In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of the Peptide Fractions Extracted from the Hemolymph of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
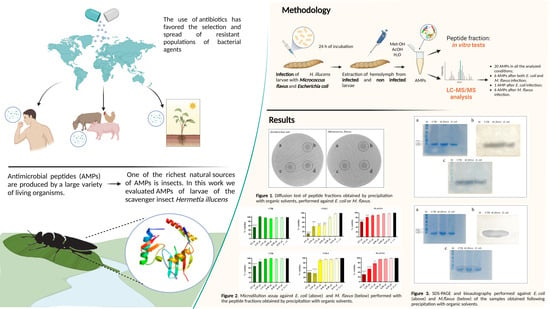
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hermetia illucens Rearing
2.2. H. illucens Larval Infection and Hemolymph Collection
2.3. Peptide Fraction Precipitation by Organic Solvents
2.4. Protein Quantification via Bradford Assay
2.5. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of Hemolymph via Antibiogram Assay
2.6. Evaluation of the Hemolymph Antibacterial Activity via Bioautography (SDS Gel Overlay Method) Experiment
2.7. Evaluation of the Hemolymph Antibacterial Activity via Microdilution Assay
2.8. SDS-PAGE and In Situ Hydrolysis
2.9. LC-MS/MS Analysis and Protein Identification
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Sample Concentration
3.2. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of Peptide Fraction of Hemolymph via Antibiogram Assay
3.3. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of Peptide Fraction of the Hemolymph via Bioautography (SDS Gel Overlay Method) Assay
3.4. Evaluation of the Biological Activity of the Peptide Fractions via Liquid Microdilution Assays
3.5. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guardabassi, L.; Kruse, H. Principles of Prudent and Rational Use of Antimicrobials in Animals. In Guide to Antimicrobial Use in Animals; Blackwell Publishing, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations; Rev. Antimicrob. Resist: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Scaglione, F. Motivi di Fallimento di Una Terapia Antimicrobica. In Guida Alla Terapia Antimicrobica Nella Pratica Clinica; Springer: Milano, Italy, 2012; pp. 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A.L.C.; Dantas, L.d.O.C.; Morão, L.G.; Gutierrez, R.F.; Polikarpov, I.; Wrenger, C.; Nascimento, A.S. Essential Metabolic Routes as a Way to ESKAPE From Antibiotic Resistance. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High Levels of Antibiotic Resistance Found Worldwide, New Data Shows. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-01-2018-high-levels-of-antibiotic-resistance-found-worldwide-new-data-shows (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Courvalin, P. Predictable and Unpredictable Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 264, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strelkauskas, A.; Edwards, A.; Fahnert, B.; Pryor, G.; Strelkauskas, J. Microbiology: A Clinical Approach, 2nd ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780429258701. [Google Scholar]
- Tonk, M.; Vilcinskas, A.; Rahnamaeian, M. Insect Antimicrobial Peptides: Potential Tools for the Prevention of Skin Cancer. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretta, A.; Scieuzo, C.; Petrone, A.M.; Salvia, R.; Manniello, M.D.; Franco, A.; Lucchetti, D.; Vassallo, A.; Vogel, H.; Sgambato, A.; et al. Antimicrobial Peptides: A New Hope in Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Fields. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernysh, S.; Gordya, N.; Suborova, T. Insect Antimicrobial Peptide Complexes Prevent Resistance Development in Bacteria. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshani, A.; Zare, H.; Akbari Eidgahi, M.R.; Hooshyar Chichaklu, A.; Movaqar, A.; Ghazvini, K. Review of Antimicrobial Peptides with Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Activity. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangoni, M.L.; Mcdermott, A.M.; Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial Peptides and Wound Healing: Biological and Therapeutic Considerations. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zharkova, M.S.; Orlov, D.S.; Golubeva, O.Y.; Chakchir, O.B.; Eliseev, I.E.; Grinchuk, T.M.; Shamova, O. Application of Antimicrobial Peptides of the Innate Immune System in Combination with Conventional Antibiotics-a Novel Way to Combat Antibiotic Resistance? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boman, H.G. Peptide Antibiotics and Their Role in Innate Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1995, 13, 61–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, V.; Feio, M.J.; Bastos, M. Role of Lipids in the Interaction of Antimicrobial Peptides with Membranes. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2012, 51, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, F.; Dennison, S.R.; Singh, J.; Phoenix, D.A. On the Selectivity and Efficacy of Defense Peptides with Respect to Cancer Cells. Med. Res. Rev. 2013, 33, 190–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, B.; Augusto, M.T.; Felício, M.R.; Hollmann, A.; Franco, O.L.; Gonçalves, S.; Santos, N.C. Designing Improved Active Peptides for Therapeutic Approaches against Infectious Diseases. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongsiriwatana, N.P.; Lin, J.S.; Kapoor, R.; Wetzler, M.; Rea, J.A.C.; Didwania, M.K.; Contag, C.H.; Barron, A.E. Intracellular Biomass Flocculation as a Key Mechanism of Rapid Bacterial Killing by Cationic, Amphipathic Antimicrobial Peptides and Peptoids. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Starr, C.G.; Wimley, W.C. A Lack of Synergy between Membrane-Permeabilizing Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides and Conventional Antibiotics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Huang, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, G.; Chen, Y. Functional Synergy of α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides and Traditional Antibiotics against Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria in Vitro and in Vivo. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, R.; Daruka, L.; Lázár, V.; Martins, A.; Vidovics, F.; Grézal, G.; Méhi, O.; Kintses, B.; Számel, M.; Jangir, P.K.; et al. Integrated Evolutionary Analysis Reveals Antimicrobial Peptides with Limited Resistance. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollmann, A.; Martinez, M.; Maturana, P.; Semorile, L.C.; Maffia, P.C. Antimicrobial Peptides: Interaction With Model and Biological Membranes and Synergism With Chemical Antibiotics. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, A.; Deb, B.; Chakraborty, S. A Crosstalk on Antimicrobial Peptides. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenssen, H.; Hamill, P.; Hancock, R.E.W. Peptide Antimicrobial Agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Hammami, R.; Cotter, P.D.; Rebuffat, S.; Said, L.B.; Gaudreau, H.; Bédard, F.; Biron, E.; Drider, D.; Fliss, I. Bacteriocins as a New Generation of Antimicrobials: Toxicity Aspects and Regulations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 45, fuaa039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Gely, I.; Lemaitre, B.; Boccard, F. Bacterial Strategies to Overcome Insect Defences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillyer, J.F. Insect Immunology and Hematopoiesis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 58, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulet, P.; Stocklin, R. Insect Antimicrobial Peptides: Structures, Properties and Gene Regulation. Protein Pept. Lett. 2005, 12, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavine, M.D.; Strand, M.R. Haemocytes from Pseudoplusia Includens Express Multiple Alpha and Beta Integrin Subunits. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2003, 12, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmaras, V.J.; Lampropoulou, M. Regulators and Signalling in Insect Haemocyte Immunity. Cell. Signal 2009, 21, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvarque, M.O.; Williams, M.J. Drosophila Cellular Immunity: A Story of Migration and Adhesion. J. Cell. Sci. 2011, 124, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scieuzo, C.; Nardiello, M.; Farina, D.; Scala, A.; Cammack, J.A.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Vogel, H.; Salvia, R.; Persaud, K.; Falabella, P. Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Odorant Binding Proteins and Their Interactions with Selected Volatile Organic Compounds: An In Silico Approach. Insects 2021, 12, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, A.; Cammack, J.A.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Franco, A.; Bufo, S.A.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Falabella, P. Rearing Substrate Impacts Growth and Macronutrient Composition of Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae Produced at an Industrial Scale. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Scieuzo, C.; Salvia, R.; Mancini, I.M.; Caniani, D.; Masi, S.; Falabella, P. A Mobile Black Soldier Fly Farm for On-Site Disposal of Animal Dairy Manure. Bull. Insectology 2022, 75, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Scieuzo, C.; Franco, A.; Salvia, R.; Triunfo, M.; Addeo, N.F.; Vozzo, S.; Piccolo, G.; Bovera, F.; Ritieni, A.; di Francia, A.; et al. Enhancement of Fruit Byproducts through Bioconversion by Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Insect. Sci. 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Schmitt, E.; Russo, A.; Falabella, P. Lipids from Insects in Cosmetics and for Personal Care Products. Insects 2021, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, A.; Scieuzo, C.; Salvia, R.; Petrone, A.M.; Tafi, E.; Moretta, A.; Schmitt, E.; Falabella, P. Lipids from Hermetia illucens, an Innovative and Sustainable Source. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triunfo, M.; Tafi, E.; Guarnieri, A.; Scieuzo, C.; Hahn, T.; Zibek, S.; Salvia, R.; Falabella, P. Insect Chitin-Based Nanomaterials for Innovative Cosmetics and Cosmeceuticals. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triunfo, M.; Tafi, E.; Guarnieri, A.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Hahn, T.; Zibek, S.; Gagliardini, A.; Panariello, L.; Coltelli, M.B.; et al. Characterization of Chitin and Chitosan Derived from Hermetia illucens, a Further Step in a Circular Economy Process. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, A.; Triunfo, M.; Scieuzo, C.; Ianniciello, D.; Tafi, E.; Hahn, T.; Zibek, S.; Salvia, R.; de Bonis, A.; Falabella, P. Antimicrobial Properties of Chitosan from Different Developmental Stages of the Bioconverter Insect Hermetia illucens. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.H.; Yun, J.H.; Chu, J.P.; Chu, K.B. Antibacterial Effect of Extracts of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae against Gram-Negative Bacteria. Entomol. Res. 2012, 42, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Kim, J.W.; Yoe, S.M. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Antibacterial Peptide from Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 52, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Müller, A.; Heckel, D.G.; Gutzeit, H.; Vilcinskas, A. Nutritional Immunology: Diversification and Diet-Dependent Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 78, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, A.; Scieuzo, C.; Salvia, R.; Popović, Ž.D.; Sgambato, A.; Falabella, P. Tools in the Era of Multidrug Resistance in Bacteria: Applications for New Antimicrobial Peptides Discovery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 2856–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, A.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; di Somma, A.; Vogel, H.; Pucci, P.; Sgambato, A.; Wolff, M.; Falabella, P. A Bioinformatic Study of Antimicrobial Peptides Identified in the Black Soldier Fly (BSF) Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Chang, B.S.; Yoe, S.M. Detection of Antimicrobial Substances from Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Entomol. Res. 2014, 44, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Somma, A.; Moretta, A.; Cané, C.; Scieuzo, C.; Salvia, R.; Falabella, P.; Duilio, A. Structural and Functional Characterization of a Novel Recombinant Antimicrobial Peptide from Hermetia illucens. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczor, M.; Bulak, P.; Proc-Pietrycha, K.; Kirichenko-Babko, M.; Bieganowski, A. The Variety of Applications of Hermetia illucens in Industrial and Agricultural Areas—Review. Biology 2023, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manniello, M.D.; Moretta, A.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Lucchetti, D.; Vogel, H.; Sgambato, A.; Falabella, P. Insect Antimicrobial Peptides: Potential Weapons to Counteract the Antibiotic Resistance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 4259–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogsette, J.A. New Diets for Production of House Flies and Stable Flies (Diptera: Muscidae) in the Laboratory. J. Econ. Entomol. 1992, 85, 2291–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhag, O.; Zhou, D.; Song, Q.; Soomro, A.A.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Screening, Expression, Purification and Functional Characterization of Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Genes from Hermetia illucens (L.). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, X.L.; Tian, J.H.; Yi, H.Y.; Wang, W.X.; Zheng, M.; Li, Y.F.; Cao, Y.; Wen, S.Y. Inducing and Isolation of Antibacterial Peptides from Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis Hendel. Insect. Sci. 2006, 13, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cytryńska, M.; Mak, P.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Suder, P.; Jakubowicz, T. Purification and characterization of eight peptides from Galleria mellonella immune hemolymph. Peptides 2007, 28, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Bulak, P.; Polakowski, C.; Bieganowski, A.; Waśko, A.; Cytryńska, M. Immune Response in the Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly Hermetia illucens. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2017, 14, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butturini, E.; Gotte, G.; Dell’Orco, D.; Chiavegato, G.; Marino, V.; Canetti, D.; Cozzolino, F.; Monti, M.; Pucci, P.; Mariotto, S. Intermolecular Disulfide Bond Influences Unphosphorylated STAT3 Dimerization and Function. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 3205–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, S.; Aulitto, M.; Iacobucci, I.; Crocamo, G.; Pucci, P.; Bartolucci, S.; Monti, M.; Contursi, P. The Interaction between the F55 Virus-Encoded Transcription Regulator and the RadA Host Recombinase Reveals a Common Strategy in Archaea and Bacteria to Sense the UV-Induced Damage to the Host DNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 1863, 194493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvia, R.; Cozzolino, F.; Scieuzo, C.; Grimaldi, A.; Franco, A.; Vinson, S.B.; Monti, M.; Falabella, P. Identification and Functional Characterization of Toxoneuron Nigriceps Ovarian Proteins Involved in the Early Suppression of Host Immune Response. Insects 2022, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.; Chaslus-Dancla, E. Use of Antimicrobials in Veterinary Medicine and Mechanisms of Resistance. Vet. Res. 2001, 32, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calza, L. Principi Di Malattie Infettive; Esculapio Medicina; Esculapio: Bologna, Italy, 2022; ISBN 9788893852944. [Google Scholar]
- Bassetti, M.; Righi, E. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria: What Is the Threat? Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2013, 2013, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, Y.J.; Romanowski, E.G.; McDermott, A.M. A Review of Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Therapeutic Potential as Anti-Infective Drugs. Curr. Eye Res. 2005, 30, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Su, Z. Overview on the Recent Study of Antimicrobial Peptides: Origins, Functions, Relative Mechanisms and Application. Peptides 2012, 37, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, W.K.K.; Gallo, R.L.; Fang, E.F.; Hu, W.; Ling, T.K.W.; Shen, J.; Chan, R.L.Y.; Lu, L.; Luo, X.M.; et al. Critical Role of Antimicrobial Peptide Cathelicidin for Controlling Helicobacter pylori Survival and Infection. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 1799–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, I.F.; Maller, A.; de Cássia Garcia Simão, R.; Kadowaki, M.K.; Angeli Alves, L.F.; Huergo, L.F.; da Conceição Silva, J.L. Proteomic Profile of Hemolymph and Detection of Induced Antimicrobial Peptides in Response to Microbial Challenge in Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Luo, H.; Ramakrishna, S. Harvesting of Antimicrobial Peptides from Insect (Hermetia illucens) and Its Applications in the Food Packaging. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Moll, L.; De Smet, J.; Paas, A.; Tegtmeier, D.; Vilcinskas, A.; Cos, P.; Van Campenhout, L. In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptides from the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) against a Selection of Human Pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0166421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Mu, L.; Wang, Y.; Bian, H.; Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, T.; Lv, J.; Feng, C.; et al. Purification and characterization of a novel defensin from the salivary glands of the black fly, Simulium bannaense. Parasit Vectors. 2015, 4, 8–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.-S.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Bang, H.-S.; Yun, E.-Y.; Kim, S.-R.; Suh, H.-J.; Kang, B.-R.; Nam, S.-H.; Jeon, J.-P.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of a Defensin-Like Peptide (Coprisin) from the Dung Beetle, Copris tripartitus. Int. J. Pept. 2009, 2009, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimarcq, J.L.; Zachary, D.; Hoffmann, J.A.; Hoffmann, D.; Reichhart, J.M. Insect Immunity: Expression of the Two Major Inducible Antibacterial Peptides, Defensin and Diptericin, in Phormia terranovae. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 2507–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liao, M.; Ueda, M.; Gong, H.; Xuan, X.; Fujisaki, K. Sequence Characterization and Expression Patterns of Two Defensin-like Antimicrobial Peptides from the Tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Peptides 2007, 28, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, N.; Chen, M.; Zhao, H.; An, J. Structural and Functional Analysis of PGRP-LC Indicates Exclusive Dap-Type PGN Binding in Bumblebees. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, E.R.; Chadee, K. Antimicrobial Human β-Defensins in the Colon and Their Role in Infectious and Non-Infectious Diseases. Pathogens 2013, 2, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, M.; Bugli, S.; Saltini, S.; Genedani, S.; Ottaviani, E. Molecular Characterization of a Defensin in the IZD-MB-0503 Cell Line Derived from Immunocytes of the Insect Mamestra brassicae (Lepidoptera). Biol. Cell. 2003, 95, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cheng, T.; Ye, M.; Deng, X.; Yi, H.; Huang, Y.; Tan, X.; Han, D.; Wang, B.; Xiang, Z.; et al. Functional Divergence among Silkworm Antimicrobial Peptide Paralogs by the Activities of Recombinant Proteins and the Induced Expression Profiles. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 18109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayamani, E.; Rajamuthiah, R.; Larkins-Ford, J.; Fuchs, B.B.; Conery, A.L.; Vilcinskas, A.; Ausubel, F.M.; Mylonakisa, E. Insect-Derived Cecropins Display Activity against Acinetobacter baumannii in a Whole-Animal High-Throughput Caenorhabditis elegans Model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro Segovia, L.J.; Téllez Ramírez, G.A.; Henao Arias, D.C.; Rivera Duran, J.D.; Bedoya, J.P.; Castaño Osorio, J.C. Identification and Characterization of Novel Cecropins from the Oxysternon conspicillatum Neotropic Dung Beetle. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 187914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.M.; Kusakabe, T.; Lee, J.M.; Tatsuke, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kang, M.W.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, K.A.; Nho, S.K. Structure and Expression Analysis of the Cecropin-E Gene from the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 1992–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, N.; Paquette, N.; Aggarwal, K. Specificity and Signaling in the Drosophila Immune Response. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2009, 6, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Kleino, A.; Silverman, N. The Drosophila IMD Pathway in the Activation of the Humoral Immune Response. Dev.Comp. Immunol. 2014, 42, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, P.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Cytryńska, M. A different repertoire of Galleria mellonella antimicrobial peptides in larvae challenged with bacteria and fungi. Develop. Compar. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastore, M.; Binda Rossetti, S.; Giovannardi, S.; Scarì, G.; Brivio, M.F. Inducible Factors with Antimicrobial Activity after Immune Challenge in the Haemolymph of Red Palm Weevil (Insecta). Innate Immun. 2015, 21, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghashree, R.N.; Nagaraj, K. Characterization of the Immune Induced Antimicrobial Peptide in Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila ananassae. EJE 2021, 118, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basseri, H.R.; Dadi-Khoen, A.; Bakhtiari, R.; Abolhassani, M.; Hajihosseini-Baghdadabadi, R. Isolation and Purification of an Antibacterial Protein from Immune Induced Hemolymph of American Cockroach, Periplaneta americana. J Arthropod-Borne Dis. 2016, 10, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Auza, F.A.; Purwanti, S.; Syamsu, J.A.; Natsir, A. Antibacterial Activities of Black Soldier Flies (Hermetia illucens. l) Extract towards the Growth of Salmonella typhimurium, E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 492, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Yun, E.Y.; Goo, T.W. Antimicrobial Activity of an Extract of Hermetia illucens Larvae Immunized with Lactobacillus casei against Salmonella Species. Insects. 2020, 11, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Uninfected Larvae | Larvae Infected with E. coli | Larvae Infected with M. flavus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation with organic solvents | 0.583 ± 0.02 µg/µL | 0.739 ± 0.07 µg/µL | 0.930 ± 0.03 µg/µL |
| Uninfected Larvae | Larvae Infected with E. coli | Larvae Infected with M. flavus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | 6.67 ± 1.2 aA | 8.67 ± 0.3 aA | 8.00 ± 0.5 aA |
| M. flavus | 6.33 ± 0.3 bA | 8.00 ± 0.6 aA | 9.67 ±0.3 aA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scieuzo, C.; Giglio, F.; Rinaldi, R.; Lekka, M.E.; Cozzolino, F.; Monaco, V.; Monti, M.; Salvia, R.; Falabella, P. In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of the Peptide Fractions Extracted from the Hemolymph of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Insects 2023, 14, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14050464
Scieuzo C, Giglio F, Rinaldi R, Lekka ME, Cozzolino F, Monaco V, Monti M, Salvia R, Falabella P. In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of the Peptide Fractions Extracted from the Hemolymph of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Insects. 2023; 14(5):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14050464
Chicago/Turabian StyleScieuzo, Carmen, Fabiana Giglio, Roberta Rinaldi, Marilena E. Lekka, Flora Cozzolino, Vittoria Monaco, Maria Monti, Rosanna Salvia, and Patrizia Falabella. 2023. "In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of the Peptide Fractions Extracted from the Hemolymph of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae)" Insects 14, no. 5: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14050464
APA StyleScieuzo, C., Giglio, F., Rinaldi, R., Lekka, M. E., Cozzolino, F., Monaco, V., Monti, M., Salvia, R., & Falabella, P. (2023). In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of the Peptide Fractions Extracted from the Hemolymph of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Insects, 14(5), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14050464