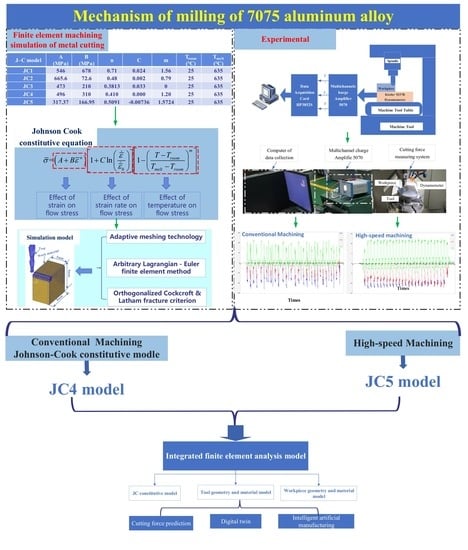
Research on Conventional and High-Speed Machining Cutting Force of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Based on Finite Element Modeling and Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Constitutive Equation Model of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy
3. Finite Element Simulation Analysis of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Machining
4. Experimental Work
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. FEA Simulation in Conventional Machining
5.2. FEA Simulation in High−Speed Machining
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dursun, T.; Soutis, C. Recent developments in advanced aircraft aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; Sharif, A.; Hussain, A.; Aamir, M.; Ali, U. Analysis of Hole Quality and Chips Formation in the Dry Drilling Process of Al7075-T6. Metals 2021, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Zhou, H.M.; Jiang, Y.Q. Modeling the high-temperature creep behaviors of 7075 and 2124 aluminum alloys by continuum damage mechanics model. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2013, 73, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.C.; Wang, B.Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.M. Constitutive modeling of flow behavior and microstructure evolution of AA7075 in hot tensile deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturi, U.M.R.; Narala, S.K.R.; Pundir, R.S. Constitutive flow stress, formulation model validation and FE cutting simulation for AA7075-T6 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 605, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkereit, B.; Österreich, M.; Schuster, P.; Kirov, G.; Mukeli, E.; Kessler, O. Dissolution and Precipitation Behavior for Hot Forming of 7021 and 7075 Aluminum Alloys. Metals 2018, 8, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Bu, H.; Li, M.; Lu, X. Prediction of Flow Stress of Annealed 7075 Al Alloy in Hot Deformation Using Strain-Compensated Arrhenius and Neural Network Models. Materials 2021, 14, 5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Zhou, H.M.; Liu, G. A new creep constitutive model for 7075 aluminum alloy under elevated temperatures. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 4350–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, M.-H.; Hung, F.-Y.; Lui, T.-S.; Lai, J.-J. Enhanced Formability and Accelerated Precipitation Behavior of 7075 Al Alloy Extruded Rod by High Temperature Aging. Metals 2018, 8, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.R.; Guo, Y.B. Finite Element Analysis of the Effect of Sequential Cuts and Tool-Chip Friction on Residual Stresses in a Machined Layer. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2000, 42, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malea, C.I.; Nitu, E.L.; Iordache, M.D. A brief review of numerical simulation in process machining. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 5th International Conference on Computing and Solutions in Manufacturing Engineering (CoSME’20), Brasov, Romania, 7–10 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Melkote, S.N.; Grzesik, W.; Outeiro, J.; Rech, J.; Schulze, V.; Attia, H.; Arrazola, P.J.; Saoubi, R.M.; Saldana, C. Advances in material and friction data for modelling of metal machining. CIRP Ann. 2017, 66, 731–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Bansal, A.; Peng, C. Numerical Simulation of Metal Machining Process with Eulerian and Total Lagrangian SPH. Eng. Anal. Boundary Elem. 2019, 117, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.R.; Cook, W.H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1983, 21, 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Calamaz, M.; Coupard, D.; Girot, F. A new material model for 2D numerical simulation of serrated chip formation when machining titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Sang, E.L.; Hong, J.W. Experimental and Numerical Investigations of High-Speed Projectile Impacts on 7075-T651 Aluminum Plates. Materials 2019, 12, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimble, D.; O’Donnell, G.E. Constitutive Modelling for elevated temperature flow behaviour of AA7075. Mater. Des. 2015, 76, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaee, S.; Mirzaei, A.H.; Almasi, D. Constitutive modelling of Al7075 using the Johnson–Cook model. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2020, 43, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Li, L.T.; Fu, Y.X.; Jiang, Y.Q. Hot compressive deformation behavior of 7075 Al alloy under elevated temperature. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.C.; Zheng, L.S.; Yang, H. Softening mechanism and microstructure evolution of as-extruded 7075 aluminum alloy during hot deformation. Mater. Charact. 2014, 90, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Qu, H.; Wu, W.; Zheng, J.H.; Zheng, H.K. A Physical-Based Plane Stress Constitutive Model for High Strength AA7075 under Hot Forming Conditions. Metals 2021, 11, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K. Numerical simulation of AA7075 under high strain rate with different shape of striker of split Hopkinson pressure bar. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Lin, C.R. Deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of 7075-T6 aluminum alloy at cryogenic temperatures. Cryogenics 2016, 79, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Zheng, J.H.; Guan, B.; Zheng, K.L. A physical-based unified constitutive model of AA7075 for a novel hot forming condition with pre-cooling. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 876, 160142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, N.S.; Joshi, V.S.; Harriset, B.W. Constitutive model constants for Al7075-T651 and Al7075-T6. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, 16th APS Topical Conference on Shock Compression of Condensed Matter, Nashville, TN, USA, 28 June–3 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Paturi, A.U.M.R.; Narala, B.S.K.R.; Kakustam, S. Investigations on the effects of different constitutive models in finite element simulation of machining. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 25295–25302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.N.; Shangguan, Q.Q.; Xie, C.J.; Liu, F. A modified Johnson–Cook model of dynamic tensile behaviors for 7075-T6 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 619, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, N. A new quantitative sensitivity analysis of the flow stress of 18 engineering materials in machining. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2005, 127, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturi, U.; Narala, S. Constitutive flow stress formulation for aeronautic aluminum alloy AA7075-T6 at elevated temperature and model validation using finite element simulation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L 2016, 230, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouki, T.; Giradin, F.; Asad, M.; Regal, J.F. Numerical and experimental study of dry cutting for an aeronautic aluminum alloy (A2024-T351). Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Johnson, E.A.; Luming, S.; Guiamasia, I.; Nguyen, G.D. Numerical investigation of the impact behavior of bio inspired nacre-like aluminum composite plates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 96, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| J–C Model | A (MPa) | B(MPa) | n | C | m | Troom (°C) | Tmelt (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JC1 [25] | 546 | 678 | 0.71 | 0.024 | 1.56 | 25 | 635 |
| JC2 [26] | 665.6 | 72.6 | 0.48 | 0.002 | 0.79 | 25 | 635 |
| JC3 [27] | 473 | 210 | 0.3813 | 0.033 | 0 | 25 | 635 |
| JC4 [28] | 496 | 310 | 0.410 | 0.000 | 1.20 | 25 | 635 |
| JC5 [29] | 317.37 | 166.95 | 0.5091 | −0.00736 | 1.5724 | 25 | 635 |
| Material/ Parameter | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·°C) | Specific Heat Capacity (J/kg·°C) | Poisson’s Ratio | Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al 7075-T6 | 68.9 | 180.175 | 910 | 0.3 | 2700 |
| WC | 650 | 58.988 | 400 | 0.25 | 11,900 |
| Parameter | Conditions |
|---|---|
| Workpiece material | 7075-T6 aluminum alloy |
| Chemical composition (wt.%) | Zn-5.6, Mg-2.5, Cu-1.6, Fe-0.5, Si-0.4, Mn-0.3, Cr-0.23, Ti-0.2, Al-Rem. |
| Cutting condition | Spindle speed n = 5000, 16,000 r/min, Cutting depth ap = 0.2 mm, Cutting width aw = 0.6 mm. |
| Machining test environments | Dry machining tests |
| Cutting tool and tool geometry | Rake angle (γ) = 8°, Clearance angle (α) = 10°, Helical angle (β) = 30°, Taper angle of the ball end mill (η) = 6°, Radius of the ball end mill (R) = 0.5 mm, Length of cutting edge in axis direction (L) = 15 mm. |
| Equipment | Experimental Condition |
|---|---|
| Machine tool | JDGR200 A10SH five-axis high precision machining center |
| Cutting tool | φ1 mm carbide double-edge taper ball milling cutter without coating |
| Workpiece material | 7075-T6 Aluminum alloy |
| Milling force measuring equipment | 9257B Kistler dynamometer |
| Data acquisition card | HP3852S |
| Charge amplifier | 5070A |
| Cutting Force (N) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fx | Fy | Fz | |
| Experimental results | 32.75 | 9.45 | 18.46 |
| JC1 | 54.38 (66.05%) | 32.75 (246.56%) | 41.35 (124.00%) |
| JC2 | 13.32 (−59.33%) | 7.62 (−19.37%) | 11.28 (−38.89%) |
| JC3 | - | - | - |
| JC4 | 24.35 (−25.65%) | 7.85 (−16.93%) | 18.41 (−0.2409%) |
| JC5 | 17.58 (−46.32%) | 5.04 (−46.67%) | 14.10 (−23.62%) |
| Cutting Force (N) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fx | Fy | Fz | |
| Experimental results | 13.79 | 8.32 | 12.63 |
| JC1 | 40.00 (190.07%) | 23.44 (181.73%) | 34.58 (173.79%) |
| JC2 | 16.10 (16.75%) | 6.35 (−23.68) | 10.68 (−15.44%) |
| JC3 | - | - | - |
| JC4 | 20.79 (50.76%) | 9.08 (9.13%) | 16.52 (30.80%) |
| JC5 | 14.58 (5.73%) | 8.06 (3.13%) | 11.28 (10.69%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Gorbachev, S.; Kuzin, V.; He, W.; Guo, J. Research on Conventional and High-Speed Machining Cutting Force of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Based on Finite Element Modeling and Simulation. Metals 2022, 12, 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12081395
Wang Z, Cao Y, Gorbachev S, Kuzin V, He W, Guo J. Research on Conventional and High-Speed Machining Cutting Force of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Based on Finite Element Modeling and Simulation. Metals. 2022; 12(8):1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12081395
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhijie, Yan Cao, Sergey Gorbachev, Victor Kuzin, Weiliang He, and Junde Guo. 2022. "Research on Conventional and High-Speed Machining Cutting Force of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Based on Finite Element Modeling and Simulation" Metals 12, no. 8: 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12081395
APA StyleWang, Z., Cao, Y., Gorbachev, S., Kuzin, V., He, W., & Guo, J. (2022). Research on Conventional and High-Speed Machining Cutting Force of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy Based on Finite Element Modeling and Simulation. Metals, 12(8), 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12081395