Relationship between Mechanical Ventilation and Histological Fibrosis in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Undergoing Open Lung Biopsy
Abstract
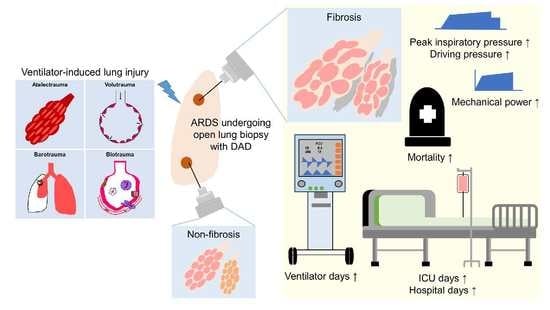
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Definitions
2.3. Data Collections
2.4. Histological Diagnosis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Populations
3.2. Histological Findings
3.3. Baseline Characteristics and Clinical Variables: Non-Fibrosis and Fibrosis Groups
3.4. Baseline Characteristics and Clinical Variables: DAD with a Fibrotic Phase and AE-IPF Groups
3.5. Clinical Outcomes: DAD with a Fibrotic Phase and AE-IPF
3.6. Factors Associated with Histological Fibrosis at OLB
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; van Haren, F.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, B.T.; Chambers, R.C.; Liu, K.D. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenstein, A.L.; Bloor, C.M.; Leibow, A.A. Diffuse alveolar damage--the role of oxygen, shock, and related factors. A review. Am. J. Pathol. 1976, 85, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guerin, C.; Bayle, F.; Leray, V.; Debord, S.; Stoian, A.; Yonis, H.; Roudaut, J.B.; Bourdin, G.; Devouassoux-Shisheboran, M.; Bucher, E.; et al. OLB in nonresolving ARDS frequently identifies diffuse alveolar damage regardless of the severity stage and may have implications for patient management. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, K.C.; Hu, H.C.; Chang, C.H.; Hung, C.Y.; Chiu, L.C.; Li, S.H.; Lin, S.W.; Chuang, L.P.; Wang, C.W.; Li, L.F.; et al. Diffuse alveolar damage associated mortality in selected acute respiratory distress syndrome patients with OLB. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorente, J.A.; Cardinal-Fernández, P.; Muñoz, D.; Frutos-Vivar, F.; Thille, A.W.; Jaramillo, C.; Ballén-Barragán, A.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Peñuelas, O.; Ortiz, G.; et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with and without diffuse alveolar damage: An autopsy study. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, E.L.; Janssen, W.J.; Riches, D.W.; Moss, M.; Downey, G.P. The fibroproliferative response in acute respiratory distress syndrome: Mechanisms and clinical significance. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabrera-Benitez, N.E.; Laffey, J.G.; Parotto, M.; Spieth, P.M.; Villar, J.; Zhang, H.; Slutsky, A.S. Mechanical ventilation-associated lung fibrosis in acute respiratory distress syndrome: A significant contributor to poor outcome. Anesthesiology 2014, 121, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichikado, K.; Muranaka, H.; Gushima, Y.; Kotani, T.; Nader, H.M.; Fujimoto, K.; Johkoh, T.; Iwamoto, N.; Kawamura, K.; Nagano, J.; et al. Fibroproliferative changes on high-resolution CT in the acute respiratory distress syndrome predict mortality and ventilator dependency: A prospective observational cohort study. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e000545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J.; Corte, T.J.; Jenkins, G.; Kondoh, Y.; Lederer, D.J.; Lee, J.S.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M.; et al. Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An International Working Group Report. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Park, J.H.; Park, B.K.; Lee, J.S.; Nicholson, A.G.; Colby, T. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Frequency and clinical features. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marchioni, A.; Tonelli, R.; Ball, L.; Fantini, R.; Castaniere, I.; Cerri, S.; Luppi, F.; Malerba, M.; Pelosi, P.; Clini, E. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Lessons learned from acute respiratory distress syndrome? Crit. Care 2018, 22, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slutsky, A.S.; Ranieri, V.M. Ventilator-induced lung injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2126–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, L.C.; Hu, H.C.; Hung, C.Y.; Chang, C.H.; Tsai, F.C.; Yang, C.T.; Huang, C.C.; Wu, H.P.; Kao, K.C. Dynamic driving pressure associated mortality in acute respiratory distress syndrome with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, L.C.; Lin, S.W.; Chuang, L.P.; Li, H.H.; Liu, P.H.; Tsai, F.C.; Chang, C.H.; Hung, C.Y.; Lee, C.S.; Leu, S.W.; et al. Mechanical power during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and hospital mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinoni, L.; Tonetti, T.; Cressoni, M.; Cadringher, P.; Herrmann, P.; Moerer, O.; Protti, A.; Gotti, M.; Chiurazzi, C.; Carlesso, E.; et al. Ventilator-related causes of lung injury: The mechanical power. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thille, A.W.; Esteban, A.; Fernández-Segoviano, P.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Aramburu, J.A.; Vargas-Errázuriz, P.; Martín-Pellicer, A.; Lorente, J.A.; Frutos-Vivar, F. Chronology of histological lesions in acute respiratory distress syndrome with diffuse alveolar damage: A prospective cohort study of clinical autopsies. Lancet Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal-Fernández, P.; Bajwa, E.K.; Dominguez-Calvo, A.; Menéndez, J.M.; Papazian, L.; Thompson, B.T. The Presence of Diffuse Alveolar Damage on OLB Is Associated With Mortality in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chest 2016, 149, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thille, A.W.; Esteban, A.; Fernández-Segoviano, P.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Aramburu, J.A.; Peñuelas, O.; Cortés-Puch, I.; Cardinal-Fernández, P.; Lorente, J.A.; Frutos-Vivar, F. Comparison of the Berlin definition for acute respiratory distress syndrome with autopsy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomashefski, J.F., Jr. Pulmonary pathology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Clin. Chest Med. 2000, 21, 435–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.K.; Smith, B.; Perlman, C.E.; Schwartz, D.A. Is Progression of Pulmonary Fibrosis due to Ventilation-induced Lung Injury? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.S.; Maia, L.A.; Oliveira, M.V.; Santos, C.L.; Moraes, L.; Pinto, E.F.; Samary, C.D.S.; Machado, J.A.; Carvalho, A.C.; Fernandes, M.V.S.; et al. Biologic Impact of Mechanical Power at High and Low Tidal Volumes in Experimental Mild Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Anesthesiology 2018, 128, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.B.; Meade, M.O.; Slutsky, A.S.; Brochard, L.; Costa, E.L.; Schoenfeld, D.A.; Stewart, T.E.; Briel, M.; Talmor, D.; Mercat, A.; et al. Driving pressure and survival in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wuyts, W.A.; Cavazza, A.; Rossi, G.; Bonella, F.; Sverzellati, N.; Spagnolo, P. Differential diagnosis of usual interstitial pneumonia: When is it truly idiopathic? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hobbs, S.; Chung, J.H.; Leb, J.; Kaproth-Joslin, K.; Lynch, D.A. Practical Imaging Interpretation in Patients Suspected of Having Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Official Recommendations from the Radiology Working Group of the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2021, 3, e200279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioni, A.; Tonelli, R.; Rossi, G.; Spagnolo, P.; Luppi, F.; Cerri, S.; Cocconcelli, E.; Pellegrino, M.R.; Fantini, R.; Tabbì, L.; et al. Ventilatory support and mechanical properties of the fibrotic lung acting as a “squishy ball”. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamo, T.; Tasaka, S.; Suzuki, T.; Asakura, T.; Suzuki, S.; Yagi, K.; Namkoong, H.; Ishii, M.; Morisaki, H.; Betsuyaku, T. Prognostic values of the Berlin definition criteria, blood lactate level, and fibroproliferative changes on high-resolution computed tomography in ARDS patients. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H.; Kradin, R.L.; Greene, R.E.; Shepard, J.A.; Digumarthy, S.R. CT predictors of mortality in pathology confirmed ARDS. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | All (n = 68) | Non-Fibrosis (n = 56) | Fibrosis (n = 12) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 60.4 ± 16 | 59.4 ± 14.8 | 65.3 ± 20.8 | 0.255 |
| Male (gender) | 39 (57%) | 31 (55%) | 8 (67%) | 0.472 |
| Body weight (kg) | 60.7 ± 11.7 | 61.0 ± 12.3 | 58.4 ± 6.1 | 0.566 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.7 ± 3.8 | 23.8 ± 3.9 | 22.8 ± 3.3 | 0.488 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 12 (18%) | 9 (16%) | 3 (25%) | 0.432 |
| Hypertension | 20 (29%) | 18 (32%) | 2 (17%) | 0.486 |
| Chronic lung diseases | 7 (10%) | 6 (11%) | 1 (8%) | 1.0 |
| Immunocompromised | 18 (27%) | 16 (29%) | 2 (17%) | 0.494 |
| ARDS etiologies | ||||
| Pulmonary causes | 58 (85%) | 47 (84%) | 11 (92%) | 0.678 |
| Extrapulmonary causes | 10 (15%) | 9 (16%) | 1 (8%) | 0.678 |
| PaO2/FiO2 at day of ARDS diagnosis (mmHg) | 135 (61–204) | 136 (61–213) | 118 (58–187) | 0.613 |
| Ventilator settings at day of ARDS diagnosis | ||||
| Mechanical power (J/min) | 24.6 ± 9 | 23.5 ± 8.2 | 29.9 ± 10.8 | 0.023 |
| Tidal volume (mL/kg PBW) | 8.6 ± 1.9 | 8.7 ± 2 | 8.4 ± 1.6 | 0.764 |
| PEEP (cm H2O) | 10.9 ± 2.4 | 11 ± 2.5 | 11 ± 2.1 | 0.566 |
| Peak inspiratory pressure (cm H2O) | 31.7 ± 5.6 | 31.1 ± 4.9 | 36.1 ± 5.3 | 0.004 |
| Mean airway pressure (cm H2O) | 17.6 ± 3.5 | 17.5 ± 3.4 | 18.5 ± 4 | 0.345 |
| Dynamic driving pressure (cm H2O) | 20.9 ± 5.2 | 20.2 ± 4.4 | 24 ± 7.5 | 0.021 |
| Total respiratory rate (breaths/min) | 24.9 ±5 | 24.3 ± 4.9 | 27.3 ± 5.2 | 0.088 |
| Dynamic compliance (mL/cm H2O) | 24.8 ± 10.5 | 24.8 ± 8.9 | 24.8 ± 16.5 | 0.989 |
| Day from ARDS diagnosis to biopsy | 8 (5–14) | 8 (5–12) | 18 (9–30) | 0.024 |
| PaO2/FiO2 at biopsy day (mmHg) | 139 (104–194) | 137 (103–199) | 141 (98–191) | 0.867 |
| Ventilator settings at biopsy day | ||||
| Mechanical power (J/min) | 23.8 ± 7.7 | 23.1 ± 6.9 | 27 ± 10.3 | 0.12 |
| Tidal volume (mL/kg PBW) | 7.7 ± 1.8 | 7.7 ± 1.7 | 7.6 ± 2.3 | 0.961 |
| PEEP (cm H2O) | 12.3 ± 2.6 | 12.5 ± 2.5 | 11.3 ± 2.6 | 0.191 |
| Peak inspiratory pressure (cm H2O) | 34.4 ± 6.9 | 33.6 ± 6.2 | 38.2 ± 9.1 | 0.037 |
| Mean airway pressure (cm H2O) | 19.3 ± 3.8 | 19.4 ± 3.6 | 18.8 ± 5.1 | 0.567 |
| Dynamic driving pressure (cm H2O) | 22.1 ± 6.8 | 21.1 ± 6.0 | 26.8 ± 8.2 | 0.007 |
| Total respiratory rate (breaths/min) | 25.2 ± 5 | 24.9 ± 4.7 | 26.3 ± 6.5 | 0.373 |
| Dynamic compliance (mL/cm H2O) | 20.5 ± 7.6 | 21.3 ± 7.6 | 17.1 ± 6.7 | 0.017 |
| Hospital mortality, n (%) | 40 (59%) | 32 (57%) | 8 (67%) | 0.748 |
| Duration of mechanical ventilator (days) | 22 (15–34) | 21 (14–32) | 35 (24–74) | 0.028 |
| Length of ICU stay (days) | 27 (17–37) | 25 (16–34) | 51 (32–80) | 0.001 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 34 (22–56) | 31 (20–46) | 55 (32–81) | 0.004 |
| Ventilator-free days at day 28 | 0 (0–5) | 0 (0–11) | 0 (0–0) | 0.036 |
| ICU-free days at day 28 | 0 (0–7) | 0 (0–8) | 0 (0–0) | 0.036 |
| ICU-free days at day 60 | 0 (0–35) | 0 (0–40) | 0 (0–0) | 0.008 |
| Hospital-free days at day 90 | 51 (29–66) | 54 (16–34) | 25 (2–54) | 0.01 |
| Characteristics | DAD with a Fibrotic Phase (n = 7) | AE-IPF (n = 5) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 59.3 ± 25.5 | 73.6 ± 8.36 | 0.204 |
| Male (gender) | 5 (71%) | 3 (60%) | 0.769 |
| Body weight (kg) | 60.5 ± 8.1 | 56.4 ± 3.2 | 0.379 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.4 ± 4.4 | 22.1 ± 1.7 | 0.657 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 1 (14%) | 2 (40%) | 0.31 |
| Hypertension | 1 (14%) | 1 (20%) | 0.793 |
| Chronic lung diseases | 1 (14%) | 0 (0%) | 0.377 |
| Immunocompromised | 2 (29%) | 0 (0%) | 0.19 |
| ARDS etiologies | |||
| Pulmonary causes | 6 (86%) | 5 (100%) | 1.0 |
| Extrapulmonary causes | 1 (14%) | 0 (0%) | 1.0 |
| PaO2/FiO2 at day of ARDS diagnosis (mmHg) | 68 (39–138) | 136 (118–176) | 0.794 |
| Ventilator settings at day of ARDS diagnosis | |||
| Mechanical power (J/min) | 30 ± 8.7 | 30 ± 14 | 0.987 |
| Tidal volume (mL/kg PBW) | 8.9 ± 1.9 | 7.8 ± 1.1 | 0.434 |
| PEEP (cm H2O) | 10.6 ± 2.2 | 10.4 ± 2.2 | 0.897 |
| Peak inspiratory pressure (cm H2O) | 34.6 ± 5.6 | 34.4 ± 5.7 | 0.971 |
| Mean airway pressure (cm H2O) | 18.6 ± 4.1 | 18.4 ± 4.4 | 0.946 |
| Dynamic driving pressure (cm H2O) | 24 ± 5.2 | 24 ± 10.7 | 1.0 |
| Total respiratory rate (breaths/min) | 27.1 ± 4.6 | 27.6 ± 6.6 | 0.889 |
| Dynamic compliance (mL/cm H2O) | 21.2 (15–24.6) | 15.9 (14.1–49) | 0.755 |
| Day from ARDS diagnosis to biopsy | 28 (17–53) | 7 (4–21) | 0.242 |
| PaO2/FiO2 at biopsy day (mmHg) | 168 (95–192) | 106 (89–141) | 0.546 |
| Ventilator settings at biopsy day | |||
| Mechanical power (J/min) | 25.2 ± 11.4 | 29.4 ± 9.2 | 0.851 |
| Tidal volume (mL/kg PBW) | 6.8 ± 2.7 | 8.8 ± 1.3 | 0.301 |
| PEEP (cm H2O) | 11 ± 3.2 | 11.8 ± 1.8 | 0.394 |
| Peak inspiratory pressure (cm H2O) | 37.4 ± 10 | 39.2 ± 8.8 | 0.757 |
| Mean airway pressure (cm H2O) | 17.7 ± 5.3 | 20.4 ± 4.9 | 0.628 |
| Dynamic driving pressure (cm H2O) | 26.4 ± 8.8 | 27.4 ± 8.3 | 0.663 |
| Total respiratory rate (breaths/min) | 25.3 ± 3.8 | 27.8 ± 9.5 | 0.537 |
| Dynamic compliance (mL/ cm H2O) | 15.8 (11.7–18.6) | 15.2 (10.1–27.6) | 0.876 |
| Outcomes | DAD with Fibrotic Phase (n = 7) | AE-IPF (n = 5) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90-day hospital mortality, n (%) | 4 (57%) | 4 (80%) | 0.242 |
| Other outcomes | |||
| Duration of mechanical ventilator (days) | 46 (22–75) | 42 (24–66) | 0.84 |
| Length of ICU stay (days) | 72 (37–81) | 48 (24–78) | 0.319 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 82 (53–93) | 57 (27–98) | 0.364 |
| Ventilator-free days at day 90 | 14 (0–23) | 0 (0–0) | 0.224 |
| ICU-free days at day 60 | 1 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.424 |
| Characteristics | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|
| MP at day of ARDS diagnosis (J/min) | 1.493 (1.014–2.200) | 0.042 |
| ARDS duration before biopsy (days) | 1.160 (1.052–1.278) | 0.003 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.-H.; Wang, C.-W.; Chang, C.-H.; Huang, C.-C.; Hsu, H.-S.; Chiu, L.-C. Relationship between Mechanical Ventilation and Histological Fibrosis in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Undergoing Open Lung Biopsy. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030474
Li H-H, Wang C-W, Chang C-H, Huang C-C, Hsu H-S, Chiu L-C. Relationship between Mechanical Ventilation and Histological Fibrosis in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Undergoing Open Lung Biopsy. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(3):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030474
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hsin-Hsien, Chih-Wei Wang, Chih-Hao Chang, Chung-Chi Huang, Han-Shui Hsu, and Li-Chung Chiu. 2022. "Relationship between Mechanical Ventilation and Histological Fibrosis in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Undergoing Open Lung Biopsy" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 3: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030474
APA StyleLi, H. -H., Wang, C. -W., Chang, C. -H., Huang, C. -C., Hsu, H. -S., & Chiu, L. -C. (2022). Relationship between Mechanical Ventilation and Histological Fibrosis in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Undergoing Open Lung Biopsy. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(3), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030474