Combining Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Cooling-Heating Curve Thermal Analysis to Study the Melting and Solidification Behavior of Al-Ce Binary Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Al-Ce Phase Diagram and Location of Tested Alloys
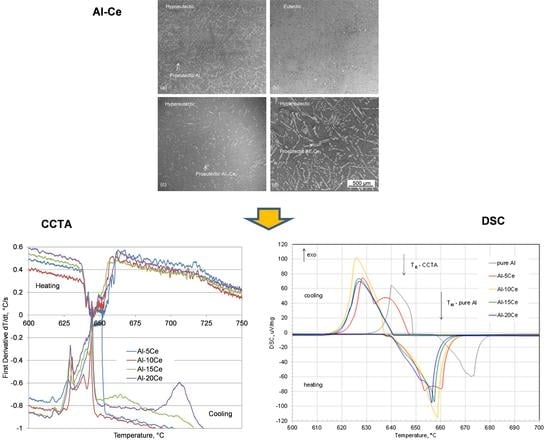
3.2. Solidification Microstructure: Effect of Ce Content
3.3. Eutectic Transformation and Product Morphology
3.4. Cooling/Heating Curves Thermal Analysis
3.4.1. Effect of Ce Content on Alloy Melting and Solidification Characteristics
3.4.2. Fraction Solid and Solidification Pathways
3.4.3. Melting Versus Solidification Characteristics
3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.5.1. Methodology of DSC Peaks Interpretation
3.5.2. Testing Reproducibility and Critical Temperatures for Al-Ce Alloys
3.6. Comparison of DSC and CCTA Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mikhail, S.; Webster, H. Thermal Analysis in Metallurgy. In Handbook of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry; Brown, M.E., Gallagher, P.K., Eds.; Elsevier B.V.: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolowski, J.; Kierkus, W.; Kasprzak, M.; Kasprzak, W. Method and Apparatus for Universal Metallurgical Simulation and Analysis. U.S. Patent 7,354,491 B2, 8 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lukas, K.; LeMaire, P.K. Differential scanning calorimetry: Fundamental overview. Resonance 2009, 14, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, F. Cerium in aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 24–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, F.; Amirkhiz, B.S. On the Al-Al11Ce3 eutectic transformation in aluminum-cerium binary alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Rollet, A.; Widom, M. Lattice stability of aluminum-rare earth binary systems: A first-principles approach. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 174120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, H. Al-Ce (Aluminum-Cerium). J. Phase. Equilib. Diff. 2011, 32, 392–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Al-Ce (Aluminum-Cerium). J. Phase Equilibria 1998, 19, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.; Verkande, M. Selected Cerium Phase Diagrams; Rare Earth Information Center, Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Drits, M.; Kadaner, E.; Shoa, N. Solid solubility of rare earth metals in aluminum. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1969, 1, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, D.; Rios, O.; Sims, Z. Casting characteristics of high cerium content aluminum alloys. In Light Metals 2017; LLNL-JRNL-738126; Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Marchwica, P.; Sokolowski, J.; Kierkus, W. Fraction solid evolution characteristics of AlSiCu alloys-dynamic baseline approach. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2011, 47, 115–236. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Chen, R.; Blandin, J.; Suery, M.; Han, E. Thermal analysis and solidification pathways of Mg–Al–Ca system alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 480, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettinger, W.; Kattner, U.; Moon, K.; Perepezko, J. DTA and Heat-Flux DSC Measurements of Alloy Melting and Freezing; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Czerwinski, F. Thermal stability of aluminum alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerwinski, F. Assessing differences between the use of cerium and scandium in aluminum alloying. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, O. Die Erhohung der chemischen Widerstandsfahigkeit mechanisch noch gut bearbeitbarer, fur Konstructionszwecke verwendbarer Legierungen; Teil II: Uber den Einfluss des Cers auf die mechanischen und chemischen Eigenschaften des Aluminiums (in German). Metall. Z. Gesamte Huttenkd. 1912, 8, 261–276. [Google Scholar]
- Gillett, H.; Schnee, V. Cerium in aluminum alloys. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1923, 15, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Kong, G.; Che, C.; Wang, Y.; Peng, H. Experimental investigation of eutectic point in Al-rich Al-La, Al-Ce, Al-Pr and Al-Nd systems. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzone, G.; Cacciamani, G.; Ferro, R. Heats of formation of aluminum-cerium intermetallic compounds. Metall. Trans. A 1991, 22, 2119–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Keita, M. Determination of the enthalpies of formation of intermetallic compounds of aluminium with cerium, erbium and gadolinium. J. Less-Common Met. 1987, 136, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatkowski, J.; Przeligorz, R.; Gontarczyk, A. The study of phase transformations of AlSi9Cu3 Alloy by DSC method. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2016, 16, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piatkowski, J.; Przeligorz, R.; Szymszal, J. The application of ATD and DSC methods to study of the EN AC-48000 alloy phase transformation. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2017, 17, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












| Alloy | Measure | Al-5Ce | Al-10Ce | Al-15Ce | Al-20Ce |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce | wt. % | 5.21 | 10.61 | 15.80 | 20.76 |
| at. % converted | 1.05 | 2.23 | 3.49 | 4.80 | |
| Trace elements | wt. % | Si 0.016–0.056; Mg 0.019–0.110; Ni 0.013–0.072; Ti 0.038 max, Mn 0.019 max; Cu 0.006 max. | |||
| Alloy | Liquidus, °C | Solidus/Eutectic, °C | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating | Cooling | Heating | Cooling | |||||
| TL | TL | TE | Tf | TE | Tf | |||
| Al-5Ce | 652.4 | - | 651.5 | - | 644.2 | 653.5 | 644.1 | 617.4 |
| Al-10Ce | The same as solidus | 645.6 | 652.8 | 645.0 | 617.0 | |||
| Al-15Ce | * | - | 742.1 | - | 644.2 | 650.4 | 645.2 | 618.8 |
| Al-20Ce | * | - | 791.2 | - | 645.1 | 653.5 | 644.9 | 617.2 |
| Alloy | Liquidus, °C | Solidus/Eutectic, °C | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating | Cooling | Heating | Cooling | |||||
| Onset | End | Onset | End | Onset | End | Onset | End | |
| Al-5Ce | * | * | 652.5 | * | 641.4 | 662.3 | 637.5 | 621.4 |
| Al-10Ce | The same as solidus | 639.1 | 661.2 | 640.5 | 621.2 | |||
| Al-15Ce | 743.3 | 747.6 | 726.4 | 708.6 | 638.7 | 658.2 | 641.5 | 621.3 |
| Al-20Ce | 794.1 | 801.2 | 774.3 | 762.4 | 642.1 | 658.6 | 641.0 | 620.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aniolek, M.; Smith, T.; Czerwinski, F. Combining Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Cooling-Heating Curve Thermal Analysis to Study the Melting and Solidification Behavior of Al-Ce Binary Alloys. Metals 2021, 11, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020372
Aniolek M, Smith T, Czerwinski F. Combining Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Cooling-Heating Curve Thermal Analysis to Study the Melting and Solidification Behavior of Al-Ce Binary Alloys. Metals. 2021; 11(2):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020372
Chicago/Turabian StyleAniolek, Marta, Tyler Smith, and Frank Czerwinski. 2021. "Combining Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Cooling-Heating Curve Thermal Analysis to Study the Melting and Solidification Behavior of Al-Ce Binary Alloys" Metals 11, no. 2: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020372
APA StyleAniolek, M., Smith, T., & Czerwinski, F. (2021). Combining Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Cooling-Heating Curve Thermal Analysis to Study the Melting and Solidification Behavior of Al-Ce Binary Alloys. Metals, 11(2), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020372