Breast Cancer: Clinical–Epidemiological Profile and Toxicities of Women Receiving Treatment with Taxanes in the Amazon Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Aspects
2.2. Chemotherapy Regimens
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Instituto Nacional Do Câncer José Alencar Gomes Da Silva—INCA. Estimativa 2023: Incidência de Câncer no Brasil. Rio de Janeiro: INCA. 2022. Available online: https://www.inca.gov.br/sites/ufu.sti.inca.local/files//media/document//estimativa-2023.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2019; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2019/cancer-facts-and-figures-2019.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Breast Tumours. International Agency for Research on Cancer. In WHO Classification of tumour series. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Breast Tumours; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sechel, G.; Rogozea, L.M.; Roman, N.A.; Ciurescu, D.; Cocuz, M.E.; Manea, R.M. Analysis of breast cancer subtypes and their correlations with receptors and ultrasound. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2021, 62, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yared, J.A.; Tkaczuk, K.H.R. Update on Taxane development: New analogs and new formulations. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2012, 6, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosó, V.; Herrero, M.J.; Santaballa, A.; Palomar, L.; Megias, J.E.; De La Cueva, H.; Rojas, L.; Marques, M.R.; Poveda, J.L.; Montalar, J.; et al. SNPs and Taxane toxicity in breast cancer patients. Pharmacogenomics 2014, 15, 1845–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute (US), Department of Health and Human Services, Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis. Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events; Version 5.0 NCI; National Cancer Institute (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017.
- Rocha, F.S.; Silva, W.S.; Do Nascimento, E.R.; Bacciotti, A.M. Epidemiological Profile of Breast Cancer in a Reference Hospital in the North Region. Mastology 2018, 28, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynoso-Noverón, N.; Villarreal-Garza, C.; Soto-Perez-de-Celis, E.; Arce-Salinas, C.; Matus-Santos, J.; Ramírez-Ugalde, M.T.; Cabrera-Galeana, P.; Meneses-Garcia, A.; Lara-Medina, F.; Bargallo-Rocha, E.; et al. Clinical and Epidemiological Profile of Breast Cancer in Mexico: Results of the Seguro Popular. J. Glob. Oncol. 2017, 3, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anothaisintawee, T.; Wiratkapun, C.; Lerdsitthichai, P.; Kasamesup, V.; Wongwaisayawan, S.; Srinakarin, J.; Hirunpat, S.; Woodtichartpreecha, P.; Boonlikit, S.; Teerawattanon, Y.; et al. Risk Factors of Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2013, 25, 368–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolussi, A.C.; Sawada, N.O. Qualidade de vida de pacientes com câncer de mama em terapia adjuvante. Rev. Gaúcha De Enferm. 2011, 32, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, C.; Caggiano, V. The influence of marital status and race/ethnicity on risk of mortality for triple negative breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balekouzou, A.; Yin, P.; Bekolo, E.C.; Pamatika, C.M.; Djeitote, M.; Nambei, S.W.; Ba-Mpoutou, B.; Mandjiza, D.R.; Shu, C.; Yin, M.; et al. Histo-epidemiological Profile of Breast Cancers Among Women in the Central African Republic: About 174 cases. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameo, S.Y.; Barbosa-Lima, R.; Ramos, M.J.O.; Fonseca, T.V.; Vassilievitch, A.C.; Costa, J.S.; Santos, J.C.O.; Santos, D.K.C.; Amorim, B.F.; Marinho, P.M.L.; et al. Clinical-epidemiological profile of women undergoing oncological treatment for invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, 11836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.S.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Z.N.; Xu, F.; Lu, H.J.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Shi, W.; Jiang, J.; Yao, P.P.; Zhu, H.P. Risk Factors and Preventions of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, J.S.; Siqueira, F.; Leal, J.V.O. Epidemiological profile of women with breast cancer in a public hospital in the Federal District of Brazil. Mastology 2021, 31, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurdana, M. Physical Activity and Cancer Risk. Actual Knowledge and Possible Biological Mechanisms. Radiol. Oncol. 2021, 55, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Fensom, G.K.; Reeves, G.k.; Key, T.J. Physical activity and breast cancer risk: Results from the UK Biobank prospective cohort. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2013–2014; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013; Available online: www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/breast-cancer-facts-figures.html (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Fouhi, M.E.; Benider, A.; Gaëtan, K.Z.A.; Mesfioui, A. Profil épdémiologique et anatomopathologique du cancer de sein au CHU Ibn Rochd, Casablanca. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 37, 21336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, K.; Stuckey, A. Breast Cancer Epidemiology and Risk Factors. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 59, 651–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, J.A.G.; Batista, L.M.; De Assis, T.S. Breast Cancer: Epidemiological and Clinical Profile in a Reference Hospital in Paraíba. Sanare Public Policy Mag. 2021, 20, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, H.R.; Jones, M.E.; Schoemaker, M.J.; Ashworth, A.; Swerdlow, A.J. Family history and risk of breast cancer: An analysis accounting for family structure. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 165, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingue, S.; Atenguena, E.O.; Zingue, L.L.; Tueche, A.B.; Njamen, D.; Nkoum, A.B.; Ndom, P. Epidemiological and clinical profile, and survival of patients followed for breast cancer between 2010 and 2015 at the Yaounde General Hospital Cameroon. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2021, 39, 26866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, R.G.; Otoni, K.M. Histological and molecular classification of breast cancer: What do we know. Mastology 2020, 30, 1–8. Available online: https://www.mastology.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/MAS_2020024_AOP.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Fragomeni, S.M.; Sciallis, A.; Jeruss, J.S. Molecular subtypes and local-regional control of breast cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. North. Am. 2018, 27, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhangi, N.; Hajjari, S.; Heydari, S.F.; Ganjizadeh, M.; Rouhollah, F.; Hasanzad, M. Breast cancer in the era of precision medicine. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 10023–10037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Oh, J.M.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.W.; Nam, S.J.; Park, W.; Park, Y.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Im, Y.-H. Comprehensive Clinical Characterization of Decade-Long Survivors of Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehifar, E.; Janbabaei, G.; Alipour, A.; Tabrizi, N.; Avan, R. Taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy and quality of life in breast cancer patients. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 26, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speck, R.M.; Sammel, M.D.; Farrar, J.T.; Hennessy, S.; Mao, J.J.; Stineman, M.G.; DeMichele, A. Impact of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy on treatment delivery in nonmetastatic breast cancer. J. Oncol. Pract. 2013, 9, e234–e240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Nasr, S.; Zribi, A.; Ben Hassen, M.; Doghri, Y.; Ben Abdallah, I.; Trigui, E.; Fendri, S.; Ayari, J.; Balti, M.; Haddaoui, A. Toxicity profile of taxanes in Tunisian cancer patients: A retrospective study of 90 cases. Bull. Cancer 2021, 108, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, U.; Killeen, R.B. Taxane Toxicity. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Picard, M.; Castells, M.C. Re-visiting Hypersensitivity Reactions to Taxanes: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 49, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francia, R.; Atripaldi, L.; Di Martino, S.; Fierro, C.; Muto, T.; Crispo, A.; Rossetti, S.; Facchini, G.; Berretta, M. Assessment of Pharmacogenomic Panel Assay for Prediction of Taxane Toxicities: Preliminary Results. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | N (%) | CI 95% |
|---|---|---|
| Age range (years) | ||
| 24 to 29 | 6 (2.0%) | 0.7–3.7 |
| 30 to 39 | 44 (14.7%) | 10.7–18.7 |
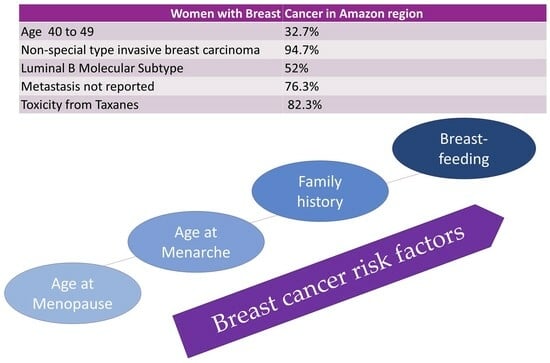
| 40 to 49 | 98 (32.7%) | 27.3–38.0 |
| 50 to 59 | 79 (26.3%) | 21.3–31.7 |
| 60 to 69 | 53 (17.7%) | 13.3–22.0 |
| 70 to 83 | 20 (6.6%) | 4.0–9.7 |
| Ethnicity * | ||
| White | 82 (27.3%) | 22.0–32.3 |
| Black | 20 (6.7%) | 3.7–9.3 |
| Brown | 198 (66%) | 61.0–71.3 |
| Marital status | ||
| Single | 88 (29.3%) | 23.7–34.7 |
| Married | 128 (42.7%) | 37.0–48.0 |
| Stable union | 46 (15.3%) | 11.3–19.7 |
| Divorced | 17 (5.7%) | 3.0–8.3 |
| Widow | 21 (7.0%) | 4.3–10.0 |
| Education | ||
| lliterate | 8 (2.7%) | 1.0–4.7 |
| Elementary School | 131 (43.7%) | 38.0–49.3 |
| High school | 127 (42.3%) | 36.7–48.0 |
| University education | 34 (11.3%) | 8.0–15.3 |
| Profession/Occupation | ||
| Rural activity | 29 (9.7%) | 6.7–13.0 |
| Retired | 20 (6.7%) | 4.0–9.7 |
| Autonomous | 47 (15.7%) | 11.7–20.0 |
| Housekeeper | 17 (5.7%) | 3.3–8.3 |
| Education Professional | 17 (5.7%) | 3.3–8.3 |
| Health professional | 15 (5%) | 2.7–7.7 |
| Without occupation | 131 (43.6%) | 38.3–49.7 |
| Others | 24 (8%) | 5.0–8.0 |
| Characteristics | N = 300 | CI 95% |
|---|---|---|
| Life Habits | ||
| Smoking | 92 (30.7%) | 25.3–36.3 |
| Alcoholism | 124 (41.3%) | 36.3–46.7 |
| Sedentary lifestyle | 228 (76%) | 19.–29.0 |
| Age at first pregnancy (years) | ||
| 13 to 17 | 52 (17.3%) | 13.3–21.3 |
| 18 to 21 | 108 (36%) | 30.3–42.0 |
| 22 to 25 | 49 (16.3%) | 12.7–21.0 |
| 26 to 29 | 34 (11.3%) | 8.0–15.0 |
| 30 to 42 | 31 (10.4%) | 6.7–13.7 |
| nulliparous | 26 (8.7%) | 5.7–12.0 |
| Breast—feeding | ||
| No | 56 (18.7%) | 14.7–23.0 |
| Yes | 244 (81.3%) | 77.0–85.3 |
| 1 son 2 or more children | 44 (18.0%) 200 (82.0%) | 13.5–23.0 77.0–86.5 |
| Age at Menarche (years) | ||
| 8 to 11 years | 42 (14%) | 10.3–18.3 |
| 12 to 13 | 143 (47.7%) | 42.0–53.0 |
| 14 to 15 | 90 (30%) | 25.0–35.3 |
| >15 | 25 (8.3%) | 5.3–11.7 |
| Age at Menopause (years) | ||
| 40 to 49 years old | 67 (22.3%) | 18.0–27.0 |
| 50 to 60 years | 76 (25.3%) | 20.7–30.0 |
| pre—menopausal | 125 (41.7%) | 36.0–47.3 |
| Hysterectomy before cancer | 32 (10.7%) | 7.3–14.3 |
| Family history of cancer | ||
| No | 106 (35.3%) | 30.0–41.0 |
| Yes | 194 (64.7%) | 59.0–70.0 |
| Characteristics | N = 300 | CI 95% |
|---|---|---|
| Histological Type | ||
| Non—special type invasive breast carcinoma | 284 (94.7%) | 92.0–96.7 |
| Special type carcinoma–invasive lobular carcinoma | 11 (3.8%) | 1.7–6.0 |
| Other Special Type Carcinomas | 5 (1.5%) | 0.3–3.0 |
| Molecular Subtype | ||
| Luminal A | 38 (12.7%) | 8.7–16.7 |
| Luminal B | 156 (52%) | 46.7–57.7 |
| HER2+ | 67 (22.3%) | 17.7–27.0 |
| Triple negative | 39 (13%) | 9.3–17.0 |
| Disease progression | ||
| No metastasis or metastasis not reported | 229 (76.3%) | 71.7–28.3 |
| Recurrence in the plastron | 4 (1.3%) | 0.3–2.7 |
| Recurrence in the contralateral breast | 10 (3.4%) | 1.3–5.3 |
| Bone metastasis | 25 (8.3%) | 5.3–11.7 |
| Lung metastasis | 10 (3.4%) | 1.3–5.3 |
| Brain metastasis | 2 (0.6%) | 0.0–1.7 |
| Metastasis from more than one site (bone, liver, lung, brain) | 20 (6.7%) | 4.0–9.7 |
| Toxicities | N = 300 | CI 95% |
|---|---|---|
| No | 52 (17.3%) | 13.0–21.7 |
| Yes | 248 (82.7%) | 78.3–87.0 |
| One | 48 (19.4%) | 11.7–20.7 |
| Two | 84 (33.9%) | 23.0–33.0 |
| Three | 77 (31%) | 20.3–30.7 |
| four or more | 39 (15.7%) | 9.3–17.0 |
| Type of Toxicity * | ||
| Neurological | 158 (52.7%) | 46.7–58.3 |
| Gastrointestinal | 150 (50%) | 44.3–55.7 |
| Musculoskeletal | 135 (45%) | 39.3–50.3 |
| Infusion Reaction | 101 (33.7%) | 28.3–39.0 |
| Hematological | 36 (12.0%) | 8.3–15.7 |
| Dermatological | 34 (11.3%) | 7.7–15.0 |
| Toxicity | Docetaxel (N = 150) | Paclitaxel (N = 150) | p-value a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal | |||
| Diarrhea | 55 (36.6%) | 29 (19.3%) | 0.0013 * |
| Constipation | 5 (3.3%) | 11 (7.3%) | 0.1989 |
| Nausea and vomiting | 44 (28.3%) | 34 (22.7%) | 0.2362 |
| Anorexia/Lack of appetite | 11 (7.3%) | 9 (6.0%) | 0.8170 |
| Mucositis | 8 (5.3%) | 1 (0.7%) | 0.0195 * |
| Neurological | |||
| Peripheral neuropathy | 67 (44.7%) | 84 (56.0%) | 0.0647 |
| Headache | 7 (4.7%) | 3 (2.0%) | 0.4346 |
| Insomnia | 1 (0.7%) | 7 (4.7%) | 0.0732 |
| Musculoskeletal | |||
| Arthralgia | 51 (34%) | 44 (29.3%) | 0.4365 |
| Myalgia | 49 (32.7%) | 34 (22.7%) | 0.0708 |
| Ostealgia | 22 (14.7%) | 24 (16%) | 0.8727 |
| Dermatological | |||
| Skin disorders | 7 (4.7%) | 7 (4.7%) | 1.000 |
| Nail disorders | 13 (8.7%) | 6 (4.0%) | 0.1549 |
| Body itch | 6 (4.0%) | 2 (1.3%) | 0.2823 |
| Hematological | |||
| Anemia | 6 (4.0%) | 20 (13.3%) | 0.0076 * |
| Neutropenia | 6 (4.0%) | 19 (12.7%) | 0.0122 * |
| Thrombocytopenia | 3 (2.0%) | 7 (4.7) | 0.3346 |
| Infusion Reaction Yes No | 66 (44%) 84 (56%) | 35 (23.3%) 115 (76.7%) | 0.0002 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, M.S.C.R.; Fernandes, M.R.; Pereira, E.E.B.; Leal, D.F.d.V.B.; Coelho, R.d.C.C.; Menezes, E.d.S.; Modesto, A.A.C.; Assumpção, P.P.d.; Burbano, R.M.R.; Santos, S.E.B.d.; et al. Breast Cancer: Clinical–Epidemiological Profile and Toxicities of Women Receiving Treatment with Taxanes in the Amazon Region. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13101458
Costa MSCR, Fernandes MR, Pereira EEB, Leal DFdVB, Coelho RdCC, Menezes EdS, Modesto AAC, Assumpção PPd, Burbano RMR, Santos SEBd, et al. Breast Cancer: Clinical–Epidemiological Profile and Toxicities of Women Receiving Treatment with Taxanes in the Amazon Region. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(10):1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13101458
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Marta Solange Camarinha Ramos, Marianne Rodrigues Fernandes, Esdras Edgar Batista Pereira, Diana Feio da Veiga Borges Leal, Rita de Cássia Calderaro Coelho, Elisa da Silva Menezes, Antônio André Conde Modesto, Paulo Pimentel de Assumpção, Rommel Mario Rodriguez Burbano, Sidney Emanuel Batista dos Santos, and et al. 2023. "Breast Cancer: Clinical–Epidemiological Profile and Toxicities of Women Receiving Treatment with Taxanes in the Amazon Region" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 10: 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13101458
APA StyleCosta, M. S. C. R., Fernandes, M. R., Pereira, E. E. B., Leal, D. F. d. V. B., Coelho, R. d. C. C., Menezes, E. d. S., Modesto, A. A. C., Assumpção, P. P. d., Burbano, R. M. R., Santos, S. E. B. d., & Santos, N. P. C. d. (2023). Breast Cancer: Clinical–Epidemiological Profile and Toxicities of Women Receiving Treatment with Taxanes in the Amazon Region. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(10), 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13101458