Review on the Recent Development of Fatty Hydrazide as Corrosion Inhibitor in Acidic Medium: Experimental and Theoretical Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Selection and Mechanism of Corrosion Inhibitors
3. Organic Corrosion Inhibitors
4. Fatty Hydrazides Derivatives as Effective Corrosion Inhibitors
5. Molecular Modelling Study on Corrosion Inhibitors
5.1. Understanding the Basic Molecular Modelling on Corrosion Inhibitor
5.2. Parameter Derived from the Molecular Modelling Study on the Corrosion Inhibitor
5.3. Recent Studies of Molecular Modelling on Corrosion Inhibition Application
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popoola, L.T.; Grema, A.S.; Latinwo, G.K.; Gutti, B.; Balogun, A.S. Corrosion problems during oil and gas production and its mitigation. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2013, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, J.; Wang, Z. Corrosion Failure Mechanism of Associated Gas Transmission Pipeline. Materials 2018, 11, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kahyarian, A.; Achour, M.; Nesic, S. “7—CO2 corrosion of mild steel”. In Trends in Oil and Gas Corrosion Research and Technologies; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 149–190. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Janabi, Y.T. “An Overview of Corrosion in Oil and Gas Industry: Upstream, Midstream, and Downstream Sectors”. In Corrosion Inhibitors in the Oil and Gas Industry; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- West, J.M. Basic Corrosion and Oxidation; Halsted Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Shetty, P. Hydrazide Derivatives: An Overview of Their Inhibition Activity against Acid Corrosion of Mild Stee. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2018, 71, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegbite, M.A. Flow Accelerated Preferential Weld Corrosion of X65 Steel in Brine Containing Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen. Doctoral Dissertation, School of Applied Sciences, Cranfield University, Cranfield, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mansfeld, F. Corrosion Mechanisms; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, A.S. Introduction to High Temperature Oxidation and Corrosion; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Olajire, A.A. Corrosion Inhibition of Offshore Oil and Gas Production Facilities Using Organic Compound Inhibitors—A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 248, 775–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, G. Corrosion Inhibitors; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mayout, A.M.; Al-Suhybani, A.A.; Al-Ameery, A.K. Corrosion inhibition of 304SS in sulfuric acid solutions by 2-methyl benzoazole derivatives. Desalination 1998, 116, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas, J.M.; Polo, J.L.; Cano, E.; Tôrres, C.L.; Díaz, E.C. Tributylamine as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 2637–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borden, K. Corrosion Monitoring and Mitigation Technologies. Oil Gas Facil. 2015, 6, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitha Rani, B.E.; Basu, B.B.J. Green Inhibitors for Corrosion Protection of Metals and Alloys: An Overview. Int. J. Corros. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Jafari, R.; Hamghalam, P.; Hajizadeh, A. Downhole corrosion inhibitors for oil and gas production—A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 6, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quraishi, M.A.; Chauhan, D.S.; Ansari, F.A. Development of environmentally benign corrosion inhibitors for organic acid environments for oil-gas industry. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z. A Review of Corrosion Inhibitors for Rust Preventative Fluids. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2019, 23, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.A. Molecular structural aspects of organic corrosion inhibitors: Experimental and computational insights. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1227, 129374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughoues, Y.; Benamira, M.; Messaadia, L.; Bouider, N.; Abdelaziz, S. Experimental and theoretical investigations of four amine derivatives as effective corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in HCl medium. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 24145–24158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandana, S.; Yadav, M.; Obot, I.B. Investigations on Eco-friendly Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Acid Environment: Electrochemical, DFT and Monte Carlo Simulation Approach. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 599, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Kadhum, A.; Al-Amiery, A.A.H.; Al-Azawi, R.J.; Abbas, R.H. Corrosion Inhibitors. A Review. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2021, 10, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Reza, N.A.; Akhmal, N.H.; Fadil, N.A.; Taib, M.F.M. A Review on Plants and Biomass Wastes as Organic Green Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Acidic Environment. Metals 2021, 11, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.M. Role of Organic and Eco-Friendly Inhibitors on the Corrosion Mitigation of Steel in Acidic Environments—A State-of-Art Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Ebenso, E.; Quraishi, M. Molecular structural aspects of organic corrosion inhibitors: Influence of –CN and –NO2 substituents on designing of potential corrosion inhibitors for aqueous media. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 316, 113874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.K.; Dewangan, Y.; Dewangan, A.K.; Asatkar, A. Heteroatom-Based Compounds as Sustainable Corrosion Inhibitors: An Overview. J. Bio Tribo-Corros. 2021, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthamma, K.; Kumari, P.; Lavanya, M.; Rao, S.A. Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in Acidic Media by N-[(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)Methyleneamino]-4-Hydroxy-Benzamide. J. Bio. Tribo-Corros. 2020, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, B.; Zhang, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, S. Synthesized carbon dots with high N and S content as excellent corrosion inhibitors for copper in sulfuric acid solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amiery, A.A.; Mohamad, A.B.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Shaker, L.M.; Wan Isahak, W.N.R.; Takriff, M.S. Experimental and Theoretical Study on the Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel by nanonedioic Acid Derivatives in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, A.E.-A.S.; El-Maksoud, S.A.A.; El-Sayed, E.H.; Elbaz, H.A.; Abousalem, A.S. Experimental and surface morphological studies of corrosion inhibition on carbon steel in HCl solution using some new hydrazide derivatives. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 13497–13512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar Singh, D.; Behera, D.; Singh, M.K.; Udayabhanu, G.; John, R.P. Investigation on Adsorption and the Corrosion Inhibition Effect of Some Novel Hydrazide Derivatives for Mild Steel in HCl Solution. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 5132–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Singh, D.; Ebenso, E.E.; Singh, M.K.; Behera, D.; Udayabhanu, G.; John, R.P. Non-Toxic Schiff Bases as Efficient Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in 1M HCl: Electrochemical, AFM, FE-SEM and Theoretical Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 250, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitra, T.K.; Mohana, K.N.; Tandon, H.C. Evaluation of Newly Synthesized Hydrazones as Mild Steel Corrosion Inhibitors by Adsorption, Electrochemical, Quantum Chemical and Morphological Studies. Arab J. Basic App. Sci. 2018, 25, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichchou, I.; Larabi, L.; Rouabhi, H.; Harek, Y.; Fellah, A. Electrochemical evaluation and DFT calculations of aromatic sulfonohydrazides as corrosion inhibitors for XC38 carbon steel in acidic media. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1198, 126898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, N.; Singh, A.K.; Chugh, B.; Akram, M.; Perveen, F.; Rasheed, I.; Altaf, F.; Pervaiz, A.C.; Saeed, A. Experimental, theoretical, and surface study for corrosion inhibition of mild steel in 1 M HCl by using synthetic anti-biotic derivatives. Ionics 2019, 25, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd, N.K.; Yeong, S.K.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Mohd Nor, S.M.; Chan, C.H.; Tang, S.W.; Lim, W.H.; Idris, Z. Corrosion Inhibitors, Adsorption Behaviour and Thermodynamics Properties of N-Cinnamalidene Palmitohydrazide on Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. J. Oil Palm Res. 2019, 32, 124–138. [Google Scholar]
- El Basiony, N.; Badr, E.E.; Baker, S.A.; El-Tabei, A. Experimental and theoretical (DFT&MC) studies for the adsorption of the synthesized Gemini cationic surfactant based on hydrazide moiety as X-65 steel acid corrosion inhibitor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 539, 148246. [Google Scholar]
- Chaouiki, A.; Chafiq, M.; Lgaz, H.; Al-Hadeethi, M.R.; Ali, I.H.; Masroor, S.; Chung, I.M. Green Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel by Hydrazone Derivatives in 1.0 M HCl. Coatings 2020, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Hameed, R.S.; Aljuhani, E.; Al-Bagawi, A.H.; Abdallah, M. Study of Sulfanyl Pyridazine Derivatives as Efficient Corrosion Inhibitors for Carbon Steel in 1.0 M HCl Using Analytical Techniques. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2020, 9, 623–643. [Google Scholar]
- Preethi Kumari, P.; Shetty, P.; Rao, S.A.; Sunil, D.; Vishwanath, T. Synthesis, characterization and anticorrosion behaviour of a novel hydrazide derivative on mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2020, 43, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, D.; Kumari, P.P.; Rao, S.A.; Shetty, P. Anticorrosion Behaviour of a Hydrazide Derivative on 6061 Al-15%(v) SiC(P) Composite in Acid Medium: Experimental and Theoretical Calculations. J. Bio. Tribo-Corros. 2020, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laggoun, R.; Ferhat, M.; Saidat, B.; Benghia, A.; Chaabani, َA. Effect of P-Toluenesulfonyl Hydrazide on Copper Corrosion in Hydrochloric Acid Solution. Corros. Sci. 2019, 165, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, T.S.; Arya, S.B.; Thippeswamy, L.R.; Quraishi, M.A.; Haque, J. Influence of Green Inhibitor on Flow-Accelerated Corrosion of API X70 Line Pipe Steel in Synthetic Oilfield Water. Int. J. Corros. Process. Corros. Cont. 2020, 55, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baghdadi, S.B.; Al-Amiery, A.A.; Gaaz, T.S.; Kadhum, A.A.H. Terephthalohydrazide and Isophthalohydrazide as New Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid: Experimental and Theoretical Approaches. Koroze Ochr. 2021, 65, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.E.S.; Abd El-Maksoud, S.A.; El-Sayed, E.H.; Elbaz, H.A.; Abousalem, A.S. Effectiveness of Some Novel Heterocyclic Compounds as Corrosion Inhibitors for Carbon Steel in 1 M HCl Using Practical and Theoretical Methods. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 19294–19309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Sherif, E.M.; Abdo, H.S.; Gad, E.S. Ethanedihydrazide as a Corrosion Inhibitor for Iron in 3.5% NaCl Solutions. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 14525–14532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Singh, A.; Chugh, B.; Singh, M.; Thakur, S.; Pani, B.; Guo, L.; Kaya, S.; Serdaroglu, G. Hydroxy Phenyl Hydrazides and Their Role as Corrosion Impeding Agent: A Detail Experimental and Theoretical Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 330, 115605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanov, R.; Bilge, S.; Bilgiç, S.; Gece, G.; Kılıç, Z. Experimental and Theoretical Calculations on Corrosion Inhibition of Steel in 1 M H2SO4 by Crown Type Polyethers. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshi, E.; Ramezanzadeh, M.; Bahlakeh, G.; Ramezanzadeh, B.; Mahdavian, M.; Motamedi, M. Glycyrrhiza Glabra Leaves Extract As a Green Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in 1 M Hydrochloric Acid Solution: Experimental, Molecular Dynamics, Monte Carlo and Quantum Mechanics Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 255, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Obot, I.B.; Bahadur, I.; Sherif, E.S.; Ebenso, E.E. Choline Based Ionic Liquids as Sustainable Corrosion Inhibitors on Mild Steel Surface in Acidic Medium: Gravimetric, Electrochemical, Surface Morphology, DFT, and Monte Carlo Simulation Studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Lateef, H.M.A. Experimental and Computational Investigation on the Corrosion Inhibition Characteristics of mild Steel by Some ovel Synthesized Imines in Hydrochloric Acid Solutions. Corros. Sci. 2015, 92, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, S.; He, Q.; Li, W. Theoretical Studies of Three Triazole Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Acidic Medium. Corros. Sci. 2014, 87, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, L.S.D.; Michelon, M.F.; Miranda, C.R. Molecular Dynamics Studies of Fluid/Oil Interfaces for Improved Oil Recovery Processes. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2012, 116, 14667–14676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Xie, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J. Effect of Surfactant Headgroups on the Oil/Water Interface: An Interfacial Tension Measurement and Simulation Study. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1052, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, N.I.N.; Sobri, S.; Yusof, Y.A.; Kassim, N.K. An Overview of Molecular Dynamic Simulation for Corrosion Inhibition of Ferrous Metals. Metals. 2021, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, P.A. Introduction to Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Comput. Soft Matter Synth. Polym. Proteins 2004, 23, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, N. Quantum Chemical Approach of Corrosion Inhibition. Electrochim. Acta. 2003, 48, 2635–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentis, F.; Traisnel, M.; Vezin, H.; Hildebrand, H.F.; Lagrenee, M. 2,5-Bis(4dimethylaminophenyl)- 1,3,4-oxadiazole and 2,5-bis(4 dimethylaminophenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole as Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Acidic Media. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 2781–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Tan, Y.; Chen, B.; Dong, J.; Wang, X. The Binding of Antiwear Additives to Iron Surfaces: Quantum Chemical Calculations and Tribological Tests. Tribol. Int. 2003, 36, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.B.; Obi-Egbedi, N.O. Theoretical Study of Benzimidazole and Its Derivatives and Their Potential Activity as Corrosion Inhibitors. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukovuts, I.; Klaman, E.; Zucchi, F. Corrosion Inhibitors—Correlation Between Electronic Structure and Efficiency. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, A. Adsorption Energy and Surface Energy Obtained through Slab Structure. Materials Square, 9 July 2021. [Online]. Available online: https://www.materialssquare.com/blog/10-adsorption-energy-and-surface-energy-obtained-through-slab-structure (accessed on 29 July 2021).
- Verma, C.; Lgaz, H.; Verma, D.K.; Ebenso, E.E.; Bahadur, I.; Quraishi, M.A. Molecular Dynamics and Monte Carlo Simulations as Powerful Tools for Study of Interfacial Adsorption Behavior of Corrosion Inhibitors in Aqueous Phase: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferkous, H.; Djellali, S.; Sahraoui, R.; Benguerba, Y.; Hamza, B.; Cukurovali, A. Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel by 2-(2-methoxybenzylidene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide in Hydrochloric Acid Solution: Experimental Measurements and Quantum Chemical Calculations. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 307, 112957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Lateef, H.M.A. Corrosion Inhibition Characteristics of a Novel Salycilidene Isatin Hydrazine T Sodium Sulfonate on Carbon Steel in HCL and a Synergistic Nickel Ions Additive: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Perspective. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 501, 144237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghiti, M.E.; Mihit, M.; Mahsoune, A.; Elmelouky, A.; Mghaiouini, R.; Barhoumi, A.; Dafali, A.; Bakasse, M.; el Mhammedi, M.A.; Abdennouri, M. Studies of Inhibition Effect “E & Z” Configurations of Hydrazide Derivatives on Mild Stell Surface in Phosphoiric Acid. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 6336–6353. [Google Scholar]
- Bouidina, A.; El-Hajjaji, F.; Drissi, M.; Taleb, M.; Hammouti, B.; Chung, I.M.; Jodeh, S.; Lgaz, H. Towards a Deeper Understanding of the Anticorrosive Properties of Hydrazine Derivatives in Acidic Medium: Experimental, DFT, and MD Simulation Assessment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 5180–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafiq, M.; Chaouiki, A.; Lgaz, H.; Salghi, R.; Gaonkar, S.L.; Bhat, K.S.; Marzouki, R.; Ali, I.H.; Khan, M.I.; Shimizu, H.; et al. Synthesis and Corrosion Inhibition Evaluation of a New Schiff Base Hydrozone for Mild Steel Corrosion in HCl Medium: Electrochemical, DFT, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies. J. Adhesi. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 1283–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





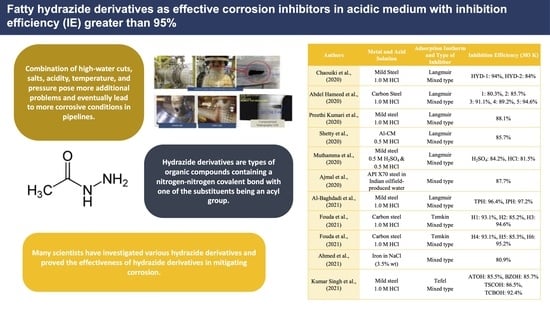
| Name of Corrosion Inhibitors | Metal and Acid Solution | Adsorption Isotherm and Type of Inhibitor | Inhibition Efficiency (303 K) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N’-(thiophene-2ylmethylene) nicotinic hydrazone (TNH) and N’-(pyrrol-2-ylmethylene) nicotinic hydrazone (PNH) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | TNH: IEw = 91.3% IEEIS = 94.7% PNH: IEw = 93.7% IEEIS = 96.4% | Kumar Singh et al., (2017) [31] |
| N’-(4-Hydroxybezylidene) nicotinic hydrazone (HBNH) and N’-(4-methylybezylidene) nicotinic hydrazone (MBNH) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | HBNH: IEw = 90.0% IEEIS = 95.5% MBNH: IEw = 94.2% IEEIS = 96.6% | Kumar Singh et al., (2018) [32] |
| 3-(cyano-dimethyl-methyl)-benzoic acid thiophen-2-ylmethylene-hydrazide (CBTH) and 3-(cyano-dimethyl-methyl)-benzoic acid furan-2-ylmethylene-hydrazide (CBFH) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | CBTH: IEEIS = 87.1% CBFH: IEEIS = 85.3% | Chaitra et al., (2018) [33] |
| N’-{(E)-[4-(dimethylamino) phenyl] methylidene} benzenesulfonohydrazide (MBSH), and N’-{(E)-[4(dimethylamino) phenyl] methylidene}-4-methylbenzenesulfonohydrazide (MpTSH) | XC38 Carbon Steel 1.0 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | MBSH: IEEIS = 91.9% MpTSH: IEEIS = 94.5% | Ichchou et al., (2019) [34] |
| (E)-N′-(4′-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene) isonicotino hydrazide (PA1), (E)-N′-(Pyridin-4′-ylmethylene) isonicotino hydrazide (PA2), and (E)-N′-(Pyridin-3′-ylmethylene) isonicotino hydrazide (PA3) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | PA1: IEEIS = 96.7% PA2: IEEIS = 81.1% PA3: IEEIS = 71.3% | Arshad et al., (2019) [35] |
| N-cinnamalidene palmitohydrazide (CPH) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | IEw = 88% IEEIS = 95% | Mohd et al., (2019) [36] |
| p-Toluenesulfonylhydrazide (p-TSH) | Copper Steel 0.5 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | IEw = 90.6% IEEIS = 93.0% | Laggoun et al., (2019) [42] |
| N,N’-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2-oxoethane-2,1-diyl)) bis (N,N-dimethyl-4-((E)-(2-((E)-octadec-9-enoyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl) benzenaminium) dichloride | X-65 Steel 1.0 M HCl | Freundlich | IEEIS = 94.7% | Basiony et al., (2020) [37] |
| Hydrazone propanehydrazide (HYD-1) and N-cyclohexylidene-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl) propanehydrazide (HYD-2) | Mild Steel 1.0 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | HYD-1: IEw = 95% IEEIS = 94% HYD-2: IEEIS = 84% | Chaouiki et al., (2020) [38] |
| (6-phenyl-pyridazin-3-ylsulfanyl)-acetic acid (1), (6-phenyl-pyridazin-3-ylsulfanyl)-acetic acid hydrazide (2), (6-Phenyl-pyridazin-3-ylsulfanyl)-acetic acid (2,4-dihydroxy-benzylidene)-hydrazide (3), (6-Phenyl-pyridazin-3-ylsulfanyl)-acetic acid (2-hydroxy-naphthalen-1-ylmethylene)-hydrazide compound (4) and (6-Phenyl-pyridazin-3-ylsulfanyl)-acetic acid (4-dimethylamino-benzylidene)-hydrazide (5) | Carbon Steel 1.0 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | 1: IEw = 83.3% IEEIS = 80.3% 2: IEw = 87.7% IEEIS = 85.7% 3: IEw = 94.2% IEEIS = 91.1% 4: IEw = 90.1% IEEIS = 89.2% 5: IEw = 91.5% IEEIS = 94.6% | Abdel Hameed et al., (2020) [39] |
| N′- [(4-methyl-1H-imidazole-5-yl) methylidene]-2-(naphthalen-2-yloxy) acetohydrazide (IMNH) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | IEw = 88.3% IEEIS = 88.1% | Preethi Kumari et al., (2020) [40] |
| 4-hydroxy-N′-[3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene] benzo- hydrazide (HBH) | Al-CM 0.5 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | IEw = 83.2% IEEIS = 85.7% | Shetty et al., (2020) [41] |
| N-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl) methyleneamino]-4-hydroxy-benzamide (DMHB) | Mild steel 0.5 M H2SO4 0.5 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | H2SO4: IEw = 86.6% IEEIS = 84.2% HCl: IEw = 81.5% IEEIS = 81.5% | Muthamma et al., (2020) [27] |
| Oleic acid hydrazide (OAH) | API X70 steel in Indian oilfield-produced water | Mixed type | IEEIS = 87.7% | Ajmal et al., (2020) [43] |
| Terephthalohydrazide (TPH), and Isophthalohydrazide (IPH) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | Langmuir Mixed type | TPH: IEw = 97.02% IEEIS = 96.4% IPH: IEw = 96.4% IEEIS = 97.2% | Al-Baghdadi et al., (2021) [44] |
| 8-Hydroxy-N’-((2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-2,3-dimethyl-8H-pyrimido [1,2-b][1,2,4]triazine-7-hydrazide (H1), N’-((2-Methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-8-oxo-4a,5-dihydro-8H-pyrimido [1,2-b][1,2,4]triazine-7-hydrazide (H2), and 6-Hydroxy-N’-((2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-2-oxo-2H-chromene-3-hydrazide (H3) | Carbon steel 1.0 M HCl | Temkin Mixed type | H1: IEw = 92.6% IEEIS = 93.1% H2: IEw = 85.3% IEEIS = 85.2% H3: IEw = 95.1% IEEIS = 94.6% | Fouda et al., (2021) [30] |
| 5-amino-N′-((2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)isoxazole-4-carbohydrazide (H4), 2,4-diamino-N′-((2-methoxy- naphthalene-1-yl)methylene)pyrimidine-5-carbohydrazide (H5) and N′-((2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-7,7-dimethyl-2,5-dioxo-4a,5,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-2H-chromene-3-carbohydrazide (H6) | Carbon steel 1.0 M HCl | Temkin Mixed type | H4: IEw = 88.3% IEEIS = 93.1% H5: IEw = 85.3% IEEIS = 85.3% H6: IEw = 95.1% IEEIS = 95.2% | Fouda et al., (2021) [45] |
| Ethanedihydrazide (EH) | Iron in NaCl (3.5% wt) | Mixed type | IEw = 87.4% IEEIS = 80.9% | Ahmed et al., (2021) [46] |
| N′-(1-(2-hydroxyphenyl) ethylidene) acetohydrazide (ATOH), N′-(1-(2-hydroxyphenyl) ethylidene) benzohydrazide (BZOH), 2-(1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene) hydrazine-1-carbothioamide (TSCOH) and N′-(1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene) hydrazinecarbothiohydrazide (TCBOH) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | Tefel Mixed type | ATOH: IEw = 85.5% IEEIS = 85.5% BZOH: IEw = 85.9% IEEIS = 85.7% TSCOH: IEw = 86.6% IEEIS = 86.5% TCBOH: IEw = 92.4% IEEIS = 92.4% | Kumar Singh et al., (2021) [47] |
| Structure | CS-H4 | CS-H5 | CS-H5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total energy | −244.22 | −267.41 | −246.99 |
| Adsorption energy | −321.15 | −291.12 | −323.92 |
| Rigid adsorption energy | −229.01 | −199.66 | −232.17 |
| Deformation energy | −92.14 | −94.46 | −91.75 |
| Inh: | −321.15 | −291.12 | −323.92 |
| Structure | CS-H4 | CS-H5 | CS-H5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total energy | −4019.83 | −4002.17 | −4028.35 |
| Adsorption energy | −4096.76 | −4025.88 | −4105.29 |
| Rigid adsorption energy | −4183.44 | −4107.05 | −4184.89 |
| Deformation energy | 86.68 | 81.17 | 79.60 |
| Inh: | −323.65 | −212.26 | −340.60 |
| −8.73 | −7.60 | −11.69 | |
| −151.74 | −154.70 | −147.92 | |
| Cl−: | −144.41 | −155.94 | −152.37 |
| Name of Corrosion Inhibitors | Metal and Acid Solution | DFT and MD Parameters | ΔE (eV) from DFT and Orientation and Eads (kJ/mol) from MD Simulation | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8-Hydroxy-N’-((2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-2,3-dimethyl-8H-pyrimido [1,2-b][1,2,4]triazine-7-hydrazide (H1), N’-((2-Methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-8-oxo-4a,5-dihydro-8H-pyrimido [1,2-b][1,2,4]triazine-7-hydrazide, and 6-Hydroxy-N’-((2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-2oxo-2H-chromene-3-hydrazide | Carbon steel 1.0 M HCl | DFT: Material studio Dmol6 DFT software, GGA basis set RPBE. MD: - | DFT: ΔE = 1.80274 (H1), 1.77942 (H2), 1.86997 (H3) MD: Planar orientation Eads = −218.075 (H1), −207.526 (H2), −221.927 (H3) | Fouda et al., (2021) [30] |
| 5-amino-N′-((2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)isoxazole-4-carbohydrazide (H4), 2,4-diamino-N′-((2-methoxy- naphthalene-1-yl)methylene)pyrimidine-5-carbohydrazide (H5), and N′-((2-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylene)-7,7-dimethyl-2,5-dioxo-4a,5,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-2H-chromene-3-carbohydrazide (H6) | Carbon steel 1.0 M HCl | DFT: Material studio Dmol6 DFT software, GGA basis set RPBE. MD: - | DFT: ΔE = 1.95288 (H1), 2.17013 (H2), 1.39953 (H3) MD: Planar orientation Eads = −321.14876 (H1), −291.1181 (H2), −323.92464 (H3) | Fouda et al., (2021) [45] |
| N,N’-((ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy))bis(2-oxoethane-2,1-diyl)) bis (N,N-dimethyl-4-((E)-(2-((E)-octadec-9-enoyl)hydrazineylidene)methyl) benzenaminium) dichloride | X-65 Steel 1.0 M HCl | DFT: Diatomic differential overlap (NDDO) Hamiltonian type in Material Studio 6.0 (MS 6.0). MD: Fe (110) (74.47, 74.47, 33.01) Å COMPASS. | DFT: ΔE = 6.026 MD: Planar orientation Eads = −1389.3 (without HCl solution), −14,074.3 (with HCl solution) | Basiony et al., (2020) [37] |
| 2-2(-methoxybenzylidene) hydrazine-1-carbothioamide (MBHCA) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | DFT: Dmol3 module in Material Studio 2017TM with DFT-B3LYP functional set. MD: Fe (001) (22.93, 22.93, 34.39) Å COMPASS | DFT: ΔE = 3.996 (Gas), 4.212 (Aqueous) MD: Planar orientation Eads = −1389.3 (without HCl solution), −14,074.3 (with HCl solution) | Ferkous et al., (2020) [64] |
| N′-(1-(2-hydroxyphenyl) ethylidene) acetohydrazide (ATOH), N′-(1-(2-hydroxyphenyl) ethylidene) benzohydrazide (BZOH), 2-(1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene) hydrazine-1-carbothioamide (TSCOH), and N′-(1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethylidene) hydrazinecarbothiohydrazide (TCBOH) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | DFT: 6–31 g(d,p), 6–311 + g(d,p) and 6–311 ++g(2df,2pd) basis set by G09W package. MD: Fe (110) (17.3, 17.3, 345.1) Å COMPASSII NVT | DFT: Aqueous- ΔE = 4.8883 (ATOH), 4.7084 (BZOH), 4.4706 (TSCOH), 4.3598 (TCBOH). MD: Planar orientation Eads = −473.1 (ATOH), −475.4 (BZOH), −475.4 (TSCOH), −477.9 (TCBOH). | Kumar Singh et al., (2021) [47] |
| 4-sodium sulfonate-2-hydroxy-3-(-((2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)hydrazineylidene)methyl)benzene sulfonate (SHMB), and Protonated 4-sodium sulfonate-2-hydroxy-3-(-((2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)hydrazineylidene)methyl)benzene sulfonate (SHMBH) | Carbon steel 1.0 M HCl | DFT: B3LYP combined with 6–31 + G(d,p) basis set using Gaussian 09. MD: Fe (110) (22, 26, 45) Å | DFT: ΔE = 0.13551 (SHMB), 0.1259 (SMHBH) MD: Planar orientation Eads = −123.451 (SMHB), −129.784 (SHMBH) | El-Lateef et al., (2020) [65] |
| Cis and Trans 1,2-bis(pyrrole-2-ylidenemethyl) hydrazine (HZ1), 1,2-bis(thiophene-2-ylidenemethyl) hydrazine (HZ2), and 1,2-bis(furyl-2-ylidenemethyl) hydrazine (HZ3), | Mild steel 2.0 M H3PO4 | DFT: B3LYP combined with 6–31 ++ G(2d,2p) basis set using Gaussian 09 W. MD: Fe (111) (35, 35, 40) Å COMPASS | DFT: ΔE = 3.7418 (HZ1(cis)), 3.7023 (HZ1(trans)), 3.6196 (HZ2(cis)), 3.7418 (HZ2(trans)), 3.6682 (HZ3(cis)), 3.6487 (HZ3(trans)) MD: Planar orientation Eads = −98.725 (HZ1(cis)), −74.845 (HZ1(trans)), −234.70 (HZ2(cis)), −163.263 (HZ2(trans)), −98.093 (HZ3(cis)), −96.274 (HZ3(trans)) | Belghiti et al., (2019) [66] |
| 1,2-dibenzyldenehydrazine (C1), and 1,2-bis(1-phenylethylidene) hydrazine (C2) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | DFT: Material Studio 6.0 at DFT/GGA level using BOP functional and DNP basis set. MD: Fe (110) (24.82, 24.82, 35.69) Å COMPASS NVT | DFT: ΔE = 2.836 (C1), 3.178 (C2) MD: Planar orientation Eads = −573.52 (C1), −407.06 (C2) | Bouidina et al., (2018) [67] |
| (E)-2-(4-(2-(methyl(pyridine-2-yl)amino)ethoxy)benzylidene)-hydrazine-1-carboxamide (MPAH) | Mild steel 1.0 M HCl | DFT: B3LYP combined with 6–31 + G(d,p) basis set using Gaussian 09. MD: Fe (110) (24.82, 24.82, 25.14) Å COMPASS NVT | DFT: ΔE = 2.394 MD: Planar orientation Eads = −476.29 | Chafiq et al., (2020) [68] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, A.; Numin, M.S.; Jumbri, K.; Kee, K.E.; Borhan, N. Review on the Recent Development of Fatty Hydrazide as Corrosion Inhibitor in Acidic Medium: Experimental and Theoretical Approaches. Metals 2022, 12, 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071058
Hassan A, Numin MS, Jumbri K, Kee KE, Borhan N. Review on the Recent Development of Fatty Hydrazide as Corrosion Inhibitor in Acidic Medium: Experimental and Theoretical Approaches. Metals. 2022; 12(7):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071058
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Almila, Mohd Sofi Numin, Khairulazhar Jumbri, Kok Eng Kee, and Noorazlenawati Borhan. 2022. "Review on the Recent Development of Fatty Hydrazide as Corrosion Inhibitor in Acidic Medium: Experimental and Theoretical Approaches" Metals 12, no. 7: 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071058
APA StyleHassan, A., Numin, M. S., Jumbri, K., Kee, K. E., & Borhan, N. (2022). Review on the Recent Development of Fatty Hydrazide as Corrosion Inhibitor in Acidic Medium: Experimental and Theoretical Approaches. Metals, 12(7), 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071058