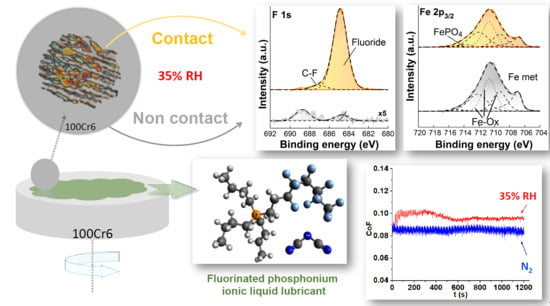
Influence of Water on Tribolayer Growth When Lubricating Steel with a Fluorinated Phosphonium Dicyanamide Ionic Liquid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ionic Liquid
2.2. Steel Samples
2.3. Mechanical Polishing of the Steel Disks
2.4. Optical Profilometry
2.5. Optical Microscopy
2.6. Macrotribological Tests
2.7. Small-area X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.8. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.9. X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
3. Results
3.1. Tribological Testing
3.1.1. Tribological Testing in Humid Air and in Nitrogen
3.1.2. Tribological Testing in Humidity-controlled Environments
3.2. AFM Results
3.3. XPS Results
3.3.1. Survey Spectra
3.3.2. High-resolution XP-Spectra
Non-contact Area
Contact Area
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L. Room-temperature ionic liquids: A novel versatile lubricant. Chem. Commun. 2001, 21, 2244–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, M.-D.; Jiménez, A.-E.; Sanes, J.; Carrión, F.-J. Ionic liquids as advanced lubricant fluids. Molecules 2009, 14, 2888–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, I. Ionic Liquids in Tribology. Molecules 2009, 14, 2286–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somers, A.E.; Howlett, P.; MacFarlane, D.; Forsyth, M. A Review of Ionic Liquid Lubricants. Lubricants 2013, 1, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H. Ionic Liquid Lubricants: Basics and Applications. Tribol. Trans. 2017, 1, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.M.; Grossiord, C.; Le Mogne, T.; Bec, S.; Tonck, A. Role of nitrogen in tribochemical interaction between ZnDDP and succinimide in boundary lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2001, 34, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglin, M.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of tribostressed samples in the presence of ZnDTP: A combinatorial approach. Tribol. Lett. 2003, 15, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelcu, I.; Piras, E.; Rossi, A.; Pasaribua, H.R. XPS analysis on the influence of water on the evolution of zinc dialkyldithiophosphate-derived reaction layer in lubricated rolling contacts. Surf. Interface Anal. 2012, 44, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maton, C.; De Vos, N.; Steven, C.V. Ionic liquid thermal stabilities: Decomposition mechanisms and analysis tools. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5963–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I.; Kamimura, H.; Mori, S. Thermo-oxidative stability of ionic liquids as lubricating fluids. J. Synth. Lubr. 2007, 24, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchan, I.; Thompsopn, G.; Walton, J.; Skeldon, P.; Tempez, A.; Legendre, S. Passivation behaviour of 304 stainless steel in an ionic liquid with a fluorinated anion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissi, I.; Bardi, U.; Caporali, S.; Lavacchi, A. High temperature corrosion properties of ionic liquids. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 2349–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabler, C.; Tomastick, C.; Brenner, J.; Pisarova, L.; Doerr, N.; Allmaier, G. Corrosion properties of ammonium based ionic liquids evaluated by SEM–EDX, XPS and ICP-OES. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2869–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Yagi, S.; Koyama, T.; Tsuboi, R.; Sasaki, S. Lubricity and corrosiveness of ionic liquids for steel-on-steel sliding contacts, Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 991–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa-Marzal, R.M.; Arcifa, A.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. Ionic liquids confined in hydrophilic nanocontacts: Structure and lubricity in the presence of water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 6491–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Marzal, R.M.; Arcifa, A.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. Microslips to “avalanches” in confined, molecular layers of ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 5, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Okada, K.; Uka, A.; Misono, T.; Endo, T.; Sasaki, S.; Abe, M.; Sakai, H. Effects of water on solvation layers of imidazolium-type room temperature ionic liquids on silica and mica. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6085–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-W.; Dienemann, J.N.; Stock, P.; Merola, C.; Chen, Y.J.; Valtiner, M. The Effect of Water and Confinement on Self-Assembly of Imidazolium Based Ionic Liquids at Mica Interfaces. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, L.A.; Kim, H.; Rossi, A.; Arcifa, A.; Schuh, J.K.; Spencer, N.D.; Leal, C.; Ewoldt, R.H.; Espinosa-Marzal, R.M. Effect of the environmental humidity on the bulk, interfacial and nanoconfined properties of an ionic liquid. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 22719–22730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcifa, A.; Rossi, A.; Ramakrishna, S.N.; Espinosa-Marzal, R.S.; Spencer, N.D. Lubrication of Si-Based Tribopairs with a Hydrophobic Ionic Liquid: The Multiscale Influence of Water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 7331–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauber, D.; Zhang, P.; Huch, V.; Kraus, T.; Hempelmann, R. Lamellar structures in fluorinated phosphonium ionic liquids: The roles of fluorination and chain length. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 27251–27258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I.; Inada, T.; Sasaki, R.; Nanao, H. Tribo-chemistry of phosphonium-derived ionic liquids. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struers A/S. Struers A/S Metalog Guide; Struers A/S: Rødovre, Denmark, 2002; ISBN 87-987767-0-3. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 15472:2010 Surface Chemical Analysis—X-ray Photoelectron Spectrometers—Calibration of Energy Scales; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO/TR 19319 Surface Chemical Analysis—Fundamental Approaches to Determination of Lateral Resolution and Sharpness in Beam-Based Methods; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Passiu, C.; Rossi, A.; Bernard, L.; Paul, D.; Hammond, J.; Unger, W.E.S.; Venkataraman, N.V.; Spencer, N.D. Fabrication and Microscopic and Spectroscopic Characterization of Planar, Bimetallic, Micro-and Nanopatterned Surfaces. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5657–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPECTRO Analytical Instruments GmbH. Analysis of Solid Metal Samples; Nr. XRF-70, Rev. 2; SPECTRO Analytical Instruments GmbH: Kleve, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- SPECTRO Analytical Instruments GmbH. Handheld XRF Spectrometer—Original Operating Instructions; SPECTRO Analytical Instruments GmbH: Kleve, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wiltner, A.; Linsmeier, C. Formation of endothermic carbides on iron and nickel. Phys. Status Solidi A 2004, 201, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangolini, F.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N. Influence of metallic and oxidized iron/steel on the reactivity of triphenyl phosphorothionate in oil solution. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangolini, F.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. Tribochemistry of triphenyl phosphorothionate (TPPT) by in situ attenuated total reflection (ATR/FT-IR) tribometry. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 5614–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsener, B.; Pisu, M.; Fantauzzi, M.; Addari, D.; Rossi, A. Electrochemical and XPS surface analytical study on the reactivity of Ni-free stainless steel in artificial saliva. Mater. Corros. 2016, 6, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundell, R.K.; Licence, P. Quaternary ammonium and phosphonium based ionic liquids: A comparison of common anions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 15278–15288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraria, A.M.; da Silva, J.D.L.; Botelho do Rego, A.M. XPS studies of directly fluorinated HDPE: Problems and solutions. Polymer 2003, 44, 7241–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murch, G.E.; Thorn, R.J. Relation between orbital binding energies and ionicities in alkali and alkaline earth flourides. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1980, 41, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantauzzi, M.; Pacella, A.; Atzei, D.; Gianfagna, A.; Andreozzi, G.B.; Rossi, A. Combined use of X-ray photoelectron and Mössbauer spectroscopic techniques in the analytical characterization of iron oxidation state in amphibole asbestos. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2889–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crobu, M.; Rossi, A.; Mangolini, F.; Spencer, N.D. Chain-length-identification strategy in zinc polyphosphate glasses by means of XPS and ToF-SIMS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1415–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide-Ektessabi, A.; Yamaguchi, T.; Tanaka, Y. RBS and XPS analyses of the composite calcium phosphate coatings for biomedical applications. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2005, 241, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedov, V.I.; Salyn Ya, V.; Leonhardt, G.; Scheibe, R. A comparison of different spectrometers and charge corrections used in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1977, 10, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipp, S.L.S.; Hochella, M.F., Jr. Structure and bonding environments at the calcite surface as observed with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and low energy electron diffraction (LEED). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 1723–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzei, D.; Fantauzzi, M.; Rossi, A.; Fermo, P.; Piazzalunga, A.; Valli, G.; Vecchi, R. Surface chemical characterization of PM10 samples by XPS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nansé, G.; Papirer, E.; Fioux, P.; Moguet, F.; Tressaud, A. Fluorination of carbon blacks: An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study: I. A literature review of XPS studies of fluorinated carbons. XPS investigation of some reference compounds. Carbon 1997, 35, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crobu, M. Synthesis, Characterization and Tribochemical Behavior. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rouxhet, P.G.; Genet, M.J. XPS analysis of bio-organic systems. Surf. Interface Anal. 2011, 43, 1453–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrock, B.J.; Dowson, D. Isothermal Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Point Contacts: Part III—Fully Flooded Results. J. Lubr. Technol. 1977, 99, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallian, T.E. On competing failure modes in rolling contact. ASLE Trans. 1967, 10, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, G.; Batchelor, A.W. Engineering Tribology; Butter Worth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Moyer, C.A.; Bahney, L.L. Modifying the Lambda Ratio to Functional Line Contacts. Tribol. Trans. 1990, 33, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarzadeh, A.; Piras, E.; Nedelcu, I.; Brizmer, V.; Wilson, M.C.T.; Morina, A.; Dowson, D.; Neville, A. Zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate antiwear tribofilm and its effect on the topography evolution of surfaces: A numerical and experimental study. Wear 2016, 362–363, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olla, M.; Navarra, G.; Elsener, B.; Rossi, A. Nondestructive in-depth composition profile of oxy-hydroxide nanolayers on iron surfaces from ARXPS measurement. Surf. Interface Anal. 2006, 38, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuberger, R.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. Reactivity of alkylated phosphorothionates with steel: A tribological and surface-analytical study. Lubr. Sci. 2008, 20, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, S.; Sasaki, S. Tribological Properties of Cyan-based Ionic Liquids under Different Environments. Tribol. Online Jpn. Soc. Tribol. 2018, 13, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosvami, N.N.; Bares, J.A.; Mangolini, F.; Konicek, A.R.; Yablon, D.G.; Carpick, R.W. Mechanisms of antiwear tribofilm growth revealed in situ by single-asperity sliding contacts. Science 2015, 348, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| 100Cr6 Steel | Fe | Cr | C | Mn | Si | S | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI52100 | 96.5–97.32 | 1.30–1.60 | 0.980–1.10 | 0.250–0.450 | 0.15–0.30 | ≤0.0250 | ≤0.0250 |
| Experimental * | 98.10 (6) | 1.60 (3) | n.d. | 0.30 (1) | <d.l. | <d.l. | <d.l. |
| Step | Type | Speed | Lubricant | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grinding | SiC #500 | 150 rpm | Ethanol | Until planarity |
| Grinding | SiC #1200 | 150 rpm | Ethanol | 3’30’’ |
| Grinding | SiC #2000 | 150 rpm | Ethanol | 3’30’’ |
| Polishing | DP-Plus + 3µm C paste | 150 rpm | Ethanol | 3’30’’ |
| Polishing | DP-Nap + 1 µm C paste | 150 rpm | Ethanol | 3’30’’ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urtis, L.A.; Arcifa, A.; Zhang, P.; Du, J.; Fantauzzi, M.; Rauber, D.; Hempelmann, R.; Kraus, T.; Rossi, A.; Spencer, N.D. Influence of Water on Tribolayer Growth When Lubricating Steel with a Fluorinated Phosphonium Dicyanamide Ionic Liquid. Lubricants 2019, 7, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7030027
Urtis LA, Arcifa A, Zhang P, Du J, Fantauzzi M, Rauber D, Hempelmann R, Kraus T, Rossi A, Spencer ND. Influence of Water on Tribolayer Growth When Lubricating Steel with a Fluorinated Phosphonium Dicyanamide Ionic Liquid. Lubricants. 2019; 7(3):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7030027
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrtis, Luigi A., Andrea Arcifa, Peng Zhang, Junxiao Du, Marzia Fantauzzi, Daniel Rauber, Rolf Hempelmann, Tobias Kraus, Antonella Rossi, and Nicholas D. Spencer. 2019. "Influence of Water on Tribolayer Growth When Lubricating Steel with a Fluorinated Phosphonium Dicyanamide Ionic Liquid" Lubricants 7, no. 3: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7030027
APA StyleUrtis, L. A., Arcifa, A., Zhang, P., Du, J., Fantauzzi, M., Rauber, D., Hempelmann, R., Kraus, T., Rossi, A., & Spencer, N. D. (2019). Influence of Water on Tribolayer Growth When Lubricating Steel with a Fluorinated Phosphonium Dicyanamide Ionic Liquid. Lubricants, 7(3), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7030027