Soil Erosion Modelling and Risk Assessment in Data Scarce Rift Valley Lake Regions, Ethiopia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
2.1. Location and Topography
2.2. Climate
2.3. Hydrology
2.4. Geology, Soil and Land Use
3. Methodology
3.1. SWAT Model
3.2. Model Development and Input Description
3.3. Sub-Watershed Delineation
3.4. Model Calibration, Validation and Evaluation
3.5. Validating SWAT Model Results with Lake Sedimentation Rate
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Flow Calibration and Validation
4.2. Sediment Yield Calibration and Validation
4.3. Spatial Distribution of Sediment Generation Hotspot Area
- ⮶
- Base Scenario (Scenario I): This scenario presents the actual condition observed in the watershed (without conservation measures)
- ⮶
- Scenario 2: Assume the slope length of the watershed is reduced by 25% for a slope greater than 5% by using physical conservation structures (Parallel Terraces, Fanya Juu, soil bund, etc.)
- ⮶
- Scenario 3: Assume the slope length of the watershed is reduced by 50% for a slope greater than 5% by using physical conservation structures (Parallel Terraces, Fanya Juu, soil bund, etc.)
4.4. Sedimentation Estimate Using Historical Lake Bathymetric Differencing
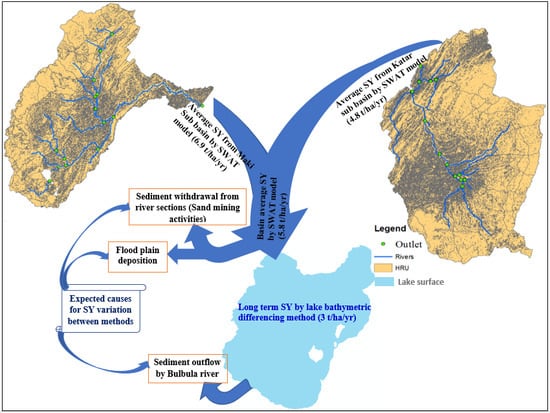
4.5. Difference between Sediment Estimated by SWAT Model and Bathymetric Differencing Techniques
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gashaw, T.; Tulu, T.; Argaw, M. Erosion risk assessment for prioritization of conservation measures in Geleda atershed, Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2017, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawwaf, M.; Willems, P. Analysis of the climate variability on Lake Nasser evaporation based on the Bowen ratio energy budget method. J. Environ. Biol. 2012, 33, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blinkov, I.; Kostadinov, S. Applicability of various erosion risk assessment methods for engineering purposes. In Proceedings of the BALWOIS 2010, Ohrid, Macedonia, 25–29 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ayele, G.T.; Teshale, E.Z.; Yu, B.; Rutherfurd, I.D.; Jeong, J. Streamflow and Sediment Yield Prediction for Watershed Prioritization in the Upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2017, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Neil, D. Temporal and spatial variation of sediment yield in the Snowy Mountains region, Australia. In Variability in Stream Erosion and Sediment Transport; IAHS Publ. No. 224; International Association of Hydrological Sciences (IAHS): London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Marttila, H.; Bjørn, K. Dynamics of erosion and suspended sediment transport from drained peatland forestry. J. Hydrol. 2010, 388, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arekhi, S.; Niazi, Y.; Kalteh, A. Soil erosion and sediment yield modeling using RS and GIS techniques: A case study, Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2010, 5, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsabilla, A.; Kusratmoko, E. Assessment of Soil Erosion Risk in Komering Watershed, South Sumatera, Using SWAT Model. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2017; Volume 1862. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeir, W.H. Predicting Rainfall-erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountain, Guide for Selection of Practices for Soil and Water Conservation. Agric. Handb. 1965, 282, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Nearing, M.; Foster, G.; Lane, L.; Finkner, S. A process-based soil erosion model for USDA-Water Erosion Prediction Project technology. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 1989, 32, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Dyke, P.; Williams, J.; Kiniry, J.; Benson, V.; Griggs, R. EPIC: An operational model for evaluation of agricultural sustainability. Agric. Syst. 1991, 37, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A.; Onstad, C.A.; Bosch, D.D.; Anderson, W.P. AGNPS: A nonpoint-source pollution model for evaluating agricultural watersheds. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1989, 44, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Beasley, D.; Huggins, L.; Monke, E. ANSWERS: A model for watershed planning. Trans. ASAE 1980, 23, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.; Quinton, J.; Smith, R.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knisel, W. CREAMS: A Field-Scale Model for Chemicals, Runoff and Erosion from Agricultural Management Systems; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): Washington, DC, USA, 1980; 640p.
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large Area Hydrologic Modeling and Assessment Part I: Model Development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.; Rorke, M. The relationship of soil loss by interill erosion to slope gradient. Catena 2000, 38, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P. AGNPS–UM: Applying the USLE–M within the agricultural nonpoint source pollution. Environ. Model. Softw. 2000, 15, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.J.; Sagong, M.; Engel, B.A.; Tang, Z.; Choi, J.; Kim, K.-S. GIS-based sediment assessment tool. CATENA 2005, 64, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisantino, T.; Bingner, R.; Chouaib, W.; Gentile, F.; Trisorio Liuzzi, G. Estimation of runoff, peak discharge and sediment load at the event scale in a medium-size mediterranean watershed using the Annagnps Model: An AGNPS evaluation for runoff, peak discharge and sediment load. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 340–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguas, E.V.; Gómez, J.A.; Denisi, P.; Mateos, L. Modelling the rainfall-runoff relationships in a large olive orchard catchment in Southern Spain. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 2361–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.; Fohrer, N. SWAT2000: Current capabilities and research opportunities in applied watershed modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.W.; Shirmohammadi, A.; Montas, H.; Sadeghi, A. Evaluation of the SWAT model sediment and nutrient components in the piedmont physiographic region of Maryland. Trans. ASAE 2004, 47, 1523–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muleta, M.K.; Nicklow, J.W. Decision support for watershed management using evolutionary algorithms. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2005, 131, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Gassman, P.W.; Arnold, J.G. Water quality modeling for the Raccoon River watershed using SWAT. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessu, S.; Melesse, A.M.; Bhat, M.; McClain, M.E. Assessment of water resources availability and demand in the Mara River basin. CATENA 2014, 115, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessu, S.; Melesse, A.M. Modelling the rainfall–runoff process ofthe Mara River basin using the soil and water assessment tool. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 4038–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessu, S.; Melesse, A.M. Impact and uncertainties of climate change on the hydrology of the Mara River basin, Kenya/Tanzania. Hydrol Process. 2013, 27, 2973–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setegn, S.; Dargahi, B.; Srinivasan, R.; Melesse, A.M. Modeling of sediment yield from Anjeni-Gauged Watershed, Ethiopia using SWAT model. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 46, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setegn, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Dargahi, B.; Melesse, A.M. Spatial delineation of soil erosion vulnerability in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 3738–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setegn, S.G.; Rayner, D.; Melesse, A.M.; Dargahi, B.; Srinivasan, R. Impact of climate change on the Hydroclimatology of Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W04511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setegn, S.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Melesse, A.M.; Dargahi, B. SWAT model application and prediction uncertainty analysis in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesuf, H.M.; Assen, M.; Alamirew, T.; Melesse, A.M. Modeling of sediment yield in Maybar gauged watershed using SWAT; Northeast Ethiopia. CATENA 2015, 127, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Dietrich, J.; Uniyal, B.; Tran, D.; Nguyen, V.T.; Dietrich, J.; Uniyal, B.; Tran, D.A. Verification and correction of the hydrologic routing in the soil and water assessment tool. Water 2018, 10, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, P.B.; Nelson, N.O.; Frees, L.D.; Mankin, K.R. Comparison of AnnAGNPS and SWAT model simulation results in USDA-CEAP agricultural watersheds in south-central Kansas. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Kang, G.; Chu, C.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. Comparison of SWAT and GWLF model simulation performance in humid south and semi-arid north of China. Water 2017, 9, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qu, S.; Shi, P.; Chen, X.; Xue, F.; Gou, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Qu, S.; Shi, P.; et al. Development and integration of sub-daily flood modelling capability within the SWAT model and a comparison with XAJ model. Water 2018, 10, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H.; Harrison, J.F.; Huang, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Harrison, J.F.; Huang, Y.-C. Modeling typhoon-induced alterations on river sediment transport and turbidity based on dynamic landslide inventories: Gaoping River Basin, Taiwan. Water 2015, 7, 6910–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Lyu, L.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Lyu, L. Effects of climate change and human activities on soil erosion in the Xihe River Basin, China. Water 2018, 10, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Babel, M.S.; Ninsawat, S.; Ochi, S.; Mishra, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Babel, M.S.; Ninsawat, S.; Ochi, S. Impact of climate change on water resources of the Bheri River Basin, Nepal. Water 2018, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, O.; St, F.; Webber, D.; Setegn, S.; Melesse, A.M. Application of the soil and water assessment tool (SWAT model) on a small tropical island (Great River watershed, Jamaica) as a tool in integrated watershed and coastal zone management. Int. J. Trop. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 62, 293–305. [Google Scholar]
- Melesse, A.M.; Graham, W.D.; Jordan, J.D. Spatially distributed watershed mapping and modeling: GIS-based storm runoff and hydrograph analysis: (part 2). J. Spat. Hydrol. 2003, 3, 2–28. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, A.A.; Seifu, A.T.; Essayas, K.A.; Abeyou, W.W.; Tewodros, T.A.; Shimelis, B.D.; Melesse, A.M. Climate change impact on sediment yield in the upper Gilgel Abay Catchment, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. In Landscape Dynamics, Soils and Hydrological Processes in Varied Climates; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 7, pp. 615–644. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Williams, J.R.; Maidment, D.R. Continuous-time water and sediment-routing model for large basins. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1995, 121, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalim, F.K.; Melesse, A.M. Modelling the impacts of subsurface drainage on surface runoff and sediment yield in the Le Sueur Watershed, Minnesota, USA. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mekonnen, M.; Melesse, A.M. Soil erosion mapping and hotspot area identification using GIS and remote sensing in Northwest Ethiopian Highlands, Near Lake Tana. In Nile River Basin; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 207–224. ISBN 978-94-007-0688-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Garza, J.; Whitney, M.; Melesse, A.; Yang, W. Prediction of sediment source areas within watersheds as affected by soil data resolution. In Environmental Modelling; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 151–185. [Google Scholar]
- Hunink, J.; Niadas, I.; Antonaropoulos, P.; Droogers, P.; de Vente, J. Targeting of intervention areas to reduce reservoir sedimentation in the Tana catchment (Kenya) using SWAT. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msaghaa, J.J.; Melesse, A.M.; Ndomba, P.M. Modeling sediment dynamics: Effect of land use, topography, and land management in the Wami-Ruvu Basin, Tanzania. In Nile River Basin; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 165–192. ISBN 978-3-319-02719-7. [Google Scholar]
- Msaghaa, J.J. Sediment yield modeling and dentification of erosion hotspots in Tropical Watersheds: The case of upper Ruvu Catchment in Tanzania. Master’s Thesis, Florida International University, University Park, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Haregeweyn, N.; Berhe, A.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; Meshesha, D.T. Integrated watershed management as an effective approach to curb land degradation: A case study of the Enabered Watershed in Northern Ethiopia. Environ. Manag. 2012, 50, 1219–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osore, A.; Moges, A. Extent of gully erosion and farmer’s perception of soil erosion in Alalicha Watershed, Southern Ethiopia. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 4, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Tongul, H.; Hobson, M. Scaling up an Integrated Watershed Management Approach through Social Protection Programmes in Ethiopia: The MERET and PSNP Schemes; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Legesse, D. Analysis of the Hydrological Response of the Ziway–Shala Lake Basin (Main Ethiopian Rift) to Changes in Climate and human Activities. Ph.D. Thesis, Aix-Marseille University, Aix-en-Provenece, France, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ayenew, T. The Hydrogeological System of the Lake District Basin, Central Main Ethiopian Rift. Ph.D. Thesis, Free University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Makin, M.J.; Kingham, T.J.; Waddams, A.E.; Birchall, C.J.; Eavis, B.W. Prospects for Irrigation Development around Lake Zwai, Ethiopia; Wageningen University and Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia Ministry of Water Resources (MOWR): Rift Valley Lakes Basin Integrated Resources Development Master Plan Study Project. Integrated Watershed Management of Western Lake Ziway Sub-basin Prefeasibility Study. Part II Prefeasibility Studies. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Unpublished work. 2010.
- Neitsch, S.; Arnold, J.; Kiniry, J.; Williams, J. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Setegn, S.G.; Melesse, A.M.; Wang, X.; Vicioso, F.; Nunez, F. Calibration and Validation of ArcSWAT Model for Prediction of Hydrological Water Balance of Rio Haina Basin, Dominica Republic; GIS & Water Resources: Orlando, FL, USA, 2010; Volume VI. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J. Sediment-yield prediction with Universal Equation using runoff energy factor. In Present and Prospective Technology for Predicting Sediment Yield and Sources; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; Volume ARS-S-40, pp. 244–252. [Google Scholar]
- Sharply, A.; Williams, J. EPIC-Erosion/Productivity Impact Calculator I, Model Documentation; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- Stefan, L. Program pcpSTAT: User’s Manual; Scribd, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Church, M. Bed material transport and the morphology of Alluvial River Channels. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006, 34, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limgis, L. Winter School on Essentials in Limnology and Geographic Information System (GIS); Centre for Ecological Sciences: Karnataka, India, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hajigholizadeh, M.; Melesse, A.M.; Fuentes, H.R. Erosion and sediment transport modelling in shallow waters: A review on approaches, models and applications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesuf, H.; Alamirew, T.; Melesse, A.; Assen, M. Bathymetric mapping for Lake Hardibo in Northeast Ethiopia using sonar. Int. J. Water Sci. 2012, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesuf, H.; Alamirew, T.; Melesse, A.; Assen, M. Bathymetric study of Lake Hayq, Ethiopia. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2013, 18, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, C.; Arnold, J.; Williams, J.R.; Dugas, W.; Srinivasan, R.; Hauck, L. Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1169–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Liew, M.W.V.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.; Hadley, R..; Lal, R.; Onstad, C.; Yair, A. Recent Developments in Erosion and Sediment Yield Studies; UNESDOC: Paris, France, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hurni, H. Land degradation, famine, and land resource scenarios in Ethiopia. In World Soil Erosion and Conservation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; pp. 27–62. [Google Scholar]








| Parameter | Maki Sub-Basin (At Station Maki) | Katar Sub-Basin (At Station Abura) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | |
| NSE | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.85 |
| R2 | 0.74 | 0.72 | 0.80 | 0.86 |
| RSR | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.45 | 0.39 |
| Parameter | Maki Sun-Basin (At Station Maki) | Katar Sub-Basin (At Station Abura) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | |
| NSE | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.79 |
| R2 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.75 |
| PBIAS | −7.87 | −12.25 | −16.68 | −16.25 |
| RSR | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.50 |
| Scenario | Percentage of Change in Sediment Flow | |
|---|---|---|
| Maki Sub-Basin | Katar Sub-Basin | |
| Base scenario | 0 | 0 |
| Scenario 2 | −13 | −12 |
| Scenario 3 | −55 | −49 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aga, A.O.; Chane, B.; Melesse, A.M. Soil Erosion Modelling and Risk Assessment in Data Scarce Rift Valley Lake Regions, Ethiopia. Water 2018, 10, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111684
Aga AO, Chane B, Melesse AM. Soil Erosion Modelling and Risk Assessment in Data Scarce Rift Valley Lake Regions, Ethiopia. Water. 2018; 10(11):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111684
Chicago/Turabian StyleAga, Alemu O., Bayou Chane, and Assefa M. Melesse. 2018. "Soil Erosion Modelling and Risk Assessment in Data Scarce Rift Valley Lake Regions, Ethiopia" Water 10, no. 11: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111684
APA StyleAga, A. O., Chane, B., & Melesse, A. M. (2018). Soil Erosion Modelling and Risk Assessment in Data Scarce Rift Valley Lake Regions, Ethiopia. Water, 10(11), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111684