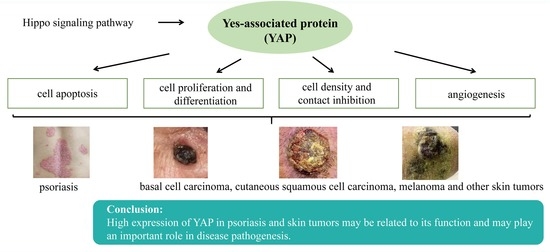
Role of Yes-Associated Protein in Psoriasis and Skin Tumor Pathogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Composition of the YAP and Hippo Signaling Pathways
3. Possible Mechanisms of YAP in Psoriasis and Skin Tumor Pathogenesis
3.1. YAP Regulates Apoptosis
3.2. YAP Regulates Cell Proliferation and Differentiation and Maintains the Three-Dimensional Structure of Skin
3.3. YAP Regulates Cell Density and Intercellular Contact Inhibition
3.4. YAP can Regulate Angiogenesis
4. Research on the Role of YAP in Psoriasis and Skin Tumors
4.1. Psoriasis
4.2. Basal Cell Carcinoma
4.3. Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
4.4. Melanoma
4.5. Other Skin Tumors and Tumor-Related Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michalek, I.M.; Loring, B.; John, S.M. A systematic review of worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.T.; Nijsten, T.; Elder, J.T. Recent Highlights in Psoriasis Research. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boehncke, W.H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cai, X.C.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Jin, M.Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, T.; Li, B.; Li, X. Global prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis in the past two decades: Current evidence. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Cho, S.I.; Jo, S.J. Risks of Comorbidities in Patients with Palmoplantar Pustulosis vs Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris or Pompholyx in Korea. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 27, e221081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanescu, A.M.A.; Simionescu, A.A.; Diaconu, C.C. Oral Vitamin D Therapy in Patients with Psoriasis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehncke, W.H. Etiology and Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 41, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marson, J.W.; Snyder, M.L.; Lebwohl, M.G. Newer Therapies in Psoriasis. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 105, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, O.; Roldán, F.A.; Varelli, C.; Bard, R.; Corvino, A.; Wortsman, X. Skin cancer: Findings and role of high-resolution ultrasound. J. Ultrasound 2019, 22, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; da Ana, R.; Vieira, V.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Dias-Ferreira, J.; Cano, A.; Zielińska, A.; Silva, A.M.; Staszewski, R.; Karczewski, J. Non-melanoma skin cancers: Physio-pathology and role of lipid delivery systems in new chemotherapeutic treatments. Neoplasia 2022, 30, 100810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cives, M.; Mannavola, F.; Lospalluti, L.; Sergi, M.C.; Cazzato, G.; Filoni, E.; Cavallo, F.; Giudice, G.; Stucci, L.S.; Porta, C.; et al. Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers: Biological and Clinical Features. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2020, 21, 5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.J.; Mihm, M.C., Jr. Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudol, M. Yes-associated protein (YAP65) is a proline-rich phosphoprotein that binds to the SH3 domain of the Yes proto-oncogene product. Oncogene 1994, 9, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar]
- Lamar, J.M.; Stern, P.; Liu, H.; Schindler, J.W.; Jiang, Z.G.; Hynes, R.O. The Hippo pathway target, YAP, promotes metastasis through its TEAD-interaction domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2441–E2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moroishi, T.; Hansen, C.G.; Guan, K.L. The emerging roles of YAP and TAZ in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Feldmann, G.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, N.; Comerford, S.A.; Gayyed, M.F.; Anders, R.A.; Maitra, A.; Pan, D. Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in Drosophila and mammals. Cell 2007, 130, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooglugt, A.; van der Stoel, M.M.; Boon, R.A.; Huveneers, S. Endothelial YAP/TAZ Signaling in Angiogenesis and Tumor Vasculature. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 612802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, A.A.; Gayyed, M.F.; Klein, A.P.; Dong, J.; Maitra, A.; Pan, D.; Montgomery, E.A.; Anders, R.A. Expression of Yes-associated protein in common solid tumors. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, P.C.; Jablons, D.M.; Yang, C.T.; You, L. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, M.; Cai, M.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; et al. Transcriptional co-activators YAP/TAZ: Potential therapeutic targets for metastatic breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.A.; Wang, R.; Miao, J.; Oliva, E.; Shen, X.; Wheeler, T.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Orsulic, S.; Goode, S. Hippo pathway effector Yap is an ovarian cancer oncogene. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8517–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Chang, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Li, M.; Fan, H.Y. YAP promotes ovarian cancer cell tumorigenesis and is indicative of a poor prognosis for ovarian cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Han, S.; Yang, A.; Wen, W.; Zhu, Q. Overexpression of YAP and TAZ is an independent predictor of prognosis in colorectal cancer and related to the proliferation and metastasis of colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, X.; Liao, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Che, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cigliano, A.; Ament, C.; et al. Overexpression of Mothers Against Decapentaplegic Homolog 7 Activates the Yes-Associated Protein/NOTCH Cascade and Promotes Liver Carcinogenesis in Mice and Humans. Hepatology 2021, 74, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cohen, S.M. The Hippo pathway acts via p53 and microRNAs to control proliferation and proapoptotic gene expression during tissue growth. Biol. Open 2013, 2, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harvey, K.F.; Pfleger, C.M.; Hariharan, I.K. The Drosophila Mst Ortholog, hippo, Restricts Growth and Cell Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis. Cell 2003, 114, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, L.; Gu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Qiao, X.; Wen, Y. Activated Yes-Associated Protein Accelerates Cell Cycle, Inhibits Apoptosis, and Delays Senescence in Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, N.; Zhang, C.; Liang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, A.; Yin, J.; Li, Z.; Luo, N.; Tan, X.; Luo, N.; et al. Yes-associated protein (YAP) increases chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by modulation of p53. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhou, M.; Xiao, L.; Feng, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, W. Activated Hippo/Yes-Associated Protein Pathway Promotes Cell Proliferation and Anti-apoptosis in Endometrial Stromal Cells of Endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baia, G.S.; Caballero, O.L.; Orr, B.A.; Lal, A.; Ho, J.S.; Cowdrey, C.; Tihan, T.; Mawrin, C.; Riggins, G.J. Yes-associated protein 1 is activated and functions as an oncogene in meningiomas. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strano, S.; Monti, O.; Pediconi, N.; Baccarini, A.; Fontemaggi, G.; Lapi, E.; Mantovani, F.; Damalas, A.; Citro, G.; Sacchi, A.; et al. The transcriptional coactivator Yes-associated protein drives p73 gene-target specificity in response to DNA Damage. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Xing, D. YAP accelerates Aβ(25-35)-induced apoptosis through upregulation of Bax expression by interaction with p73. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danovi, S.A.; Rossi, M.; Gudmundsdottir, K.; Yuan, M.; Melino, G.; Basu, S. Yes-associated protein (YAP) is a critical mediator of c-Jun-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camargo, F.D.; Gokhale, S.; Johnnidis, J.B.; Fu, D.; Bell, G.W.; Jaenisch, R.; Brummelkamp, T.R. YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, R.L.; Kohlmaier, A.; Polesello, C.; Veelken, C.; Edgar, B.A.; Tapon, N. The Hippo pathway regulates intestinal stem cell proliferation during Drosophila adult midgut regeneration. Development 2010, 137, 4147–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlegelmilch, K.; Mohseni, M.; Kirak, O.; Pruszak, J.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Zhou, D.; Kreger, B.T.; Vasioukhin, V.; Avruch, J.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; et al. Yap1 acts downstream of α-catenin to control epidermal proliferation. Cell 2011, 144, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Pasolli, H.A.; Fuchs, E. Yes-associated protein (YAP) transcriptional coactivator functions in balancing growth and differentiation in skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2270–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beverdam, A.; Claxton, C.; Zhang, X.; James, G.; Harvey, K.F.; Key, B. Yap controls stem/progenitor cell proliferation in the mouse postnatal epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Addario, I.; Abbruzzese, C.; lo Iacono, M.; Teson, M.; Golisano, O.; Barone, V. Overexpression of YAP1 induces immortalization of normal human keratinocytes by blocking clonal evolution. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 134, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Byun, M.R.; Furutani-Seiki, M.; Hong, J.H.; Jung, H.S. YAP and TAZ regulate skin wound healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbediwy, A.; Vincent-Mistiaen, Z.I.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Stone, R.K.; Boeing, S.; Wculek, S.K.; Cordero, J.; Tan, E.H.; Ridgway, R.; Brunton, V.G.; et al. Integrin signalling regulates YAP and TAZ to control skin homeostasis. Development 2016, 143, 1674–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonsa, A.M.; Na, T.Y.; Gumbiner, B.M. E-cadherin in contact inhibition and cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4769–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Hong, W. The emerging role of the hippo pathway in cell contact inhibition, organ size control, and cancer development in mammals. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mana-Capelli, S.; Paramasivam, M.; Dutta, S.; McCollum, D. Angiomotins link F-actin architecture to Hippo pathway signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 1676–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Gong, A.; Pan, Z.; Shi, H.; Yang, H.; Fu, H.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; et al. HucMSC Exosome-Delivered 14-3-3ζ Orchestrates Self-Control of the Wnt Response via Modulation of YAP During Cutaneous Regeneration. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 2485–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overholtzer, M.; Zhang, J.; Smolen, G.A.; Muir, B.; Li, W.; Sgroi, D.C.; Deng, C.X.; Brugge, J.S.; Haber, D.A. Transforming properties of YAP, a candidate oncogene on the chromosome 11q22 amplicon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12405–12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Hong, Y.J.; Kim, M. Angiogenesis in Chronic Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viallard, C.; Larrivée, B. Tumor angiogenesis and vascular normalization: Alternative therapeutic targets. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Zhang, H.; Park, H.; Choi, K.S.; Lee, H.W.; Agrawal, V.; Kim, Y.M.; Kwon, Y.G. Yes-associated protein regulates endothelial cell contact-mediated expression of angiopoietin-2. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Park, D.Y.; Bae, H.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, K.H.; Hong, S.P.; Jang, S.P.; Kubota, Y.; et al. YAP/TAZ regulates sprouting angiogenesis and vascular barrier maturation. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3441–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Kim, N.G.; Gumbiner, B.M. Regulation of Hippo pathway by mitogenic growth factors via phosphoinositide 3-kinase and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2569–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janse van Rensburg, H.J.; Lai, D.; Azad, T.; Hao, Y.; Yang, X. TAZ enhances mammary cell proliferation in 3D culture through transcriptional regulation of IRS1. Cell Signal. 2018, 52, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Montminy, T.; Azad, T.; Lightbody, E.; Hao, Y.; SenGupta, S.; Asselin, E.; Nicol, C.; Yang, X. PI3K Positively Regulates YAP and TAZ in Mammary Tumorigenesis Through Multiple Signaling Pathways. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azad, T.; Nouri, K.; Janse van Rensburg, H.J.; Hao, Y.; Yang, X. Monitoring Hippo Signaling Pathway Activity Using a Luciferase-based Large Tumor Suppressor (LATS) Biosensor. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 139, 58416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azad, T.; Janse van Rensburg, H.J.; Lightbody, E.D.; Neveu, B.; Champagne, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Kay, V.R.; Hao, Y.; Shen, H.; Yeung, B.; et al. A LATS biosensor screen identifies VEGFR as a regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Luo, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y. Yes-associated protein promotes the abnormal proliferation of psoriatic keratinocytes via an amphiregulin dependent pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Wang, N.; Zheng, Y.; Mo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, S.; Liu, J.; Yan, F.; Li, H.; Chen, D. RAS-association domain family 1A regulates the abnormal cell proliferation in psoriasis via inhibition of Yes-associated protein. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 5070–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Mo, X.; Liu, J.; Yan, F.; Wang, N.; Lin, Y.; Li, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, D. Mechanism of danshensu-induced inhibition of abnormal epidermal proliferation in psoriasis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 868, 172881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Xu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Robichaud, P.; Betcher, S.; Calderone, K.; He, T.; Johnson, T.M.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Elevated YAP and its downstream targets CCN1 and CCN2 in basal cell carcinoma: Impact on keratinocyte proliferation and stromal cell activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonilla, X.; Parmentier, L.; King, B.; Bezrukov, F.; Kaya, G.; Zoete, V.; Seplyarskiy, V.B.; Sharpe, H.J.; McKee, T.; Letourneau, A.; et al. Genomic analysis identifies new drivers and progression pathways in skin basal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.A.; Patel, V.A.; Ratner, D. Advances in the management of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, J.; Li, C.; Luo, S.; Liu-Smith, F.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, N.; Lai, B.; Lei, T.; Wang, Q.; et al. Yes-Associated Protein Contributes to the Development of Human Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Activation of RAS. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Kong, F.; Wang, J.; Hu, E.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, W.; He, D.; Xiao, X. S100A7 induction is repressed by YAP via the Hippo pathway in A431 cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38133–38142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.E.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C. The role of the hippo pathway in melanocytes and melanoma. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menzel, M.; Meckbach, D.; Weide, B.; Toussaint, N.C.; Schilbach, K.; Noor, S.; Eigentler, T.; Ikenberg, K.; Busch, C.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; et al. In melanoma, Hippo signaling is affected by copy number alterations and YAP1 overexpression impairs patient survival. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallet-Staub, F.; Marsaud, V.; Li, L.; Gilbert, C.; Dodier, S.; Bataille, V.; Sudol, M.; Herlyn, M.; Mauviel, A. Pro-invasive activity of the Hippo pathway effectors YAP and TAZ in cutaneous melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, H.; Yu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Chen, W.; Tong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Shi, Y. Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) Promotes Tumorigenesis in Melanoma Cells Through Stimulation of Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 (LRP1). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.X.; Luo, J.; Mo, J.S.; Liu, G.; Kim, Y.C.; Meng, Z.; Zhao, L.; Peyman, G.; Ouyang, H.; Jiang, W.; et al. Mutant Gq/11 promote uveal melanoma tumorigenesis by activating YAP. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hugo, W.; Shi, H.; Sun, L.; Piva, M.; Song, C.; Kong, X.; Moriceau, G.; Hong, A.; Dahlman, K.B.; Johnson, D.B.; et al. Non-genomic and Immune Evolution of Melanoma Acquiring MAPKi Resistance. Cell 2015, 162, 1271–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moroishi, T.; Hayashi, T.; Pan, W.W.; Fujita, Y.; Holt, M.V.; Qin, J.; Carson, D.A.; Guan, K.L. The Hippo Pathway Kinases LATS1/2 Suppress Cancer Immunity. Cell 2016, 167, 1525–1539.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cappellesso, R.; Bellan, A.; Saraggi, D.; Salmaso, R.; Ventura, L.; Fassina, A. YAP immunoreactivity is directly related to pilomatrixoma size and proliferation rate. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2015, 307, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Srivastava, R.K.; Elmets, C.A.; Afaq, F.; Athar, M. Arsenic-induced cutaneous hyperplastic lesions are associated with the dysregulation of Yap, a Hippo signaling-related protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 438, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andl, T.; Zhou, L.; Yang, K.; Kadekaro, A.L.; Zhang, Y. YAP and WWTR1: New targets for skin cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 2017, 396, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, D.; Lettan, R.; Damodaran, K.; Strellec, S.; Reyes-Mugica, M.; Rebbaa, A. Identification, mechanism of action, and antitumor activity of a small molecule inhibitor of hippo, TGF-β, and Wnt signaling pathways. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, J.; Wang, Y.; Mo, X.; Chen, D. Role of Yes-Associated Protein in Psoriasis and Skin Tumor Pathogenesis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12060978
Jia J, Wang Y, Mo X, Chen D. Role of Yes-Associated Protein in Psoriasis and Skin Tumor Pathogenesis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(6):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12060978
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Jinjing, Yuqian Wang, Xiumei Mo, and Dacan Chen. 2022. "Role of Yes-Associated Protein in Psoriasis and Skin Tumor Pathogenesis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 6: 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12060978
APA StyleJia, J., Wang, Y., Mo, X., & Chen, D. (2022). Role of Yes-Associated Protein in Psoriasis and Skin Tumor Pathogenesis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(6), 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12060978