Habitat Use by Pseudochondrostoma duriense and Squalius carolitertii Downstream of a Small-Scale Hydropower Plant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
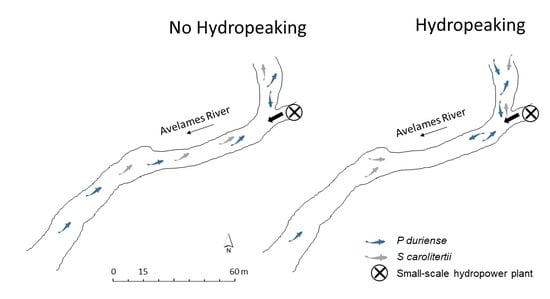
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Telemetry
2.4. Hydrodynamic Modeling
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Telemetry
3.2. Habitat Use
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zarfl, C.; Lumsdon, A.E.; Berlekamp, J.; Tydecks, L.; Tockner, T. A global boom in hydropower dam construction. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 77, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IHA. Hydropower Status Report: Sector Trends and Insights; IHA: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, C.; Reidy, C.A.; Dynesius, M.; Revenga, C. Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science 2005, 308, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, U. Hydropower Pressure on European Rivers. The Story in Numbers; WWF, RiverWatch, EuroNatur, GEOTA: Gland, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Demirbas, A. Focus on the World: Status and Future of Hydropower. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2007, 2, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, H.; Plichard, L.; Bergé, J.; Pella, H.; Ovidio, M.; McNeil, E.; Lamouroux, N. Fish habitat selection in a large hydropeaking river: Strong individual and temporal variations revealed by telemetry. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korman, J.; Campana, S.E. Effects of Hydropeaking on Nearshore Habitat Use and Growth of Age-0 Rainbow Trout in a Large Regulated River. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2009, 138, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragana, I.; Boavida, I.; Cortes, R.; Pinheiro, A. Hydropower Plant Operation Scenarios to Improve Brown Trout Habitat. River Res. Appl. 2017, 33, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benejam, L.; Saura-Mas, S.; Bardina, M.; Solá, C.; Munné, A.; García-Berthou, E. Ecological impacts of small hydropower plants on headwater stream fish: From individual to community effects. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2016, 25, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.; Meier, P.; Trautwein, C.; Schmid, M.; Robinson, C.T.; Weber, C.; Brodersen, J. Basin-scale effects of small hydropower on biodiversity dynamics. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2018, 16, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Moggridge, H.; Warren, P.; Shucksmith, J. The impacts of “run-of-river” hydropower on the physical and ecological condition of rivers. Water Environ. J. 2015, 29, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kibler, K.M.; Tullos, D.D. Cumulative biophysical impact of small and large hydropower development in Nu River, China. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3104–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, R.M. Review of Ecological Effects of Rapidly Varying Flows Downstream from Hydroelectric Facilities. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1985, 5, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.S.; Cech, J.J.; Thompson, L.C. Hydropower-related pulsed-flow impacts on stream fishes: A brief review, conceptual model, knowledge gaps, and research needs. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2011, 21, 713–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.J.; Fuentes-Pérez, J.F.; Boavida, I.; Tuhtan, J.A.; Pinheiro, A.N. Fish under pressure: Examining behavioural responses of Iberian barbel under simulated hydropeaking with instream structures. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rocaspana, R.; Aparicio, E.; Vinyoles, D.; Palau, A. Effects of pulsed discharges from a hydropower station on summer diel feeding activity and diet of brown trout (Salmo trutta Linnaeus 1115, 1758) in an Iberian stream. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2016, 32, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puffer, M.; Berg, O.K.; Huusko, A.; Vehanen, T.; Einum, S. Effects of intra- and interspecific competition and hydropeaking on growth of juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2017, 26, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollset, K.W.; Skoglund, H.; Wiers, T.; Barlaup, B. Effects of hydropeaking on the spawning behaviour of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar and brown trout Salmo trutta. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 88, 2236–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, I.; Santos, J.M.J.M.; Ferreira, T.; Pinheiro, A. Barbel habitat alterations due to hydropeaking. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, S.; Zeiringer, B.; Führer, S.; Tonolla, D.; Schmutz, S. Effects of river bank heterogeneity and time of day on drift and stranding of juvenile European grayling (Thymallus thymallus L.) caused by hydropeaking. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, I.; Harby, A.; Clarke, K.D.; Heggenes, J. Move or stay: Habitat use and movements by Atlantic salmon parr (Salmo salar) during induced rapid flow variations. Hydrobiologia 2017, 785, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halleraker, J.H.; Saltveit, S.J.; Harby, A.; Arnekleiv, J.V.; Fjeldstad, H.-P.; Kohler, B. Factors influencing stranding of wild juvenile brown trout (Salmo trutta) during rapid and frequent flow decreases in an artificial stream. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecher, H.A.; Caldwell, B.A.; DeMond, S.B. Evaluation of Depth and Velocity Preferences of Juvenile Coho Salmon in Washington Streams. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2002, 22, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, I.; Santos, J.M.J.M.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Ferreira, M.T. Fish habitat availability simulations using different morphological variables. Limnetica 2011, 30, 393–404. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, J. Assessing the Habitat Requirements of Stream Fishes: An Overview and Evaluation of Different Approaches. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.C. A review of fish swimming mechanics and behaviour in altered flows. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. R. Soc. 2007, 362, 1973–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tritico, H.M.; Cotel, A.J. The effects of turbulent eddies on the stability and critical swimming speed of creek chub (Semotilus atromaculatus). J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 2284–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacey, R.W.J.; Neary, V.S.; Liao, J.C.; Enders, E.C.; Tritico, H.M. The ipos framework: Linking fish swimming performance in altered flows from laboratory experiments to rivers. River Res. Appl. 2012, 28, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Rivaes, R.; Boavida, I.; Branco, P. Structural microhabitat use by endemic cyprinids in a Mediterranean-type river: Implications for restoration practices. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2017, 28, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.J.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Boavida, I. Habitat Enhancement Solutions for Iberian Cyprinids Affected by Hydropeaking: Insights from Flume Research. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribi, J.-M.; Boillat, J.-L.; Peter, A.; Schleiss, A.J. Attractiveness of a lateral shelter in a channel as a refuge for juvenile brown trout during hydropeaking. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 76, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.K.; Cooke, S.J. Repeatability of movement behaviour in a wild salmonid revealed by telemetry. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 84, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, J.; Kelly, S.; McDermott, T.; Hyland, J.; Jackson, D.; Bolton-Warberg, M. Assessment of PIT tag retention, growth and post-tagging survival in juvenile lumpfish, Cyclopterus lumpus. Anim. Biotelemetry 2020, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, J.-M.M.; Haro, A.; Cunjak, R.A.A. Field test of a new method for tracking small fishes in shallow rivers using passive integrated transponder (PIT) technology. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, E.; Zerafa, B.; Brooker, A.J.; Davie, A.; Migaud, H. Application of passive-acoustic telemetry to explore the behaviour of ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta) and lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) in commercial Scottish salmon sea-pens. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, K.; White, G. Analysis of movement and habitat use from telemetry data. In Analysis and Interpretation of Freshwater Fisheries Data; Guy, S., Brown, M., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007; pp. 625–676. [Google Scholar]
- Doadrio. Atlas y Libro Rojo de los Peces Continentales de España. Dirección General de Conservación de la Naturaléza Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2001.
- Strahler, A.N. Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1957, 38, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bovee, K.D.; Lamb, B.L.; Bartholow, J.M.; Stalnaker, C.B.; Taylor, J.; Henriksen, J. Stream Habitat Analysis using the Instream Flow Incremental Methodology; U.S. Geological Survey, Biological Resources Division: Reston, VA, USA, 1998; p. 131.
- Ross, M.J.; McCormick, J.H. Effects of External Radio Transmitters on Fish. Progress. Fish Culturist 1981, 43, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.B.; Cary, J.B.; Smith, A.D.; Pregler, K.C.; Kim, S.; Kanno, Y. Detection Efficiency of a Portable PIT Antenna for Two Small-Bodied Fishes in a Piedmont Stream. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2017, 37, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEN. Water Quality: Sampling of Fish with Electricity. European Standard EN 14011; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- INAG. Manual Para a Avaliação Biológica da Qualidade da Água em Sistemas Fluviais Segundo a Directiva Quadro da Água: Protocolo de Amostragem e Análise Para a Fauna Piscícola; Ministério do Ambiente, do Ordenamento do Território e do Desenvolvimento Regional, Instituto da Água, I.P: Lisbon, Portugal, 2008.
- Trincão, M. Aplicabilidade da Ferramenta COSH-Tool no Estudo do Fenómeno do Hydropeaking em Pequenos Aproveitamentos Hidroelétricos Localizados em Portugal Continental; Instituto Superior Técnico, University of Lisbon: Lisbon, Portugal, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, K. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. London, Edinburgh, Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses. Package ‘factoextra’; CRAN: Vienna, Austria, 2017; p. 77. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/factoextra/index.html (accessed on 9 September 2020).
- Anderson, M.J.; Robinson, J. Permutation tests for linear models. Aust. N. Z. J. Stat. 2001, 43, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, K.; Coen, L.D. A comparison of statistical approaches to analyzing community convergence between natural and constructed oyster reefs. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 330, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Community Ecology Package. Package ‘Vegan’; CRAN: Vienna, Austria, 2019; p. 296. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 9 September 2020).
- Venables, W.N.; Smith, D.M. An Introduction to R Notes on R: A Programming Environment for Data Analysis and Graphics; CRAN: Vienna, Austria, 2019; p. 105. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/r-release/R-intro.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2020).
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Henry, L.; Pederson, T.L.; Takahashi, K.; Wilke, C.; Woo, K.; Yutani, H.; Dunnington, D. Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics. Package ‘ggplot2’; CRAN: Vienna, Austria, 2020; p. 277. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggplot2/index.html (accessed on 9 September 2020).
- Horikoshi, M.; Tang, Y.; Dickey, A.; Grenié, M.; Thompson, R.; Selzer, L.; Strbenac, D.; Voronin, K. Data Visualization Tools for Statistical Analysis Results. Package ‘ggfortify’; CRAN: Vienna, Austria, 2020; p. 85. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggfortify/index.html (accessed on 9 September 2020).
- Wei, T.; Simko, V.; Levy, M.; Xie, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zemla, J. Visualization of a Correlation Matrix. Package ‘corrplot’; CRAN: Vienna, Austria, 2017; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Pedroso, N.M.; Sales-Luís, T.; Santos-Reis, M. The Eurasian otter Lutra lutra (Linnaeus, 1758) in Portugal. Munibe Monogr. Nat. Ser. 2014, 3, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Godinho, F.; Ferreira, M. Microhabitat use by Iberian nase Chondrostoma polylepis and Iberian chub Squalius carolitertii in three small streams, north-west Portugal. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2004, 13, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Reino, L.; Porto, M.; Oliveira, J.; Pinheiro, P.; Almeida, P.R.; Cortes, R.; Ferreira, M.T. Complex size-dependent habitat associations in potamodromous fish species. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 73, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, J.A.; Doadrio, I.; Márquez, A.L.; Real, R.; Hugueny, B.; Vargas, J.M. Distribution patterns of indigenous freshwater fishes in the Tagus River basin, Spain. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1999, 54, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.T.; Sousa, L.; Santos, J.M.; Reino, L.; Oliveira, J.; Almeida, P.R.; Cortes, R.V. Regional and local environmental correlates of native Iberian fish fauna. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2007, 16, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.; Sostoa, A.; Freeman, M.; Lobon-Cerviá, J. Microhabitat use in a mediterranean riverine fish assemblage. Fishes of the upper Matarraña. Oecologia 1987, 73, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, G.; Freeman, M. Microhabitat use in a stream fish assemblage. J. Zool. 1987, 212, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Hernández, J.; Vieira-Lanero, R.; Servia, M.J.; Cobo, F. Feeding habits of four sympatric fish species in the Iberian Peninsula: Keys to understanding coexistence using prey traits. Hydrobiologia 2011, 667, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.A.; Casals, F.; Solà, C.; Caiola, N.; Sostoa, A.; García-Berthou, E. Efficacy of population size structure as a bioassessment tool in freshwaters. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heggenes, J. Effects of Short-Term Flow Fluctuations on Displacement of, and Habitat Use by, Brown Trout in a Small Stream. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1988, 117, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.C.; Cocherell, S.A.; Chun, S.N.; Cech, J.J.; Klimley, A.P. Longitudinal movement of fish in response to a single-day flow pulse. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 90, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flodmark, L.E.W.; Forseth, T.; L’Abee-Lund, J.H.; Vøllestad, L.A. Behaviour and growth of juvenile brown trout exposed to fluctuating flow. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2006, 15, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.L. Dissolved oxygen and fish behavior. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1987, 18, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamish, F.W.H.; Sa-Ardrit, P.; Tongnunui, S. Habitat characteristics of the cyprinidae in small rivers in Central Thailand. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2006, 76, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.J.; Boavida, I.; Almeida, V.; Cooke, S.J.; Pinheiro, A.N. Do artificial velocity refuges mitigate the physiological and behavioural consequences of hydropeaking on a freshwater Iberian cyprinid? Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, J.; Amorim, M.C.P.; Fonseca, P.J.; Teixeira, A.; Natário, S.; Carrola, J.; Varandas, S.; Pereira, L.T.; Cortes, R.V. Acoustic barriers as an acoustic deterrent for native potamodromous migratory fish species. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickle, M.F.; Higgs, D.M. Integrating techniques: A review of the effects of anthropogenic noise on freshwater fish. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 75, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, J.; Doadrio, I. Threatened fishes of the world: Leuciscus carolitertii Doadrio 1, 1988 (Cyprinidae). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2000, 57, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón, P.A.P.; Barrachina, P.; Bernat, Y. Microhabitat use by 0+ juvenile cyprinids during summer in a Mediterranean river. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1992, 125, 323–337. [Google Scholar]
- Godinho, F.N.; Ferreira, M.T.; Santos, J.M. Variation in fish community composition along an Iberian river basin from low to high discharge: Relative contributions of environmental and temporal variables. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2000, 9, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, I.; Jesus, J.B.; Pereira, V.; Santos, C.; Lopes, M.; Cortes, R.V. Fulfilling spawning flow requirements for potamodromous cyprinids in a restored river segment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, M.; Robinson, C. Structure, Performance, and Assumptions of Riverine Habitat Suitability Index Models; Aquatic Resources Research Series 88-3; Alabama Cooperative Fish and Wildlife Research Unit: Auburn, AL, USA, 1988.
- Lucas, M.C.; Frear, P.A. Effects of a flow-gauging weir on the migratory behaviour of adult barbel, a riverine cyprinid. J. Fish Biol. 1997, 50, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Ronda, F.J.; Bravo-Córdoba, F.J.; Fuentes-Pérez, J.F.; Castro-Santos, T.R. Ascent ability of brown trout, Salmo trutta, and two Iberian cyprinids—Iberian barbel, Luciobarbus bocagei, and northern straight-mouth nase, Pseudochondrostoma duriense—In a vertical slot fishway. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2016, 417, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanz-Ronda, F.J.; Ruiz-Legazpi, J.; Bravo-Córdoba, F.J.; Makrakis, S.; Castro-Santos, T. Sprinting performance of two Iberian fish: Luciobarbus bocagei and Pseudochondrostoma duriense in an open channel flume. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, E.; Stickler, M.; Pennell, C.; Cote, D.; Alfredson, K.; Scruton, D.A. Variations in distribution and mobility of Atlantic salmon parr during winter in a small, steep river. Hydrobiologia 2008, 609, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, C.; Brodersen, J.; Bronmark, C.; Hansson, L.-A.; Hertonsson, P.; Nilsson, P.A. Evaluation of PIT-tagging in cyprinids. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 67, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das Mahapatra, K.; Gjerde, B.; Reddy, P.V.G.K.; Sahoo, M.; Jana, R.K.; Saha, J.N.; Rye, M. Tagging: On the use of passive integrated transponder (PIT) tags for the identification of fish. Aquac. Res. 2001, 32, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plichard, L.; Capra, H.; Mons, R.; Pella, H.; Lamouroux, N. Comparing electrofishing and snorkelling for characterizing fish assemblages over time and space. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, E. Fundamentals of ecology. Sci. Educ. 1954, 38, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, M. Hydropower Operations and Environmental Conservation: St. Mary’s River, Ontario and Michigan, Canada and USA. Ithaca; International Lake Superior Board of Control: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schmutz, S.; Bakken, T.H.; Friedrich, T.; Greimel, F.; Harby, A.; Jungwirth, M.; Melcher, A.; Unfer, G.; Zeiringer, B. Response of Fish Communities to Hydrological and Morphological Alterations in Hydropeaking Rivers of Austria. River Res. Appl. 2015, 31, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boavida, I.; Caetano, L.; Pinheiro, A.N. E-flows to reduce the hydropeaking impacts on the Iberian barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei) habitat. An effectiveness assessment based on the COSH Tool application. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Allan, J.D.; Bain, M.B.; Karr, J.R.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Ritcher, E.S.; Sparks, R.E.; Stromberg, J.C. The natural flow regime. Bioscience 1997, 47, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder, A.; Tonolla, D.; Schweizer, S.P.; Vollenweider, S.; Langhans, S.D.; Wüest, A. A conceptual framework for hydropeaking mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Downstream | Upstream | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HP | NHP | HP | NHP | |
| P. duriense | 17 | 17 | 17 | 25 |
| S. carolitertii | 13 | 10 | 14 | 12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boavida, I.; Ambrósio, F.; Costa, M.J.; Quaresma, A.; Portela, M.M.; Pinheiro, A.; Godinho, F. Habitat Use by Pseudochondrostoma duriense and Squalius carolitertii Downstream of a Small-Scale Hydropower Plant. Water 2020, 12, 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092522
Boavida I, Ambrósio F, Costa MJ, Quaresma A, Portela MM, Pinheiro A, Godinho F. Habitat Use by Pseudochondrostoma duriense and Squalius carolitertii Downstream of a Small-Scale Hydropower Plant. Water. 2020; 12(9):2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092522
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoavida, Isabel, Filipa Ambrósio, Maria João Costa, Ana Quaresma, Maria Manuela Portela, António Pinheiro, and Francisco Godinho. 2020. "Habitat Use by Pseudochondrostoma duriense and Squalius carolitertii Downstream of a Small-Scale Hydropower Plant" Water 12, no. 9: 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092522
APA StyleBoavida, I., Ambrósio, F., Costa, M. J., Quaresma, A., Portela, M. M., Pinheiro, A., & Godinho, F. (2020). Habitat Use by Pseudochondrostoma duriense and Squalius carolitertii Downstream of a Small-Scale Hydropower Plant. Water, 12(9), 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092522