Circulating Tumor Cells for the Management of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Renal Cell Carcinomas (RCC)
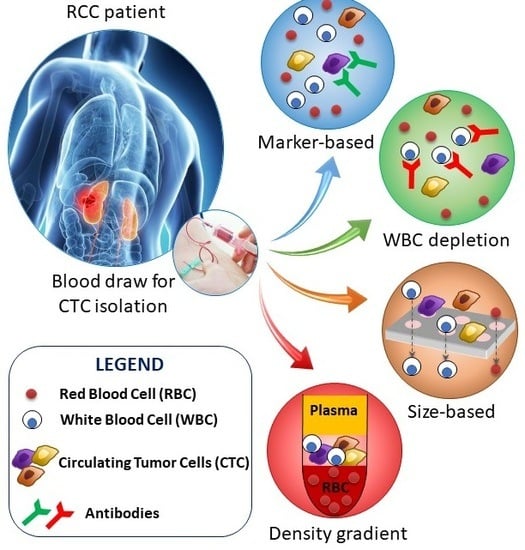
4. CTC Collection/Detection in Renal Cell Carcinoma
4.1. Epithelial Marker-Dependent Isolation/Detection of CTC in Renal Cell Carcinoma
4.2. Other Marker-Dependent Isolation of CTC in Renal Cell Carcinoma
4.3. RT-PCR-Based Methods for CTC Interrogation in Renal Cell Carcinoma
4.4. Negative CTC Enrichment by Hematopoietic Cell Depletion in Renal Cell Carcinoma
4.5. Cell Size-Based Enrichment, Morphological and Genetic Detection of CTC in Renal Cell Carcinoma
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Motzer, R.J.; Bander, N.H.; Nanus, D.M. Renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, J.S.; Shvarts, O.; Leppert, J.T.; Figlin, R.A.; Belldegrun, A.S. Renal cell carcinoma 2005: New frontiers in staging, prognostication and targeted molecular therapy. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashida, S.; Okuda, H.; Chikazawa, M.; Tanimura, M.; Sugita, O.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Moriyama, M.; Shuin, T. Detection of circulating cancer cells with von Hippel-Lindau gene mutation in peripheral blood of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 3817–3822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bedke, J.; Gouttefangeas, C.; Singh-Jasuja, H.; Stevanović, S.; Behnes, C.L.; Stenzl, A. Targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma: Moving from molecular agents to specific immunotherapy. World J. Urol. 2014, 32, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minguet, J.; Smith, K.H.; Bramlage, C.P.; Bramlage, P. Targeted therapies for treatment of renal cell carcinoma: Recent advances and future perspectives. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 76, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.H.K.; Chow, C.; To, K.F. Latest development of liquid biopsy. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S1645–S1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondo, F.; Morosi, L.; Corbetta, S.; Chinello, C.; Brambilla, P.; Della Mina, P.; Villa, A.; Albo, G.; Battaglia, C.; Bosari, S.; et al. Differential protein profiling of renal cell carcinoma urinary exosomes. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 1220–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellinger, J.; Gevensleben, H.; Müller, S.C.; Dietrich, D. The emerging role of non-coding circulating RNA as a biomarker in renal cell carcinoma. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 16, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Clinical Applications of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA as Liquid Biopsy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dizman, N.; Bergerot, P.; Bergerot, C.; Lanman, R.B.; Raymond, V.M.; Banks, K.C.; Jones, J.; Pal, S.K. Exceptional Response to Nivolumab Rechallenge in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma with Parallel Changes in Genomic Profile. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergerot, P.G.; Hahn, A.W.; Bergerot, C.D.; Jones, J.; Pal, S.K. The Role of Circulating Tumor DNA in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2018, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrò, C.; Hejhal, T.; Poyet, C.; Sulser, T.; Hermanns, T.; Winder, T.; Prager, G.; Wild, P.J.; Frew, I.; Moch, H.; et al. Detecting circulating tumor DNA in renal cancer: An open challenge. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2017, 102, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbosh, C.; Birkbak, N.J.; Wilson, G.A.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Constantin, T.; Salari, R.; Le Quesne, J.; Moore, D.A.; Veeriah, S.; Rosenthal, R.; et al. Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution. Nature 2017, 545, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klein, C.A.; Seidl, S.; Petat-Dutter, K.; Offner, S.; Geigl, J.B.; Schmidt-Kittler, O.; Wendler, N.; Passlick, B.; Huber, R.M.; Schlimok, G.; et al. Combined transcriptome and genome analysis of single micrometastatic cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Hu, S.; Huo, X.; Zhang, Y. Dr.seq2: A quality control and analysis pipeline for parallel single cell transcriptome and epigenome data. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKiernan, J.M.; Buttyan, R.; Bander, N.H.; de la Taille, A.; Stifelman, M.D.; Emanuel, E.R.; Bagiella, E.; Rubin, M.A.; Katz, A.E.; Olsson, C.A.; et al. The detection of renal carcinoma cells in the peripheral blood with an enhanced reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay for MN/CA9. Cancer 1999, 86, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Passebosc-Faure, K.; Gentil-Perret, A.; Lambert, C.; Genin, C.; Tostain, J. Cadherin-6 gene expression in conventional renal cell carcinoma: A useful marker to detect circulating tumor cells. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burczynski, M.E.; Twine, N.C.; Dukart, G.; Marshall, B.; Hidalgo, M.; Stadler, W.M.; Logan, T.; Dutcher, J.; Hudes, G.; Trepicchio, W.L.; et al. Transcriptional profiles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells prognostic of clinical outcomes in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluemke, K.; Bilkenroth, U.; Meye, A.; Fuessel, S.; Lautenschlaeger, C.; Goebel, S.; Melchior, A.; Heynemann, H.; Fornara, P.; Taubert, H. Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood of patients with renal cell carcinoma correlates with prognosis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 2190–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradilone, A.; Iacovelli, R.; Cortesi, E.; Raimondi, C.; Gianni, W.; Nicolazzo, C.; Petracca, A.; Palazzo, A.; Longo, F.; Frati, L.; et al. Circulating tumor cells and “suspicious objects” evaluated through CellSearch® in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 4219–4221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Heliebi, A.; Kroneis, T.; Zöhrer, E.; Haybaeck, J.; Fischereder, K.; Kampel-Kettner, K.; Zigeuner, R.; Pock, H.; Riedl, R.; Stauber, R.; et al. Are morphological criteria sufficient for the identification of circulating tumor cells in renal cancer? J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nel, I.; Gauler, T.C.; Bublitz, K.; Lazaridis, L.; Goergens, A.; Giebel, B.; Schuler, M.; Hoffmann, A.C. Circulating Tumor Cell Composition in Renal Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hou, S.; Hu, S.; Wu, J.; Jing, Y.; Sun, H.; Yu, F.; Zhao, L.; et al. Combined cell surface carbonic anhydrase 9 and CD147 antigens enable high-efficiency capture of circulating tumor cells in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59877–59891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagaya, N.; Kanayama, M.; Nagata, M.; Horie, S. The Surge in the Number of Circulating Tumor Cells Following Treatment with Sunitinib for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report. Intern. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broncy, L.; Njima, B.B.; Méjean, A.; Béroud, C.; Romdhane, K.B.; Ilie, M.; Hofman, V.; Muret, J.; Hofman, P.; Bouhamed, H.C.; Paterlini-Bréchot, A.P. Single-cell genetic analysis validates cytopathological identification of circulating cancer cells in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20058–20074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Scarpelli, M.; Montironi, R.; Kirkali, Z. 2004 WHO classification of the renal tumors of the adults. Eur. Urol. 2006, 49, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, J.I. Renal tumors with clear cells. A review. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2013, 209, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnecka, A.M.; Kornakiewicz, A.; Kukwa, W.; Szczylik, C. Frontiers in clinical and molecular diagnostics and staging of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majer, W.; Kluzek, K.; Bluyssen, H.; Wesoły, J. Potential Approaches and Recent Advances in Biomarker Discovery in Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuthi, L.; Jenei, A.; Hajdu, A.; Németh, I.; Varga, Z.; Bajory, Z.; Pajor, L.; Iványi, B. Prognostic Factors for Renal Cell Carcinoma Subtypes Diagnosed According to the 2016 WHO Renal Tumor Classification: A Study Involving 928 Patients. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2017, 23, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.J.; Purdue, M.P.; Signoretti, S.; Swanton, C.; Albiges, L.; Schmidinger, M.; Heng, D.Y.; Larkin, J.; Ficarra, V. Renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Yoshizato, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Maekawa, S.; Okuno, Y.; Kamura, T.; Shimamura, T.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Nagae, G.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Integrated molecular analysis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandriota, S.J.; Turner, K.J.; Davies, D.R.; Murray, P.G.; Morgan, N.V.; Sowter, H.M.; Wykoff, C.C.; Maher, E.R.; Harris, A.L.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; et al. HIF activation identifies early lesions in VHL kidneys: Evidence for site-specific tumor suppressor function in the nephron. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harten, S.K.; Shukla, D.; Barod, R.; Hergovich, A.; Balda, M.S.; Matter, K.; Esteban, M.A.; Maxwell, P.H. Regulation of renal epithelial tight junctions by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene involves occludin and claudin 1 and is independent of E-cadherin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, P.H.; Wiesener, M.S.; Chang, G.W.; Clifford, S.C.; Vaux, E.C.; Cockman, M.E.; Wykoff, C.C.; Pugh, C.W.; Maher, E.R.; Ratcliffe, P.J. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 1999, 399, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebbins, C.E.; Kaelin, W.G.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure of the VHL-ElonginC-ElonginB complex: Implications for VHL tumor suppressor function. Science 1999, 284, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossage, L.; Eisen, T.; Maher, E.R. VHL, the story of a tumour suppressor gene. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Sáez, O.; Gajate Borau, P.; Alonso-Gordoa, T.; Molina-Cerrillo, J.; Grande, E. Targeting HIF-2 α in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: A promising therapeutic strategy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 111, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Li, W.; Xiao, T.; Liu, X.S.; Kaelin, W.G. Inactivation of the PBRM1 tumor suppressor gene amplifies the HIF-response in VHL-/- clear cell renal carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, I.; Tarpey, P.; Raine, K.; Huang, D.; Ong, C.K.; Stephens, P.; Davies, H.; Jones, D.; Lin, M.-L.; Teague, J.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies frequent mutation of the SWI/SNF complex gene PBRM1 in renal carcinoma. Nature 2011, 469, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nargund, A.M.; Pham, C.G.; Dong, Y.; Wang, P.I.; Osmangeyoglu, H.U.; Xie, Y.; Aras, O.; Han, S.; Oyama, T.; Takeda, S.; et al. The SWI/SNF Protein PBRM1 Restrains VHL-Loss-Driven Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 2893–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstung, M.; Beisel, C.; Rechsteiner, M.; Wild, P.; Schraml, P.; Moch, H.; Beerenwinkel, N. Reliable detection of subclonal single-nucleotide variants in tumour cell populations. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerlinger, M.; Rowan, A.J.; Horswell, S.; Larkin, J.; Endesfelder, D.; Gronroos, E.; Martinez, P.; Matthews, N.; Stewart, A.; Tarpey, P.; et al. Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlinger, M.; Horswell, S.; Larkin, J.; Rowan, A.J.; Salm, M.P.; Varela, I.; Fisher, R.; McGranahan, N.; Matthews, N.; Santos, C.R.; et al. Genomic architecture and evolution of clear cell renal cell carcinomas defined by multiregion sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patard, J.J.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Masson, D.; Zerrouki, S.; Jouan, F.; Collet, N.; Dubourg, C.; Lobel, B.; Denis, M.; Fergelot, P. Absence of VHL gene alteration and high VEGF expression are associated with tumour aggressiveness and poor survival of renal-cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Hou, Y.; Yin, X.; Bao, L.; Tang, A.; Song, L.; Li, F.; Tsang, S.; Wu, K.; Wu, H.; et al. Single-cell exome sequencing reveals single-nucleotide mutation characteristics of a kidney tumor. Cell 2012, 148, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.T.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, H.O.; Song, H.J.; Jeong, D.E.; Shin, S.; Kim, H.; Shin, Y.; Nam, D.H.; Jeong, B.C.; et al. Application of single-cell RNA sequencing in optimizing a combinatorial therapeutic strategy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wu, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Lin, L.; Niu, Z.; Li, R.; Cai, Z.; Li, L. Single-cell exome sequencing identifies mutations in KCP, LOC440040, and LOC440563 as drivers in renal cell carcinoma stem cells. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.H.; Eisen, T. Prognostic factors in renal cell cancer. BJU Int. 2007, 99, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paterlini-Bréchot, P. Circulating Tumor Cells: Who is the Killer? Cancer Microenviron. 2014, 7, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hofman, V.J.; Ilie, M.I.; Bonnetaud, C.; Selva, E.; Long, E.; Molina, T.; Vignaud, J.M.; Fléjou, J.F.; Lantuejoul, S.; Piaton, E.; et al. Cytopathologic detection of circulating tumor cells using the isolation by size of epithelial tumor cell method: Promises and pitfalls. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 135, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofman, V.; Long, E.; Ilie, M.; Bonnetaud, C.; Vignaud, J.M.; Fléjou, J.F.; Lantuejoul, S.; Piaton, E.; Mourad, N.; Butori, C.; et al. Morphological analysis of circulating tumour cells in patients undergoing surgery for non-small cell lung carcinoma using the isolation by size of epithelial tumour cell (ISET) method. Cytopathology 2012, 23, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantel, K.; Denève, E.; Nocca, D.; Coffy, A.; Vendrell, J.P.; Maudelonde, T.; Riethdorf, S.; Alix-Panabières, C. Circulating epithelial cells in patients with benign colon diseases. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, N.P.; Reyes, E.; Badínez, L.; Orellana, N.; Fuentealba, C.; Olivares, R.; Porcell, J.; Dueñas, R. Circulating Prostate Cells Found in Men with Benign Prostate Disease Are P504S Negative: Clinical Implications. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jo/2013/165014/ (accessed on 22 August 2018).
- Cauley, C.E.; Pitman, M.B.; Zhou, J.; Perkins, J.; Kuleman, B.; Liss, A.S.; Fernandez-Del Castillo, C.; Warshaw, A.L.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Thayer, S.P. Circulating Epithelial Cells in Patients with Pancreatic Lesions: Clinical and Pathologic Findings. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2015, 221, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poruk, K.E.; Valero, V.; He, J.; Ahuja, N.; Cameron, J.L.; Weiss, M.J.; Lennon, A.M.; Goggins, M.; Wood, L.D.; Wolfgang, C.L. Circulating Epithelial Cells in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms and Cystic Pancreatic Lesions. Pancreas 2017, 46, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Toom, E.E.; Verdone, J.E.; Gorin, M.A.; Pienta, K.J. Technical challenges in the isolation and analysis of circulating tumor cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62754–62766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smadja, D.M.; Mauge, L.; Sanchez, O.; Silvestre, J.-S.; Guerin, C.; Godier, A.; Henno, P.; Gaussem, P.; Israël-Biet, D. Distinct patterns of circulating endothelial cells in pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J.; Habuka, M.; Tahmasebpoor, S.; Danielsson, A.; Edlund, K.; et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Zhao, A.; Li, R.; Du, R.; He, L.; Sun, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, C. CD147 renal expression as a biomarker for progressive IgAN. J. Nephrol. 2015, 28, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raval, R.R.; Lau, K.W.; Tran, M.G.B.; Sowter, H.M.; Mandriota, S.J.; Li, J.L.; Pugh, C.W.; Maxwell, P.H.; Harris, A.L.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in von Hippel-Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 5675–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.A.; Simon, M.C. Biology of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha in development and disease. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordan, J.D.; Lal, P.; Dondeti, V.R.; Letrero, R.; Parekh, K.N.; Oquendo, C.E.; Greenberg, R.A.; Flaherty, K.T.; Rathmell, W.K.; Keith, B.; et al. HIF-alpha effects on c-Myc distinguish two subtypes of sporadic VHL-deficient clear cell renal carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimazui, T.; Oosterwijk-Wakka, J.; Akaza, H.; Bringuier, P.P.; Ruijter, E.; Debruyne, F.M.; Schalken, J.A.; Oosterwijk, E. Alterations in expression of cadherin-6 and E-cadherin during kidney development and in renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2000, 38, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maertens, Y.; Humberg, V.; Erlmeier, F.; Steffens, S.; Steinestel, J.; Bögemann, M.; Schrader, A.J.; Bernemann, C. Comparison of isolation platforms for detection of circulating renal cell carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 87710–87717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeriswyl, V.; Christofori, G. The angiogenic switch in carcinogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2009, 19, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, J.I.; Shields, D.J.; Barillas, S.G.; Acevedo, L.M.; Murphy, E.; Huang, J.; Scheppke, L.; Stockmann, C.; Johnson, R.S.; Angle, N.; et al. A role for VEGF as a negative regulator of pericyte function and vessel maturation. Nature 2008, 456, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linehan, W.M.; Srinivasan, R.; Schmidt, L.S. The genetic basis of kidney cancer: A metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2010, 7, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Huntoon, K.; Ksendzovsky, A.; Zhuang, Z.; Lonser, R.R. Proteostasis modulators prolong missense VHL protein activity and halt tumor progression. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kats-Ugurlu, G.; Roodink, I.; de Weijert, M.; Tiemessen, D.; Maass, C.; Verrijp, K.; van der Laak, J.; de Waal, R.; Mulders, P.; Oosterwijk, E.; et al. Circulating tumour tissue fragments in patients with pulmonary metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2009, 219, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugino, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ogura, G.; Saito, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Hoshi, N.; Yoshida, S.; Goodison, S.; Suzuki, T. Morphological evidence for an invasion-independent metastasis pathway exists in multiple human cancers. BMC Med 2004, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cima, I.; Kong, S.L.; Sengupta, D.; Tan, I.B.; Phyo, W.M.; Lee, D.; Hu, M.; Iliescu, C.; Alexander, I.; Goh, W.L.; et al. Tumor-derived circulating endothelial cell clusters in colorectal cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 345ra89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kats-Ugurlu, G.; Oosterwijk, E.; Muselaers, S.; Oosterwijk-Wakka, J.; van de Hulsbergen-Kaa, C.; de Weijert, M.; van Krieken, H.; Desar, I.; van Herpen, C.; Maass, C.; et al. Neoadjuvant sorafenib treatment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma and release of circulating tumor fragments. Neoplasia 2014, 16, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Küsters, B.; Kats, G.; Roodink, I.; Verrijp, K.; Wesseling, P.; Ruiter, D.J.; de Waal, R.M.W.; Leenders, W.P.J. Micronodular transformation as a novel mechanism of VEGF-A-induced metastasis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5808–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiegler, H.; Geigl, J.B.; Langer, S.; Rigler, D.; Porter, K.; Unger, K.; Carter, N.P.; Speicher, M.R. High resolution array-CGH analysis of single cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, J.; Henrique, R.; Ribeiro, F.R.; Barros-Silva, J.D.; Peixoto, A.; Santos, C.; Pinheiro, M.; Costa, V.L.; Soares, M.J.; Oliveira, J.; et al. Feasibility of differential diagnosis of kidney tumors by comparative genomic hybridization of fine needle aspiration biopsies. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2010, 49, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, J.; Couturier, J.; Molinié, V.; Vieillefond, A.; Sibony, M. Clear-cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: 24 cases of a distinct low-grade renal tumour and a comparative genomic hybridization array study of seven cases. Histopathology 2011, 58, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Reviewed Studies | CTC Collection Method | CTC Detection Method | Patients |
|---|---|---|---|
| McKiernan et al. 1999 [16] | Density gradient centrifugation | CA9 RT-PCR | 9 metastatic RCC, 28 localized RCC, 5 benign renal lesions and 54 healthy controls |
| Ashida et al. 2000 [3] | Density gradient centrifugation | VHL mutation-specific PCR | 29 sporadic ccRCC |
| Allard et al. 2004 [17] | CellSearch® (EpCAM-based) | Cytokeratin expression | 11 metastatic RCC, 199 benign diseases and 145 healthy controls |
| Li et al. 2005 [18] | Density gradient centrifugation | Cadherin-6 RT-PCR | 11 metastatic RCC, 35 localized RCC and 25 healthy controls |
| Burzynski et al. 2005 [19] | Density gradient centrifugation | Global RT-PCR | 45 advanced RCC |
| Bluemke et al. 2009 [20] | Density gradient centrifugation and immunomagnetic depletion of leucocytes by AutoMacs | Morphological assessment and cytokeratin expression by immunocytochemistry | 154 RCC |
| Gradilone et al. 2011 [21] | CellSearch® (EpCAM-based) | Cytokeratin expression | 25 metastatic RCC |
| El-Heliebi et al. 2013 [22] | ScreenCell® Cyto filtration | Morphological assessment | 30 advanced RCC and 10 benign renal tumors |
| Nel et al. 2016 [23] | Density gradient centrifugation and hematopoietic cell depletion | Cytokeratin, N-Cadherin or CD133 expression by immunofluorescence | 14 metastatic RCC and 14 healthy donors |
| Liu et al. 2016 [24] | NanoVelcro microfluidic platform (CA9-/CD147-capture antibodies) | Cellular diameter of 13–50 μm and positive cytokeratin expression | 76 RCC, 10 benign renal tumors and 15 healthy controls |
| Nagaya et al. 2018 [25] | CytoQuest™ (EpCAM-based) | Cytokeratin expression without CD45 expression | 1 RCC (case report) |
| Broncy et al. 2018 [26] | ISET® filtration | Morphological assessment and single-cell VHL-targeted PCR | 2 metastatic RCC and 28 localized RCC |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Broncy, L.; Paterlini-Bréchot, P. Circulating Tumor Cells for the Management of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics8030063
Broncy L, Paterlini-Bréchot P. Circulating Tumor Cells for the Management of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics. 2018; 8(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics8030063
Chicago/Turabian StyleBroncy, Lucile, and Patrizia Paterlini-Bréchot. 2018. "Circulating Tumor Cells for the Management of Renal Cell Carcinoma" Diagnostics 8, no. 3: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics8030063
APA StyleBroncy, L., & Paterlini-Bréchot, P. (2018). Circulating Tumor Cells for the Management of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics, 8(3), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics8030063