An Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian Formulation for Modelling Cavitation in the Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Line Contacts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Formulation
2.1.1. Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication
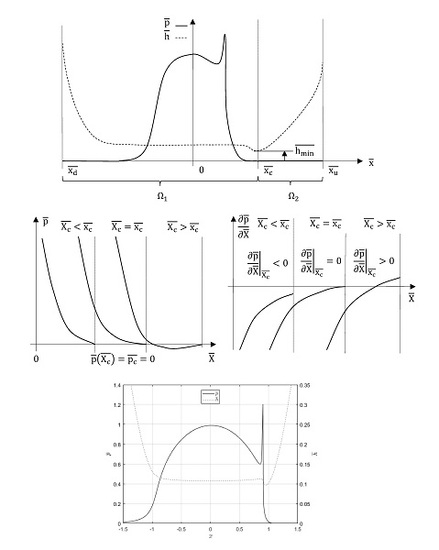
2.1.2. Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian Formulation
2.2. Numerical Method
2.2.1. Steady-State Solution Procedure
2.2.2. Transient Solution Procedure
2.3. Investigation of the Minimum Film Thickness
2.4. Comparison of the ALE Formulation with the Heaviside Approach
3. Results
3.1. Steady-State Simulations
3.2. Transient Simulations
3.3. Analysis of the Minimum Film Thickness
3.4. Analysis of the ALE Formulation and Heaviside Approach
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Hertzian contact half-width (m) | |
| Dynamic loading coefficient | |
| Dowson-Higginson compressibility constants (Pa,1) | |
| Reduced Young’s modulus (Pa) | |
| Young’s moduli of the contacting bodies (Pa) | |
| Material parameter | |
| Film thickness, contact separation (m) | |
| Non-dimensional film thickness, contact separation, and minimum film thickness | |
| Minimum film thickness | |
| Moe’s load parameter | |
| Moe’s material parameter | |
| Number of elements, maximum number of elements | |
| Fluid pressure, saturated vapour pressure (Pa) | |
| Non-dimensional pressure and saturated vapour pressure | |
| Hertzian contact pressure (Pa) | |
| Roeland’s reference pressure (Pa) | |
| Reduced contact radius (m) | |
| Radii of the contacting bodies (m) | |
| Time, oscillating time period (s) | |
| Time to compute (s) | |
| Non-dimensional time and oscillating time period | |
| Entrainment velocity (m/s) | |
| Surface velocity of the contacting bodies (m/s) | |
| Speed parameter | |
| Load per unit length, transient and steady-state (N/m) | |
| Load parameter | |
| Coordinate direction, material and spatial frames of reference (m) | |
| Non-dimensional coordinate directions, material and spatial frames of reference | |
| Pressure-viscosity coefficient | |
| Pressure-viscosity parameter (Pa−1) | |
| Compressibility (Pa−1) | |
| Non-dimensional scaling variable | |
| Dynamic load variation | |
| Roelands fluid viscosity (Pas) | |
| Non-dimensional viscosity | |
| Viscosity at ambient pressure (Pas) | |
| Roeland’s reference viscosity (Pas) | |
| Non-dimensional scaling parameter | |
| Poisson’s ratios of the contacting bodies | |
| Dowson-Higginson fluid density (kg/m3) | |
| Non-dimensional density | |
| Density at ambient pressure (kg/m3) | |
| ALE constant | |
| ALE derivative | |
| Liquid and vapour domains, spatial frame of reference | |
| Liquid and vapour domains, material frame of reference |
Appendix B
References
- Gohar, R. Elastohydrodynamics, 2nd ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dowson, D. History of Tribology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, A. Basic Lubrication Theory; Longman: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Floberg, L. Cavitation boundary conditions with regard to the number of streamers and tensile strength of the liquid. In Cavitation and Related Phenomena in Lubrication; IMechE: London, UK, 1974; pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson, B.; Floberg, L. The Finite Journal Bearing, Considering Vaporization; Gumperts Förlag: Göteborg, Sweden, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, K.-O. Cavitation in Dynamically Loaded Bearings; Scandinavian University Books: Göteborg, Sweden, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- von Mohrenstein-Ertel, A. Die Berechnung der Hydrodynamischen Schmierung Gekrümmter Oberflächen unter Hoher Belastung und Relativbewegung. In Fortschrittsberichte VDI; Series 1; No. 115. First Published in 1945 in Russian under the name A. M. Ertel; Lang, O.R., Oster, P., Eds.; VDI Verlag: Düsseldorf, Germany, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Grubin, A.N. Investigation of the Contact of Machine Components; DSIR Translation No. 337; Central Scientific Research Institute for Technology and Mechanical Engineering: Moscow, Russia, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Dowson, D.; Higginson, G.R. Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Venner, C.H. Multilevel Solution of the EHL Line and Point Contact Problems; University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Venner, C.H.; Lubrecht, A.A. Multi-Level Methods in Lubrication, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Habchi, W.; Eyheramendy, D.; Vergne, P.; Morales-Espejel, G.E. Stabilized fully-coupled finite elements for elastohydrodynamic lubrication problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2012, 46, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.R. A penalty formulation and numerical approximation of the Reynolds-Hertz problem of elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1986, 24, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrod, H.G. A cavitation algorithm. J. Tribol. 1981, 103, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, D.; Keith, T.G., Jr. Development and evaluation of a cavitation algorithm. STLE Tribol. Trans. 1989, 32, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayada, G.; Martin, S.; Vázquez, C. Two-scale homogenization of a hydrodynamic Elrod-Adams model. Asymptot. Anal. 2005, 44, 75–110. [Google Scholar]
- Bayada, G.; Martin, S.; Vázquez, C. An average flow model of the Reynolds roughness including a mass-flow preserving cavitation model. J. Tribol. 2005, 127, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayada, G.; Martin, S.; Vázquez, C. Micro-roughness effects in (elasto)hydrodynamic lubrication including a mass-flow preserving cavitation model. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlin, F.; Almqvist, A.; Larsson, R.; Glavatskih, S. A cavitation algorithm for arbitrary lubricant compressibility. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacopini, M.; Fowell, M.T.; Dini, D.; Strozzi, A. A mass-conserving complementary formulation to study lubricant films in the presence of cavitation. J. Tribol. 2010, 132, 041702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocchi, L.; Dini, D.; Giacopini, M.; Fowell, M.T.; Baldini, A. Fluid film lubrication in the presence of cavitation: A mass-conserving two-dimensional formulation for compressible, piezoviscous and non-Newtonian fluids. Tribol. Int. 2013, 67, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Behdinan, K. The evaluation of LCP method in modeling the fluid cavitation for squeeze film damper with off-centered whirling motion. Lubricants 2017, 5, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Almqvist, A.; Fabricius, J.; Larsson, R.; Wall, P. A new approach for studying cavitation in lubrication. J. Tribol. 2014, 136, 0117061–0117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almqvist, A.; Wall, P. Modelling cavitation in (elasto)hydrodynamic lubrication. In Advances in Tribology; Darji, P.H., Ed.; INTECH Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 197–213. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Keith, T.G., Jr. An elastohydrodynamic cavitation algorithm for piston ring lubrication. STLE Tribol. Trans. 1995, 38, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraskari, M.; Hemmati, F.; Jalali, A.; Alqaradawi, M.Y.; Gadala, M.S. A robust modification to the universal cavitation algorithm in journal bearings. J. Tribol. 2017, 139, 031703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, B.; Garvey, S.; Webster, J. A thermal elasto-hydrodynamic lubricated analysis of highly-loaded journal bearings, with varying bulk modulus, to allow high areas of cavitation to be solved. In Proceedings of the 6th World Tribology Congress, Beijing, China, 17–22 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, G.; Moreno, C.; Vázquez, C. Elrod–Adams cavitation model for a new nonlinear Reynolds equation in piezoviscous hydrodynamic lubrication. Appl. Math. Model. 2017, 44, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woloszynski, T.; Podsiadlo, P.; Stachowiak, G.W. Efficient solution to the cavitation problem in hydrodynamic lubrication. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 58, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Booker, F. A finite element cavitation algorithm. J. Tribol. 1991, 113, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grando, F.P.; Priest, M.; Prata, A.T. A two-phase flow approach to cavitation modelling in journal bearings. Tribol. Trans. 2006, 21, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayada, G.; Chupin, L. Compressible fluid model for hydrodynamic lubrication cavitation. ASME Trans. J. Tribol. 2013, 135, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyere, V.; Fillot, N.; Morales-Espejel, G.E.; Vergne, P. A two-phase flow approach for the outlet of lubricated line contacts. J. Tribol. 2012, 134, 041503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Odyck, D.E.A.; Venner, C.H. Compressible Stokes flow in thin films. J. Tribol. 2003, 125, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Emden, E.; Venner, C.H.; Morales-Espejel, G.E. Aspects of flow and cavitation around an EHL contact. Tribol. Int. 2016, 95, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Emden, E.; Venner, C.H.; Morales-Espejel, G.E. A challenge to cavitation modelling in the outlet flow of an EHL contact. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyere, V.; Fillot, N.; Morales-Espejel, G.E.; Vergne, P. Computational fluid dynamics and full elasticity model for sliding line thermal elastohydrodynamic contacts. Tribol. Int. 2012, 46, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartinger, M.; Dumont, M.-L.; Ioannides, S.; Gosman, D.; Spikes, H. CFD modelling of a thermal and shear-thinning elastohydrodynamic line contact. J. Tribol. 2008, 130, 041503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishafiee, A.; Kadiric, A.; Ioannides, S.; Dini, D. A coupled finite-volume CFD solver for two-dimensional hydrodynamic lubrication problems with particular application to roller bearings. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärrholm, F.P.; Weller, H.; Nordin, N. Modelling injector flow including cavitation effects for diesel applications. In Proceedings of the 5th Joint ASME/JSME Fluids Engineering Conference (FEDSM2007), San Diego, CA, USA, 30 July–2 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Donea, J.; Huerta, A.; Ponthot, J.-P.; Rodríguez-Ferran, A. Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian methods. In Encyclopedia of Computational Mechanics; Stein, E., de Borst, R., Hughes, T.J.R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer, B. ALE formulation of Reynolds fluid film equation. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 2008, 88, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raske, N.; Hewson, R.W.; Kapur, N.; de Boer, G.N. A predictive model for discrete cell gravure roll coating. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 062101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, R.W. Free surface model derived from the analytical solution of Stokes flow in a wedge. J. Fluids Eng. 2009, 131, 041205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, D.; Higginson, G.R. Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication: The Fundamentals of Roller and Gear Lubrication; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Roelands, C. Correlational Aspects of the Viscosity-Temperature-Pressure Relationship of Lubricating Oils. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 27 April 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Winslow, A. Numerical solution of the quasi-linear Poisson equations in a nonuniform triangle mesh. J. Comput. Phys. 1967, 2, 149–172. [Google Scholar]
- COMSOL Inc., USA. COMSOL Multiphysics 5.3 [Computer Software]. 2017. Available online: https://www.comsol.com/ (accessed on 21 December 2017).
- Joppich, W. Multigrid implementation in COMSOL Multiphysics—Comparison of theory and practice. In Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2013, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 23–25 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hamrock, B.J.; Jacobson, B.O. Elasto-hydrodynamic lubrication of line contacts. ASLE Trans. 1984, 27, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Hamrock, B.J. Simple formulas for performance parameters in elastohydrodynamically lubricated line contacts. ASME J. Tribol. 1989, 111, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrecht, A.A.; Breukink, G.A.C.; Moes, H.; ten Napel, W.E.; Bosma, R. Solving Reynolds equation for EHL line contacts by application of a multigrid method. Tribol. Ser. 1987, 11, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Lubrecht, A.A.; Venner, C.H.; Colin, F. Film thickness calculation in elasto-hydrodynamic lubricated line and elliptical contacts: The Dowson-Higginson, Hamrock contribution. J. Eng. Tribol. 2009, 223, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MathsWorks Inc., USA. Matlab vR017a [Computer Software]. 2017. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/ (accessed on 21 December 2017).











| Parameter | Value [Units] |
|---|---|
| 1.076 [mm] | |
| 0.59 [GPa], 1.34 | |
| 200 [GPa] | |
| 0 [Pa] | |
| 1.183 [GPa] | |
| 0.196 [GPa] | |
| 100 [mm] | |
| 1, 0 [m/s] | |
| 2 [MN/m] | |
| 0.4486 | |
| 1 [Pas] | |
| 6.31 × 10−5 [Pas] | |
| 0.3 | |
| 850 [kg/m3] | |
| 103 |
| Parameter | Value [Units] |
|---|---|
| 0.01 [s] | |
| 0.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Boer, G.; Dowson, D. An Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian Formulation for Modelling Cavitation in the Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Line Contacts. Lubricants 2018, 6, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010013
De Boer G, Dowson D. An Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian Formulation for Modelling Cavitation in the Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Line Contacts. Lubricants. 2018; 6(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Boer, Gregory, and Duncan Dowson. 2018. "An Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian Formulation for Modelling Cavitation in the Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Line Contacts" Lubricants 6, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010013
APA StyleDe Boer, G., & Dowson, D. (2018). An Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian Formulation for Modelling Cavitation in the Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Line Contacts. Lubricants, 6(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010013