Differential Impacts of Road De-icers on Freshwater Bacterial Communities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. De-Icers
2.2. Aquatic Mesocosms
2.3. Community Sampling
2.4. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Properties of the De-Icer-Amended Mesocosms



3.2. Microbiota in the De-icer-Amended Mesocosms
3.3. Dissimilarity Comparisons with Different De-Icers
4. Discussion
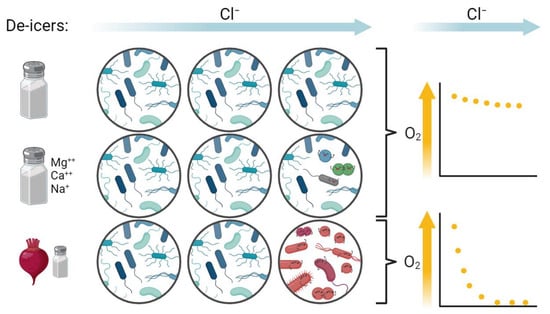
4.1. Little Change in Mesocosms after Amendment with Road Salt
4.2. Shifts in Microbiota at High Concentrations of “Eco-Friendly” De-Icers
4.3. Implications for Aquatic Food Webs, Prospects, and Practical Considerations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Environment and Climate Change Canada. Code of Practice for the Environmental Management of Road Salts. 2004. Available online: https://canadagazette.gc.ca/rp-pr/p1/2004/2004-04-03/pdf/g1-13814.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Bolen, W.P. Mineral Commodity Summaries, January 2022. U.S. Geological Survey. 2022. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2022/mcs2022-salt.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- D’Itri, F.M. Chemical Deicers and the Environment; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Findlay, S.E.G.; Kelly, V.R. Emerging indirect and long-term road salt effects on ecosystems. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1223, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, M.H.; Mousavi, S.Z.; Potapova, A.; McIntyre, J.; Shi, X. Toxicological impacts of roadway deicers on aquatic resources and human health: A Review. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 1855–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haake, D.M.; Krchma, S.; Meyners, C.W.; Virag, R. Impacts of urbanization on chloride and stream invertebrates: A 10-year citizen science field study of road salt in stormwater runoff. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2022, 18, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wersebe, M.J.; Weider, L.J. Resurrection genomics provides molecular and phenotypic evidence of rapid adaptation to salinization in a keystone aquatic species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2217276120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Chloride. 2011. Available online: https://ccme.ca/fr/res/2011-chloride-ceqg-scd-1460-en.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- US EPA. Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Chloride. 1988. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-08/documents/chloride-aquatic-life-criteria-1988.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Nutile, S.A.; Solan, M.E. Toxicity testing of “eco-friendly” de-icing formulations using Chironomus dilutus. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarek, S.; Górecka, A.; Salabert, B.; Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A. Acute toxicity of seven de-icing salts on four zooplankton species—Is there an “eco-friendly” alternative? Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2022, 22, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintz, W.D.; Relyea, R.A. A review of the species, community, and ecosystem impacts of road salt salinisation in fresh waters. Freshwater Biol. 2019, 64, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, N.A.; Bushey, J.T.; Tobias, C.R.; Song, B.; Vadas, T.M. Impact of chloride on denitrification potential in roadside wetlands. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarek, S.; Górecka, A.; Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A. The effects of road salt on freshwater ecosystems and solutions for mitigating chloride pollution—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 805, 150289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; She, D.; Shi, Z.; Cao, T.; Xia, Y.; Shan, J. Salinity and high pH reduce denitrification rates by inhibiting denitrifying gene abundance in a saline-alkali soil. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Likens, G.E.; Pace, M.L.; Utz, R.M.; Haq, S.; Gorman, J.; Grese, M. Freshwater salinization syndrome on a continental scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E574–E583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Reimer, J.E.; Mayer, P.M.; Shatkay, R.R.; Maas, C.M.; Nguyen, W.D.; Boger, W.L.; Yaculak, A.M.; Doody, T.R.; Pennino, M.J.; et al. Freshwater salinization syndrome alters retention and release of chemical cocktails along flowpaths: From stormwater management to urban streams. Freshw. Sci. 2022, 41, 420–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.D.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, I.S.; Yang, E.I. A Comparison Study of Performance and Environmental Impacts of Chloride-Based Deicers and Eco-Label Certified Deicers in South Korea. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 143, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.S.; Relyea, R.A. Road Salt and organic additives affect mosquito growth and survival: An emerging problem in wetlands. Oikos 2018, 127, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecher, W.T.; Emad Al Madadha, M.; DasSarma, P.; Ekulona, F.; Schott, E.J.; Crowe, K.; Gut, B.S.; DasSarma, S. Effects of road salt on microbial communities: Halophiles as biomarkers of road salt pollution. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, I.B.; Lovejoy, C.; Vincent, W.F. Road salt versus urban snow effects on lake microbial communities. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L.; Dudgeon, D. Freshwater biodiversity conservation: Recent progress and future challenges. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2010, 29, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda, O.; Solagaistua, L.; Atristain, M.; de Guzmán, I.; Larrañaga, A.; von Schiller, D.; Elosegi, A. Impact of wastewater effluent pollution on stream functioning: A whole-ecosystem manipulation experiment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nott, M.A.; Driscoll, H.E.; Takeda, M.; Vangala, M.; Corsi, S.R.; Tighe, S.W. Advanced biofilm analysis in streams receiving organic deicer runoff. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T. Assessing the Effects of “Eco-Friendly” Road De-Icer Alternatives on Freshwater Plankton Communities. Masters Thesis, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada, 2023. Available online: https://qspace.library.queensu.ca/items/626de799-3360-451f-ae79-358914273be8 (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Fay, L.; Shi, X. Environmental impacts of chemicals for snow and ice control: State of the knowledge. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 2751–2770. Available online: https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?p=AONE&u=anon~62105e98&id=GALE|A360119818&v=2.1&it=r&sid=googleScholar&asid=1b29bb16 (accessed on 10 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Kelly, V.R.; Findlay, S.E.; Weathers, K.C. Road Salt: The Problem, the Solution, and How to Get There; Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies: Millbrook, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Health Canada. Hazardous Products Regulations, 2019. Available online: https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/PDF/SOR-2015-17.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Sorichetti, R.J.; Raby, M.; Holeton, C.; Benoit, N.; Carson, L.; DeSellas, A.; Diep, N.; Edwards, B.A.; Howell, T.; Kaltenecker, G.; et al. Chloride trends in Ontario’s surface and groundwaters. J. Great Lakes Res. 2022, 48, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, L.; Jackson, D.A. Salty summertime streams—Road salt contaminated watersheds and estimates of the proportion of impacted species. Facets 2021, 6, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreyling, J.; Schweiger, A.H.; Bahn, M.; Ineson, P.; Migliavacca, M.; Morel-Journel, T.; Christiansen, J.R.; Schtickzelle, N.; Larsen, K.S. To replicate, or not to replicate—That is the question: How to tackle nonlinear responses in ecological experiments. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, A.L.; Brown, B.L.; Perrin, E.M.; Keitt, T.H.; Leibold, M.A. Environmental fluctuations induce scale-dependent compensation and increase stability in plankton ecosystems. Ecology 2008, 89, 3204–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanshew, A.S.; Mason, C.J.; Raffa, K.F.; Currie, C.R. Minimization of chloroplast contamination in 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing of insect herbivore bacterial communities. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 95, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, C.R.; Lu-Irving, P.; Copeland, J.; Guttman, D.S.; Wang, P.W.; Baltrus, D.A. Chloroplast sequence variation and the efficacy of peptide nucleic acids for blocking host amplification in plant microbiome studies. Microbiome 2018, 6, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/4615964 (accessed on 16 December 2023).
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of compositions of microbiomes with bias correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K.; Vaughan, D. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation (R Package Version 1.1.0). 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Henry, L.; Pedersen, T.L.; Takahashi, K.; Wilke, C.; Woo, K.; Yutani, H.; Dunnington, D. ggplot2: Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics (R Package Version 3.4.1). 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggplot2/ggplot2.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Wood, S. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2011, 73, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S. Mixed GAM Computation Vehicle with Automatic Smoothness Estimation. R Package Version 1.8-42. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/mgcv/mgcv.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://socialsciences.mcmaster.ca/jfox/Books/Companion/ (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S.; Price, B. Car: Companion to Applied Regression. R Package Version 3.1-1. 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/car/index.html (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Bartoń, K. MuMIn: Multi-Model Inference. R Package Version 1.46.0. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 0-387-95457-0. Available online: https://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/pub/MASS4/ (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Ripley, B. MASS: Support Functions and Datasets for Venables and Ripley’s MASS. R Package Version 7.3-58.2. 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MASS/index.html (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- McKnight, M.M.; Qu, Z.; Copeland, J.K.; Guttman, D.S.; Walker, V.K. A practical assessment of nano-phosphate on soybean (Glycine max) growth and microbiome establishment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juurakko, C.L.; diCenzo, G.C.; Walker, V.K. Cold acclimation in Brachypodium is accompanied by changes in above-ground bacterial and fungal communities. Plants 2021, 10, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; McMahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilkina, M.I.; Zakharova, Y.R.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Petrova, D.P.; Bukin, Y.S.; Domysheva, V.M.; Blinov, V.V.; Likhoshway, Y.V. Bacterial community composition in the water column of the deepest freshwater Lake Baikal as determined by next-generation sequencing. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, I.; Sarmento, H.; Priscu, J.C.; Chiuchiolo, A.; González, J.M.; Grossart, H.P. Diversity and distribution of freshwater aerobic anoxygenic phototrophic bacteria across a wide latitudinal gradient. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruch, L.; Paruch, A.M.; Eiken, H.G.; Sørheim, R. Faecal pollution affects abundance and diversity of aquatic microbial community in anthropo-zoogenically influenced lotic ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.I.; Dossena, M.; Bohan, D.A.; Jeppesen, E.; Kordas, R.L.; Ledger, M.E.; Meerhoff, M.; Moss, B.; Mulder, C.; Shurin, J.B.; et al. Mesocosm experiments as a tool for ecological climate-change research. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2013, 48, 71–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Hawkins, C.P.; Kefford, B.J.; Schäfer, R.B.; Dyack, B.J.; Brucet, S.; Buchwalter, D.; Dunlop, J.; Frör, O.; Lazorchak, J.; et al. Saving freshwater from salts. Science 2016, 351, 914–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11436–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Kong, W.; Ji, M.; Liu, J.; Morgan-Kiss, R.M. Community response of microbial primary producers to salinity is primarily driven by nutrients in lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 134001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.W. Description of seven candidate species affiliated with the phylum Actinobacteria, representing planktonic freshwater bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerakietkhajorn, S.; Kato, Y.; Kasalický, V.; Matsuura, T.; Watanabe, H. Betaproteobacteria Limnohabitans strains increase fecundity in the crustacean Daphnia magna: Symbiotic relationship between major bacterioplankton and zooplankton in freshwater Ecosystem. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcher, M.M.; Šimek, K. Isolation and cultivation of planktonic freshwater microbes Is essential for a comprehensive understanding of their ecology. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 77, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintz, W.D.; Arnott, S.E.; Symons, C.C.; Greco, D.A.; McClymont, A.; Brentrup, J.A.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A. Current water quality quidelines across North America and Europe do not protect lakes from salinization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2115033119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hébert, M.P.; Symons, C.C.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Arnott, S.E.; Derry, A.M.; Fugère, V.; Beisner, B.E. Lake salinization drives consistent losses of zooplankton abundance and diversity across coordinated mesocosm Eexperiments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2023, 8, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, R.J.; Mount, D.R.; Highland, T.L.; Hockett, J.R.; Hoff, D.J.; Jenson, C.T.; Norberg-King, T.J.; Peterson, K.N. The acute toxicity of major ion salts to Ceriodaphnia dubia. II. Empirical relationships in binary salt mixtures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satari, L.; Guillén, A.; Latorre-Pérez, A.; Porcar, M. Beyond archaea: The table salt bacteriome. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 714110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, W.R.; Jones, S.E.; Muscarella, M.E.; Behringer, M.G.; Lehmkuhl, B.K.; Lennon, J.T. Microbial population dynamics and evolutionary outcomes under extreme energy limitation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101691118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.L.; Sargeant, S.; Nightingale, P.D.; Colin Murrell, J. Gradients in microbial methanol uptake: Productive coastal upwelling waters to oligotrophic gyres in the Atlantic Ocean. ISME J. 2013, 7, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, T.A.; Prithiviraj, B.; Wahlen, B.D.; Fields, M.W.; Peyton, B.M. A lipid-accumulating alga maintains growth in outdoor, alkaliphilic raceway pond with mixed microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byappanahalli, M.N.; Nevers, M.B.; Przybyla-Kelly, K.; Ishii, S.; King, T.L.; Aunins, A.W. Great lakes cadophora harbors phylogenetically diverse nitrogen-fixing microorganisms. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjezi, N.; Yaghoubian, I.; Smith, D.L. Cell-free supernatant of Devosia sp. (Strain SL43) mitigates the adverse effects of salt stress on soybean (Glycine max L.) seed vigor index. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1071346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). Bureau of Indian Standards Specification for Drinking Water. 2003. Available online: https://law.resource.org/pub/in/bis/S06/is.10500.1991.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Sleator, R.D.; Hill, C. Bacterial osmoadaptation: The role of osmolytes in bacterial stress and virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, P.L.; Salerno, J.; Bennett, C.J.; Kudla, Y.; Smith, M. The relative toxicity of road salt alternatives to freshwater mussels; Examining the potential risk of eco-friendly de-icing products to sensitive aquatic species. ACS ES&T Water 2021, 1, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picinic, B.; Durant, A.; Donini, A. Effect of salt and brine-beet juice de-Icer on osmoregulatory physiology of the freshwater smphipod Hyalella azteca (Saussure, 1858) (Amphipoda: Hyalellidae). J. Crustacean Biol. 2022, 42, ruac025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, L.G.; Conaway, K.; Rebar, J.; Graettinger, A.J. Alternative deicers for winter road maintenance—A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.S.; Ahmerkamp, S.; Pjevac, P.; Hausmann, B.; Milucka, J.; Kuypers, M.M.M. How low can they go? Aerobic respiration by microorganisms under apparent anoxia. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuac006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Houten, R.T.; Lettinga, G. Biological Sulphate Reduction with Synthesis Gas: Microbiology and Technology. In Immobilized Cells: Basics and Applications; Buitelaar, R.M., Bucke, C., Tramper, J., Wijffels, R.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, K.; Schindler, D.E.; Horner-Devine, M.C. Resource availability and spatial heterogeneity control bacterial community response to nutrient enrichment in lakes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, R.J.; McLellan, S.L. A unique assemblage of cosmopolitan freshwater bacteria and higher community diversity differentiate an urbanized estuary from oligotrophic Lake Michigan. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goris, T.; Diekert, G. The Genus Sulfurospirillum. In Organohalide-Respiring Bacteria; Adrian, L., Löffler, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Hua, Y.; Zhao, J.; Huguet, A.; Li, S. Shifts in microbial communities in shallow lakes depending on trophic states: Feasibility as an evaluation index for eutrophication. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Zeng, H.; Gao, Y.; Mo, T.; Li, Y. Bio-hydrogen production by dark anaerobic fermentation of organic wastewater. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 978907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Bano, A.; Singh, S.P.; Dubey, N.K.; Chandra, R.; Iqbal, H.M. Recent advancements in microbial-assisted remediation strategies for toxic contaminants. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.C. Minimal dissolved oxygen requirements of aquatic life with emphasis on Canadian species: A review. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1975, 32, 2295–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitburg, D.L.; Loher, T.; Pacey, C.A.; Gerstein, A. Varying effects of low dissolved oxygen on trophic interactions in an estuarine food web. Ecol. Monogr. 1997, 67, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hastings, A.; Guo, H. Exploring change of internal nutrients cycling in a shallow lake: A dynamic nutrient driven phytoplankton model. Ecol. Model. 2015, 313, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.B.G.; Hilt, S.; Kosten, S.; de Klein, J.J.M.; Paerl, H.W.; van de Waal, D.B. Shifting states, shifting services: Linking regime shifts to changes in ecosystem services of shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Ushio, M.; Suzuki, K.; Abe, M.S.; Yamamichi, M.; Iwayama, K.; Canarini, A.; Hayashi, I.; Fukushima, K.; Fukuda, S.; et al. Alternative stable states, nonlinear behavior, and predictability of microbiome dynamics. Microbiome 2023, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin, T.A.; Juurakko, C.L.; Harrison, T.; Arnott, S.E.; Walker, V.K. Differential Impacts of Road De-icers on Freshwater Bacterial Communities. Water 2024, 16, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030426
Martin TA, Juurakko CL, Harrison T, Arnott SE, Walker VK. Differential Impacts of Road De-icers on Freshwater Bacterial Communities. Water. 2024; 16(3):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030426
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin, Troy A., Collin L. Juurakko, Tia Harrison, Shelley E. Arnott, and Virginia K. Walker. 2024. "Differential Impacts of Road De-icers on Freshwater Bacterial Communities" Water 16, no. 3: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030426
APA StyleMartin, T. A., Juurakko, C. L., Harrison, T., Arnott, S. E., & Walker, V. K. (2024). Differential Impacts of Road De-icers on Freshwater Bacterial Communities. Water, 16(3), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030426