschke, A.; Adler, R.F. Evaluation of tmpa satellite-based research and real-time rainfall estimates during six tropical-related heavy rainfall events over louisiana, USA. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, A.T.; Yan, F.; Habib, E. Accuracy of the cmorph satellite-rainfall product over lake tana basin in eastern africa. Atmos. Res. 2014, 163, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grody, N.C. Classification of snow cover and precipitation using the special sensor microwave imager. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1991, 96, 7423–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, R.R.; Grody, N.C.; Marks, G.F. Effects of surface conditions on rain identification using the DMSP-SSM/I. Remote Sens. Rev. 1994, 11, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Hossain, F. How well can we estimate error variance of satellite precipitation data around the world? Atmos. Res. 2015, 154, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Arkin, P.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Gruber, A.; Janowiak, J.; McNab, A.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U. The global precipitation climatology project (gpcp) combined precipitation dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.J.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; Wolff, D.B. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P.P. Cmorph: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Mission: An Overview. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=20060026287 (accessed on 12 December 2016).
- Tapiador, F.J.; Turk, F.J.; Petersen, W.; Hou, A.Y.; García-Ortega, E.; Machado, L.A.T.; Angelis, C.F.; Salio, P.; Kidd, C.; Huffman, G.J. Global precipitation measurement: Methods, datasets and applications. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104–105, 70–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement (GPM) mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Mitra, A.K.; Aghakouchak, A.; Liu, Z.; Norouzi, H.; Pai, D.S. A preliminary assessment of GPM-based multi-satellite precipitation estimates over a monsoon dominated region. J. Hydrol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Behrangi, A.; Hong, Y.; Ndayisaba, F.; Hu, J.; Stepanian, P.M. Early assessment of integrated multi-satellite retrievals for global precipitation measurement over China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176–177, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of GPM day-1 imerg and TMPA version-7 legacy products over mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2015, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P.P. Performance of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.P.; Xiong, A.Y. A conceptual model for constructing high-resolution gauge-satellite merged precipitation analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salio, P.; Hobouchian, M.P.; Skabar, Y.G.; Vila, D. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates over southern south america using a dense rain gauge network. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, V.; Meyers, P.C.; Robinson, M.D. A review of merged high-resolution satellite precipitation product accuracy during the tropical rainfall measuring mission (TRMM) era. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.A.J.; Braga, R.C.; Vila, D.A.; Morales, C.A. Evaluation of GPROF-SSMI/S rainfall estimates over land during the brazilian chuva-vale campaign. Atmos. Res. 2014, 163, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Maggioni, V.; Vila, D.; Morales, C. Characteristics and diurnal cycle of GPM rainfall estimates over the central amazon region. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Eylander, J.B.; Joyce, R.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Hsu, K.L.; Turk, F.J.; Garcia, M.; Zeng, J. Component analysis of errors in satellite-based precipitation estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Tian, Y.; Yan, F.; Habib, E. An improved procedure for the validation of satellite-based precipitation estimates. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Hossain, F. Tracing hydrologic model simulation error as a function of satellite rainfall estimation bias components and land use and land cover conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W11509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Yatagai, A.; Chen, M.; Hayasaka, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, S. A gauge-based analysis of daily precipitation over east Asia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J. A high spatiotemporal gauge-satellite merged precipitation analysis over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.L.; Gao, X.G.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Mitra, A.K.; Pai, D.S.; Aghakouchak, A. From TRMM to GPM: How well can heavy rainfall be detected from space? Adv. Water Res. 2015, 88, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaona, M.F.R.; Overeem, A.; Leijnse, H.; Uijlenhoet, R. First-year evaluation of GPM-rainfall over the Netherlands: Imerg day-1 final run (v03d). J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 2799–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.; Hong, Y.; Olson, W.S.; Yang, S.; Adler, R.F.; McCollum, J.; Ferraro, R.; Petty, G.; Shin, D.B.; Wilheit, T.T. The evolution of the goddard profiling algorithm (GPROF) for rainfall estimation from passive microwave sensors. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1801–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, S.; Levizzani, V.; Anagnostou, E.; Bauer, P.; Kasparis, T.; Lane, J.E. Precipitation: Measurement, remote sensing, climatology and modeling. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Tian, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Wen, Y. First evaluation of the climatological calibration algorithm in the real-time tmpa precipitation estimates over two basins at high and low latitudes. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2461–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Region | Dataset | Total Bias | False Bias | Missed Bias | Hit Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South part | PrecipitationUncal | 58.2% | 38.6% | −20.8% | 40.4% |
| PrecipitationCal | 27.7% | 32.5% | −20.8% | 16.0% | |
| North part | PrecipitationUncal | −13.6% | 17.0% | −23.8% | −6.8% |
| PrecipitationCal | 12.9% | 23% | −23.8% | 13.7% |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Shen, Y.; Du, Z. Tracing the Source of the Errors in Hourly IMERG Using a Decomposition Evaluation Scheme. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7120161
Xu S, Shen Y, Du Z. Tracing the Source of the Errors in Hourly IMERG Using a Decomposition Evaluation Scheme. Atmosphere. 2016; 7(12):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7120161
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shiguang, Yan Shen, and Zhe Du. 2016. "Tracing the Source of the Errors in Hourly IMERG Using a Decomposition Evaluation Scheme" Atmosphere 7, no. 12: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7120161
APA StyleXu, S., Shen, Y., & Du, Z. (2016). Tracing the Source of the Errors in Hourly IMERG Using a Decomposition Evaluation Scheme. Atmosphere, 7(12), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7120161