Effects of Strong East Asian Cold Surges on Improving the Air Quality over Mainland China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Statistical Analysis Methods
2.3. Definition of SEACS
3. Results
3.1. Activities SEACSs and Spatial Distribution of Air Quality over Mainland China
3.2. Air Quality Improvement by SEACSs
3.2.1. Spatial Features in Air Quality Improvement
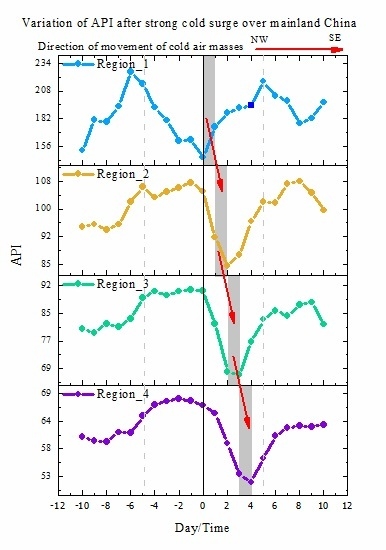
3.2.2. Temporal Evolution of Air Quality Improvement
3.2.3. Removal Effect of SEACSs on Air Pollutants in Different Regions
3.3. Temporal Evolution of Weather Factors Associated with SEACSs
3.3.1. Dynamic Changes of SLP
3.3.2. Temporal Evolution of Temperature and Meridional Wind at 925 hPa
3.3.3. Trajectory of SEACSs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEACS | Strong East Asian Cold Surge |
| API | Air Pollution Index |
| RE | Removal Efficiency |
| SLP | Sea Level Pressure |
| AOD | Aerosol Optical Depth |
References
- Qian, Y.; Gong, D.; Fan, J.; Leung, L.R.; Bennartz, R.; Chen, D.; Wang, W. Heavy pollution suppresses light rain inChina: Observations and modeling. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Dickinson, R.E.; Liang, S.L. Clear sky visibility has decreased over land globally from 1973 to 2007. Science 2009, 323, 1468–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monks, P.; Granier, C.; Fuzzi, S.; Stohl, A.; Williams, M.; Akimoto, H.; Amann, M.; Baklanov, A.; Baltensperger, U.; Bey, I. Atmospheric composition change–Global and regional air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5268–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, P.; Tao, J.; Wang, Z. Formation process of the widespread extreme haze pollution over northern Chinain January 2013: Implications for regional air quality and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynard, A.; Clerbaux, C.; Clarisse, L.; Safieddine, S.; Pommier, M.; Van Damme, M.; Bauduin, S.; Oudot, C.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Hurtmans, D.; et al. First simultaneous space measurements of atmospheric pollutants in the boundary layer from iasi: A case study in the north China plain. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yan, L.; Zhao, H. Seasonal variations of atmospheric pollution and air quality in Beijing. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1753–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yan, F.; Xie, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, J.; Fu, Q. Impact of meteorological conditions on a nine-day particulate matter pollution event observed in December 2013, Shanghai, China. Particuology 2015, 20, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wu, D.; Fan, Q.; Wang, B.M.; Li, H.W.; Fan, S.J. Observational studies of the meteorological characteristics associated with poor air quality over the Pearl River Deltain China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10755–10766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hui, Y.; Yin, Z.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Xie, X.; Fang, J. Deteriorating haze situation and the severe haze episode during December 18–25 of 2013 in Xi’an China, the worst event on record. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.; Harrison, R.M.; Baker, J. The wind speed dependence of the concentrations of airborne particulate matter and Nox. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Hu, M.; Wu, Z.J.; Yue, D.L.; He, L.Y.; Huang, X.F.; Liu, X.G.; Wiedensohler, A. Long-term measurements of particle number size distributions and the relationships with air mass history and source apportionment in the summer of Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10159–10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, E.; Davis, T.; Martin, R.S.; Silva, P.J. Meteorological and environmental aspects of one of the worst national air pollution episodes (January 2004) in Logan, Cache Valley, Utah, USA. Atmos. Res. 2006, 79, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloulakou, A.; Kassomenos, P.; Spyrellis, N.; Demokritou, P.; Koutrakis, P. Measurements of PM10 and PM2.5 particle concentrations in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hien, P.D.; Loc, P.D.; Dao, N.V. Air pollution episodes associated with East Asian winter monsoons. Sci. Total. Environ. 2011, 409, 5063–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.W.; Ho, C.H.; Jeong, S.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Park, S.K.; Song, C.K. Different characteristics of cold day and cold surge frequency over East Asianin a global warming situation. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sperber, K.R.; Boyle, J.S. Climatology and interannual variation of the East Asian winter monsoon: Results from the 1979–95 NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 2605–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Ho, C.H. Changes in occurrence of cold surges over East Asia in association with arctic oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCiM, G.R. The horizontal and vertical structure of East Asia winter monsoon pressure surges. QJR Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 29–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Lung, S.-C.C.; Guo, H.-R.; Wu, P.-C.; Su, H.-J. Climate variability of cold surge and its impact on the air quality of Taiwan. Clim. Chang. 2008, 94, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.L.; Meng, F.; Xu, J.; He, Y.J. Process analysis about the impact of a strong cold front on air pollution transportation in eastern China in spring. Res. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 34–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Gao, S. Effect of cold wave on winter visibility over eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 2394–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The era-interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. QJR Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Minstry of Environmental Protection (MEP). Available online: http://datacenter.mep.gov.cn (accessed on 5 August 2015).
- Li, L.; Qian, J.; Ou, C.Q.; Zhou, Y.X.; Guo, C.; Guo, Y. Spatial and temporal analysis of air pollution index and its timescale-dependent relationship with meteorological factors in Guangzhou, China, 2001–2011. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 190, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Wang, T.; Jiang, Z.; Xie, M.; Zhang, R.; Huang, X.; Zhu, J. Characterization of visibility and its affecting factors over Nanjing, China. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, A.; Baier, F.; Benedetti, A.; Bouarar, I.; Chabrillat, S.; Clark, H.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.; Engelen, R.J.; Errera, Q.; et al. The MACC reanalysis: An 8 year data set of atmospheric composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4073–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, R.S. A survey of clustering techniques. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2010, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.G.; Caramelo, L.; Orozco, C.V.; Costa, R.; Tonini, M. Space-time clustering analysis performance of an aggregated dataset: The case of wildfires in Portugal. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2015, 72, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Losada, Á.; Pires, J.C.M.; Pino-Mejías, R. Time series clustering for estimating particulate matter contributions and its use in quantifying impacts from deserts. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 117, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.; Rolph, G. Cited 2003: HYSPLIT (Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model; NOAA/Air Resources Laboratory, Silver Spring: College Park, MD, USA, 2003.
- Stein, A.; Draxler, R.; Rolph, G.; Stunder, B.; Cohen, M.; Ngan, F. Noaa’s hysplit atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.; Yen, M.C.; Huang, W.R.; Gallus, W.A. An East Asian cold surge: Case study. Mon. Weather Rev. 2002, 130, 2271–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, F.; Shahgedanova, M.; Hannachi, A.; Stephenson, D.B. Observed trends and teleconnections of the Siberian high: A recently declining center of action. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-R.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chan, J.C.L. Discrepancies between global reanalyses and observations in the interdecadal variations of southeast Asian cold surge. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 2272–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Kanno, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Takaya, K. An isentropic analysis of the temporal evolution of East Asian cold air outbreaks. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 9337–9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfold, M.J.; Pyle, J.A.; Robinson, A.D.; Meneguz, E.; Nadzir, M.S.M.; Phang, S.M.; Samah, A.A.; Ong, S.; Ung, H.E.; Peng, L.K.; et al. Rapid transport of East Asia pollution to the deep tropics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3565–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-C.; Huang, W.-R.; Yoon, J.-H. Interannual variation of the East Asia cold surge activity. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.H.; Kim, B.M.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Lim, G.H. Decadal changes in surface air temperature variability and cold surge characteristics over northeast Asia and their relation with the arctic oscillation for the past three decades (1979–2011). J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Z.; Bengtsson, L.; Arpe, K. Impact of global warming on the Asian winter monsoon in a coupled GCM. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 4607–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liang, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Si, D.; Liang, P.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J. Interdecadal variability of the East Asian winter monsoon and its possible links to global climate change. J. Meteor. Res. 2014, 28, 693–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Niu, T.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.E.; Ueda, H. Impact of global warming on the east asian winter monsoon as revealed by nine coupled atmosphere-ocean GCMs. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Date | SLPS/hPa | Ngrid | APIbefore | Date | SLPS/hPa | Ngrid | APIbefore |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001/11/24 | 1036.2 | 1865 | 118 | 2006/1/29 | 1035.5 | 735 | 95 |
| 2001/12/18 | 1041.7 | 130 | 88 | 2006/3/10 | 1039.2 | 2070 | 94 |
| 2001/12/24 | 1036.6 | 488 | 91 | 2007/1/6 | 1035.8 | 582 | 89 |
| 2002/12/5 | 1038.3 | 1067 | 110 | 2008/1/11 | 1042.2 | 1302 | 111 |
| 2002/12/21 | 1039.3 | 295 | 86 | 2008/12/3 | 1042.3 | 1931 | 84 |
| 2003/1/1 | 1039.6 | 547 | 99 | 2008/12/19 | 1035.6 | 1752 | 89 |
| 2003/12/5 | 1036.4 | 908 | 97 | 2009/1/22 | 1045.3 | 1959 | 89 |
| 2004/1/15 | 1036.0 | 286 | 83 | 2009/2/15 | 1037.2 | 770 | 81 |
| 2004/1/31 | 1037.5 | 439 | 86 | 2009/10/31 | 1039.6 | 1476 | 82 |
| 2004/11/23 | 1040.0 | 1979 | 90 | 2009/11/10 | 1035.5 | 988 | 86 |
| 2005/1/7 | 1036.6 | 626 | 90 | 2009/12/24 | 1036.8 | 1591 | 91 |
| 2005/1/11 | 1037.1 | 133 | 88 | 2010/1/3 | 1036.6 | 832 | 90 |
| 2005/1/23 | 1036.4 | 863 | 85 | 2010/1/19 | 1041.5 | 2053 | 92 |
| 2005/3/10 | 1036.7 | 1294 | 85 | 2010/1/31 | 1038.8 | 1114 | 82 |
| 2005/12/1 | 1035.7 | 760 | 99 | 2010/12/12 | 1037.5 | 773 | 87 |
| 2005/12/14 | 1037.6 | 175 | 82 | 2010/12/22 | 1036.2 | 1800 | 97 |
| 2005/12/19 | 1041.1 | 570 | 92 | 2011/12/20 | 1035.6 | 213 | 83 |
| 2005/12/25 | 1035.3 | 300 | 99 | 2012/1/1 | 1044.1 | 911 | 94 |
| 2006/1/2 | 1037.1 | 1179 | 96 | 2012/1/14 | 1039.5 | 1308 | 87 |
| 2006/1/21 | 1036.8 | 430 | 80 |
| Region | APImax | APImin | ∆APImax-min | RE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 124 | 78 | 46 | 36.8% |
| B | 91 | 59 | 32 | 35.4% |
| C | 94 | 65 | 29 | 30.8% |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xie, X. Effects of Strong East Asian Cold Surges on Improving the Air Quality over Mainland China. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7030038
Wang Z, Liu X, Xie X. Effects of Strong East Asian Cold Surges on Improving the Air Quality over Mainland China. Atmosphere. 2016; 7(3):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7030038
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhaosheng, Xiaodong Liu, and Xiaoning Xie. 2016. "Effects of Strong East Asian Cold Surges on Improving the Air Quality over Mainland China" Atmosphere 7, no. 3: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7030038
APA StyleWang, Z., Liu, X., & Xie, X. (2016). Effects of Strong East Asian Cold Surges on Improving the Air Quality over Mainland China. Atmosphere, 7(3), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7030038