Evaluating the Impact of Wastewater Effluent on Microbial Communities in the Panke, an Urban River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
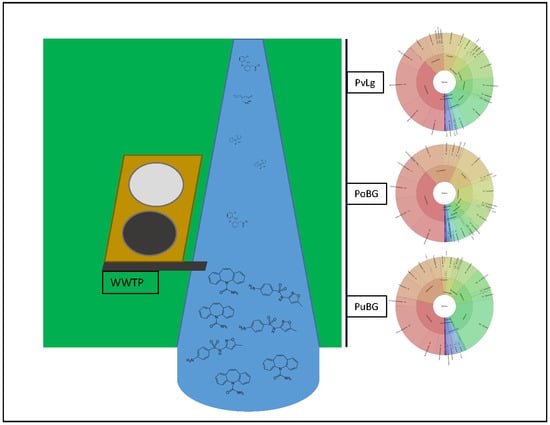
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Water Sampling and Water Analysis
2.3. Sediment Sampling, DNA and RNA Extraction
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.5.1. Physicochemical Parameters and Micropollutant Concentrations
2.5.2. Statistics on the Alpha Diversity of Microbial Communities
2.5.3. Statistics on the Beta Diversity of Microbial Communities
2.5.4. Statistics of Significant Environmental Variables on Individual OTUs
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of the Panke
3.2. Determination of Micropollutants
3.3. Alpha and Beta Diversity of the Microbial Community
3.4. Effect on Individual OTUs
3.5. Composition and Distribution of the Microbial Communities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gessner, M.; Hinkelmann, R.; Nützmann, G.; Jekel, M.; Singer, G.; Lewandowski, J.; Nehls, T.; Barjenbruch, M. Urban water interfaces. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.W.; Riley, T.M.; Taylor, R.D. Water quality of effluent-dominated ecosystems: Ecotoxicological, hydrological, and management considerations. Hydrobiologia 2006, 556, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeb, F.; Singer, H.; Pernet-Coudrier, B.; Qi, W.; Liu, H.; Longrée, P.; Müller, B.; Berg, M. Organic micropollutants in rivers downstream of the megacity Beijing: Sources and mass fluxes in a large-scale wastewater irrigation system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8680–8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paíga, P.; Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Ramos, S.; Jorge, S.; Silva, J.G.; Delerue-Matos, C. Presence of pharmaceuticals in the Lis river (Portugal): Sources, fate and seasonal variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, E.; Hornek-Gausterer, R.; Saçan, M.T. Single and mixture toxicity of pharmaceuticals and chlorophenols to freshwater algae Chlorella vulgaris. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 129, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barra Caracciolo, A.; Topp, E.; Grenni, P. Pharmaceuticals in the environment: Biodegradation and effects on natural microbial communities. A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 106, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggen, R.I.L.; Behra, R.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Escher, B.I.; Schweigert, N. Challenges in Ecotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 58A–64A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.B.; Pomati, F.; Eggen, R.I.L. The toxicity of chemical pollutants in dynamic natural systems: The challenge of integrating environmental factors and biological complexity. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fent, K.; Weston, A.A.; Caminada, D. Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 122–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; LaVergne, J.M.; Carpenter, C.M.G.; Desai, R.; Zhang, X.; Gray, K.A.; Helbling, D.E.; Wells, G.F. Exploring Co-occurrence Patterns between Organic Micropollutants and Bacterial Community Structure in a Mixed-Use Watershed. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2019, 573, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.R.; Swerhone, G.D.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Neu, T.R. Effects of selected pharmaceuticals on riverine biofilm communities. Can. J. Microbiol. 2005, 51, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabater, S.; Guasch, H.; Ricart, M.; Romaní, A.; Vidal, G.; Klünder, C.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. Monitoring the effect of chemicals on biological communities. The biofilm as an interface. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proia, L.; Cassió, F.; Pascoal, C.; Tlili, A.; Romaní, A.M. The Use of Attached Microbial Communities to Assess Ecological Risks of Pollutants in River Ecosystems: The Role of Heterotrophs. In Emerging and Priority Pollutants in Rivers, 19th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 147–179. [Google Scholar]
- Proia, L.; Osorio, V.; Soley, S.; Köck-Schulmeyer, M.; Pérez, S.; Barceló, D.; Romaní, A.M.; Sabater, S. Effects of pesticides and pharmaceuticals on biofilms in a highly impacted river. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proia, L.; Lupini, G.; Osorio, V.; Pérez, S.; Barceló, D.; Schwartz, T.; Amalfitano, S.; Fazi, S.; Romaní, A.M.; Sabater, S. Response of biofilm bacterial communities to antibiotic pollutants in a Mediterranean river. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxall, A.B.A.; Rudd, M.A.; Brooks, B.W.; Caldwell, D.J.; Choi, K.; Hickmann, S.; Innes, E.; Ostapyk, K.; Staveley, J.P.; Verslycke, T.; et al. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in the Environment: What Are the Big Questions? Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosi-Marshall, E.J.; Royer, T.V. Pharmaceutical Compounds and Ecosystem Function: An Emerging Research Challenge for Aquatic Ecologists. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonova, T.; Labanowski, J.; Cournoyer, B.; Chardon, C.; Keck, F.; Laurent, É.; Mondamert, L.; Vasselon, V.; West, L.; Bouchez, A. River biofilm community changes related to pharmaceutical loads emitted by a wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9254–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashgahi, S.; Aydin, R.; Dimitrov, M.R.; Sipkema, D.; Hamonts, K.; Lahti, L.; Maphosa, M.; Kruse, T.; Saccenti, E.; Springael, D.; et al. Impact of a wastewater treatment plant on microbial community composition and function in a hyporheic zone of a eutrophic river. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wakelin, S.A.; Colloff, M.J.; Kookana, R.S. Effect of Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent on Microbial Function and Community Structure in the Sediment of a Freshwater Stream with Variable Seasonal Flow. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoll, N.; Acuña, V.; Barceló, D.; Casellas, M.; Guasch, H.; Huerta, B.; Petrovic, M.; Ponsatí, L.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Sabater, S. Pollution-induced community tolerance to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in fluvial biofilm communities affected by WWTP effluents. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yergeau, E.; Lawrence, J.R.; Waiser, M.J.; Korber, D.R.; Greer, C.W. Metatranscriptomic analysis of the response of river biofilms to pharmaceutical products, using anonymous DNA microarrays. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5432–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drury, B.; Rosi-Marshall, E.; Kelly, J.J. Wastewater treatment effluent reduces the abundance and diversity of benthic bacterial communities in urban and suburban rivers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, C.; Schneider, M.; Mutz, M.; Haustein, M.; Halle, M.; Seidel, M.; Sieker, H.; Wolter, C.; Hinkelmann, R. Optimization of ecologically oriented structures in the urban river Panke—Final report (German); Technical University Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the miseq illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graspeuntner, S.; Bohlmann, M.K.; Gillmann, K.; Speer, R.; Kuenzel, S.; Mark, H.; Hoellen, F.; Lettau, R.; Griesinger, G.; König, I.R.; et al. Microbiota-based analysis reveals specific bacterial traits and a novel strategy for the diagnosis of infectious infertility. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2018. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Bushnell, B. BBTools Software Package. 2018. Available online: http://jgi.doe.gov/data-and-tools/bbtools/ (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huse, S.M.; Welch, D.M.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L. Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westcott, S.L.; Schloss, P.D. OptiClust, an Improved Method for Assigning Amplicon-Based Sequence Data to Operational Taxonomic Units. mSphere 2017, 2, e00073-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddard, S.F.; Smith, B.J.; Hein, R.; Roller, B.R.K.; Schmidt, T.M. rrnDB: Improved tools for interpreting rRNA gene abundance in bacteria and archaea and a new foundation for future development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D593–D598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; R Core Team. Nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme (accessed on 29 January 2019).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/vegandevs/vegan (accessed on 29 January 2019).
- Akaike, H. Akaike’s Information Criterion. In International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science; Lovric, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aristi, I.; von Schiller, D.; Arroita, M.; Barceló, D.; Ponsatí, L.; García-Galán, M.J.; Sabater, S.; Elosegi, A.; Acuña, V. Mixed effects of effluents from a wastewater treatment plant on river ecosystem metabolism: Subsidy or stress? Freshwater Biol. 2015, 60, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, A.; Solimini, A.G.; Carchini, G. Effects of a waste water treatment plant on organic matter dynamics and ecosystem functioning in a Mediterranean stream. Int. J. Limnol. 2006, 42, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Inamdar, S. Extreme storms and changes in particulate and dissolved organic carbon in runoff: Entering uncharted waters? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ternes, T.A. Analytical methods for the determination of pharmaceuticals in aqueous environmental samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2001, 20, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Gourse, R.; Baughman, G. Regulation of the Synthesis of Ribosomes and Ribosomal Components. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1984, 53, 75–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, H.J.; Martinez, R.J.; Story, S.; Sobecky, P.A. Characterization of Microbial Community Structure in Gulf of Mexico Gas Hydrates: Comparative Analysis of DNA- and RNA-Derived Clone Libraries. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3235–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nogales, B.; Moore, E.R.B.; Llobet-Brossa, E.; Rossello-Mora, R.; Amann, R.; Timmis, K.N. Combined Use of 16S Ribosomal DNA and 16S rRNA To Study the Bacterial Community of Polychlorinated Biphenyl-Polluted Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1874–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urban, N.R.; Brezonik, P.L.; Baker, L.A.; Sherman, L.A. Sulfate reduction and diffusion in sediments of Little Rock Lake, Wisconsin. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 797–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.D.; Masuda, H.; Kusakabe, M.; Yanagisawa, F.; Zeng, H.A. Degradation of groundwater quality due to anthropogenic sulfur and nitrogen contamination in the Sichuan Basin, China. Geochem. J. 2006, 40, 309–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, B.W.; Bottrell, S.H. Discrimination of sulfur sources in pristine and polluted New Zealand river catchments using stable isotopes. Appli. Geochem. 1997, 12, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Shanley, J.B.; Bailey, S.W.; Mitchell, M.J. Identifying sources of stream water sulfate after a summer drought in the Sleepers River watershed (Vermont, USA) using hydrological, chemical, and isotopic techniques. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberer, T. Occurrence, fate, and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment: A review of recent research data. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 131, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberer, T.; Reddersen, K.; Mechlinski, A. From municipal sewage to drinking water: Fate and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment in urban areas. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A. Occurrence of drugs in german sewage treatment plants and rivers. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2260–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschka, M.; Eubeler, J.P.; Knepper, T.P. Occurrence and fate of barbiturates in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7200–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ager, D.; Evans, S.; Li, H.; Lilley, A.K.; van der Gast, C.J. Anthropogenic disturbance affects the structure of bacterial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebele, A.J.; Abou-Elwafa Abdallah, M.; Harrad, S. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the freshwater aquatic environment. Emerging Contam. 2017, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleuvers, M. Aquatic ecotoxicity of pharmaceuticals including the assessment of combination effects. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 142, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, F.; Szewzyk, U. Environmentally relevant concentrations of pharmaceuticals influence the initial adhesion of bacteria. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 87, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sampling Sites Date Sample Number | PuBG 12 October 16 n = 6 | PoBG 12 October 16 n = 6 | PvLg 13 October 16 n = 6 | PuBG1 26 June 17 n = 6 | PoBG1 27 June 17 n = 6 | PvLg1 26 June 17 n = 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissolved oxygen a | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 8.3 ± 0.3 | 8.1 ± 0.1 | 4.9 ± 1.0 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | |
| DOC a | 6.6 ± 1.6* | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 2.0 ± 1.5 | 8.82 ± 1.1* | 7.4 ± 0.2* | 4.4 ± 0.5 | |
| Nitrate a | 38.3 ± 11.8 | 3.0 ± 0 | 2.7 ± 0.5 | 30.0 ± 0 | 3.3 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | |
| pH | 7.7 ± 0.1 | 8.0 ± 0.1 | 8.0 ± 0 | 7.3 ± 0 | 7.9 ± 0.1 | 7.7 ± 0 | |
| Sulfate a | 116.7 ± 7.5 | 85 ± 15.3 | 100 ± 15.3 | 83.3 ± 14.9 | 101.7 ± 3.7 | 38.3 ± 5.5 | |
| Water temperature b | 14.8 ± 0 | 9.7 ± 0.1 | 9.7± 0.1 | 19.5 ± 0.4 | 15 ± 0 | 16.8 ± 0.1 |
| Condition | Slope | Standard Error | DF | Wald χ2 | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfate | |||||||
| PoBG:S1 1 | 0.87 | 0.25 | 1 | 12.08 | 0.001 | 0.002 | ** |
| PoBG:S2 2 | 9.10 | 0.52 | 1 | 302.96 | <0.001 | <0.001 | *** |
| PuBG:S1 | −0.11 | 0.72 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.883 | 0.883 | |
| PuBG:S2 | 0.56 | 0.26 | 1 | 4.51 | 0.034 | 0.068 | . |
| PvLg:S1 | −0.50 | 0.20 | 1 | 6.16 | 0.013 | 0.039 | * |
| PvLg:S2 | −2.45 | 0.44 | 1 | 31.71 | <0.001 | <0.001 | *** |
| Clofibric acid | |||||||
| S1 | 149.76 | 40.90 | 1 | 13.41 | <0.001 | <0.001 | *** |
| S2 | 2333.71 | 358.03 | 1 | 42.49 | <0.001 | <0.001 | *** |
| Phenobarbital | |||||||
| PoBG | 1550.77 | 150.14 | 1 | 106.68 | <0.001 | <0.001 | *** |
| PuBG | −708.96 | 195.57 | 1 | 13.92 | <0.001 | <0.001 | *** |
| PvLg | −626.11 | 132.99 | 1 | 22.17 | <0.001 | <0.001 | *** |
| Condition | Degrees of Freedom | F Statistic | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfate | |||||
| PoBG:S1 1 | 1 | 2.37 | 0.017 | 0.034 | * |
| PoBG:S2 2 | 1 | 6.27 | <0.001 | 0.001 | *** |
| PuBG:S1 | 1 | 3.86 | <0.001 | 0.001 | *** |
| PuBG:S2 | 1 | 1.92 | 0.021 | 0.034 | * |
| PvLg:S1 | 1 | 1.48 | <0.001 | 0.001 | *** |
| PvLg:S2 | 1 | 7.39 | <0.001 | 0.001 | *** |
| Phenobarbital | |||||
| PoBG | 1 | 5.37 | <0.001 | <0.001 | *** |
| PuBG | 1 | 1.13 | 0.331 | 0.331 | . |
| PvLg | 1 | 4.05 | <0.001 | <0.001 | *** |
| Condition | OTU | Class of Bacteria | Base Mean | Log2(fold-change) | lfcSE | p-Value | Padj |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfate | |||||||
| PoBG:S2 | 1 | Nitrospira | 91.8 | −0.2758 | 6.49 × 10−2 | 2.12 × 10−5 | 4.80 × 10−4 |
| 3 | Nitrospira | 79.8 | −0.2920 | 6.30 × 10−2 | 3.57 × 10−6 | 1.41 × 10−4 | |
| 4 | Betaproteo- bacteria | 45.2 | 0.1362 | 3.58 × 10−2 | 1.41 × 10−4 | 2.07 × 10−3 | |
| 6 | Actinobacteria | 60.7 | 0.1881 | 3.87 × 10−2 | 1.12 × 10−6 | 6.79 × 10−5 | |
| 12 | Actinobacteria | 30.1 | 0.1171 | 2.97 × 10−2 | 8.13 × 10−5 | 1.43 × 10−3 | |
| 13 | Actinobacteria | 38.2 | 0.1363 | 3.33 × 10−2 | 4.20 × 10−5 | 8.17 × 10−4 | |
| 56 | Deltaproteo- bacteria | 23.9 | 0.2551 | 3.60 × 10−2 | 1.46 × 10−12 | 3.97 × 10−10 | |
| PuBG:S1 | 303 | Bacteroidia | 43.8 | 0.1233 | 3.39 × 10−2 | 2.80 × 10−4 | 8.89 × 10−3 |
| 489 | Nitrospira | 42.9 | −0.1112 | 2.80 × 10−2 | 7.03 × 10−5 | 4.43 × 10−3 | |
| 509 | Opitutae | 44.5 | 0.2438 | 5.24 × 10−2 | 3.21 × 10−6 | 6.07 × 10−4 | |
| PvLg:S2 | 4 | Betaproteobacteria | 21.3 | 0.1381 | 2.47 × 10−2 | 2.36 × 10−8 | 6.40 × 10−7 |
| 7 | Betaproteobacteria | 23.9 | −0.1333 | 3.76 × 10−2 | 3.90 × 10−4 | 2.33 × 10−3 | |
| 10 | Acidimicrobiia | 92.7 | 0.2175 | 2.92 × 10−2 | 9.45 × 10−14 | 1.62 × 10−11 | |
| 13 | Actinobacteria | 24.1 | 0.1107 | 2.77 × 10−2 | 6.52 × 10−5 | 5.47 × 10−4 | |
| 15 | Gammaproteo- bacteria | 45.9 | 0.1814 | 2.23 × 10−2 | 4.40 × 10−16 | 1.13 × 10−13 | |
| 23 | Alphaproteo- bacteria | 23.0 | −0.1441 | 2.74 × 10−2 | 1.40 × 10−7 | 2.79 × 10−6 | |
| 27 | Gammaproteo- bacteria | 33.0 | 0.2329 | 2.44 × 10−2 | 1.15 × 10−21 | 5.93 × 10−19 | |
| Bezafibrate | |||||||
| S1 | 341 | Thermoleophilia | 20.1 | −0.1661 | 4.24 × 10−2 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 1.29 × 10−2 |
| Phenobarbital | |||||||
| PoBG | 12 | Actinobacteria | 39.8 | 0.1044 | 2.89 × 10−2 | 3.05 × 10−4 | 1.14 × 10−2 |
| 13 | Actinobacteria | 45.4 | 0.1292 | 3.05 × 10−2 | 2.22 × 10−5 | 2.10 × 10−3 | |
| 56 | Deltaproteo- bacteria | 19.7 | 0.2039 | 5.01 × 10−2 | 4.76 × 10−5 | 3.75 × 10−3 | |
| PvLg | 5 | Betaproteo- bacteria | 25.1 | 0.0891 | 2.44 × 10−2 | 2.61 × 10−4 | 3.47 × 10−3 |
| 10 | Acidimicrobiia | 50.1 | 0.1744 | 3.43 × 10−2 | 3.56 × 10−7 | 1.33 × 10−5 | |
| 15 | Gammaproteo- bacteria | 33.0 | 0.1670 | 2.20 × 10−2 | 3.18 × 10−14 | 3.17 × 10−12 | |
| 23 | Alphaproteo- bacteria | 28.3 | −0.1230 | 3.01 × 10−2 | 1.55 × 10−5 | 4.22 × 10−4 | |
| 27 | Gammaproteo -bacteria | 21.7 | 0.2081 | 2.80 × 10−2 | 1.14 × 10−13 | 9.74 × 10−12 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nega, M.; Braun, B.; Künzel, S.; Szewzyk, U. Evaluating the Impact of Wastewater Effluent on Microbial Communities in the Panke, an Urban River. Water 2019, 11, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050888
Nega M, Braun B, Künzel S, Szewzyk U. Evaluating the Impact of Wastewater Effluent on Microbial Communities in the Panke, an Urban River. Water. 2019; 11(5):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050888
Chicago/Turabian StyleNega, Marcella, Burga Braun, Sven Künzel, and Ulrich Szewzyk. 2019. "Evaluating the Impact of Wastewater Effluent on Microbial Communities in the Panke, an Urban River" Water 11, no. 5: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050888
APA StyleNega, M., Braun, B., Künzel, S., & Szewzyk, U. (2019). Evaluating the Impact of Wastewater Effluent on Microbial Communities in the Panke, an Urban River. Water, 11(5), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050888