An Evidence-Based Update on the Potential Association between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
Abstract
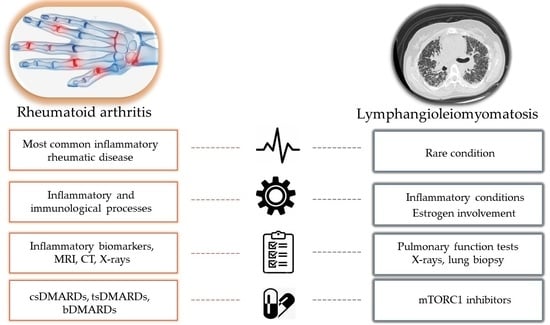
:1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology and the Impact of Scientific Literature
3. Pathophysiological Mechanisms with Molecular Implications
3.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
3.2. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
4. Diagnosis and Pharmacotherapeutic Management
4.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
4.2. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
5. Evidence-Based Assessment of a Patient with RA and LAM
6. Common Features of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radu, A.F.; Bungau, S.G.; Negru, P.A.; Marcu, M.F.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L. In-depth bibliometric analysis and current scientific mapping research in the context of rheumatoid arthritis pharmacotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radu, A.F.; Bungau, S.G. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Cells 2021, 10, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvien, T.K.; Uhlig, T.; Ødegård, S.; Heiberg, M.S. Epidemiological aspects of rheumatoid arthritis: The sex ratio. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1069, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, C.; Buttgereit, F.; Combe, B. Glucocorticoids in rheumatoid arthritis: Current status and future studies. RMD Open 2020, 6, e000536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teaha, D.I.M.; Pascalău, N.A.; Lazăr, L. Comparative study of the clinical response of patients to different treatment regimens in rheumatoid arthritis. Farmacia 2019, 67, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, A. Rehabilitation in rheumatoid arthritis: A critical review. Musculoskeletal Care 2004, 2, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, L.; Abasolo, L.; Carmona, L.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, L.; Lamas, J.R.; Hernandez-Garcia, C.; Jover, J.A.; Alegre, J.; Alonso, J.L.; Alvarez, M.; et al. Orthopedic surgery in rheumatoid arthritis in the era of biologic therapy. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 1850–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieb, K.; Hofstaetter, S.G. Treatment strategies in surgery for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 71, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungau, S.G.; Behl, T.; Singh, A.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Chigurupati, S.; Vijayabalan, S.; Das, S.; Palanimuthu, V.R. Targeting Probiotics in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Sharma, P.; Chandel, P.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Naved, T.; Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Bungau, S.; Behl, T. Circumstantial Insights into the Potential of Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plants as a Therapeutic Approach in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Du, K.; Liang, C.; Wang, S.; Owusu Boadi, E.; Li, J.; Pang, X.; He, J.; Chang, Y.X. Traditional herbal medicine: Therapeutic potential in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Mehta, K.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Ahmadi, A.; Arora, S.; Bungau, S. Exploring the role of polyphenols in rheumatoid arthritis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 5372–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, S.; Spagnolo, P.; Cocconcelli, E.; Luisi, F.; Cottin, V. Recent advances in the pathobiology and clinical management of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018, 24, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weill, D.; Benden, C.; Corris, P.A.; Dark, J.H.; Davis, R.D.; Keshavjee, S.; Lederer, D.J.; Mulligan, M.J.; Patterson, G.A.; Singer, L.G.; et al. A consensus document for the selection of lung transplant candidates: 2014—An update from the Pulmonary Transplantation Council of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2015, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Kerschbaumer, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Sepriano, A.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; de Wit, M.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radner, H.; Neogi, T.; Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D. Performance of the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature review. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannini, C.; Ryu, J.H.; Matteson, E.L. Lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2008, 20, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, H.; Ogura, T.; Kameda, H.; Kishaba, T.; Iwasawa, T.; Takemura, T.; Kuwano, K. Decision-Making Strategy for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (RA-ILD). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamattina, A.M.; Taveira-Dasilva, A.; Goldberg, H.J.; Bagwe, S.; Cui, Y.; Rosas, I.O.; Moss, J.; Henske, E.P.; El-Chemaly, S. Circulating Biomarkers From the Phase 1 Trial of Sirolimus and Autophagy Inhibition for Patients With Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Chest 2018, 154, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taillé, C.; Borie, R.; Crestani, B. Current management of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2011, 17, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis-Symptoms. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/lam/symptoms (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- O’Mahony, A.M.; Lynn, E.; Murphy, D.J.; Fabre, A.; McCarthy, C. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: A clinical review. Breathe 2020, 16, 200007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Lee, H.S.; Ryu, J.H.; Taveira-DaSilva, A.M.; Beck, G.J.; Lee, J.C.; McCarthy, K.; Finlay, G.A.; Brown, K.K.; Ruoss, S.J.; et al. The NHLBI LAM Registry: Prognostic Physiologic and Radiologic Biomarkers Emerge From a 15-Year Prospective Longitudinal Analysis. Chest 2019, 155, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.R.; Cordier, J.F.; Lazor, R.; Cottin, V.; Costabel, U.; Harari, S.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Boehler, A.; Brauner, M.; Popper, H.; et al. European Respiratory Society guidelines for the diagnosis and management of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, S.R.; Whale, C.I.; Hubbard, R.B.; Lewis, S.A.; Tattersfield, A.E. Survival and disease progression in UK patients with lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Thorax 2004, 59, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brentani, M.M.; Carvalho, C.R.R.; Saldiva, P.H.; Pacheco, M.M.; Oshima, C.T. Steroid receptors in pulmonary lymphangiomyomatosis. Chest 1984, 85, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvet, S.C.; McCormack, F.X.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Downey, G.P. Molecular pathogenesis of lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Lessons learned from orphans. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 36, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taveira-DaSilva, A.M.; Steagall, W.K.; Moss, J. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Cancer Control 2006, 13, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.J.; Anzaghe, M.; Schülke, S. Update on the Pathomechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells 2020, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, C.; Gupta, N.; Johnson, S.R.; Yu, J.J.; McCormack, F.X. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis, and management. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, H.U.; Häupl, T.; Burmester, G.R. The etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alivernini, S.; Firestein, G.S.; McInnes, I.B. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunity 2022, 55, 2255–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, C.; Perdriger, A.; Amé, P. Definition of B cell helper T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and their behavior during treatment. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Buckley, C.D.; Isaacs, J.D. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis—shaping the immunological landscape. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elemam, N.M.; Hannawi, S.; Maghazachi, A.A. Role of Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2020, 9, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geusens, P. The role of RANK ligand/osteoprotegerin in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2012, 4, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmona, F.D.; Martín, J. The potential of PTPN22 as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsby, L.M.; Orozco, G.; Denton, J.; Worthington, J.; Ray, D.W.; Donn, R.P. Functional evaluation of TNFAIP3 (A20) in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2010, 28, 708–714. [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz, J. The rheumatoid arthritis HLA-DRB1 shared epitope. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2010, 22, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taveira-DaSilva, A.M.; Moss, J. Epidemiology, pathogenesis and diagnosis of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Expert Opin. Orphan Drugs 2016, 4, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darling, T.N.; Pacheco-Rodriguez, G.; Gorio, A.; Lesma, E.; Walker, C.; Moss, J. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis and TSC2−/− cells. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2010, 8, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.J.; Ying, X.J.; Chen, H.L.; Ye, P.J.; Chen, Z.L.; Li, G.; Jiang, H.F.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.Z. Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces lymphangiogenesis and facilitates lymphatic metastasis in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 7788–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyama, K.; Kumasaka, T.; Souma, S.; Sato, T.; Kurihara, M.; Mitani, K.; Tominaga, S.; Fukuchi, Y. Vascular endothelial growth factor-D is increased in serum of patients with lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2006, 4, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Tatsuguchi, A.; Valencia, J.; Yu, Z.X.; Bechtle, J.; Beasley, M.B.; Avila, N.; Travis, W.D.; Moss, J.; Ferrans, V.J. Extrapulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): Clinicopathologic features in 22 cases. Hum. Pathol. 2000, 31, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cobbold, S.P.; of Cellular Immunology, P.; William, S. The mTOR pathway and integrating immune regulation. Immunology 2013, 140, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logginidou, H.; Ao, X.; Russo, I.; Henske, E.P. Frequent estrogen and progesterone receptor immunoreactivity in renal angiomyolipomas from women with pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Chest 2000, 117, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grzegorek, I.; Lenze, D.; Chabowski, M.; Janczak, D.; Szolkowska, M.; Langfort, R.; Szuba, A.; Dziegiel, P. Immunohistochemical evaluation of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 3353–3360. [Google Scholar]
- Combe, B.; Landewe, R.; Daien, C.I.; Hua, C.; Aletaha, D.; Álvaro-Gracia, J.M.; Bakkers, M.; Brodin, N.; Burmester, G.R.; Codreanu, C.; et al. 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of early arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. JAMA 2018, 320, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, T.; Sokka, T. Laboratory Tests to Assess Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Advantages and Limitations. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 35, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, M.A.; Haavardsholm, E.A.; van der Laken, C.J. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis; What is the current role of established and new imaging techniques in clinical practice? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 30, 586–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.F.; Lo, B.H. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Differential diagnosis and optimal management. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2014, 10, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, T.; Kumasaka, T.; Mitani, K.; Okada, Y.; Kondo, T.; Date, H.; Chen, F.; Oto, T.; Miyoshi, S.; Shiraishi, T.; et al. Bronchial involvement in advanced stage lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Histopathologic and molecular analyses. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 50, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Meraj, R.; Tanase, D.; James, L.E.; Seyama, K.; Lynch, D.A.; Akira, M.; Meyer, C.A.; Ruoss, S.J.; Burger, C.D.; et al. Accuracy of chest high-resolution computed tomography in diagnosing diffuse cystic lung diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, M.; Seyama, K.; Inoue, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Kubo, K. The epidemiology of lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Japan: A nationwide cross-sectional study of presenting features and prognostic factors. Respirology 2007, 12, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Kurihara, M.; Kataoka, H.; Ueyama, M.; Togo, S.; Sato, T.; Doi, T.; Iwakami, S.I.; Takahashi, K.; Seyama, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose sirolimus for treatment of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Respir. Investig. 2013, 51, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, F.X.; Inoue, Y.; Moss, J.; Singer, L.G.; Strange, C.; Nakata, K.; Barker, A.F.; Chapman, J.T.; Brantly, M.L.; Stocks, J.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sirolimus in lymphangioleiomyomatosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapamune® (sirolimus). Orphan Medicinal Product for the Treatment of Sporadic Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/orphan-designations/eu-3-16-1704 (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- McCormack, F.X.; Gupta, N.; Finlay, G.R.; Young, L.R.; Taveira-Da Silva, A.M.; Glasgow, C.G.; Steagall, W.K.; Johnson, S.R.; Sahn, S.A.; Ryu, J.H.; et al. Official American Thoracic Society/Japanese Respiratory Society Clinical Practice Guidelines: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 748–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Manning, B.D. A complex interplay between Akt, TSC2 and the two mTOR complexes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oprescu, N.; McCormack, F.X.; Byrnes, S.; Kinder, B.W. Clinical predictors of mortality and cause of death in lymphangioleiomyomatosis: A population-based registry. Lung 2013, 191, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathirareuangchai, S.; Shimizu, D.; Vierkoetter, K.R. Pulmonary Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Hawai’i J. Health Soc. Welf. 2020, 79, 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.Y.; Hwang, J.J.; Kim, D.S.; Song, J.W. Efficacy and safety of low-dose Sirolimus in Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, M.; Xiang, B.; Chen, S.; Ji, Y. The efficacy and safety of pharmacological treatments for lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Criner, R.N.; Al-abcha, A.; Lambert, A.A.; Han, M.L.K. Lung Diseases Unique to Women. Clin. Chest Med. 2021, 42, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, M.A.; Harper, J.; Folkman, J. Doxycycline treatment for lymphangioleiomyomatosis with urinary monitoring for MMPs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2621–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.; Johnson, S.R. Cross-sectional study of reversible airway obstruction in LAM: Better evidence is needed for bronchodilator and inhaled steroid use. Thorax 2019, 74, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krymskaya, V.P.; Courtwright, A.M.; Fleck, V.; Dorgan, D.; Kotloff, R.; McCormack, F.X.; Kreider, M. A phase II clinical trial of the Safety Of Simvastatin (SOS) in patients with pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis and with tuberous sclerosis complex. Respir. Med. 2020, 163, 105898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Chemaly, S.; Taveira-DaSilva, A.; Bagwe, S.; Klonowska, K.; Machado, T.; Lamattina, A.M.; Goldberg, H.J.; Jones, A.M.; Julien-Williams, P.; Maurer, R.; et al. Celecoxib in lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Results of a phase I clinical trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1902370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steagall, W.K.; Zhang, L.; Cai, X.; Pacheco-Rodriguez, G.; Moss, J. Genetic heterogeneity of circulating cells from patients with lymphangioleiomyomatosis with and without lung transplantation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 854–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Committee on Hospital Care, Section on Surgery, and Section on Critical Care. Policy statement—Pediatric organ donation and transplantation. Pediatrics 2010, 125, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.E.; Kim, S.Y.; Song, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Chang, J.; Lee, J.G.; Paik, H.C.; Park, M.S. Comparison of short-term outcomes for connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis after lung transplantation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khawar, M.U.; Yazdani, D.; Zhu, Z.; Jandarov, R.; Dilling, D.F.; Gupta, N. Clinical outcomes and survival following lung transplantation in patients with lymphangioleiomyomatosis. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, H.; Watanabe, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Noda, M.; Ejima, Y.; Saiki, Y.; Seyama, K.; Kondo, T.; Okada, Y. Single lung transplantation for lymphangioleiomyomatosis: A single-center experience in Japan. Surg. Today 2018, 48, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpodonu, J.; Massad, M.G.; Chaer, R.A.; Caines, A.; Evans, A.; Snow, N.J.; Geha, A.S. The US experience with lung transplantation for pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2005, 24, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirbu, E.; Buleu, F.; Tudor, A.; Dragan, S. Vitamin D and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A retrospective study in a Romanian cohort. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2020, 67, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organ Transplant Reporting and Waiting List in Romania. Available online: http://transplant.ro/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Lista-asteptare-2021.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Behl, T.; Upadhyay, T.; Singh, S.; Chigurupati, S.; Alsubayiel, A.M.; Mani, V.; Vargas-De-la-cruz, C.; Uivarosan, D.; Bustea, C.; Sava, C.; et al. Polyphenols Targeting MAPK Mediated Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Molecules 2021, 26, 6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szekanecz, Z.; McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G.; Szamosi, S.; Benkő, S.; Szűcs, G. Autoinflammation and autoimmunity across rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antin-Ozerkis, D.; Evans, J.; Rubinowitz, A.; Homer, R.J.; Matthay, R.A. Pulmonary manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Chest Med. 2010, 31, 451–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futami, S.; Arai, T.; Hirose, M.; Sugimoto, C.; Ikegami, N.; Akira, M.; Kasai, T.; Kitaichi, M.; Hayashi, S.; Inoue, Y. Comorbid connective tissue diseases and autoantibodies in lymphangioleiomyomatosis: A retrospective cohort study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, K.V.; Goyal, S.; Kumar, S.; Shah, A.D.; Rana, Y. Pulmonary Lymphangioleiomyomatosis and Role of Pleurodesis: Rare Case Reports. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2021, 15, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Moss, J.; Beck, G.J.; Lee, J.C.; Brown, K.K.; Chapman, J.T.; Finlay, G.A.; Olson, E.J.; Ruoss, S.J.; Maurer, J.R.; et al. The NHLBI lymphangioleiomyomatosis registry: Characteristics of 230 patients at enrollment. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, P.C. VEGF and imaging of vessels in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, S99–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Finlay, G.A.; Kotloff, R.M.; Strange, C.; Wilson, K.C.; Young, L.R.; Taveira-DaSilva, A.M.; Johnson, S.R.; Cottin, V.; Sahn, S.A.; et al. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis Diagnosis and Management: High-Resolution Chest Computed Tomography, Transbronchial Lung Biopsy, and Pleural Disease Management. An Official American Thoracic Society/Japanese Respiratory Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerosa, M.; De Angelis, V.; Riboldi, P.; Meroni, P.L. Rheumatoid arthritis: A female challenge. Women’s Health 2008, 4, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prizant, H.; Taya, M.; Lerman, I.; Light, A.; Sen, A.; Mitra, S.; Foster, T.H.; Hammes, S.R. Estrogen maintains myometrial tumors in a lymphangioleiomyomatosis model. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoh, Y. Metalloproteinases in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Potential Therapeutic Targets to Improve Current Therapies. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 148, 327–338. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrans, V.J.; Yu, Z.X.; Nelson, W.K.; Valencia, J.C.; Tatsuguchi, A.; Avila, N.A.; Riemenschn, W.; Matsui, K.; Travis, W.D.; Moss, J. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): A review of clinical and morphological features. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2000, 67, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laragione, T.; Gulko, P.S. mTOR regulates the invasive properties of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, W.S.; Hong, K.W.; Kim, C.D. HMGB1 induces angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis via HIF-1α activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, K.M.; Yang, J.; Shen, M.H.; Sampson, J.R.; Tee, A.R. mTORC1 drives HIF-1α and VEGF-A signalling via multiple mechanisms involving 4E-BP1, S6K1 and STAT3. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2239–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Scheme 28. | Painful/Swollen Joints (Number) | VAS | DAS 28 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation and symmetrical joint pain, bilateral functional hand deficit and stiffness over 90 min, and neurasthenia (I and II) | 12/12 | 70 | 5.57 |
| 11/15 | 90 | 5.1 | |
| Loss of appetite, vomiting, nausea, dyspnea on exertion, and discomfort after methotrexate administration (III) | 6/9 | 70 | 5.9 |
| Decreased muscle strength, persistent dyspnea, hair loss, hemoptysis, and severe neurasthenia and/or depression (IV) | 10/15 | 90 | 5.88 |
| Respiratory infections and severe dyspnea (V) | 3/2 | 20 | 2.1 |
| Weight loss (approx. 5 kg/4 weeks); hair loss; both hands, elbows, and knees present polyarthralgia + swelling of the small joints; cyclophosphamide treatment followed by frequent hemorrhagic cystitis (VI) | 14/12 | 80 | 6.1 |
| ESR mm/h/ CRP mg/L | RF UI | ACPA U/mL/VEGF-D pg/mL | Treatment (Visit Number) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45/25 | 70 | 40/Nd | Refused (I) |
| 80/26 | 140 | 100/Nd | Methotrexate at 20 mg/week, corticosteroids (Prednison) at 0.5 mg/kg body weight, folic acid at 5mg/week, and vitamin D at 1000 IU/day (II) |
| 80/25 | 356 | 1245/Nd | Daily Leflunomide at 20 mg + Prednison at 10 mg + Sulfasalazine at 3 g and Salbutamol at 400 µg (nebulizer treatment) (III) |
| 75/30 | Nd | Adalimumab at 40 mg (1 ampoule)/2 weeks, daily Leflunomide at 20 mg + Naproxen 1100 mg, and Salbutamol at 800 µg (nebulizer treatment) (IV) | |
| 29/6.8 | Daily Cyclophosphamide at 200 mg + Hydroxychloroquine 2 × 200 mg + Medrol at 16 mg + Colchicine at 1 mg (V) | ||
| 85/20 | Rituximab at 1000 mg, i.v., repeated after 2 weeks and Hydroxychloroquine at 400 mg/day (VI) | ||
| 90/30 | Nd | Nd/≥800 | Daily Hydroxychloroquine at 400 mg + Sirolimus at 2 mg (VII) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pascalau, N.A.; Radu, A.-F.; Cseppento, D.C.N.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Jurcau, A.; Mos, C.; Bungau, A.F.; Bungau, S.G. An Evidence-Based Update on the Potential Association between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040607
Pascalau NA, Radu A-F, Cseppento DCN, Andronie-Cioara FL, Jurcau A, Mos C, Bungau AF, Bungau SG. An Evidence-Based Update on the Potential Association between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(4):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040607
Chicago/Turabian StylePascalau, Nicoleta Anamaria, Andrei-Flavius Radu, Delia Carmen Nistor Cseppento, Felicia Liana Andronie-Cioara, Anamaria Jurcau, Calin Mos, Alexa Florina Bungau, and Simona Gabriela Bungau. 2023. "An Evidence-Based Update on the Potential Association between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 4: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040607
APA StylePascalau, N. A., Radu, A. -F., Cseppento, D. C. N., Andronie-Cioara, F. L., Jurcau, A., Mos, C., Bungau, A. F., & Bungau, S. G. (2023). An Evidence-Based Update on the Potential Association between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(4), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040607