Phospholipid Vesicles in Media for Tribological Studies against Live Cartilage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Overview
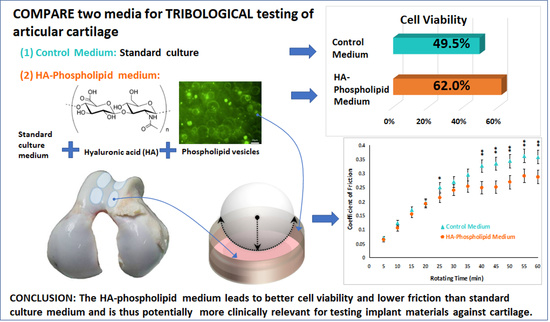
2.2. The Media
2.2.1. The Control Medium
2.2.2. The HA–Phospholipid Medium
2.3. Cartilage Procurement and Cell Viability
2.4. Rheological Measurements
2.5. Friction Test
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability
3.2. Liposome Formation
3.3. Rheological Measurements
3.4. Friction Measurements for a CoCrMo Ball Articulating against Bovine Cartilage
4. Discussion
4.1. Cell Viability
4.2. Liposome Formation
4.3. Rheological Measurements
4.4. Friction Measurements
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jafarzadeh, S.R.; Felson, D.T. Updated estimates suggest a much higher prevalence of arthritis in US adults than previous ones. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, E.M.; Garrett, N.; Lindquist, T.; Isham, G.J. The boomers are coming: A total cost of care model of the impact of population aging on health care costs in the United States by Major Practice Category. Health Serv. Res. 2007, 42, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala, E.; Trono, M.; Bitonti, A.; Lucidi, G. Hip hemiarthroplasty for femur neck fractures: Minimally invasive direct anterior approach versus postero-lateral approach. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2016, 26, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, B.D.; Scott, R.D.; Sah, A.P.; Carrington, R. McKeever hemiarthroplasty of the knee in patients less than sixty years old. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2006, 88, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrel, J.R.; Trinh, T.Q.; Fischer, R.A. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures: A systematic review. J. Orthop. Trauma 2015, 29, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phadnis, J.; Watts, A.C.; Bain, G.I. Elbow hemiarthroplasty for the management of distal humeral fractures: Current technique, indications and results. Shoulder Elb. 2016, 8, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, K.; Amilon, A.; Rizzo, M. Pyrolytic carbon hemiarthroplasty in the management of proximal interphalangeal joint arthritis. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2015, 40, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevino, R.L. Mechanobiological Response of Cartilage to Self-Mating and Prosthetic Contact through In Vitro Modeling of Joint Articulation. Ph.D. Thesis, Rush University, Chicago, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.I.; Argyle, D.J.; Clements, D.N. In vitro models for the study of osteoarthritis. Vet. J. 2016, 209, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Asayama, Y. Animal-cell culture media: History, characteristics, and current issues. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2017, 16, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mow, V.C.; Huiskes, R. Basic Orthopaedic Biomechanics & Mechano-Biology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mow, V.C.; Ratcliffe, A.; Poole, A.R. Cartilage and diarthrodial joints as paradigms for hierarchical materials and structures. Biomaterials 1992, 13, 67–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Sah, R. Effect of Synovial Fluid on Boundary Lubrication of Articular Cartilage. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2007, 15, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.M.T.; Neu, C.P.; Komvopoulos, K.; Reddi, A.H. The Role of Lubricant Entrapment at Biological Interfaces: Reduction of Friction and Adhesion in Articular Cartilage. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 2015–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fam, H.; Bryant, J.T.; Kontopoulou, M. Rheological properties of synovial fluids. Biorheology 2007, 44, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stoia, J.L. Cartilage-on-Cartilage Articulating System as a Wear Benchmark for Artificial Replacement Materials. Master’s Thesis, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.M. Modèle Bio-Tribologique des Articulations. Rôle Mécanique et Physicochimique des Assemblages Moléculaires du Fluide Synovial. Ph.D. Thesis, INSA de Lyon, Villeurbanne, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Corneci, M.C.; Dekkiche, F.; Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.M.; Meurisse, M.H.; Berthier, Y.; Rieu, J.P. Tribological properties of fluid phase phospholipid bilayers. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Leng, C.G.; Toriumi, H.; Hamada, Y.; Akamatsu, N.; Ohno, S. Ultrastructural study of upper surface layer in rat articular cartilage by “in vivo cryotechnique” combined with various treatments. Med. Electron. Microsc. 2000, 33, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirea, D.A.; Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.M.; Matei, C.I.; Munteanu, B.; Piednoir, A.; Rieu, J.P.; Blanchin, M.G.; Berthier, Y. Role of the biomolecular interactions in the structure and tribological properties of synovial fluid. Tribol. Int. 2013, 59, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, B.A. Oligolamellar lubrication of joints by surface active phospholipid. J. Rheumatol. 1989, 16, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sorkin, R.; Dror, Y.; Kampf, N.; Klein, J. Mechanical stability and lubrication by phosphatidylcholine boundary layers in the vesicular and in the extended lamellar phases. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5005–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivan, S.; Schroeder, A.; Verberne, G.; Merkher, Y.; Diminsky, D.; Priev, A.; Maroudas, A.; Halperin, G.; Nitzan, D.; Etsion, I.; et al. Liposomes act as effective biolubricants for friction reduction in human synovial joints. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, A.; Wang, M.; Zander, T.; Wieland, D.C.F.; Liu, X.; An, J.; Garamus, V.M.; Willumeit-Römer, R.; Fielden, M.; Claesson, P.M.; et al. Lubrication synergy: Mixture of hyaluronan and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) vesicles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 488, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.J.; Ko, C.J.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chien, C.T.; Huang, L.H.; Lee, C.W.; Jiang, C.C. Proteomic analysis of osteoarthritic chondrocyte reveals the hyaluronic acid-regulated proteins involved in chondroprotective effect under oxidative stress. J. Proteom. 2014, 99, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, M.; Baynes, J.W.; Spiteller, G. The reaction of hyaluronic acid and its monomers, glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine, with reactive oxygen species. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 321, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeser, R.F.; Shanker, G. Autocrine stimulation by insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor 2 mediates chondrocyte survival in vitro. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirea, D.A.; Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.M.; Piednoir, A.; Rieu, J.P.; Blanchin, M.G.; Berthier, Y. AFM Study of the Interactions between Synovial Liquid’s Molecular Components in Boundary Lubrication. J. Balk. Tribol. Assoc. 2011, 17, 642–651. [Google Scholar]
- Sava, M.M.; Boulocher, C.; Matei, C.I.; Munteanu, B.; Schramme, M.; Viguier, E.; Roger, T.; Berthier, Y.; Blanchin, M.G.; Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.M. Structural and tribological study of healthy and biomimetic, SF. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 16 (Suppl. 1), 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sava, M.M.; Munteanua, B.; Renault, E.; Berthier, Y.; Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.M. Tribological Analysis of UHMWPE Tibial Implants in Unicompartmental Knee Replacements: From Retrieved to In Vitro Studies. Biotribology 2018, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkiche, F.; Corneci, M.C.; Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.M.; Munteanu, B.; Berthier, Y.; Kaabar, W.; Rieu, J.P. Stability and tribological performances of fluid phospholipid bilayers: effect of buffer and ions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 80, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.A.; Gastelum, N.S.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Schumacher, B.L.; Sah, R.L. Boundary lubrication of articular cartilage: Role of synovial fluid constituents. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvelli, M.; Che, B.; Saeui, C.; Singh, A.; Elisseeff, J. Biodynamic performance of hyaluronic acid versus synovial fluid of the knee in osteoarthritis. Methods 2015, 84, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Seror, J.; Day, A.J.; Kampf, N.; Klein, J. Ultra-low friction between boundary layers of hyaluronan-phosphatidylcholine complexes. Acta Biomater. 2017, 59, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, A.V.; Powell, G.L.; LaBerge, M. Phospholipid composition of articular cartilage boundary lubricant. J. Orthop. Res. 2001, 19, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Franses, E.I. New protocols for preparing dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine dispersions and controlling surface tension and competitive adsorption with albumin at the air/aqueous interface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2005, 43, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, J.M.M.; Pascau, J. Image Processing with ImageJ; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2003; Volume 11, pp. 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual Garrido, C.; Hakimiyan, A.A.; Rappoport, L.; Oegema, T.R.; Wimmer, M.A.; Chubinskaya, S. Anti-apoptotic treatments prevent cartilage degradation after acute trauma to human ankle cartilage. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2009, 17, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmer, M.A.; Grad, S.; Kaup, T.; Hänni, M.; Schneider, E.; Gogolewski, S.; Alini, M. Tribology approach to the engineering and study of articular cartilage. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhawat, V.K. Influence of Kinematics on Mechano-Biological Response of Articular Cartilage—An In Vitro Investigation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Raghuraman, H.; Shrivastava, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Monitoring the looping up of acyl chain labeled NBD lipids in membranes as a function of membrane phase state. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, R.B.; Armstrong, R.C.; Hassager, O. Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids, Fluid Dynamics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Oungoulian, S.R.; Durney, K.M.; Jones, B.K.; Ahmad, C.S.; Hung, C.T.; Ateshian, G.A. Wear and damage of articular cartilage with friction against orthopedic implant materials. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Takahashi, T.; Ide, H.; Fukushima, T.; Tabata, M.; Sekine, F.; Kobayashi, K.; Negishi, M.; Niwa, Y. Antioxidant activity of synovial fluid, hyaluronic acid, and two subcomponents of hyaluronic acid. Synovial fluid scavenging effect is enhanced in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorkin, R.; Kampf, N.; Dror, Y.; Shimoni, E.; Klein, J. Origins of extreme boundary lubrication by phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5465–5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, Z.; Yusuf, K.Q.; Pai, R.; Urbaniak, W. Repulsive surfaces and lamellar lubrication of synovial joints. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 623–624, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leckband, D.; Israelachvili, J. Intermolecular Forces in Biology; Cambridge University Press Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics: Cambridge, UK, 2001; Volume 34, pp. 105–267. [Google Scholar]
- Matei, C.I.; Boulocher, C.; Boulé, C.; Schramme, M.; Viguier, E.; Roger, T.; Berthier, Y.; Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.M.; Blanchin, M.G. Ultrastructural analysis of healthy synovial fluids in three mammalian species. Microsc. Microanal. 2014, 20, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurz, J.; Ribitsch, V. Rheology of synovial fluid. Biorheology 1987, 24, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollet, A.J. The intrinsic viscosity of synovial fluid hyaluronic acid. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1956, 48, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dahl, L.B.; Dahl, I.M.; Engström-Laurent, A.; Granath, K. Concentration and molecular weight of sodium hyaluronate in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other arthropathies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1985, 44, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haward, S.J.; Jaishankar, A.; Oliveira, M.S.; Alves, M.A.; McKinley, G.H. Extensional flow of hyaluronic acid solutions in an optimized microfluidic cross-slot device. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 044108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caligaris, M.; Ateshian, G.A. Effects of sustained interstitial fluid pressurization under migrating contact area, and boundary lubrication by synovial fluid, on cartilage friction. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, A.; Wang, C. Analysis of friction between articular cartilage and polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel artificial cartilage. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsey, R.W.; Fisher, J.; Thompson, J.; Stone, M.H.; Bell, C.; Ingham, E. The effect of hyaluronic acid and phospholipid based lubricants on friction within a human cartilage damage model. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4581–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, P.; Loeuille, D.; Watrin, A.; Walter, F.; Etienne, S.; Netter, P.; Gillet, P.; Blum, A. Structural evaluation of articular cartilage: Potential contribution of magnetic resonance techniques used in clinical practice. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torzilli, P.A.; Deng, X.-H.; Ramcharan, M. Effect of compressive strain on cell viability in statically loaded articular cartilage. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2006, 5, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, A.F.; Dowson, D.; Wright, V. The Rheology of Synovial Fluid and Some Potential Synthetic Lubricants for Degenerate Synovial Joints. Eng. Med. 1978, 7, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Cellgro®DMEM (Mediatech, Inc., Manassas, VA, USA), 1X |
|
| Cellgro®Ham’s F-12 (Mediatech, Inc.), 1X |
|
| Mini ITS+ (Prepared according to Loeser et al. [27], all ingredients from Thermo Fisher Scientific Corp., Waltham, MA, USA) |
|
| Gilbco®Gentamicin Reagent Solution (Thermo Fisher Scientific Corp., Waltham, MA, USA) 50 mg/mL |
|
| Gilbco®Antibiotic-Antimycotic (Thermo Fisher Scientific Corp.), 100×→diluted to 1× |
|
| Hyaluronic acid sodium salt from Streptococcus equi |
|
| 16:0 PC (DPPC) 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
|
| Ethyl Alcohol 200 Proof |
|
| Chloroform |
|
| 14:0–06:0 NBD PC Fluorescent Marker |
|
| Viscosity (mPa·s) at Various Shear Rates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA Concentration (wt %) | 10 s−1 | 100 s−1 | 1000 s−1 | 10,000 s−1 | |
| Phosphate Buffered Solution [52] | 0.3 | 68.0 | 40.8 | 16.3 | 6.3 |
| HA–Phospholipid Medium | 0.243 | 60.4 | 36.4 | 13.9 | 5.1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Veselack, T.; Aldebert, G.; Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A.-M.; Schmid, T.M.; Laurent, M.P.; Wimmer, M.A. Phospholipid Vesicles in Media for Tribological Studies against Live Cartilage. Lubricants 2018, 6, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010019
Veselack T, Aldebert G, Trunfio-Sfarghiu A-M, Schmid TM, Laurent MP, Wimmer MA. Phospholipid Vesicles in Media for Tribological Studies against Live Cartilage. Lubricants. 2018; 6(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleVeselack, Teresa, Gregoire Aldebert, Ana-Maria Trunfio-Sfarghiu, Thomas M. Schmid, Michel P. Laurent, and Markus A. Wimmer. 2018. "Phospholipid Vesicles in Media for Tribological Studies against Live Cartilage" Lubricants 6, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010019
APA StyleVeselack, T., Aldebert, G., Trunfio-Sfarghiu, A. -M., Schmid, T. M., Laurent, M. P., & Wimmer, M. A. (2018). Phospholipid Vesicles in Media for Tribological Studies against Live Cartilage. Lubricants, 6(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6010019