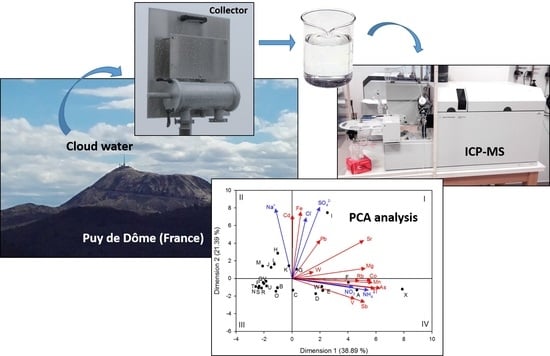
Trace Metals in Cloud Water Sampled at the Puy De Dôme Station
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloud Water Sampling and Physico-Chemical Parameters
2.2. ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) Analysis
2.3. PCA (Principal Component Analysis) and HCA (Hierarchic Cluster Analysis)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Principal Components Analysis (PCA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deguillaume, L.; Leriche, M.; Desboeufs, K.; Mailhot, G.; George, C.; Chaumerliac, N. Transition metals in atmospheric liquid phases: Sources, reactivity, and sensitive parameters. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3388–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desboeufs, K.V.; Sofikitis, A.; Losno, R.; Colin, J.L.; Ausset, P. Dissolution and solubility of trace metals from natural and anthropogenic aerosol particulate matter. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, R.; Desboeufs, K.V.; Journet, E. Variability of dust iron solubility in atmospheric waters: Investigation of the role of oxalate organic complexation. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6510–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, R.; Desboeufs, K.V. Effect of atmospheric organic complexation on iron-bearing dust solubility. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plessow, K.; Acker, K.; Heinrichs, H.; Möller, D. Time study of trace elements and major ions during two cloud events at the Mt. Brocken. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.; Reynolds, B.; Neal, C.; Hill, S.; Neal, M.; Harrow, M. Major, minor and trace element composition of cloudwater and rainwater at Plynlimon. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 1997, 1, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yuan, Q.; Li, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Trace metals in atmospheric fine particles in one industrial urban city: Spatial variations, sources, and health implications. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, N.J.; Norra, S.; Chai, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Cen, K.; Yu, Y.; Stüben, D. Temporal variability of trace metal mobility of urban particulate matter from Beijing—A contribution to health impact assessments of aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7248–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, H.; Sigel, A.; Dekker, M. Metal Ions in Biological Systems; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; p. 848. ISBN 0-8247-9549-0. [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm, E.G.; Keeler, G.J.; Lawson, S.T.; Sherbatskoy, T.D. Mercury and trace elements in cloud water and precipitation collected on Mt. Mansfield, Vermont. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nriagu, J.O. A global assessment of natural sources of atmospheric trace metals. Nature 1989, 338, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mahowald, N.; Scanza, R.A.; Journet, E.; Desboeufs, K.; Albani, S.; Kok, J.F.; Zhuang, G.; Chen, Y.; Cohen, D.D.; et al. Modeling the global emission, transport and deposition of trace elements associated with mineral dust. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 5771–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fomba, K.W.; van Pinxteren, D.; Müller, K.; Iinuma, Y.; Lee, T.; Collett, J.L.; Herrmann, H. Trace metal characterization of aerosol particles and cloud water during HCCT 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8751–8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cini, R.; Prodi, F.; Santachiara, G.; Porcù, F.; Bellandi, S.; Stortini, A.; Oppo, C.; Udisti, R.; Pantani, F. Chemical characterization of cloud episodes at a ridge site in Tuscan Appennines, Italy. Atmos. Res. 2002, 61, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Collett, J.L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W. Microscopic evaluation of trace metals in cloud droplets in an acid precipitation region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4172–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghauri, B.M.; Mirza, I.M.; Richter, R.; Dutkiewicz, V.A.; Rusheed, A.; Khan, A.R.; Husain, L. Composition of aerosols and cloud water at a remote mountain site (2.8 kms) in Pakistan. Chemosphere Glob. Chang. Sci. 2001, 3, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieber, R.J.; Peake, B.; Willey, J.D.; Jacobs, B. Iron speciation and hydrogen peroxide concentrations in New Zealand rainwater. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 6041–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguillaume, L.; Leriche, M.; Monod, A.; Chaumerliac, N. The role of transition metal ions on HOx radicals in clouds: A numerical evaluation of its impact on multiphase chemistry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.; Sinha, B.; van Pinxteren, D.; Tilgner, A.; Fomba, K.W.; Schneider, J.; Roth, A.; Gnauk, T.; Fahlbusch, B.; Mertes, S.; et al. Enhanced role of transition metal ion catalysis during in-cloud oxidation of SO2. Science 2013, 340, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, H.; Ervens, B.; Jacobi, H.-W.; Wolke, R.; Nowacki, P.; Zellner, R. CAPRAM 2.3: A chemical aqueous phase radical mechanism for tropospheric chemistry. J. Atmos. Chem. 2000, 36, 231–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervens, B. Modeling the processing of aerosol and trace gases in clouds and fogs. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4157–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouchel-Vallon, C.; Deguillaume, L.; Monod, A.; Perroux, H.; Rose, C.; Ghigo, G.; Long, Y.; Leriche, M.; Aumont, B.; Patryl, L.; et al. CLEPS 1.0: A new protocol for cloud aqueous phase oxidation of VOC mechanisms. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 1339–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilgner, A.; Bräuer, P.; Wolke, R.; Herrmann, H. Modelling multiphase chemistry in deliquescent aerosols and clouds using CAPRAM3.0i. J. Atmos. Chem. 2013, 70, 221–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Charbouillot, T.; Brigante, M.; Mailhot, G.; Delort, A.-M.; Chaumerliac, N.; Deguillaume, L. Evaluation of modeled cloud chemistry mechanism against laboratory irradiation experiments: The HxOy/iron/carboxylic acid chemical system. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, C.; Tilgner, A.; Bräuer, P.; Herrmann, H. Modeling the impact of iron–carboxylate photochemistry on radical budget and carboxylate degradation in cloud droplets and particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5652–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheize, M.; Sarthou, G.; Croot, P.L.; Bucciarelli, E.; Baudoux, A.-C.; Baker, A.R. Iron organic speciation determination in rainwater using cathodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 736, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinatier, V.; Wirgot, N.; Joly, M.; Sancelme, M.; Abrantes, M.; Deguillaume, L.; Delort, A.-M. Siderophores in coud waters and potential impact on atmospheric chemistry: Production by microorganisms isolated at the Puy de Dôme station. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9315–9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passananti, M.; Vinatier, V.; Delort, A.-M.; Mailhot, G.; Brigante, M. Siderophores in cloud waters and potential impact on atmospheric chemistry: Photoreactivity of iron complexes under sun-simulated conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9324–9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freney, E.J.; Sellegri, K.; Canonaco, F.; Boulon, J.; Hervo, M.; Weigel, R.; Pichon, J.M.; Colomb, A.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Laj, P. Seasonal variations in aerosol particle composition at the puy-de-Dôme research station in France. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 13047–13059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venzac, H.; Sellegri, K.; Villani, P.; Picard, D.; Laj, P. Seasonal variation of aerosol size distributions in the free troposphere and residual layer at the puy de Dôme station, France. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1465–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguillaume, L.; Charbouillot, T.; Joly, M.; Vaïtilingom, M.; Parazols, M.; Marinoni, A.; Amato, P.; Delort, A.-M.; Vinatier, V.; Flossmann, A.; et al. Classification of clouds sampled at the puy de Dôme (France) based on 10 years of monitoring of their physicochemical properties. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1485–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauvigné, A. Impact radiatif des aérosols de haute altitude. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Blaise Pascal, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hervo, M. Etude des propriétés optiques et radiatives des aérosols en atmosphère réelle : Impact de l’hygroscopicité. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Blaise Pascal, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brantner, B.; Fierlinger, H.; Puxbaum, H.; Berner, A. Cloudwater chemistry in the subcooled droplet regime at Mount Sonnblick (3106 M A.S.L., Salzburg, Austria). Water Air Soil Pollut. 1994, 74, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addinsoft Xlstat, version 2016; Data Analysis and Statistical Solution for Microsoft Excel; Addinsoft: Paris, France, 2016.
- Putaud, J.-P.; Raes, F.; Van Dingenen, R.; Brüggemann, E.; Facchini, M.-C.; Decesari, S.; Fuzzi, S.; Gehrig, R.; Hüglin, C.; Laj, P.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology—2: Chemical characteristics of particulate matter at kerbside, urban, rural and background sites in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2579–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, J.W.; Robinson, M.S.; McIlwraith, H.; Kingston, J.T.; Herckes, P. The chemistry of intercepted clouds in Northern Arizona during the north american monsoon season. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 199, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wai, K.-M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, P.; Guo, J.; Xu, P.; Wang, W. Evaluation of trace elements contamination in cloud/fog water at an elevated mountain site in Northern China. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.D.; Fergusson, J.E. The concentrations, distribution and sources of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc in the atmosphere of an urban environment. Sci. Total Environ. 1994, 144, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lion, L.W.; Leckie, J.O. The Biogeochemistry of the Air-Sea Interface. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1981, 9, 449–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowicz, S.R.; Duce, R.A.; Fasching, J.L.; Weisel, C.P. Bursting bubbles and their effect on the sea-to-air transport of Fe, Cu and Zn. Mar. Chem. 1979, 7, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogen, J. Trace elements in atmospheric aerosol in the heidelberg area, measured by instrumental neutron activation analysis. Atmos. Environ. 1973, 7, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlastelic, I.; Suchorski, K.; Sellegri, K.; Colomb, A.; Nauret, F.; Bouvier, L.; Piro, J.-L. The trace metal signature of atmospheric aerosols sampled at a European regional background site (puy de Dôme, France). J. Atmos. Chem. 2014, 71, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péwé, T.L. Origin and transportation. In Desert Dust: Origin, Characteristics, and Effect on Man; American Association for the Advancement of Science; The Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1981; pp. 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Deguillaume, L. Mesures de la phase aqueuse du nuage du SO BEAM. Available online: http://wwwobs.univ-bpclermont.fr/SO/beam/data.php (accessed on 15 September 2017).
- Williams, C.R.; Harrison, R.M. Cadmium in the atmosphere. Experientia 1984, 40, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, J.T.; Maldonado, M.T. Biogeochemistry of Cadmium and Its Release to the Environment. In Cadmium: From Toxicity to Essentiality; Sigel, A., Sigel, H., Sigel, R.K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 11, pp. 31–62. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, S.K.; Kamber, B.S.; McGowan, H.A. Scavenging of atmospheric trace metal pollutants by mineral dusts: Inter-regional transport of Australian trace metal pollution to New Zealand. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2460–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, T.; Querol, X.; Castillo, S.; Alastuey, A.; Cuevas, E.; Herrmann, L.; Mounkaila, M.; Elvira, J.; Gibbons, W. Geochemical variations in aeolian mineral particles from the Sahara–Sahel Dust Corridor. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameter | pH | Cl− | Na+ | NO3− | SO42− | NH4+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | 4.1 | 2.0 | 3.2 | 6.1 | 8.0 | 0.0 |
| 1st Qu. | 5.3 | 7.9 | 10.6 | 19.9 | 15.8 | 0.0 |
| Median | 5.5 | 22.3 | 17.9 | 22.9 | 25.1 | 1.1 |
| Mean | 5.5 | 33.0 | 30.5 | 53.9 | 40.4 | 51.9 |
| 3rd Qu. | 5.7 | 52.6 | 45.7 | 53.0 | 38.6 | 87.5 |
| Max. | 6.9 | 98.0 | 99.0 | 224.1 | 247.4 | 252.4 |
 |
|---|
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bianco, A.; Vaïtilingom, M.; Bridoux, M.; Chaumerliac, N.; Pichon, J.-M.; Piro, J.-L.; Deguillaume, L. Trace Metals in Cloud Water Sampled at the Puy De Dôme Station. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110225
Bianco A, Vaïtilingom M, Bridoux M, Chaumerliac N, Pichon J-M, Piro J-L, Deguillaume L. Trace Metals in Cloud Water Sampled at the Puy De Dôme Station. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(11):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110225
Chicago/Turabian StyleBianco, Angelica, Mickaël Vaïtilingom, Maxime Bridoux, Nadine Chaumerliac, Jean-Marc Pichon, Jean-Luc Piro, and Laurent Deguillaume. 2017. "Trace Metals in Cloud Water Sampled at the Puy De Dôme Station" Atmosphere 8, no. 11: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110225
APA StyleBianco, A., Vaïtilingom, M., Bridoux, M., Chaumerliac, N., Pichon, J. -M., Piro, J. -L., & Deguillaume, L. (2017). Trace Metals in Cloud Water Sampled at the Puy De Dôme Station. Atmosphere, 8(11), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110225