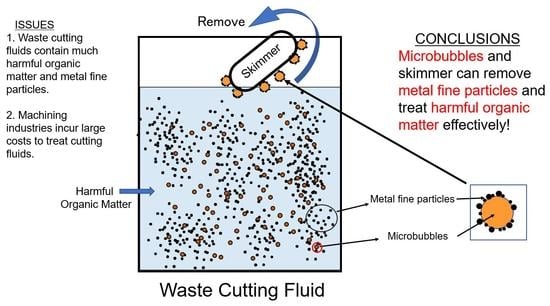
Treatment and Effective Removal of Metal Fine Particles from Waste Cutting Fluids by Flotation via Microbubbles and Skimming
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Conditions and Sample Collection
2.2. Microbubbles
2.3. Concentrations of Iron Fine Particles (IFPs)
2.4. Determination of Organic Carbon and Nitrogen
2.5. Monitoring of Odor
2.6. Determinations of pH
3. Results
3.1. Changes in IFP Concentrations
3.2. Changes of Carbon and Nitrogen Concentrations
3.3. Fluctuations of Odor
3.4. Changes in pH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sokovic, M.; Mijanovic, K. Ecological aspects of the cutting fluids and its influence on quantifiable parameters of the cutting processes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 109, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-M.; Choi, Y.-H.; Ha, J.-H.; Woo, W.-S. Eco-friendly technology for recycling of cutting fluids and metal chips: A review. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2017, 4, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenko, Y.; Bezovska1, M.; Kuznetsov, V.; Muntian, A. Technological and Ecological Aspects of Disposal of Spent Cutting Fluids. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najiha, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Yusoff, A.R. Environmental impacts and hazards associated with metal working fluids and recent advances in the sustainable systems: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 1008–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadevan, S.; Graham, N.J.; Thompson, I.P. Treatment of waste metalworking fluid by a hybrid ozone-biological process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waydande, R.; Ghatge, D. Performance evaluation of different types of cutting fluids in the machining of hardened steel—A review. Int. J. Mech. Prod. Eng. 2016, 4, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrazek, A.H.; Choudhury, I.A.; Nukman, Y.; Kazi, S.N. Metal cutting lubricants and cutting tools: A review on the performance improvement and sustainability assessment. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 4221–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaly, S.; Giwa, A.; Hasan, S.W. Recent improvements in oily wastewater treatment: Progress, challenges, and future opportunities. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murić, A.; Petrinić, I.; Christensen, M.L. Comparison of ceramic and polymeric ultrafiltration membranes for treating wastewater from metalworking industry. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroki, T.; Watanabe, H.; Okubo, M.; Yamamoto, T. Regeneration technology of cutting oil using electrolytic bubble flotation method. Simultaneous removal of fine aluminum particles and sludge contaminant. IEEJ Trans. Ind. Appl. 2006, 126, 330–336, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temesgen, T.; Bui, T.T.; Han, M.; Kim, T.-I.; Park, H. Micro and nanobubble technologies as a new horizon for water-treatment techniques: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 246, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srithongouthai, S.; Endo, A.; Inoue, A.; Kinoshita, K.; Yoshioka, M.; Sato, A.; Iwasaki, T.; Teshiba, I.; Nashiki, H.; Hama, D.; et al. Control of dissolved oxygen levels of water in net pens for fish farming by a microscopic bubble generating system. Fish. Sci. 2006, 72, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, A.; Srithongouthai, S.; Nashiki, H.; Teshiba, I.; Iwasaki, T.; Hama, D.; Tsutsumi, H. DO-increasing effects of a microscopic bubble generating system in a fish farm. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 57, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colt, J.; Kroeger, E.; Rust, M. Characteristics of oxygen flow through fine bubble diffusers used in the aquaculture hauling applications. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 43, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, D.; Xie, J. Modeling re-oxygenation performance of fine-bubble–diffusing aeration system in aquaculture ponds. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Takahashi, M.; Chiba, K. Degradation of phenol by the collapse of microbubbles. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, H.; Hong, X.; Han, H.; Shan, S. Effect of pure oxygen fine bubbles on the organic matter removal and bacterial community evolution treating coal gasification wastewater by membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, P.E.; Ong, W.Y.J.; Lau, E.V.; Chong, M.N. Investigation on micro-bubble flotation and coagulation for the treatment of anaerobically treated palm oil mill effluent (POME). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Liu, Y. Enhanced microbubbles assisted cleaning of diesel contaminated sand. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Xia, Z. Application of ozone micro-nano-bubbles to groundwater remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oya, M. Effect of fine bubbles on removal of linear alkyl benzene sulfonate surfactant during the rinsing stage of laundry washing. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2020, 23, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, H.; Qian, H.; Yao, W. Effects of ozone-microbubble treatment on the removal of residual pesticides and the adsorption mechanism of pesticides onto the apple matrix. Food Control 2021, 120, 107548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, C.; Fujiwara, N.; Shigekawa, Y.; Tada, K.; Yano, J.; Yokoyama, T.; Minamoto, Y.; Nakayama, S. Effect of acidic conditions on decomposition of methylene blue in aqueous solution by air microbubbles. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukami, K.; Oogi, T.; Motomura, K.; Morita, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Hata, T. Effective Purification of Eutrophic Wastewater from the Beverage Industry by Microbubbles. Water 2021, 13, 3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, R.; Majumder, S.K. Microbubble generation and microbubble-aided transport process intensification-A state-of-the-art report. Chem. Eng. Process. 2013, 64, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleka, E.N.; Gallios, G.P.; Matis, K.A. A perspective on flotation: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.R.H.; Granville, A.M.; Browne, C.I.; Dagastine, R.R.; Yap, R.; Jefferson, B.; Henderson, R.K. Determining how polymer-bubble interactions impact algal separation using the novel “Posi”-dissolved air flotation process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 201, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghia, N.H.; Van, P.T.; Giang, P.T.; Hanh, N.T.; St-Hilaire, S.; Domingos, J.A. Control of Vibrio parahaemolyticus (AHPND strain) and improvement of water quality using nanobubble technology. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 2727–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhy, A.; Tao, D. Nanobubble column floatation of fine coal particles and associated fundamentals. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 124, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gayar, D.A.; Khodary, M.A.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; Khalil, M.F. Effect of disk skimmer material and oil viscosity on oil spill recovery. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikasa, Y.; Yamawaki, N.; Shida, H.; Okumura, H.; Akamatu, S.; Nishiuchi, Y.; Hata, T. Study on fixed salt removal effect by fine bubbles. In Proceedings of the 18th Asian Pacific Confederation of Chemical Engineering Congress (APCChE 2019), Sapporo, Japan, 23–27 September 2019; Volume 333, p. 02009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, U.C. Studies on the o-phenathroline method for determining iron in plant materials. Plant Soil 1968, 28, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensadok, K.; Belkacem, M.; Nezzal, G. Treatment of cutting oil/water emulsion by coupling coagulation and dissolved air flotation. Desalination 2007, 206, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, F.; Suzuki, K. Recycling of water-soluble metalworking fluids with anion exchange membrane electrodialysis system. Cent. Inst. Toyota R D Rev. 1999, 34, 43–50, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Demirbas, E.; Kobya, M. Operating cost and treatment of metalworking fluid wastewater by chemical coagulation and electrocoagulation processes. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 105, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.R.; Yu, J.J.; Yin, J.X.; Wang, S.P.; Ma, H.J. Treatment of waste cutting fluid by coagulation-anaerobic hydrolysis (with or without cosubstrate glucose)-aeration process. Water Pract. Technol. 2022, 17, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofrad, M.M.G.; Pourzamani, H.; Amin, M.M.; Parseh, I.; Alipour, M. In situ treatment of metalworking wastewater by chemical addition-dissolved air flotation coupled with UV, H2O2 & ZnO. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacholski, P.; Sęk, J. Experimental analysis of chemical demulsification of cutting oil. Acta Innov. 2018, 26, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Characteristics of Odor Sensing by XP-329IIIR. Available online: https://www.new-cosmos.co.jp/wp/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/XP-3293R%E5%8F%82%E8%80%83%E5%80%A4%E3%83%87%E3%83%BC%E3%82%BF.pdf (accessed on 31 July 2022). (In Japanese).
- Yamamoto, T.; Kageyama, T.; Yoshida, H.; Fukui, K. Effect of new blade of centrifugal separator on particle separation Performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 162, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Busca, G.; Hankins, N.; Mohammad, A.W. The use of ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes in the treatment of metal-working fluids. Desalination 2004, 167, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, T.; Kumakura, H.; Wada, H. Magnetic separation using superconducting magnets. Physica C 2001, 357–360, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, Y.; Mishima, F.; Akiyama, Y.; Nishijima, S. Development of high gradient magnetic separation system under dry condition. Physica C 2010, 470, 1812–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchepare, R.; Azevedo, A.; Calgaroto, S.; Rubio, J. Removal of ferric hydroxide by flotation with micro and nanobubbles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 184, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukami, K.; Ogata, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawamura, K.; Mitani, I.; Sakamoto, M. Treatment and Effective Removal of Metal Fine Particles from Waste Cutting Fluids by Flotation via Microbubbles and Skimming. Water 2022, 14, 2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162575
Fukami K, Ogata N, Yamamoto K, Kawamura K, Mitani I, Sakamoto M. Treatment and Effective Removal of Metal Fine Particles from Waste Cutting Fluids by Flotation via Microbubbles and Skimming. Water. 2022; 14(16):2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162575
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukami, Kimio, Namiko Ogata, Kenji Yamamoto, Kazuki Kawamura, Iwao Mitani, and Masaoki Sakamoto. 2022. "Treatment and Effective Removal of Metal Fine Particles from Waste Cutting Fluids by Flotation via Microbubbles and Skimming" Water 14, no. 16: 2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162575
APA StyleFukami, K., Ogata, N., Yamamoto, K., Kawamura, K., Mitani, I., & Sakamoto, M. (2022). Treatment and Effective Removal of Metal Fine Particles from Waste Cutting Fluids by Flotation via Microbubbles and Skimming. Water, 14(16), 2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14162575