A Novel Reticular Retained Austenite on the Weld Fusion Line of Low Carbon Martensitic Stainless Steel 06Cr13Ni4Mo and the Influence on the Mechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results
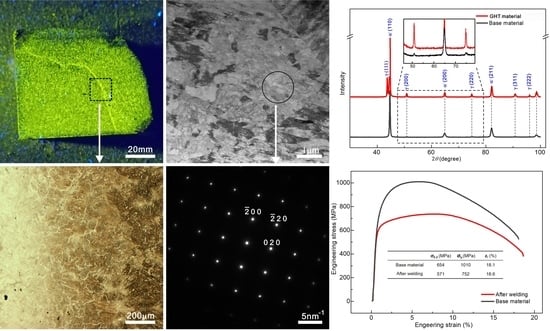
3.1. Microstructures of the Fusion Line
3.2. Mechanical Properties after Welding
3.3. Microstructures of the Roasted Blocks
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Reticular Austenite
4.2. Formation Mechanism of Reticular Austenite
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The reticular phase on the weld fusion line was induced by the thermal effect of welding on the base metal. It is one kind of retained austenite.
- (2)
- Due to its non-ferromagnetic nature, reticular austenite induces FMPI on the weld fusion line of 06Cr13Ni4Mo.
- (3)
- Though reticular retained austenite decreases the mechanical properties of the welding-repaired zone, the yield strength σ0.2, tensile strength σb, elongation to failure εf, and microhardness of the welding joint are 571 MPa, 752 MPa, 18.6%, and 279 MPa, respectively, and still exceed the required values in related standard specifications.
- (4)
- 06Cr13Ni4Mo welding-repaired zones showing FMPI induced by reticular retained austenite should not be judged to be unqualified. This special case of reticular retained austenite-induced FMPI should be taken into consideration when performing FMPT on 06Cr13Ni4Mo welding-repaired zones.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- dos Santos Fernandes, M.C.; Nakamatsu, S.; De Rezende, S.C.; Maestrelli, S.C.; de Sousa, L.L.; Mariano, N.A. Tempering Temperature Influence on 13Cr4Ni0.02C Steel Corrosion Resistance. Mater. Res.-Ibero-Am. J. Mater. 2017, 20, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-T.; Liu, F.-M.; Hou, W.-H. Application and Characteristics of Low-Carbon Martensitic Stainless Steels on Turbine Blades. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Zhang, Z. Advanced manufacturing tethnologies of large martensitic stainless steel castings with ultra low carbon and high cleanliness. China Foundry 2010, 7, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Cui, J.; Rong, L. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 06Cr13Ni4Mo Steel Treated by Quenching–Tempering–Partitioning Process. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S.E.a.T. Commission. JB/T10384 Steel Castings for Water Passage Components of Small and Medium Sized Hydraulic Turbines; S.E.a.T. Commission: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- A.S.f.T.a. Materials, ASTM A743/A743M; Standard Specification for Castings, Iron-Chromium, Iron- Chromium-Nickel, Corrosion Resistant, for General Applications. ASTM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013.
- De Sanctis, M.; Lovicu, G.; Buccioni, M.; Donato, A.; Richetta, M.; Varone, A. Study of 13Cr-4Ni-(Mo) (F6NM) Steel Grade Heat Treatment for Maximum Hardness Control in Industrial Heats. Metals 2017, 7, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, S.; Xiao, N.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Effect of delta ferrite on impact properties of low carbon 13Cr–4Ni martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2010, 527, 3210–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Lu, S.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Phase Transformation during Intercritical Tempering with High Heating Rate in a Fe-13%Cr-4%Ni-Mo Stainless Steel. Acta Met. Sin.-Engl. Lett. 2013, 26, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burja, J.; Šuler, B.; Češnjaj, M.; Nagode, A. Effect of Intercritical Annealing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 0.1C-13Cr-3Ni Martensitic Stainless Steel. Metals 2021, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, K.C.; Vaz, C.T. Influence of Temperature and Time of the Double-stage Tempering Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of the Weld Metal 13% Cr, 4% Ni and 0.4% Mo. Soldag. Insp. 2020, 25, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, K.-S.; Park, C.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, K.-W. Weldability of Low-Carbon ASTM A356 CA6NM Martensitic Stainless Steel Casting for Power Plants. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2011, 49, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, F.; Apel, D.; Danoix, F.; Hald, J.; Somers, M. Evolution of substructure in low-interstitial martensitic stainless steel during tempering. Mater. Charact. 2020, 167, 110494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, F. Austenite reversion in low-carbon martensitic stainless steels—A CALPHAD-assisted review. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meimandi, S.; Vanderesse, N.; Thibault, D.; Bocher, P.; Viens, M. Macro-defects characterization in cast CA-6NM martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2017, 124, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenni, B.; Society, A.W.; Brochu, M.; Godin, S.; Thibault, D. Shielding Gas and Inclusion Content Effects on Impact Toughness and Tensile Properties of 410NiMo Steel Welds. Weld. J. 2021, 100, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafan, S.; Wanjara, P.; Gholipour, J.; Champliaud, H.; Mathieu, L. Mehanical Properties of Electron Beam Welded Joints in Thick Gage CA6NM Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 4768–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirakhorli, F.; Cao, X.; Pham, X.-T.; Wanjara, P.; Fihey, J. Phase structures and morphologies of tempered CA6NM stainless steel welded by hybrid laser-arc process. Mater. Charact. 2017, 123, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirakhorli, F.; Cao, X.; Pham, X.-T.; Wanjara, P.; Fihey, J.-L. Post-weld Tempered Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Laser-Arc Welded Cast Martensitic Stainless Steel CA6NM. Met. Mater. Trans. B-Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2016, 47, 3245–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, M.A. Nondestructive Testing Methods and New Applications; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zolfaghari, A.; Kolahan, F. Reliability and sensitivity of magnetic particle nondestructive testing in detecting the surface cracks of welded components. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2018, 33, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Cai, X.; Kang, Y. Investigation on the Formation Mechanism of Crack Indications and the Influences of Related Parameters in Magnetic Particle Inspection. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 9444; Magnetic Particle Testing for Steel Castings. N.s. Administration: Beijing, China, 2007.
- A.S.f.T.a. Materials, ASTM E 125; Standard Reference Photographs for Magnetic Particle Indications on Ferrous Castings. ASTM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008.
- A.S.f.T.a. Materials, ASTM E709; Standard Guide for Magnetic Particle Testing. Astm: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015.
- Sanghani, V.; Mody, A.; Pradhan, D.; Patel, P. Non destructive examination for detection and evaluation of defects in plant equipments: A study. Non-Destr. Test. 1992, 92, 466–470. [Google Scholar]
- Mirakhorli, F.; Cao, X.; Pham, X.-T.; Wanjara, P.; Fihey, J.-L. Hybrid Laser-Arc Welding of 10-mm-Thick Cast Martensitic Stainless Steel CA6NM: As-Welded Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Met. Mater. Trans. A-Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2016, 47, 3545–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Shen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Park, J.M.; Choi, Y.T.; Schell, N.; Maawad, E.; Zhou, N.; Kim, H.S. Dissimilar laser welding of a CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy to 316 stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 2021, 206, 114219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Shen, J.; Escobar, J.; Salvador, C.; Schell, N.; Zhou, N.; Benafan, O. Laser welding of H-phase strengthened Ni-rich NiTi-20Zr high temperature shape memory alloy. Mater. Des. 2021, 202, 109533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Rong, L.; Li, Y. Anomalous Phase Transformation from Martensite to Austenite in Fe-13%Cr-4%Ni-Mo Martensitic Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Rong, L.; Ping, D.; Yin, F.; Li, Y. Formation of the reversed austenite during intercritical tempering in a Fe–13%Cr–4%Ni–Mo martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1411–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, S.P.; Li, D.Z.; Li, Y.Y. Investigation on the phase tranformation of low carbon martensitic stainless steel 06Cr13Ni4Mo in tempering process with low heating rate. Acta Metall. Sin. 2008, 44, 681–685. [Google Scholar]
- De, A.K.; Murdock, D.C.; Mataya, M.C.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K. Quantitative measurement of deformation-induced martensite in 304 stainless steel by X-ray diffraction. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Clouston, S. Optimizing magnetic flux- leakage inspection sizing model performance using high- resolution non-destructive examination data. J. Pipeline Eng. 2012, 11, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Rong, L.; Li, Y. The influence of tempering temperature on the reversed austenite formation and tensile properties in Fe–13%Cr–4%Ni–Mo low carbon martensite stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2011, 528, 4075–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, N.; Tsuchiyama, T.; Takaki, S.; Miyano, N. Temperature Dependence of Austenite Nucleation Behavior from Lath Martensite. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Element | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | Cu | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt.%) | 0.07 | 0.88 | 0.63 | 0.011 | 0.008 | 12.4 | 4.1 | 0.58 | 0.28 | 0.13 |
| Process Parameter | Value | Process Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preheat Temperature | 120 °C | Interpass Temperature | 180 °C |
| Voltage | 30 V | Welding wire | 410 NiMo |
| Current | 240 A | Shielding gas | 95% Ar + 5% CO2 |
| Travel speeding | 300 mm/min | Position of groove | Flat |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, F.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Long, J. A Novel Reticular Retained Austenite on the Weld Fusion Line of Low Carbon Martensitic Stainless Steel 06Cr13Ni4Mo and the Influence on the Mechanical Properties. Metals 2022, 12, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030432
Peng F, Feng Z, Zhao Y, Long J. A Novel Reticular Retained Austenite on the Weld Fusion Line of Low Carbon Martensitic Stainless Steel 06Cr13Ni4Mo and the Influence on the Mechanical Properties. Metals. 2022; 12(3):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030432
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Fan, Zhourong Feng, Yu Zhao, and Jianzhou Long. 2022. "A Novel Reticular Retained Austenite on the Weld Fusion Line of Low Carbon Martensitic Stainless Steel 06Cr13Ni4Mo and the Influence on the Mechanical Properties" Metals 12, no. 3: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030432
APA StylePeng, F., Feng, Z., Zhao, Y., & Long, J. (2022). A Novel Reticular Retained Austenite on the Weld Fusion Line of Low Carbon Martensitic Stainless Steel 06Cr13Ni4Mo and the Influence on the Mechanical Properties. Metals, 12(3), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030432