Evaluating a Surface Energy Balance Model for Partially Wetted Surfaces: Drip and Micro-Sprinkler Systems in Hazelnut Orchards (Corylus Avellana L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
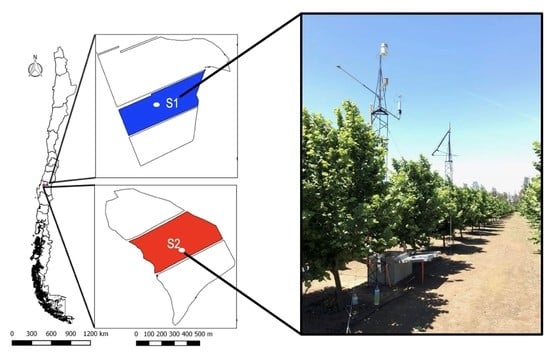
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Climatic Conditions at the Study Site
2.3. The Modified SEB-PW Model
2.4. ET and Micrometeorological Measurements
2.5. Soil Moisture Measurements
2.6. Soil Evaporation Measurements
2.7. Footprint Analysis
2.8. Model Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Calibration
3.1.1. Surface Energy Balance Measurements during Calibration
3.1.2. Diurnal Dynamics of ET and E after Calibration
3.1.3. Comparison of Diurnal, Nightly, and Daily Soil E
3.2. E and Actual ET Comparison for Micro-Sprinkler and Drip Irrigation Systems
3.3. Model Validation: Seasonal Dynamics of E, Crop T, and ET
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Summary of the SEB-PW Model
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 22 May 2019).
- Valentini, N.; Moraglio, S.T.; Rolle, L.; Tavella, L.; Botta, R. Nut and Kernel Growth and Shell Hardening in Eighteen Hazelnut Cultivars (Corylus avellana L.). Hortic. Sci. 2015, 42, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fideghelli, C.; De Salvador, F.R. World Hazelnut Situation and Perspectives. Vii Int. Congr. Hazelnut 2009, 845, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ODEPA Ficha Nacional. Available online: https://bibliotecadigital.odepa.gob.cl/bitstream/handle/20.500.12650/69897/FichaNacional2022.pdf (accessed on 18 May 2022).
- Revista MundoAgro. Gigante En Camino: “El 1° Día Internacional Del Avellano Europeo”. Available online: http://www.mundoagro.cl/revistas/numero-113-abril-2019/ (accessed on 24 May 2019).
- Bignami, C.; Cristofori, V.; Bertazza, G. Effects of Water Availability on Hazelnut Yield and Seed Composition during Fruit Growth. Acta Hortic. 2011, 922, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofori, V.; Muleo, R.; Bignami, C.; Rugini, E. Long Term Evaluation of Hazelnut Response to Drip Irrigation. Acta Hortic. 2014, 1052, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, C.; Cammilli, C.; Moretti, G.; Romoli, F. Irrigation of Corylus avellana L.: Effects on Canopy Development and Production of Young Plants. Acta Hortic. 2000, 537, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.; Gonçalves, B.; Moutinho-Pereira, J.; Carvalho, J.L.; Silva, A.P. Effect of Irrigation on Physiological and Biochemical Traits of Hazelnuts (Corylus avellana L.). Acta Hortic. 2005, 686, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, C.; Natali, S. Influence of Irrigation on the Growth and Production of Young Hazelnuts. Acta Hortic. 1997, 445, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombesi, A. Influence of Soil Water Levels on Assimilation and Water Use Efficiency in Hazelnuts. Acta Hortic. 1994, 351, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindula, G.N.; Orang, M.N.; Snyder, R.L. Survey of Irrigation Methods in California in 2010. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, C.M.; Howes, D.J.; Mutziger, A. Evaporation Estimates for Irrigated Agriculture in California. In Proceedings of the 2001 Irrigation Association Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 4–6 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Souto, C.; Lagos, O.; Holzapfel, E.; Maskey, M.L.; Wunderlich, L.; Shapiro, K.; Marino, G.; Snyder, R.; Zaccaria, D. A Modified Surface Energy Balance to Estimate Crop Transpiration and Soil Evaporation in Micro-Irrigated Orchards. Water 2019, 11, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, C.M.; Mutziger, A.J.; Allen, R.G.; Howell, T.A. Evaporation Research: Review and Interpretation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idso, S.B.; Reginato, R.J.; Jackson, R.D.; Kimball, B.A.; Nakayama, F.S. The Three Stages of Drying of a Field Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1974, 38, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deol, P.; Heitman, J.; Amoozegar, A.; Ren, T.; Horton, R. Quantifying Nonisothermal Subsurface Soil Water Evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montoro, A.; Ma, F. Transpiration and Evaporation of Grapevine, Two Components Related to Irrigation Strategy. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandiño, M.; Cancela, J.J.; Rey, B.J.; Martínez, E.M.; Rosa, R.G.; Pereira, L.S. Using the Dual-Kc Approach to Model Evapotranspiration of Albariño with Consideration of Active Ground Cover (Vitis vinifera L. Cv. Albariño) with Consideration of Active Ground Cover. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 112, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancela, J.J.; Fandiño, M.; Rey, B.J.; Martínez, E.M. Automatic Irrigation System Based on Dual Crop Coefficient, Soil and Plant Water Status for Vitis vinifera (Cv Godello and Cv Mencía). Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 151, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paço, T.A.; Paredes, P.; Pereira, L.S.; Silvestre, J.; Santos, F.L. Crop Coefficients and Transpiration of a Super Intensive Arbequina Olive Orchard Using the Dual K c Approach and the K Cb Computation with the Fraction of Ground Cover and Height. Water 2019, 2, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bignami, C.; Cristofori, V.; Ghini, P.; Rugini, E. Effects of Irrigation on Growth and Yield Components of Hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) in Central Italy. Acta Hortic. 2009, 845, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Farías, S.; Villalobos-Soublett, E.; Riveros-Burgos, C.; Zúñiga, M.; Ahumada-Orellana, L.E. Effect of Irrigation Cut-off Strategies on Yield, Water Productivity and Gas Exchange in a Drip-Irrigated Hazelnut (Corylus avellana L. Cv. Tonda Di Giffoni) Orchard under Semiarid Conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 238, 106173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300, p. D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-Based Energy Balance for Mapping Evapotranspiration with Internalized Calibration (METRIC)—Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, W.J.; Wallace, J.S. Evaporation from Sparse Crops-an Energy Combination Theory. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1985, 111, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.J.; Monteith, J.L. A Four-Layer Model for the Heat Budget of Homogeneous Land Surfaces. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1988, 114, 373–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, W.J. Towards One-Step Estimation of Crop Water Requirements. Trans. ASABE 2006, 49, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Octavio, L.; Derrel, L. Surface Energy Balance Model of Transpiration from Variable Canopy Cover and Evaporation from Residue-Covered or Bare Soil Systems: Model Evaluation. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagos, L.O.; Merino, G.; Martin, D.; Verma, S.; Suyker, A. Evapotranspiration of Partially Vegetated Surfaces. In Evapotranspiration-Remote Sensing and Modeling; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes-Peñailillo, F.; Ortega-Farías, S.; Acevedo-Opazo, C.; Fonseca-Luengo, D. Implementation of a Two-Source Model for Estimating the Spatial Variability of Olive Evapotranspiration Using Satellite Images and Ground-Based Climate Data. Water 2018, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega-Farías, S.; Carrasco, M.; Olioso, A.; Acevedo, C.; Poblete, C. Latent Heat Flux over Cabernet Sauvignon Vineyard Using the Shuttleworth and Wallace Model. Irrig. Sci. 2007, 25, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, H.J.; Ahuja, L.R. Evapotranspiration Modeling of Partial Canopy/Residue-Covered Fields. Trans. ASAE 1996, 39, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iritz, Z.; Lindroth, A.; Heikinheimo, M.; Grelle, A.; Kellner, E. Test of a Modified Shuttleworth-Wallace Estimate of Boreal Forest Evaporation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 98, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaizzi, P.D.; Agam, N.; Tolk, J.A.; Evett, S.R.; Howell, T.A.; Gowda, P.H.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C. Two-Source Energy Balance Model to Calculate E, T, and ET: Comparison of Priestley-Taylor and Penman-Monteith Formulations and Two Time Scaling Methods. Trans. ASABE 2014, 57, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odhiambo, L.O.; Irmak, S. Performance of Extended Shuttleworth-Wallace Model for Estimating and Partitioning of Evapotranspiration in a Partial Residue-Covered Subsurface Drip-Irrigated Soybean Field. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häusler, M.; Conceição, N.; Tezza, L.; Sánchez, J.M.; Campagnolo, M.L.; Häusler, A.J.; Silva, J.M.N.; Warneke, T.; Heygster, G.; Ferreira, M.I. Estimation and Partitioning of Actual Daily Evapotranspiration at an Intensive Olive Grove Using the STSEB Model Based on Remote Sensing. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Farí as, S.; López-Olivari, R. Validation of a Two-Layer Model to Estimate Latent Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration in a Drip-Irrigated Olive Orchard. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibáñez, F.; Santibáñez, P.; Caroca, C.; González, P. Atlas Agroclimático de Chile. Tomo IV: Regiones Del Biobío y de La Araucanía. In Atlas Agroclimático de Chile: Estado Actual y Tendencias del Clima; Universidad de Chile, Facultad de Ciencias Agronómicas, FIA: Santiago, Chile, 2017; pp. 1–77. ISBN 9789561910485. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y. Effect of Sand Mulches of Different Particle Sizes on Soil Evaporation during the Freeze—Thaw Period. Water 2018, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kisekka, I.; Oker, T.; Nguyen, G.; Aguilar, J.; Rogers, D. Revisiting Precision Mobile Drip Irrigation under Limited Water. Irrig. Sci. 2017, 35, 483–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kljun, N.; Calanca, P.; Rotach, M.W.; Schmid, H.P. A Simple Two-Dimensional Parameterisation for Flux Footprint Prediction (FFP). Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 3695–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagos, L.O.; Martin, D.L.; Verma, S.B.; Suyker, A.; Irmak, S. Surface Energy Balance Model of Transpiration from Variable Canopy Cover and Evaporation from Residue-Covered or Bare-Soil Systems. Irrig. Sci. 2009, 28, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Du, T.; Tong, L.; Kang, S. Comparison of Dual Crop Coefficient Method and Shuttleworth-Wallace Model in Evapotranspiration Partitioning in a Vineyard of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Farías, S.; Ortega-Salazar, S.; Poblete, T.; Kilic, A.; Allen, R.; Poblete-Echeverría, C.; Ahumada-Orellana, L.; Zuñiga, M.; Sepúlveda, D. Estimation of Energy Balance Components over a Drip-Irrigated Olive Orchard Using Thermal and Multispectral Cameras Placed on a Helicopter-Based Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV). Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Olivari, R.; Ortega-Farías, S.; Poblete-Echeverría, C. Partitioning of Net Radiation and Evapotranspiration over a Superintensive Drip-Irrigated Olive Orchard. Irrig. Sci. 2016, 34, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testi, L.; Villalobos, F.J.; Orgaz, F. Evapotranspiration of a Young Irrigated Olive Orchard in Southern Spain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 121, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, J.; Stockle, C.O.; Kjelgaard, J. Measurement of Evapotranspiration and Its Components in a Corn (Zea mays L.) Field. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1998, 92, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaizzi, P.D.; Agam, N.; Tolk, J.A.; Evett, S.R.; Howell, T.A.; Gowda, P.H.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C. Advances in a Two-Source Energy Balance Model: Partitioning of Evaporation and Transpiration for Cotton. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fereres, E.; Martinich, D.A.; Aldrich, T.M.; Castel, J.R.; Holzapfel, E.; Schulbach, H. others Drip Irrigation Saves Money in Young Almond Orchards. Calif. Agric. 1982, 36, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Marino, G.; Zaccaria, D.; Snyder, R.L.; Lagos, O.; Lampinen, B.D.; Ferguson, L.; Grattan, S.R.; Little, C.; Shapiro, K.; Maskey, M.L.; et al. Actual Evapotranspiration and Tree Performance of Mature Micro-Irrigated Pistachio Orchards Grown on Saline-Sodic Soils in the San Joaquin Valley of California. Agriculture 2019, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marsal, J.; Johnson, S.; Casadesus, J.; Lopez, G.; Girona, J.; Stöckle, C.O. Fraction of Canopy Intercepted Radiation Relates Differently with Crop Coefficient Depending on the Season and the Fruit Tree Species. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 184, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Kang, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, L. Comparison of Three Evapotranspiration Models to Bowen Ratio-Energy Balance Method for a Vineyard in an Arid Desert Region of Northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblete-Echeverría, C.; Ortega-Farías, S. Estimation of Actual Evapotranspiration for a Drip-Irrigated Merlot Vineyard Using a Three-Source Model. Irrig. Sci. 2009, 28, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Characteristic | Site S1 | Site S2 |
|---|---|---|
| Planting year | 2011 | 2013 |
| Planting density (trees ha−1) | 800 | 571 |
| Tree spacing (m × m) | 5.0 × 2.5 | 5.0 × 3.5 |
| Block size (ha) | 14.4 | 4.3 |
| Soil depth (m) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| avg (Mg cm−3) 1 | 1.45 | 1.29 |
| θPMPavg (cm3 cm−3) 1 | 0.226 | 0.197 |
| θFCavg (cm3 cm−3) 1 | 0.401 | 0.358 |
| Topographic slope (%) | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| Study Site | r2 | RMSE (W m−2) | NSE | da | MAE (W m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.96 | 54.1 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 40.3 |
| S2 | 0.92 | 58.5 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 48.9 |
| Variable | Fields Campaigns (S1 and S2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Diurnal | Nightly | Daily | |
| r2 | 0.87 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| RMSE (mm d−1) | 0.50 | 0.13 | 0.40 |
| NSE | 0.62 | 0.60 | 0.69 |
| da | 0.85 | 0.90 | 0.88 |
| MAE (mm d−1) | 0.40 | 0.09 | 0.30 |
| Variable | S1 | S2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017–2018 | 2018–2019 | 2020–2021 | 2017–2018 | 2018–2019 | 2020–2021 | |
| Hourly λE | ||||||
| r2 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.70 |
| RMSE (W m−2) | 48.6 | 54.3 | 75.4 | 51.2 | 55.4 | 95.1 |
| NSE | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.70 |
| da | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.85 |
| MAE (W m−2) | 29.4 | 31.3 | 40.3 | 32.9 | 37.0 | 55.8 |
| Regression slope | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.76 |
| Actual daily ET | ||||||
| r2 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.88 |
| RMSE (mm d−1) | 0.35 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.75 |
| NSE | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.84 |
| da | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.87 |
| MAE (mm d−1) | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.45 |
| Regression slope | 1.01 | 1.03 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 0.93 |
| Variable (mm Season−1) | S1 | S2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017–2018 | 2018–2019 | 2020–2021 | 2017–2018 | 2018–2019 | 2020–2021 | |
| ETast | 750 | 860 | 765 | 615 | 760 | 720 |
| ETc SEB–PW | 720 | 850 | 780 | 600 | 780 | 690 |
| λEc SEB–PW | 547 | 612 | 570 | 510 | 639 | 560 |
| λEsoil SEB–PW | 173 | 238 | 210 | 90 | 141 | 130 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souto, C.; Lagos, O.; Holzapfel, E.; Ruybal, C.; Bryla, D.R.; Vidal, G. Evaluating a Surface Energy Balance Model for Partially Wetted Surfaces: Drip and Micro-Sprinkler Systems in Hazelnut Orchards (Corylus Avellana L.). Water 2022, 14, 4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244011
Souto C, Lagos O, Holzapfel E, Ruybal C, Bryla DR, Vidal G. Evaluating a Surface Energy Balance Model for Partially Wetted Surfaces: Drip and Micro-Sprinkler Systems in Hazelnut Orchards (Corylus Avellana L.). Water. 2022; 14(24):4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244011
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouto, Camilo, Octavio Lagos, Eduardo Holzapfel, Christopher Ruybal, David R. Bryla, and Gladys Vidal. 2022. "Evaluating a Surface Energy Balance Model for Partially Wetted Surfaces: Drip and Micro-Sprinkler Systems in Hazelnut Orchards (Corylus Avellana L.)" Water 14, no. 24: 4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244011
APA StyleSouto, C., Lagos, O., Holzapfel, E., Ruybal, C., Bryla, D. R., & Vidal, G. (2022). Evaluating a Surface Energy Balance Model for Partially Wetted Surfaces: Drip and Micro-Sprinkler Systems in Hazelnut Orchards (Corylus Avellana L.). Water, 14(24), 4011. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14244011