Genetic Structure and Colonization of North America by Depressaria depressana (Fabricius 1775) (Lepidoptera: Depressariidae) over 15 Years; Contrasts with Westward Expansion of Depressaria radiella (Goeze, 1783) over 160 Years
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. D. depressana Sampling
2.2. DNA Extractions and PCR Amplification
2.3. Alignment and Gene Characterization
2.4. Haplotype Network Construction and Analysis
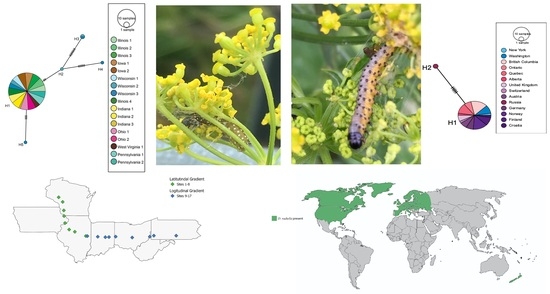
3. Results
3.1. Depressaria Depressana Haplotypes
3.2. Depressaria radiella Haplotypes
3.3. Reconstruction of the History of Invasion of North America by D. radiella
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pysek, P.; Richardson, D.M. Invasive species, environmental change and management, and health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 25–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, R.N.; Simberloff, D.; Lonsdale, M.; Evens, H.; Clout, M.; Bazzaz, F.A. Biotic invasions: Causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbi, S.R. Humans as the world’s greatest evolutionary force. Science 2001, 293, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, L.; Worner, S.P. Biological and ecological traits that assist establishment of alien invasive insects. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2008, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, G.M.; Dearden, P.K. Invasive insects: Management methods explored. J. Insect Sci. 2019, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, C.J.; Leroy, B.; Bellard, C.; Roiz, D.; Albert, C.; Fournier, A.; Barbet-Massin, M.; Salles, J.M.; Simard, F.; Courchamp, F. Massive yet grossly underestimated global costs of invasive insects. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.; Dean, C.A.E.; Parks, K.; Berenbaum, M.R. Depressaria depressana (Fabricius) (Depressariidae), new to the Midwestern USA. J. Lepid. Soc. 2016, 70, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, J.F.; Vazrick, N.; Dewaard, J.R.; Mutanen, M.; Lopez-Vaamonde, C.; Huemer, P.; Hebert, P.D. Shared but overlooked: 30 species of Holarctic Microlepidoptera revealed by DNA barcodes and morphology. Zootaxa 2013, 3749, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethune, C.J.S. Larvae infesting the parsnip. Can. Entomol. 1869, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, C.V. The parsnip webworm (Depressaria heracliana DeG). Insect Life 1889, 1, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Southwick, E.B. The parsnip webworm. Insect Life 1892, 5, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Busck, A. A review of the American moths of the genus Depressaria Haworth, with descriptions of new species. Proc. U. S. Natl. Mus. 1902, 24, 721–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, W.H.; Gooderham, C.B. An insect enemy of the parsnip. Can. Entomol. 1916, 48, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averill, K.M.; DiTommaso, A. Wild parsnip (Pastinaca sativa): A troublesome species of increasing concern. Weed Technol. 2007, 21, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangerl, A.R.; Berenbaum, M.R. Increase in toxicity of an invasive weed after reassociation with its coevolved herbivore. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15529–15532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenbaum, M.R.; Zangerl, A.R. Genetics of physiological and behavioral resistance to host furanocoumarins in the parsnip webworm. Evolution 1992, 46, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, B.H. Parsnip moth established in New Zealand. Weta 2004, 27, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zangerl, A.R.; Stanley, M.C.; Berenbaum, M.R. Selection for chemical trait remixing in an invasive weed after reassociation with a coevolved specialist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 12, 4547–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.A.; Zhang, X. The evolution of coevolution in the study of species interactions. Evolution 2021, 75, 1594–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenbaum, M.R.; Zangerl, A.R. Acquisition of a native hostplant by an introduced oligophagous herbivore. Oikos 1991, 62, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. Bold: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 2006, 5, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. PopART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. TCS: A computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 1657–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonnet, E.; Van de Peer, Y. zt: A software tool for simple and partial Mantel tests. J. Stat. Softw. 2002, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbi, E.I.; Tosto, D.S.; Flores, F.M.; Arneodo, J.D. Evidence for multiple maternal lineages of the invasive pest Helicoverpa armigera in Argentina. Phytoparasitica 2020, 48, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, I. Genetic variation in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae) in China inferred from mitochondrial COI gene sequence. Eur. J. Entomol. 2006, 103, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N.; Meagher, R.L.; Hay-Roe, M. Inferring the annual migration patterns of fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the United States from mitochondrial haplotypes. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoshi, R.N.; Rosas-García, N.M.; Meagher, R.L.; Fleischer, S.J.; Westbrook, J.K.; Sappington, T.W.; Hay-Roe, M.; Thomas, J.M.; Murúa, G.M. Haplotype profile comparisons between Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) populations from Mexico with those from Puerto Rico, South America, and the United States and their implications to migratory behavior. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.S.; Seo, B.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Song, J.H.; Lee, W. First report of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith, 1797) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae), a new migratory pest in Korea. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2020, 59, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wenjun, B. Exploring large-scale patterns of genetic variation in the COI gene among Insecta: Implications for DNA barcoding and threshold-based species delimitation studies. Insects 2020, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangerl, A.R.; Berenbaum, M.R. Phenotype matching in wild parsnip and parsnip webworms: Causes and consequences. Evolution 2003, 57, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, W.W. Niche width and genetic variation in Hawaiian Drosophila. Am. Nat. 1977, 111, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Lacy, R.C. Niche breadth and abundance as determinants of genetic variation in populations of mycophagous drosophilid flies (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Evolution 1982, 36, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitter, C.; Futuyma, D.J. Population genetic consequences of feeding habits in some forest Lepidoptera. Genetics 1979, 92, 1005–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdyck, P.; Desender, K. Mono-and oligophagous Phyllotreta (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) species: The relation between host plant range and genetic diversity. Belg. J. Zool. 2003, 133, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, J.F.G. Revision of the North American moths of the family Oecophoridae, with descriptions of new genera and species. Proc. U. S. Natl. Mus. 1941, 90, 33–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dustan, A.G. Vegetable insects and their control. Dep. Agric. Bull. 1932, 16, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Jogesh, T.; Zangerl, A.; Stanley, M.; Berenbaum, M. Implications of enemy escape on chemically mediated interactions with mutualists: Wild parsnip pollination in two hemispheres. J. Pollinat. Ecol. 2013, 11, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, N.; Gracy, R.G.; Ashika, T.R.; Mohan, G.; Swathi, R.S.; Mohan, M.; Chaudhary, M.; Bakthavatsalam, N.; Venkatesan, T. Population structure and genetic diversity of invasive Fall Armyworm after 2 years of introduction in India. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, W.E.; Evans, E.W. Ecological effects of invasive arthropod generalist predators. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2006, 37, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.; Ashour, M.; Singab, A.N.; Salama, O. Bioassay guided fractionation and cytotoxic activity of Daucus carota var. boissieri. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 4, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Site | State | Latitude | Longitude | Collection Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Illinois 1 | 40.12854 | −88.1439 | July, 2020 |
| 2 | Illinois 2 | 40.62144 | −89.4234 | July, 2020 |
| 3 | Illinois 3 | 40.87883 | −90.0877 | July, 2020 |
| 4 | Iowa 1 | 41.63711 | −90.5679 | July, 2020 |
| 5 | Iowa 2 | 42.45517 | −90.6786 | July, 2020 |
| 6 | Wisconsin 1 | 43.112 | −90.7066 | July, 2020 |
| 7 | Wisconsin 2 | 44.10483 | −90.8402 | July, 2020 |
| 8 | Wisconsin 3 | 44.64364 | −91.3084 | July, 2020 |
| 9 | Illinois 4 | 40.11962 | −87.9631 | July, 2021 |
| 10 | Indiana 1 | 40.04634 | −86.7499 | July, 2021 |
| 11 | Indiana 2 | 39.99172 | −85.8628 | July, 2021 |
| 12 | Indiana 3 | 40.00483 | −85.4401 | July, 2021 |
| 13 | Ohio 1 | 40.05559 | −84.6591 | July, 2021 |
| 14 | Ohio 2 | 39.95099 | −82.7309 | July, 2021 |
| 15 | West Virginia 1 | 40.05095 | −80.68 | July, 2021 |
| 16 | Pennsylvania 1 | 40.16912 | −80.2041 | July, 2021 |
| 17 | Pennsylvania 1 | 40.16586 | −77.5982 | July, 2021 |
| Total | Variable Positions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | State/Prov | BOLD ID | Bases | AGATAAT | ||
| COMPLETE SEQUENCES | EUROPE | Austria | NOE | DEEUR158-11 | 658 | ....... |
| Austria | TIR | LEATJ1038-15 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Austria | VOR | LEATC528-13 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Finland | Ab | LEFIF849-10 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Finland | Al | LEFID175-10 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Germany | BY | FBLMU176-09 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Germany | BY | FBLMU177-09 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Germany | BY | FBLMU703-09 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Norway | Aker | LEPVM100-12 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Norway | Aust-Ag | LEPVM101-12 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Norway | Vest | LON2555-15 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Russia | Caucasus | DEEUR477-15 | 658 | GACCG.. | ||
| Switzerland | VS | DEEUR045-11 | 658 | ....... | ||
| UK | ENG | CGUKA083-09 | 658 | ....... | ||
| UK | ENG | CGUKC898-09 | 658 | ....... | ||
| N AMERICA | UK | ENG | CGUKD655-09 | 658 | ....... | |
| Canada | BC | LALPA1354-12 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Canada | BC | LALPA1355-12 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Canada | BC | LBCW061-08 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Canada | Ont | MECB697-05 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Canada | Que | MEC086-04 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Canada | Que | RDLQD598-06 | 658 | ....... | ||
| Canada | Que | RDLQD599-06 | 658 | ....... | ||
| USA | NY | LNAUT2820-14 | 658 | ....... | ||
| USA | WA | EHL851-12 | 658 | ....... | ||
| USA | WA | RWWC908-12 | 658 | ....... | ||
| PARTIAL SEQUENCES | EUROPE | Croatia | Lika-Senj | LON6919-18 | 632 | ......G |
| Finland | Ab | LEFIF848-10 | 656 | ....... | ||
| Finland | Al | LEFIB073-10 | 647 | ....... | ||
| Norway | Trond | GMNWK4200-14 | 618 | ....... | ||
| Norway | Trond | GMNWL3227-14 | 567 | ....... | ||
| Norway | Trond | GMNWK4187-14 | 534 | ....... | ||
| N AMERICA | Canada | Alta | SMTPM6085-15 | 588 | ....... | |
| Canada | BC | LOWCE394-06 | 617 | ....... | ||
| Canada | BC | LOWCE442-06 | 612 | ....... | ||
| Canada | BC | LOWCE437-06 | 610 | ....... | ||
| Canada | BC | LOWCE397-06 | 599 | ....... | ||
| Canada | Ont | SMTPB5733-13 | 543 | ....... | ||
| Canada | Ont | MEC171-04 | 642 | .....GG | ||
| Canada | Que | MEC339-04 | 629 | ....... | ||
| Canada | Que | RDLQD600-06 | 649 | ....... | ||
| USA | NY | LNAUT2821-14 | 307 | ....... | ||
| USA | WA | RWWC1236-13 | 591 | ....... | ||
| USA | WA | RWWC1336-14 | 585 | ....... | ||
| USA | WA | RWWC1331-14 | 579 | ....... |
| State/Province | Date | Type | Record |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ontario | 1862 | Personal Observation | Bethune (1869) |
| Pennsylvania | 1888 | Collection Record | Collected by T Pergande, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| “Eastern United States” | 1889 | Personal Observation | Riley (1889) |
| Michigan | 1890 | Preserved Specimen | The Albert J. Cook Arthropod Research Collection |
| Illinois | 1900 | Collection Record | Collected by WD Kearfott, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| Quebec | 1903 | Collection Record | Collected by CH Young, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| Utah | 1907 | Collection Record | Collected by ESG Titus, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| Oregon | 1914 | Collection Record | Collected by L Leland, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| Nova Scotia | 1915 | Collection Record | No Collector Credited, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| Connecticut | 1919 | Preserved Specimen | The Yale Peabody Museum |
| Massachusetts | 1920 | Collection Record | Collected by JD Caffrey, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| Rhode Island | 1920 | Collection Record | No Collector Credited, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| Maine | 1923 | Preserved Specimen | The Yale Peabody Museum |
| Arizona | 1925 | Collection Record | Collected by OC Poling, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| British Columbia | 1925 | Collection Record | Collected by LE Marmont, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| Washington | 1930 | Collection Record | Collected by WW Baker, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| Indiana | 1931 | Collection Record | Collected by GS Walley, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| “All provinces of Canada” | 1932 | Personal Observation | Dustan (1932) |
| New York | 1939 | Collection Record | Collected by JFG Clarke, reported in Clarke (1941) |
| Minnesota | 1947 | Preserved Specimen | The University of Minnesota Insect Collection |
| Kentucky | 1955 | Collection Record | Evidence of webworm activity in herbarium sample, reported in Zangerl and Berenbaum (2005) |
| Ohio | 1961 | Preserved Specimen | The Cleveland Museum of Natural History Invertebrate Zoology Collection |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dean, C.A.E.; Easley, J.; Katz, A.D.; Berlocher, S.H.; Berenbaum, M.R. Genetic Structure and Colonization of North America by Depressaria depressana (Fabricius 1775) (Lepidoptera: Depressariidae) over 15 Years; Contrasts with Westward Expansion of Depressaria radiella (Goeze, 1783) over 160 Years. Insects 2022, 13, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13090789
Dean CAE, Easley J, Katz AD, Berlocher SH, Berenbaum MR. Genetic Structure and Colonization of North America by Depressaria depressana (Fabricius 1775) (Lepidoptera: Depressariidae) over 15 Years; Contrasts with Westward Expansion of Depressaria radiella (Goeze, 1783) over 160 Years. Insects. 2022; 13(9):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13090789
Chicago/Turabian StyleDean, Charles A. E., Jack Easley, Aron D. Katz, Stewart H. Berlocher, and May R. Berenbaum. 2022. "Genetic Structure and Colonization of North America by Depressaria depressana (Fabricius 1775) (Lepidoptera: Depressariidae) over 15 Years; Contrasts with Westward Expansion of Depressaria radiella (Goeze, 1783) over 160 Years" Insects 13, no. 9: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13090789
APA StyleDean, C. A. E., Easley, J., Katz, A. D., Berlocher, S. H., & Berenbaum, M. R. (2022). Genetic Structure and Colonization of North America by Depressaria depressana (Fabricius 1775) (Lepidoptera: Depressariidae) over 15 Years; Contrasts with Westward Expansion of Depressaria radiella (Goeze, 1783) over 160 Years. Insects, 13(9), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13090789