Geochemical Behavior of Uranium and Radon in Groundwater of Jurassic Granite Area, Icheon, Middle Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Bedrock Geology
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Groundwater Chemistry and Water Types
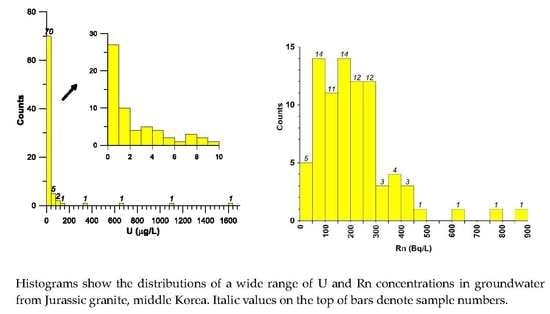
3.2. Uranium Concentration and Spatial Distribution
3.3. Radon Concentration and Spatial Distribution
3.4. Relationships between Uranium/Radon and pH/Eh
3.5. Statistical Analyses of Groundwater
3.5.1. Correlation Coefficients
3.5.2. Factor Analysis
3.6. Geochemical Implications for Jurassic Granite Aquifer
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langmuir, D. Actinides and Their Daughter and Fission Products. In Aqueous Environmental Geochemistry; Prentice Hall Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 486–557. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.S.; Cheng, T. Uranium release from sediment to groundwater: Influence of water chemistry and insights into release mechanisms. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2014, 164, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahermo, P.; Juntunen, R. Radiogenic elements in Finnish soils and groundwaters. Appl. Geochem. 1991, 6, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.W.; Sung, I.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Park, S.K. A preliminary investigation of radon concentrations in groundwater of South Korea. J. Soil Ground. Environ. 2007, 12, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Prat, O.; Vercouter, T.; Ansoborlo, E.; Fichet, P.; Perret, P.; Kurttio, P.; Salonen, L. Uranium speciation in drinking-water from drilled wells in southern Finland and its potential links to health effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thivya, C.; Chidambaram, S.; Tirumalesh, K.; Prasanna, M.V.; Thilagavathi, R.; Nepolian, M. Occurrence of the radionuclides in groundwater of crystalline hard rock regions of central Tamil Nadu, India. J. Radio. Nucl. Chem. 2014, 302, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thivya, C.; Chidambaram, S.; Keesari, T.; Prasanna, M.V.; Thilagavathi, R.V.S.; Adithya, V.S.; Singaraja, C. Lithological and hydrochemical controls on distribution and speciation of uranium in groundwaters of hard-rock granitic aquifers of Madurai District, Tamil Nadu (India). Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.W.; Choo, C.O.; Kim, M.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Yun, U.; Lee, S. Spatial relationships between radon and topographical, geological, and geochemical factors and their relevance in all of South Korea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5155–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, U.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Choo, C.O.; Cho, B.W. Natural radon reduction rate of the community groundwater system in South Korea. Appl. Rad. Isotopes 2017, 126, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.W.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, M.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Yoon, U.; Cho, S.Y.; Choo, C.O. Radon concentrations in the community groundwater system of South Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsson, G.; Olofsson, B. Radon content in groundwater from drilled wells in the Stockholm region of Sweden. Norg. Geol. Under. Bull. 2002, 439, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Asikainen, M.; Kahlos, H. Anomalously high concentration of uranium, radium and radon in water from drilled wells in the Helsinki region. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frengstad, B.; Midtgard, A.K.; Banks, D.; Krog, R.K.; Siewers, U. The chemistry of Norwegian groundwater III. The distribution of trace elements in 476 crystalline bedrock groundwaters, as analyzed by ICP-MS techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 246, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, V.; Altzitzoglou, T.; Malo, P.; Tanner, V.; Hult, M. A brief overview on radon measurements in drinking water. J. Environ. Radio. 2017, 173, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). Study on the Radionuclide Concentrations in Groundwater (I); KIGAM Report; Ministry of Environment of Korea: Seoul, Korea, 1997; p. 338.
- National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). A Detailed Study on the Radionuclide Concentrations in the Groundwater (II); NIER Report; Ministry of Environment of Korea: Seoul, Korea, 2009; p. 273.
- National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). Study on the Naturally Occurring Radionuclides in Groundwater of the Two High Potential Areas; KIGAM Report; Ministry of Environment of Korea: Seoul, Korea, 2011; p. 253.
- National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). Studies on the Naturally Occurring Radionuclides in Groundwater; KIGAM Report; Ministry of Environment of Korea: Sejong, Korea, 2016; p. 213.
- Ministry of Environment (MOE). Standards for Drinking Water Quality. Ministry of Environment of Korea; Legislation 792 (acted on 1 January, 2019). Available online: http://www.law.go.kr/lsInfoP.do?urlMode=lsInfoP&lsId=007134#AJAX. (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM). Geological Report of the Icheon Sheet (1:50,000); KIGAM Report; Geological and Mining Institute Korea: Seoul, Korea, 1974.
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Prentice Hall Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, B.W.; Yun, U.; Choo, C.O. Uranium and radon concentration in groundwater of the Taejeon area, Korea. In Proceedings of the Groundwater Quality Sustainability, Krakow, Poland, 12–17 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, S.H.; Hwang, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Hyun, S.P.; Bae, B.K.; Park, Y. Establishing the origin of elevated concentrations in groundwater near the central Ogcheon metamorphic belt, Korea. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J. Occurrence of U-minerals and source of U in groundwater in Daebo granite, Daejeon area. J. Eng. Geol. 2013, 23, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.L.; Santos, I.R.; Perkins, A.; Maher, D.T. Dissolved radon and uranium in groundwater in a potential coal seam gas development region (Richmond River Catchment, Australia). J. Environ. Radio. 2016, 154, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baradonett, M.O.; Jardine, P.M.; Brooks, S.C. U(VI) adsorption to heterogeneous subsurface media: Application of a surface complexation model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.A.; Meece, D.E.; Kohler, M.; Curtis, G.P. Approaches to surface complexation modeling of uranium (VI) adsorption on aquifer sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 3621–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krestou, A.; Panias, D. Uranium (VI) speciation diagrams in the UO22+/CO32−/H2O system at 25 °C. Eur. J. Miner. Process. Environ. Protec. 2004, 4, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilescu, M.; Pavel, L.V.; Cretescu, I. Characterization and remediation of soils contaminated with uranium. J. Hazard. Mat. 2009, 163, 475–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkandawire, M. Biogeochemical behaviour and bioremediation of uranium in waters of abandoned mines. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2013, 20, 7740–7767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duff, M.; Hunter, D.; Bertsch, P.; Amrhein, C. Factors influencing uranium reduction and solubility in evaporation pond sediments. Biogeochem 1999, 45, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, W.M.; Shock, E.L. Environmental aqueous geochemistry of actinides. In Uranium: Mineralogy, Geochemistry and the Environment; Burns, P.C., Finch, R., Eds.; Reviews in Mineralogy; Mineralogical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; Volume 38, pp. 221–253. [Google Scholar]
- Vinson, D.S.; Vengosh, A.; Hirschfeld, D.; Dwyer, G.S. Relationships between radium and radon occurrence and hydrochemistry in fresh groundwater from fractured crystalline rocks, North Carolina (USA). Chem. Geol. 2009, 260, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.H.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, T.S.; Han, J.S.; Cho, B.W. Occurrence of natural radioactive materials in borehole groundwater and rockcore in the Icheon area. J. Eng. Geol. 2012, 22, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeger, A.I.; Ruderman, N.C. Hydrogeologic controls on radon-222 a buried valley-fractured bedrock aquifer system. Ground Water 1998, 36, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinelli, E.; Lima, A.; De Vivo, B.; Albanese, S.; Cicchella, D.; Valera, P. Hydrogeochemical analysis on Italian bottled mineral waters: Effects of geology. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 107, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, C.; Ribeiro, L.; Cruz, J. Classification of natural mineral and spring bottled waters of Portugal using principal component analysis. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 107, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyebog, S.A.; Ako, A.A.; Nkeng, G.E.; Suh, E.C. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of some Cameroon bottled waters, investigated by multivariate statistical analyses. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 112, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, P.; Somashekar, R.K. Principal component analysis and hydrochemical facies characterization to evaluate groundwater quality in Varahi river basin, Karnataka state, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizdziel, J.; Farmer, D.; Hodge, V.; Lindley, K.; Stetzenbach, K. 234U/238U isotope ratios in groundwater from Southern Nevada: A comparison of alpha counting and magnetic sector ICP-MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 350, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, C.O. Characteristics of uraniferous minerals in Daebo granite and significance of mineral species. J. Miner. Soc. Korea 2002, 15, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Baik, M.H. Uranium and other trace elements’ distribution in Korean granite: Implications for the influence of iron oxides on uranium migration. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, R.R.; Gunderson, L.C.S. Geologic and climatic controls on the radon emanation coefficient. Environ. Int. 1996, 22, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Singh, H.; Singh, S.; Bajwa, B.S. Estimation of uranium and radon concentration in some drinking water samples of Upper Siwaliks, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 154, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, A.B. Radon migration in the ground: A supplementary review. In Proceedings of the Natural Radiation Environment 111; Gessell, T.F., Lowder, W.M., Eds.; U.S. CONF-780422; Department of Energy Report: Wahsington, DC, USA, 1980; pp. 15–56. [Google Scholar]
- Przylibski, T.A. Estimating the radon emanation coefficient from crystalline rocks into groundwater. Appl. Rad. Isotopes 2000, 53, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Smitherman, P.; Hess, C.T.; Culbertson, C.W.; Marvinney, R.G.; Smith, A.E.; Zheng, Y. Uranium and radon in private bedrock well water in Maine: Geospatial analysis at two scales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4298–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeppström, K.; Olofsson, B. Uranium and radon in groundwater. Eur. Water 2007, 17/18, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, D.; Røset, O.; Strand, T.; Skarphagen, H. Radioelement (U, Th, Rn) concentrations in Norwegian bedrock groundwaters. Environ. Geol. 1995, 25, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| U (μg/L) | Rn (Bq/L) | pH | EC (μS/cm) | Eh(mV) | DO | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | F− | NO3− | HCO3− | Sr | SiO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. | 1640.0 | 865.8 | 8.57 | 707.0 | 350.0 | 11.0 | 5.14 | 36.23 | 88.90 | 12.30 | 75.80 | 40.50 | 2.60 | 78.60 | 219.8 | 1.36 | 43.20 |
| Min. | 0.02 | 1.48 | 5.38 | 61.0 | −139.0 | 0.86 | 0.34 | 6.49 | 2.13 | 0.30 | 1.98 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 14.10 | 0.04 | 7.40 |
| Mean | 56.77 | 211.29 | 6.77 | 216.15 | 210.8 | 7.22 | 1.29 | 14.48 | 22.29 | 2.98 | 12.50 | 7.01 | 0.43 | 24.63 | 64.46 | 0.32 | 26.92 |
| Med. | 3.03 | 176.86 | 6.74 | 205.50 | 232.0 | 8.20 | 0.91 | 13.85 | 19.20 | 2.59 | 9.13 | 6.11 | 0.28 | 20.0 | 51.50 | 0.22 | 29.40 |
| Std. | 228.63 | 151.20 | 0.61 | 98.59 | 96.0 | 2.57 | 1.07 | 5.18 | 14.21 | 1.90 | 11.18 | 6.19 | 0.49 | 20.12 | 41.48 | 0.30 | 8.13 |
| Comp. | U | Rn | pH | EC | Eh | DO | K | Na | Ca | Mg | Cl− | SO42− | F− | NO3− | HCO3− | Sr | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| Rn | 0.05 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
| pH | 0.20 | 0.18 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| EC | 0.16 | −0.03 | −0.06 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| Eh | −0.54 | −0.13 | −0.37 | −0.05 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| DO | −0.51 | −0.03 | −0.39 | −0.46 | 0.55 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| K | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.22 | −0.67 | −0.41 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Na | 0.05 | −0.08 | −0.30 | 0.75 | −0.02 | −0.14 | 0.18 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Ca | 0.30 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.92 | −0.18 | −0.58 | 0.28 | 0.53 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Mg | 0.05 | −0.01 | −0.05 | 0.79 | 0.07 | −0.39 | 0.12 | 0.41 | 0.71 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Cl− | −0.01 | −0.02 | −0.27 | 0.83 | −0.07 | −0.27 | 0.24 | 0.85 | 0.65 | 0.59 | 1.00 | ||||||
| SO42− | 0.13 | −0.05 | −0.01 | 0.77 | −0.09 | −0.46 | 0.26 | 0.52 | 0.74 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 1.00 | |||||
| F− | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.76 | 0.01 | −0.49 | −0.44 | 0.44 | −0.12 | 0.21 | −0.13 | −0.17 | −0.05 | 1.00 | ||||
| NO3− | −0.23 | 0.02 | −0.46 | 0.24 | 0.49 | 0.49 | −0.17 | 0.48 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.22 | −0.07 | −0.36 | 1.00 | |||
| HCO3− | 0.45 | 0.04 | 0.40 | 0.65 | −0.41 | −0.77 | 0.36 | 0.18 | 0.85 | 0.59 | 0.35 | 0.60 | 0.37 | −0.43 | 1.00 | ||
| Sr | 0.63 | 0.09 | 0.37 | 0.55 | −0.62 | −0.74 | 0.64 | 0.39 | 0.64 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.53 | −0.14 | 0.69 | 1.00 | |
| SiO2 | −0.44 | −0.21 | −0.52 | 0.09 | 0.72 | 0.52 | −0.68 | 0.34 | −0.13 | 0.08 | 0.21 | −0.11 | −0.62 | 0.57 | −0.41 | −0.49 | 1.00 |
| Components | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | 0.13 | 0.69 | −0.14 | −0.12 |
| Rn | −0.04 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.80 |
| pH | 0.06 | 0.22 | −0.70 | 0.48 |
| EC | 0.95 | 0.09 | 0.22 | 0.04 |
| Eh | −0.00 | −0.89 | 0.17 | −0.06 |
| DO | −0.54 | −0.56 | 0.42 | 0.03 |
| K+ | 0.14 | 0.79 | 0.12 | 0.28 |
| Na+ | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.67 | −0.00 |
| Ca2+ | 0.93 | 0.19 | −0.06 | 0.11 |
| Mg2+ | 0.86 | −0.10 | 0.00 | −0.03 |
| Cl− | 0.76 | 0.10 | 0.48 | −0.05 |
| SO42− | 0.84 | 0.11 | 0.01 | −0.10 |
| F− | 0.02 | 0.47 | −0.45 | 0.57 |
| NO3− | 0.06 | −0.35 | 0.78 | 0.18 |
| HCO3− | 0.75 | 0.37 | −0.46 | 0.02 |
| Sr | 0.53 | 0.73 | −0.06 | 0.18 |
| SiO2 | 0.07 | −0.73 | 0.47 | −0.22 |
| Eigenvalue | 6.48 | 4.35 | 1.42 | 1.12 |
| Cumulative | ||||
| eigenvalue | 6.48 | 10.82 | 12.24 | 13.37 |
| % Variance | ||||
| explained | 38.13 | 25.61 | 8.35 | 6.61 |
| Cumulative | ||||
| % variance | 38.13 | 63.74 | 72.08 | 78.69 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, B.W.; Choo, C.O. Geochemical Behavior of Uranium and Radon in Groundwater of Jurassic Granite Area, Icheon, Middle Korea. Water 2019, 11, 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061278
Cho BW, Choo CO. Geochemical Behavior of Uranium and Radon in Groundwater of Jurassic Granite Area, Icheon, Middle Korea. Water. 2019; 11(6):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061278
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Byong Wook, and Chang Oh Choo. 2019. "Geochemical Behavior of Uranium and Radon in Groundwater of Jurassic Granite Area, Icheon, Middle Korea" Water 11, no. 6: 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061278
APA StyleCho, B. W., & Choo, C. O. (2019). Geochemical Behavior of Uranium and Radon in Groundwater of Jurassic Granite Area, Icheon, Middle Korea. Water, 11(6), 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061278