Potential Cancer Risk in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Longitudinal Korean Population-Based Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
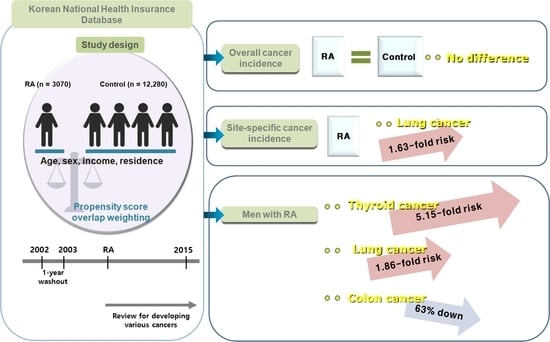
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Definition of Rheumatoid Arthritis
2.4. Definition of Cancers
2.5. Participant Selection
2.6. Covariates
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Incidence of Malignancies in the RA Group and Control Group
3.3. Association of the Incidence of Malignancy in the RA and Control Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, I.A.; Lee, J.S.; Song, Y.W.; Lee, E.Y. Mortality, disability, and healthcare expenditure of patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis in Korea: A nationwide population-based study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, E.; Sawada, T.; Tahara, K.; Hayashi, H.; Tago, M.; Mori, H.; Nishino, J.; Matsui, T.; Tohma, S. The age at onset of rheumatoid arthritis is increasing in Japan: A nationwide database study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Chang, Y.-T.; Wang, C.-B.; Wu, C.-Y. The risk of cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A nationwide cohort study in Taiwan. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 63, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, A.; Chiba, N.; Tsuno, H.; Komiya, A.; Furukawa, H.; Matsui, T.; Nishino, J.; Tohma, S. Incidence of Malignancy and the Risk of Lymphoma in Japanese Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Compared to the General Population. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Shim, J.-S.; Choi, C.-B.; Bae, S.-C. Mortality and Incidence of Malignancy in Korean Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smitten, A.L.; Simon, T.A.; Hochberg, M.C.; Suissa, S. A meta-analysis of the incidence of malignancy in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simon, T.A.; Thompson, A.; Gandhi, K.K.; Hochberg, M.C.; Suissa, S. Incidence of malignancy in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolfe, F.; Michaud, K. Biologic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of malignancy: Analyses from a large US observational study. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2886–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh-Patel, A.; White, R.H.; Allen, M.; Cress, R. Risk of cancer among rheumatoid arthritis patients in California. Cancer Causes Control 2009, 20, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padyukov, L.; Silva, C.; Stolt, P.; Alfredsson, L.; Klareskog, L.; for the Epidemiological Investigation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Study Group. A gene-environment interaction between smoking and shared epitope genes in HLA-DR provides a high risk of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 3085–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Li, M.; Fang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Duan, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, R.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Chinese Registry of rheumatoid arthritis (CREDIT): II. prevalence and risk factors of major comorbidities in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, S.M.; Kwok, S.-K.; Ju, J.H.; Park, Y.-B.; Park, S.-H. Risk of malignancy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis after anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results from Korean National Health Insurance claims data. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.M.; Moon, S.-J. Prevalence, incidence, and risk factors of malignancy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A nationwide cohort study from Korea. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-K.; Lee, J.; Han, M.; Bae, S.-C.; Sung, Y.-K. The risk of malignancy and its incidence in early rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with biologic DMARDs. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Oh, D.J.; Choi, H.G. Tobacco Smoking and Alcohol Consumption Are Related to Benign Parotid Tumor: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 12, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, Y.-K.; Cho, S.-K.; Choi, C.-B.; Bae, S.-C. Prevalence and incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in South Korea. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-K.; Sung, Y.-K.; Choi, C.-B.; Kwon, J.-M.; Lee, E.-K.; Bae, S.-C. Development of an algorithm for identifying rheumatoid arthritis in the Korean National Health Insurance claims database. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 2985–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.M.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.-M.; Sundararajan, V. Updating and Validating the Charlson Comorbidity Index and Score for Risk Adjustment in Hospital Discharge Abstracts Using Data From 6 Countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Dalton, J.E. A unified approach to measuring the effect size between two groups using SAS. In Proceedings of the SAS Conference Proceedings: SAS Global Forum 2012, Orlando, FL, USA, 22–25 April; 2012; p. 335. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, P.C. Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples. Stat. Med. 2009, 28, 3083–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H. The Risk of Malignancy in Korean Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Yonsei Med, J. 2019, 60, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibere, J.; Sibley, J.; Haga, M. Rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of malignancy. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, C.-M.; Jung, K.-W.; Won, Y.-J.; Shin, A.; Kong, H.-J.; Lee, J.-S. Age-Period-Cohort Analysis of Thyroid Cancer Incidence in Korea. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 47, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Mu, K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yao, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.-A. Increased Risk of Thyroid Dysfunction Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khil, H.; Kim, S.M.; Hong, S.; Gil, H.M.; Cheon, E.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, Y.A.; Keum, N. Time trends of colorectal cancer incidence and associated lifestyle factors in South Korea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2413–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, F.V.N.; Theodoratou, E.; Farrington, S.M.; Tenesa, A.; Barnetson, R.A.; Cetnarskyj, R.; Stark, L.; Porteous, M.E.; Campbell, H.; Dunlop, M. Effect of aspirin and NSAIDs on risk and survival from colorectal cancer. Gut 2010, 59, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, M.; Pukkala, E.; Isomäki, H. Low incidence of colorectal cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1996, 14, 551–553. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, G.W.; Cummings, K.M. Tobacco and lung cancer: Risks, trends, and outcomes in patients with cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2013, 33, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cock, D.; Hyrich, K. Malignancy and rheumatoid arthritis: Epidemiology, risk factors and management. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 869–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, D.; Nishimura, K.; Tamaki, K.; Tsuji, G.; Nakazawa, T.; Morinobu, A.; Kumagai, S. Impact of smoking as a risk factor for developing rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baecklund, E.; Iliadou, A.; Askling, J.; Ekbom, A.; Backlin, C.; Granath, F.; Catrina, A.I.; Rosenquist, R.; Feltelius, N.; Sundström, C.; et al. Association of chronic inflammation, not its treatment, with increased lymphoma risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Total Participants | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (n, %) | Control (n, %) | SMD | |
| Total number | 3070 (100.0) | 12,280 (100.0) | |
| Age (years old) | 0.00 | ||
| 40–44 | 109 (3.6) | 436 (3.6) | |
| 45–49 | 363 (11.8) | 1452 (11.8) | |
| 50–54 | 662 (21.6) | 2648 (21.6) | |
| 55–59 | 584 (19.0) | 2336 (19.0) | |
| 60–64 | 539 (17.6) | 2156 (17.6) | |
| 65–69 | 414 (13.5) | 1656 (13.5) | |
| 70–74 | 235 (7.7) | 940 (7.7) | |
| 75–79 | 127 (4.1) | 508 (4.1) | |
| 80–84 | 32 (1.0) | 128 (1.0) | |
| 85+ | 5 (0.2) | 20 (0.2) | |
| Sex | 0.00 | ||
| Male | 810 (26.4) | 3240 (26.4) | |
| Female | 2260 (73.6) | 9040 (73.6) | |
| Income | 0.00 | ||
| 1 (lowest) | 514 (16.7) | 2056 (16.7) | |
| 2 | 463 (15.1) | 1852 (15.1) | |
| 3 | 533 (17.4) | 2132 (17.4) | |
| 4 | 646 (21.0) | 2584 (21.0) | |
| 5 (highest) | 914 (29.8) | 3656 (29.8) | |
| Region of residence | 0.00 | ||
| Urban | 1320 (43.0) | 5280 (43.0) | |
| Rural | 1750 (57.0) | 7000 (57.0) | |
| Obesity † | 0.06 | ||
| Underweight | 59 (1.9) | 287 (2.3) | |
| Normal | 1169 (38.1) | 4394 (35.8) | |
| Overweight | 802 (26.1) | 3329 (27.1) | |
| Obese I | 952 (31.0) | 3877 (31.6) | |
| Obese II | 88 (2.9) | 393 (3.2) | |
| Smoking status | 0.04 | ||
| Nonsmoker | 2524 (82.2) | 10,254 (83.5) | |
| Past smoker | 209 (6.8) | 749 (6.1) | |
| Current smoker | 337 (11.0) | 1277 (10.4) | |
| Alcohol consumption | 0.05 | ||
| <1 time a week | 2476 (80.7) | 9676 (78.8) | |
| ≥1 time a week | 594 (19.4) | 2604 (21.2) | |
| Systolic blood pressure | 0.06 | ||
| <120 mmHg | 1009 (32.9) | 3982 (32.4) | |
| 120–139 mmHg | 1472 (48.0) | 5642 (45.9) | |
| ≥140 mmHg | 589 (19.2) | 2656 (21.6) | |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 0.05 | ||
| <80 mmHg | 1511 (49.2) | 5742 (46.8) | |
| 80–89 mmHg | 1049 (34.2) | 4304 (35.1) | |
| ≥90 mmHg | 510 (16.6) | 2234 (18.2) | |
| Fasting blood glucose | 0.08 | ||
| <100 mg/dL | 2138 (69.6) | 8126 (66.2) | |
| 100–125 mg/dL | 724 (23.6) | 3192 (26.0) | |
| ≥126 mg/dL | 208 (6.8) | 962 (7.8) | |
| Total cholesterol | 0.03 | ||
| <200 mg/dL | 1595 (52.0) | 6254 (50.9) | |
| 200–239 mg/dL | 1033 (33.7) | 4146 (33.8) | |
| ≥240 mg/dL | 442 (14.4) | 1880 (15.3) | |
| CCI score ‡ | 0.38 | ||
| 0 | 1791 (58.3) | 9327 (76.0) | |
| 1 | 801 (26.1) | 1832 (14.9) | |
| ≥2 | 478 (15.6) | 1121 (9.1) | |
| All of cancers | 170 (5.5) | 662 (5.4) | 0.01 |
| Gastric cancer | 34 (1.1) | 124 (1.0) | 0.01 |
| Thyroid cancer | 35 (1.1) | 138 (1.1) | 0.00 |
| Colorectal cancer | 27 (0.9) | 155 (1.3) | 0.04 |
| Lung cancer | 38 (1.2) | 89 (0.7) | 0.05 |
| Hepatic cancer | 14 (0.5) | 57 (0.5) | 0.00 |
| Bladder cancer | 7 (0.2) | 23 (0.2) | 0.01 |
| Pancreatic cancer | 7 (0.2) | 24 (0.2) | 0.01 |
| Gallbladder/biliary duct | 8 (0.3) | 41 (0.3) | 0.01 |
| Kidney cancer | 3 (0.1) | 18 (0.2) | 0.01 |
| Hematologic malignancy | 10 (0.3) | 43 (0.4) | 0.00 |
| Dependent Variable | IR/1000 PY | IRD/1000 PY(95% CI) | Hazard Ratios for Cancers (95% CI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA (n = 3070) | Control (n = 12,280) | Crude † | p | Model 1 †,‡ | p | Model 2 †,§ | p | ||
| All cancers (n = 832) | 8.12 | 7.86 | 0.26 (−1.09–1.61) | 1.04 (0.88–1.23) | 0.637 | 1.02 (0.86–1.21) | 0.825 | 1.02 (0.86–1.21) | 0.819 |
| Gastric (n = 158) | 1.59 | 1.45 | 0.14 (−0.43–0.72) | 1.11 (0.76–1.62) | 0.594 | 1.11 (0.76–1.63) | 0.600 | 1.12 (0.76–1.64) | 0.565 |
| Thyroid (n = 173) | 1.64 | 1.61 | 0.03 (−0.57–0.63) | 1.01 (0.70–1.47) | 0.951 | 1.01 (0.70–1.47) | 0.949 | 1.01 (0.69–1.46) | 0.980 |
| Colorectal (n = 182) | 1.26 | 1.81 | −0.55 (−1.16–0.07) | 0.69 (0.46–1.04) | 0.072 | 0.68 (0.45–1.03) | 0.070 | 0.68 (0.45–1.02) | 0.062 |
| Lung (n = 127) | 1.77 | 1.03 | 0.74 (0.22–1.25) | 1.74 (1.19–2.55) | 0.004 * | 1.64 (1.11–2.41) | 0.013 * | 1.63 (1.11–2.40) | 0.014 * |
| Hepatic (n = 71) | 0.65 | 0.66 | −0.01 (−0.39–0.37) | 1.01 (0.56–1.82) | 0.971 | 0.95 (0.52–1.73) | 0.875 | 0.96 (0.53–1.76) | 0.903 |
| Bladder (n = 30) | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.06 (−0.19–0.31) | 1.25 (0.54–2.91) | 0.610 | 1.24 (0.53–2.91) | 0.616 | 1.27 (0.54–2.97) | 0.585 |
| Pancreatic (n = 31) | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.05 (−0.21–0.30) | 1.16 (0.50–2.70) | 0.724 | 1.21 (0.52–2.83) | 0.663 | 1.23 (0.52–2.89) | 0.638 |
| GB/BD (n = 49) | 0.37 | 0.47 | −0.10 (−0.42–0.21) | 0.77 (0.36–1.65) | 0.506 | 0.71 (0.33–1.54) | 0.390 | 0.70 (0.32–1.51) | 0.361 |
| Kidney (n = 21) | 0.14 | 0.21 | −0.07 (−0.28–0.14) | 0.66 (0.20–2.25) | 0.508 | 0.67 (0.20–2.30) | 0.523 | 0.68 (0.20–2.35) | 0.543 |
| Hematologic (n = 53) | 0.46 | 0.50 | −0.03 (−0.36–0.30) | 0.94 (0.47–1.87) | 0.861 | 0.87 (0.43–1.75) | 0.694 | 0.87 (0.43–1.76) | 0.705 |
| Dependent Variable | IR/1000 PY | IRD/1000 PY (95% CI) | Hazard Ratios for Cancers (95% CI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA | Control | Crude † | p | Model 1 †,‡ | p | Model 2 †,§ | p | ||
| Men (n = RA: 810, Control: 3240) | |||||||||
| All cancers (n = 309) | 14.11 | 12.20 | 1.91 (−1.62–5.44) | 1.17 (0.90–1.54) | 0.248 | 1.12 (0.85–1.47) | 0.422 | 1.13 (0.86–1.49) | 0.376 |
| Gastric (n = 70) | 3.44 | 2.63 | 0.81 (−0.84–2.45) | 1.35 (0.78–2.34) | 0.285 | 1.32 (0.75–2.32) | 0.330 | 1.35 (0.77–2.37) | 0.299 |
| Thyroid (n = 11) | 1.20 | 0.25 | 0.96 (0.31–1.60) | 4.90 (1.49–16.07) | 0.009 * | 5.19 (1.53–17.64) | 0.008 * | 5.15 (1.48–17.95) | 0.010 * |
| Colorectal (n = 78) | 1.40 | 3.52 | −2.12 (−3.85–−0.40) | 0.38 (0.18–0.83) | 0.015 * | 0.38 (0.17–0.82) | 0.014 * | 0.37 (0.17–0.80) | 0.012 * |
| Lung (n = 65) | 4.41 | 2.11 | 2.29 (0.73–3.86) | 2.09 (1.25–3.50) | 0.005 * | 1.83 (1.07–3.11) | 0.026 * | 1.86 (1.09–3.18) | 0.022 * |
| Hepatic (n = 39) | 1.00 | 1.67 | −0.67 (−1.88–0.54) | 0.62 (0.24–1.58) | 0.317 | 0.60 (0.23–1.62) | 0.314 | 0.63 (0.24–1.71) | 0.367 |
| Bladder (n = 19) | 0.60 | 0.79 | −0.19 (−1.03–0.66) | 0.78 (0.23–2.69) | 0.698 | 0.77 (0.22–2.66) | 0.674 | 0.79 (0.22–2.75) | 0.705 |
| Pancreatic (n = 13) | 0.60 | 0.49 | 0.11 (−0.59–0.80) | 1.20 (0.33–4.39) | 0.778 | 1.22 (0.31–4.91) | 0.775 | 1.11 (0.25–4.95) | 0.893 |
| GB/biliary duct (n = 15) | 0.80 | 0.54 | 0.26 (−0.49–1.01) | 1.44 (0.45–4.54) | 0.538 | 1.68 (0.49–5.76) | 0.407 | 1.56 (0.44–5.53) | 0.495 |
| Kidney (n = 10) | 0.40 | 0.39 | 0.01 (−0.61–0.62) | 1.03 (0.22–4.85) | 0.971 | 0.99 (0.20–4.79) | 0.987 | 1.02 (0.20–5.09) | 0.982 |
| Hematologic (n = 18) | 0.80 | 0.69 | 0.11 (−0.71–0.93) | 1.19 (0.39–3.63) | 0.758 | 0.90 (0.29–2.84) | 0.862 | 1.03 (0.32–3.35) | 0.956 |
| Women (n = RA: 2260, Control: 9040) | |||||||||
| All cancers (n = 523) | 6.33 | 6.53 | −0.20 (−1.59–1.19) | 0.97 (0.78–1.20) | 0.773 | 0.95 (0.77–1.18) | 0.659 | 0.95 (0.76–1.18) | 0.618 |
| Gastric (n = 88) | 1.03 | 1.08 | −0.05 (−0.61–0.51) | 0.94 (0.55–1.60) | 0.819 | 0.95 (0.56–1.62) | 0.852 | 0.95 (0.56–1.62) | 0.846 |
| Thyroid (n = 162) | 1.77 | 2.03 | −0.27 (−1.03–0.50) | 0.87 (0.58–1.30) | 0.491 | 0.86 (0.58–1.29) | 0.472 | 0.86 (0.57–1.28) | 0.457 |
| Colorectal (n = 104) | 1.22 | 1.28 | −0.06 (−0.67–0.55) | 0.95 (0.58–1.55) | 0.831 | 0.94 (0.58–1.54) | 0.811 | 0.93 (0.57–1.51) | 0.756 |
| Lung (n = 62) | 0.97 | 0.70 | 0.27 (−0.20–0.74) | 1.42 (0.80–2.52) | 0.229 | 1.48 (0.83–2.63) | 0.181 | 1.51 (0.85–2.69) | 0.159 |
| Hepatic (n = 32) | 0.54 | 0.35 | 0.20 (−0.14–0.53) | 1.57 (0.72–3.39) | 0.254 | 1.45 (0.66–3.16) | 0.357 | 1.43 (0.64–3.16) | 0.383 |
| Bladder (n = 11) | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.14 (−0.06–0.33) | 2.26 (0.66–7.72) | 0.194 | 2.28 (0.64–8.19) | 0.205 | 2.43 (0.66–8.94) | 0.182 |
| Pancreatic (n = 18) | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.03 (−0.22–0.28) | 1.14 (0.37–3.45) | 0.822 | 1.11 (0.37–3.39) | 0.85 | 1.14 (0.37–3.52) | 0.814 |
| GB/biliary duct (n = 34) | 0.24 | 0.45 | −0.21 (−0.56–0.13) | 0.53 (0.19–1.51) | 0.234 | 0.51 (0.17–1.49) | 0.217 | 0.50 (0.17–1.46) | 0.206 |
| Kidney (n = 11) | 0.06 | 0.15 | −0.09 (−0.29–0.11) | 0.38 (0.05–3.00) | 0.362 | 0.41 (0.05–3.23) | 0.394 | 0.40 (0.05–3.22) | 0.387 |
| Hematologic (n = 35) | 0.36 | 0.44 | −0.08 (−0.43–0.27) | 0.82 (0.34–1.99) | 0.666 | 0.82 (0.34–1.99) | 0.661 | 0.79 (0.32–1.93) | 0.601 |
| Dependent Variable | IR/1000 PY | IRD/1000 PY(95% CI) | Hazard Ratios for Cancers (95% CI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA | Control | Crude † | p | Model 1 †,‡ | p | Model 2 †,§ | p | ||
| Age < 60 (n = RA: 1718, Control: 6872) | |||||||||
| All cancers (n = 367) | 4.93 | 5.74 | −0.81 (−2.24–0.62) | 0.86 (0.66–1.13) | 0.281 | 0.83 (0.64–1.09) | 0.182 | 0.83 (0.63–1.08) | 0.171 |
| Gastric (n = 53) | 0.60 | 0.84 | −0.24 (−0.78–0.29) | 0.71 (0.33–1.50) | 0.369 | 0.65 (0.31–1.39) | 0.266 | 0.66 (0.31–1.40) | 0.278 |
| Thyroid (n = 127) | 1.65 | 1.97 | −0.32 (−1.15–0.51) | 0.83 (0.53–1.32) | 0.435 | 0.83 (0.52–1.31) | 0.423 | 0.82 (0.52–1.30) | 0.401 |
| Colorectal (n = 77) | 0.74 | 1.25 | −0.51 (−1.15–0.13) | 0.60 (0.31–1.16) | 0.127 | 0.59 (0.31–1.16) | 0.126 | 0.60 (0.31–1.16) | 0.127 |
| Lung (n = 36) | 0.89 | 0.45 | 0.45 (0.01–0.88) | 2.01 (1.01–4.02) | 0.048 * | 1.99 (0.99–4.00) | 0.054 | 2.00 (0.99–4.04) | 0.053 |
| Hepatic (n = 29) | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.11 (−0.28–0.50) | 1.29 (0.55–3.03) | 0.554 | 1.16 (0.48–2.80) | 0.748 | 1.21 (0.50–2.93) | 0.671 |
| Bladder (n = 11) | 0.15 | 0.17 | −0.02 (−0.26–0.22) | 0.90 (0.20–4.18) | 0.896 | 0.58 (0.12–2.92) | 0.508 | 0.60 (0.11–3.26) | 0.551 |
| Pancreatic (n = 12) | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.15 (−0.10–0.40) | 1.99 (0.60–6.62) | 0.260 | 2.22 (0.64–7.71) | 0.210 | 2.20 (0.62–7.74) | 0.221 |
| GB/biliary duct (n = 13) | 0.15 | 0.20 | −0.06 (−0.32–0.21) | 0.73 (0.16–3.28) | 0.679 | 0.79 (0.17–3.76) | 0.765 | 0.65 (0.13–3.18) | 0.594 |
| Kidney (n = 11) | 0.15 | 0.17 | −0.02 (−0.26–0.22) | 0.87 (0.19–4.02) | 0.858 | 1.00 (0.21–4.72) | 0.999 | 0.89 (0.19–4.25) | 0.882 |
| Hematologic (n = 21) | 0.07 | 0.37 | −0.30 (−0.63–0.04) | 0.20 (0.03–1.51) | 0.119 | 0.17 (0.02–1.29) | 0.086 | 0.15 (0.02–1.17) | 0.070 |
| Age ≥ 60 (n = RA: 1352, Control: 5408) | |||||||||
| All cancers (n = 465) | 13.53 | 11.38 | 2.16 (−0.54–4.85) | 1.19 (0.96–1.49) | 0.112 | 1.17 (0.94–1.46) | 0.161 | 1.18 (0.94–1.46) | 0.150 |
| Gastric (n = 105) | 3.26 | 2.45 | 0.81 (−0.44–2.06) | 1.34 (0.86–2.09) | 0.194 | 1.40 (0.89–2.19) | 0.145 | 1.41 (0.90–2.21) | 0.136 |
| Thyroid (n = 46) | 1.62 | 1.02 | 0.60 (−0.22–1.42) | 1.59 (0.84–3.02) | 0.158 | 1.56 (0.82–2.97) | 0.177 | 1.56 (0.82–2.97) | 0.179 |
| Colorectal (n = 105) | 2.12 | 2.72 | −0.60 (−1.85–0.64) | 0.75 (0.45–1.27) | 0.290 | 0.75 (0.45–1.27) | 0.289 | 0.73 (0.43–1.24) | 0.244 |
| Lung (n = 91) | 3.23 | 2.00 | 1.23 (0.07–2.38) | 1.64 (1.04–2.60) | 0.033* | 1.51 (0.95–2.40) | 0.084 | 1.50 (0.94–2.39) | 0.089 |
| Hepatic (n = 42) | 0.87 | 1.07 | −0.21 (−0.99–0.57) | 0.83 (0.37–1.87) | 0.653 | 0.78 (0.34–1.79) | 0.559 | 0.81 (0.35–1.88) | 0.631 |
| Bladder (n = 19) | 0.62 | 0.43 | 0.19 (−0.34–0.72) | 1.47 (0.53–4.09) | 0.460 | 1.44 (0.51–4.01) | 0.490 | 1.46 (0.52–4.10) | 0.469 |
| Pancreatic (n = 19) | 0.37 | 0.49 | −0.12 (−0.65–0.41) | 0.75 (0.22–2.57) | 0.645 | 0.70 (0.20–2.45) | 0.572 | 0.64 (0.17–2.37) | 0.500 |
| GB/biliary duct (n = 36) | 0.74 | 0.92 | −0.18 (−0.90–0.54) | 0.79 (0.33–1.90) | 0.598 | 0.75 (0.31–1.81) | 0.516 | 0.73 (0.30–1.80) | 0.499 |
| Kidney (n = 10) | 0.12 | 0.28 | −0.15 (−0.53–0.23) | 0.45 (0.06–3.54) | 0.446 | 0.54 (0.06–4.53) | 0.568 | 0.50 (0.06–4.67) | 0.547 |
| Hematologic (n = 32) | 1.11 | 0.71 | 0.41 (−0.28–1.09) | 1.58 (0.73–3.43) | 0.244 | 1.52 (0.69–3.32) | 0.298 | 1.52 (0.69–3.35) | 0.299 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.G.; Kang, H.S.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.-J.; Nam, E.S.; Min, K.-W.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, N.Y.; et al. Potential Cancer Risk in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Longitudinal Korean Population-Based Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12060965
Choi HG, Kang HS, Lim H, Kim J-H, Kim JH, Cho S-J, Nam ES, Min K-W, Park HY, Kim NY, et al. Potential Cancer Risk in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Longitudinal Korean Population-Based Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(6):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12060965
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hyo Geun, Ho Suk Kang, Hyun Lim, Joo-Hee Kim, Ji Hee Kim, Seong-Jin Cho, Eun Sook Nam, Kyueng-Whan Min, Ha Young Park, Nan Young Kim, and et al. 2022. "Potential Cancer Risk in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Longitudinal Korean Population-Based Analysis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 6: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12060965
APA StyleChoi, H. G., Kang, H. S., Lim, H., Kim, J. -H., Kim, J. H., Cho, S. -J., Nam, E. S., Min, K. -W., Park, H. Y., Kim, N. Y., & Kwon, M. J. (2022). Potential Cancer Risk in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Longitudinal Korean Population-Based Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(6), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12060965