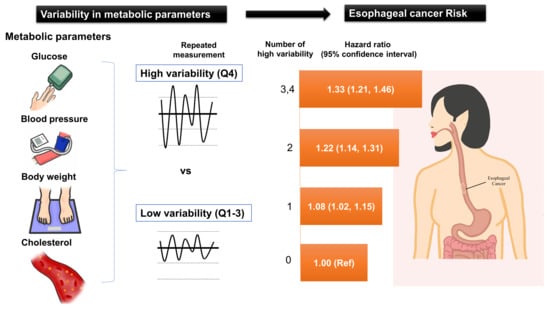
Association of Metabolic Parameter Variability with Esophageal Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Population
2.2. Study Outcomes and Follow-Up
2.3. Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Study Population
3.2. Risk of Esophageal Cancer According to Selected Metabolic Parameters
3.3. Risk of Esophageal Cancer According to Level of Each Metabolic Parameter Variability
3.4. Stratified Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Koulaouzidis, A.; Marlicz, W.; Lok, V.; Chu, C.; Ngai, C.H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, P.; Wang, S.; Yuan, J.; et al. Global Burden, Risk Factors, and Trends of Esophageal Cancer: An Analysis of Cancer Registries from 48 Countries. Cancers 2021, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, A.; Won, Y.J.; Jung, H.K.; Kong, H.J.; Jung, K.W.; Oh, C.M.; Choe, S.; Lee, J. Trends in incidence and survival of esophageal cancer in Korea: Analysis of the Korea Central Cancer Registry Database. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drahos, J.; Ricker, W.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Cook, M.B. Metabolic syndrome and risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma in elderly patients in the United States: An analysis of SEER-Medicare data. Cancer 2017, 123, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zuo, C.; Liu, G.; Che, P.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Chen, H. Cumulative evidence for the relationship between body mass index and the risk of esophageal cancer: An updated meta-analysis with evidence from 25 observational studies. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Shin, C.M.; Han, K.D.; Yoon, H.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, N.; Lee, D.H. Abdominal obesity increases risk for esophageal cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study of South Korea. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-D.; Park, C.-S.; Han, K.D.; Joo, Y.-H. Hypertension is associated with oral, laryngeal, and esophageal cancer: A nationwide population-based study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, C. Diabetes mellitus carries a risk of esophageal cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, R. Metabolic syndrome and esophageal cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.Y.; Han, K.; Shin, D.W.; Cho, M.H.; Yoo, J.E.; Cho, J.H. Associations of Variability in Metabolic Parameters with Lung Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Yoo, J.J.; Cho, E.J.; Han, K.; Kim, D.; Kim, B.Y.; Chung, G.E.; Cho, Y.; Shin, D.W.; Yu, S.J. Weight fluctuation and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A nationwide population-based 8-million-subject study. Hepatol. Int. 2021, 15, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.J.; Kawk, J.S.; Yoon, H.J.; Park, M. Body weight variability and cancer incidence in men aged 40 years and older-Korean National Insurance Service Cohort. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Shin, S.A.; Kim, K. Cohort Profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Cho, J.; Shin, D.W.; Lee, S.P.; Hwang, S.S.; Oh, J.; Yang, H.K.; Hwang, S.H.; Son, K.Y.; Chun, S.H.; et al. Association of cardiovascular health screening with mortality, clinical outcomes, and health care cost: A nationwide cohort study. Prev. Med. 2015, 70, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.J.; Cho, E.J.; Han, K.; Heo, S.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Shin, D.W.; Yu, S.J. Glucose Variability and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2021, 30, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Han, K.; Cho, H.; Park, Y.M.; Kwon, H.S.; Kang, G.; Yoon, K.H.; Kim, M.K. Variability in metabolic parameters and risk of dementia: A nationwide population-based study. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Howard, S.C.; Dolan, E.; O’Brien, E.; Dobson, J.E.; Dahlof, B.; Sever, P.S.; Poulter, N.R. Prognostic significance of visit-to-visit variability, maximum systolic blood pressure, and episodic hypertension. Lancet 2010, 375, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Howard, S.C.; Dolan, E.; O’Brien, E.; Dobson, J.E.; Dahlöf, B.; Poulter, N.R.; Sever, P.S. Effects of β blockers and calcium-channel blockers on within-individual variability in blood pressure and risk of stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Giovannucci, E.L. Light to moderate intake of alcohol, drinking patterns, and risk of cancer: Results from two prospective US cohort studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramteke, P.; Deb, A.; Shepal, V.; Bhat, M.K. Hyperglycemia Associated Metabolic and Molecular Alterations in Cancer Risk, Progression, Treatment, and Mortality. Cancers 2019, 11, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-h.; Noh, E.; Kim, J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, Y.-B.; Roh, E.; Choi, K.M.; Baik, S.H.; Cho, G.J.; et al. Fasting Plasma Glucose Variability and Gastric Cancer Risk in Individuals Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, e00221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, D.; Noto, H.; Takahashi, O.; Shimbo, T. Glycemic variability and subsequent malignancies among the population without diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 159, 107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ceriello, A.; Esposito, K.; Piconi, L.; Ihnat, M.A.; Thorpe, J.E.; Testa, R.; Boemi, M.; Giugliano, D. Oscillating glucose is more deleterious to endothelial function and oxidative stress than mean glucose in normal and type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindkvist, B.; Johansen, D.; Stocks, T.; Concin, H.; Bjørge, T.; Almquist, M.; Häggström, C.; Engeland, A.; Hallmans, G.; Nagel, G.; et al. Metabolic risk factors for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma: A prospective study of 580,000 subjects within the Me-Can project. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahmann, P.H.; Pandeya, N.; Webb, P.M.; Green, A.C.; Whiteman, D.C.; Cancer, A.C.S.J. Body mass index, long-term weight change, and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Is the inverse association modified by smoking status? Cancer 2012, 118, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabotto, E.; Pellegatta, G.; Sheijani, A.D.; Ziola, S.; Zentilin, P.; De Marzo, M.G.; Giannini, E.G.; Ghisa, M.; Barberio, B.; Scarpa, M.; et al. Prevention Strategies for Esophageal Cancer—An Expert Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohacker, K.; McFarlin, B.K. Influence of obesity, physical inactivity, and weight cycling on chronic inflammation. Front. Biosci. 2010, 2, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamet, P. Cancer and hypertension: A potential for crosstalk? J. Hypertens. 1997, 15, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, S.; Sobue, T.; Zha, L.; Kitamura, T.; Sawada, N.; Iwasaki, M.; Shimazu, T.; Tsugane, S. Long-term antihypertensive drug use and risk of cancer: The Japan Public Health Center-based prospective study. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, M.; Kohata, Y.; Nagaike, H.; Koshibu, M.; Gima, H.; Hiromura, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Mori, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Fukui, T.; et al. Association of glucose and blood pressure variability on oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension: A cross-sectional study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, K.M.; Veerabhadrappa, P.; Kashem, M.A.; Feairheller, D.L.; Sturgeon, K.M.; Williamson, S.T.; Crabbe, D.L.; Brown, M.D. Relationship of visit-to-visit and ambulatory blood pressure variability to vascular function in African Americans. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-I.; Lee, J.-H.; Chang, H.-J.; Cho, Y.-S.; Youn, T.-J.; Chung, W.-Y.; Chae, I.-H.; Choi, D.-J.; Park, K.U.; Kim, C.-H. Association between blood pressure variability and inflammatory marker in hypertensive patients. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Micucci, C.; Valli, D.; Matacchione, G.; Catalano, A. Current perspectives between metabolic syndrome and cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38959–38972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radišauskas, R.; Kuzmickienė, I.; Milinavičienė, E.; Everatt, R. Hypertension, serum lipids and cancer risk: A review of epidemiological evidence. Medicina 2016, 52, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.; Choi, I.Y.; Han, K.; Jeong, S.M.; Yoo, J.E.; Rhee, S.Y.; Park, Y.G.; Shin, D.W. Lipid Level, Lipid Variability, and Risk of Multiple Myeloma: A Nationwide Population-Based Study of 3,527,776 Subjects. Cancers 2021, 13, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Yang, H. The role of cholesterol metabolism in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Webb, A.J.; Fischer, U.; Mehta, Z.; Rothwell, P.M. Effects of antihypertensive-drug class on interindividual variation in blood pressure and risk of stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangalore, S.; Breazna, A.; DeMicco, D.A.; Wun, C.C.; Messerli, F.H.; TNT Steering Committee and Investigators. Visit-to-visit low-density lipoprotein cholesterol variability and risk of cardiovascular outcomes: Insights from the TNT trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, M.R.; Barbieri, M.; Marfella, R.; Paolisso, G. Reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation by blunting daily acute glucose fluctuations in patients with type 2 diabetes: Role of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibition. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Metabolic Parameter Variability Index 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3,4 | p-Value 2 |
| 2,844,142 | 3,283,601 | 1,712,015 | 536,475 | ||
| Age (years) | 47.7 ± 12.7 | 48.4 ± 13.8 | 49.6 ± 14.7 | 51.3 ± 15.7 | <0.0001 |
| Sex (male) | 1,768,372 (62.2) | 1,893,571 (57.7) | 928,613 (54.2) | 276,325 (51.5) | <0.0001 |
| Smoking | <0.0001 | ||||
| Non-smoker | 1,615,543 (56.8) | 1,934,020 (58.9) | 1,038,406 (60.7) | 333,159 (62.1) | |
| Ex-smoker | 507,319 (17.8) | 524,227 (16.0) | 255,203 (14.9) | 77,095 (14.4) | |
| Current smoker | 721,280 (25.4) | 825,354 (25.1) | 418,406 (24.4) | 126,221 (23.5) | |
| Alcohol consumption | <0.0001 | ||||
| None | 1,360,299 (47.8) | 1,684,049 (51.3) | 935,173 (54.6) | 312,442 (58.2) | |
| Mild to moderate (<30 g/day) | 1,262,834 (44.4) | 1,350,945 (41.1) | 649,196 (37.9) | 184,053 (34.3) | |
| Heavy (≥30 g/day) | 221,009 (7.8) | 248,607 (7.6) | 127,646 (7.5) | 39,980 (7.5) | |
| Regular physical activity | 575,148 (20.2) | 638,725 (19.5) | 319,768 (18.7) | 94,591 (17.6) | <0.0001 |
| Household income | <0.0001 | ||||
| Q1 + medical aid | 507,532 (17.8) | 652,828 (19.9) | 367,788 (21.5) | 120,566 (22.5) | |
| Q2 | 482,107 (17.0) | 624,070 (19.0) | 350,624 (20.5) | 114,106 (21.3) | |
| Q3 | 761,070 (26.8) | 917,239 (27.9) | 482,447 (28.2) | 151,350 (28.2) | |
| Q4 | 1,093,433 (38.5) | 1,089,464 (33.2) | 511,156 (29.9) | 150,453 (28.0) | |
| Diabetes, yes | 144,774 (5.1) | 271,244 (8.3) | 211,523 (12.4) | 99,768 (18.6) | <0.0001 |
| Hypertension, yes | 654,110 (23.0) | 910,482 (27.7) | 562,981 (32.9) | 210,196 (39.2) | <0.0001 |
| Dyslipidemia, yes | 423,202 (14.9) | 604,694 (18.4) | 386,067 (22.6) | 147,318 (27.5) | <0.0001 |
| Metabolic syndrome, yes | 618,082 (21.7) | 843,078 (25.7) | 516,276 (30.2) | 191,601 (35.7) | <0.0001 |
| Weight (kg) | 65.1 ± 11.2 | 64.3 ± 11.5 | 63.6 ± 11.8 | 62.8 ± 12.1 | <0.0001 |
| Height (cm) | 165.1 ± 9.0 | 164.2 ± 9.2 | 163.2 ± 9.4 | 162.2 ± 9.5 | <0.0001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 80.6 ± 8.7 | 80.6 ± 8.9 | 80.7 ± 9.1 | 80.9 ± 9.3 | <0.0001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.8 ± 3.0 | 23.8 ± 3.1 | 23.8 ± 3.3 | 23.7 ± 3.4 | <0.0001 |
| Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | 95.6 ± 17.4 | 96.9 ± 21.9 | 98.8 ± 26.7 | 101.6 ± 32.7 | <0.0001 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 122.7 ± 13.2 | 122.5 ± 14.7 | 122.6 ± 16.0 | 122.8 ± 17.6 | <0.0001 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 76.7 ± 9.4 | 76.4 ± 9.8 | 76.3 ± 10.3 | 76.2 ± 10.9 | <0.0001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 198.6 ± 33.6 | 195.8 ± 36.0 | 193.2 ± 38.9 | 190.6 ± 42.5 | <0.0001 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 55.1 ± 22.7 | 55.4 ± 24.2 | 55.5 ± 25.5 | 55.6 ± 28.0 | <0.0001 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 117.6 ± 34.9 | 114.6 ± 37.2 | 111.8 ± 39.5 | 109.0 ± 42.3 | <0.0001 |
| Triglycerides (geometric mean) | 114.4 (114.4, 114.5) | 113.3 (113.2, 113.4) | 114.4 (114.3, 114.5) | 115.6 (115.4, 115.8) | <0.0001 |
| Glucose VIM | 7.1 ± 3.1 | 9.9 ± 5.7 | 9.9 ± 5.7 | 15.8 ± 6.6 | <0.0001 |
| Weight VIM | 1.3 ± 0.6 | 1.9 ± 1.3 | 2.5 ± 1.7 | 3.4 ± 1.9 | <0.0001 |
| Systolic BP VIM | 7.0 ± 2.9 | 9.3 ± 5.0 | 11.5 ± 5.6 | 14.0 ± 5.4 | <0.0001 |
| Total cholesterol VIM | 13.8 ± 5.8 | 19.0 ± 11.3 | 25.3 ± 13.8 | 32.5 ± 14.2 | <0.0001 |
| N | Events (n) | Follow-up Duration (Person-Years) | Incidence Rate per 100,000 | Model 1 HR 1 | Model 2 aHR 2 | Model 3 aHR 3 | Model 4 aHR 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| <100 | 5,728,765 | 3368 | 50,851,612 | 6.62 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| ≥100 or on meds 5 | 2,647,468 | 3087 | 23,136,523 | 13.34 | 2.02 (1.92, 2.12) | 1.18 (1.12, 1.23) | 1.13 (1.08, 1.19) | 1.18 (1.12, 1.24) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | ||||||||
| <25 | 5,597,386 | 4648 | 49,389,063 | 9.41 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| ≥25 | 2,778,847 | 1807 | 24,599,072 | 7.35 | 0.78 (0.74, 0.82) | 0.75 (0.71, 0.79) | 0.78 (0.73, 0.82) | 0.76 (0.72, 0.80) |
| Blood pressure (mmHg) | ||||||||
| <130/85 | 4,534,843 | 1991 | 40,384,710 | 4.93 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| ≥130/85 or on meds 6 | 3,841,390 | 4464 | 33,603,425 | 13.28 | 2.70 (2.56, 2.84) | 1.19 (1.13, 1.26) | 1.15 (1.09, 1.21) | 1.24 (1.17, 1.31) |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | ||||||||
| <240 | 7,427,173 | 5790 | 65,606,785 | 8.83 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| ≥240 or on meds 7 | 949,060 | 665 | 8,381,350 | 7.93 | 0.90 (0.83, 0.97) | 1.03 (0.95, 1.11) | 1.01 (0.93, 1.10) | 1.03 (0.95, 1.12) |
| N | Events (n) | Follow-up Duration (Person-Years) | Incidence Rate per 100,000 | Model 1 HR 1 | Model 2 aHR 2 | Model 3 aHR 3 | Model 4 aHR 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose variability (VIM) | ||||||||
| Q1 | 2,094,061 | 1477 | 18,424,532 | 8.02 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q2 | 2,094,172 | 1470 | 18,545,087 | 7.93 | 0.99 (0.92, 1.06) | 1.04 (0.97, 1.12) | 1.02 (0.95, 1.10) | 1.02 (0.95, 1.09) |
| Q3 | 2,093,939 | 1568 | 18,568,704 | 8.44 | 1.05 (0.98, 1.13) | 1.10 (1.03, 1.19) | 1.06 (0.99, 1.14) | 1.05 (0.98, 1.13) |
| Q4 | 2,094,061 | 1940 | 18,449,812 | 10.52 | 1.31 (1.22, 1.40) | 1.21 (1.14, 1.30) | 1.13 (1.06, 1.21) | 1.11 (1.03, 1.18) |
| p for trend | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.002 | ||||
| Weight variability (VIM) | ||||||||
| Q1 | 2,093,667 | 1576 | 18,516,003 | 8.51 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q2 | 2,092,118 | 1572 | 18,582,887 | 8.46 | 0.99 (0.93, 1.07) | 1.09 (1.01, 1.17) | 1.07 (1.00, 1.15) | 1.05 (0.98, 1.13) |
| Q3 | 2,096,354 | 1540 | 18,577,380 | 8.29 | 0.97 (0.91, 1.04) | 1.08 (1.01, 1.16) | 1.06 (0.99, 1.13) | 1.02 (0.95, 1.10) |
| Q4 | 2,094,094 | 1767 | 18,311,865 | 9.65 | 1.13 (1.06, 1.21) | 1.27 (1.18, 1.36) | 1.22 (1.14, 1.31) | 1.15 (1.07, 1.23) |
| p for trend | 0.0009 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0003 | ||||
| Systolic blood pressure variability (VIM) | ||||||||
| Q1 | 2,094,065 | 1471 | 18,460,408 | 7.97 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q2 | 2,094,057 | 1408 | 18,610,077 | 7.57 | 0.95 (0.88, 1.02) | 1.04 (0.97, 1.12) | 1.04 (0.96, 1.12) | 1.04 (0.96, 1.11) |
| Q3 | 2,094,074 | 1652 | 18,569,332 | 8.90 | 1.12 (1.04, 1.20) | 1.11 (1.04, 1.20) | 1.09 (1.02, 1.17) | 1.09 (1.02, 1.17) |
| Q4 | 2,094,037 | 1924 | 18,348,318 | 10.49 | 1.32 (1.23, 1.41) | 1.13 (1.06, 1.21) | 1.09 (1.02, 1.17) | 1.08 (1.01, 1.16) |
| p for trend | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.006 | 0.0127 | ||||
| Total cholesterol variability (VIM) | ||||||||
| Q1 | 2,094,058 | 1410 | 18,476,792 | 7.63 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Q2 | 2,094,067 | 1358 | 18,630,457 | 7.29 | 0.95 (0.89, 1.03) | 1.00 (0.93, 1.08) | 0.99 (0.92, 1.07) | 0.99 (0.92, 1.06) |
| Q3 | 2,094,050 | 1517 | 18,593,772 | 8.16 | 1.07 (0.99, 1.15) | 1.09 (1.01, 1.17) | 1.07 (1.00, 1.15) | 1.06 (0.98, 1.13) |
| Q4 | 2,094,058 | 2170 | 18,287,114 | 11.87 | 1.56 (1.46, 1.66) | 1.29 (1.21, 1.38) | 1.26 (1.18, 1.35) | 1.23 (1.15, 1.32) |
| p for trend | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Cumulative number of high-variability (Q4) in each parameter | ||||||||
| 0 | 2,844,142 | 1730 | 25,329,242 | 6.83 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 1 | 3,283,601 | 2417 | 29,041,630 | 8.32 | 1.22 (1.15, 1.30) | 1.13 (1.07, 1.21) | 1.10 (1.03, 1.17) | 1.08 (1.02, 1.15) |
| 2 | 1,712,015 | 1637 | 14,996,225 | 10.92 | 1.60 (1.50, 1.71) | 1.33 (1.25, 1.43) | 1.26 (1.18, 1.35) | 1.22 (1.14, 1.31) |
| 3,4 | 536,475 | 671 | 4,621,038 | 14.52 | 2.13 (1.95, 2.33) | 1.53 (1.40, 1.67) | 1.41 (1.29, 1.54) | 1.33 (1.21, 1.46) |
| p for trend | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.E.; Han, K.; Yoo, J.; Yeo, Y.; Cho, I.Y.; Cho, B.; Kwon, H.; Shin, D.W.; Cho, J.H.; Park, Y.-M. Association of Metabolic Parameter Variability with Esophageal Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030375
Lee JE, Han K, Yoo J, Yeo Y, Cho IY, Cho B, Kwon H, Shin DW, Cho JH, Park Y-M. Association of Metabolic Parameter Variability with Esophageal Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(3):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030375
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji Eun, Kyungdo Han, Juhwan Yoo, Yohwan Yeo, In Young Cho, Belong Cho, Hyuktae Kwon, Dong Wook Shin, Jong Ho Cho, and Yong-Moon Park. 2022. "Association of Metabolic Parameter Variability with Esophageal Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Population-Based Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 3: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030375
APA StyleLee, J. E., Han, K., Yoo, J., Yeo, Y., Cho, I. Y., Cho, B., Kwon, H., Shin, D. W., Cho, J. H., & Park, Y. -M. (2022). Association of Metabolic Parameter Variability with Esophageal Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(3), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030375