Tunable Complex Permittivity and Strong Microwave Absorption Properties of Novel Dielectric-Conductive ZnO/C Hybrid Composite Absorbents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of ZnO Powders
2.3. Preparation of ZnO/C Composite Absorbents and C Powders
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.2. XRD, Raman, and XPS Spectrum Analysis
3.3. Surface Morphology and EDS Analysis
3.4. Complex Permittivity and Electrical Conductivity
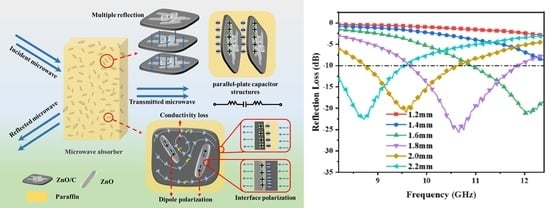
3.5. Microwave Absorption Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Micheli, D.; Vricella, A.; Pastore, R.; Marchetti, M. Synthesis and electromagnetic characterization of frequency selective radar absorbing materials using carbon nanopowders. Carbon 2014, 77, 756–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Tai, N.H. Carbon materials and their composites for electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness in X-band. Carbon 2019, 152, 159–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Cheng, X.; Yu, R.; Stucky, G.D. Electromagnetic microwave absorption theory and recent achievements in microwave absorbers. Carbon 2020, 168, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Fang, C.; Hou, X.; Xie, L. Recent advances in MXenes composites for electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 136, 105956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Xia, L.; Ma, S.; Yin, Z.; Huang, Y. A Review on Metal–Organic Framework-Derived Porous Carbon-Based Novel Microwave Absorption Materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, B.; Song, W.; Ning, M.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, D.; Cao, M.; Jin, H. Chemical reduction dependent dielectric properties and dielectric loss mechanism of reduced graphene oxide. Carbon 2018, 127, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.-L.; Wu, H.-Y.; Lu, M.-M.; Chen, Y.-J.; Zhu, C.-L.; Gao, P.; Cao, M.-S.; Li, C.-Y.; Ouyang, Q.-Y. Quaternary Nanocomposites Consisting of Graphene, Fe3O4@Fe Core@Shell, and ZnO Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Excellent Electromagnetic Absorption Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6436–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Q.; Fu, Y.; Liu, T. A review on carbon/magnetic metal composites for microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 86, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Hu, Q.; Wei, R.; Mai, X.; Naik, N.; Pan, D.; Guo, Z.; Shi, Z. Review on the electromagnetic interference shielding properties of carbon based materials and their novel composites: Recent progress, challenges and prospects. Carbon 2021, 176, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Lee, S.; Ro, J.C.; Suh, S.-J. Yolk–shell Fe–Fe3O4@C nanoparticles with excellent reflection loss and wide bandwidth as electromagnetic wave absorbers in the high-frequency band. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 573, 151469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sun, L.; Qi, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Q.; Pan, C. A novel strategy to enhance the multiple interface effect using amorphous carbon packaged hydrogenated TiO2 for stable and effective microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 6152–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, R.; Feng, S.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Q.; Chen, B. Recent progress in biomass-derived carbonaceous composites for enhanced microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 406–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, T.; Cheng, J.; Chai, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Zheng, G.; Cao, M. Light-weight and low-cost electromagnetic wave absorbers with high performances based on biomass-derived reduced graphene oxides. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 445708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.P.; Ji, G.; Xu, Z.J. Biomass-Derived Porous Carbon-Based Nanostructures for Microwave Absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Bao, X.; Zhou, X.; Shi, G. Excellent microwave absorption of lamellar LaOCl/C nanocomposites with LaOCl nanoparticles embedded in carbon matrix. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 764, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, L.D.; Wu, H.J. Synthesis, Characterization and Microwave Absorption Properties of Dendrite-Like Fe3O4 Embedded within Amorphous Sugar Carbon Matrix. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 290, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, J.; Kuritka, I.; Masar, M.; Machovsky, M.; Urbanek, P.; Bazant, P.; Janota, P.; Dvorackova, M. Contributions of morphological and structural parameters at different hierarchical morphology levels to photocatalytic activity of mesoporous nanostructured ZnO. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 513, 145773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, L.; Ouyang, J.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Reduced graphene oxide decorated with in-situ growing ZnO nanocrystals: Facile synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 2016, 108, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.X.; Wang, Z.L. Mesoporous Polyhedral Cages and Shells Formed by Textured Self-Assembly of ZnO Nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11299–11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.V.; Ferreira, R.V.; Yoshida, M.I.; Pasa, V.M. Zinc nanowires synthesized on a large scale by a simple carbothermal process. Solid State Sci. 2009, 11, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.K.; Gao, C. Supraparamagnetic, Conductive, and Processable Multifunctional Graphene Nanosheets Coated with High-Density Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2010, 2, 3201–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Xiong, X.H.; Chen, P.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R.C.; Chu, H.R. Air@rGO€Fe3O4 Microspheres with Spongy Shells: Self-Assembly and Microwave Absorption Performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 10518–10528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Z.M.; Yu, J.R.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. Porous Core-Shell Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-Derived Co/NPC@ZnO-Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide for Lightweight and Broadband Electromagnetic Wave Absorber. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 818, 152932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandra, V.R.; Enrique, G.B.; Lavier, H.F.; Jose, G.D.; Alejandro, A.C.; Silva, A.M.; Maser, W.K.; Benito, A.M. Controlling the Surface Chemistry of Graphene Oxide: Key Towards Efficient ZnO-GO Photocatalysts. Catal. Today 2020, 357, 350–360. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Du, X.M.; Wu, C.Y.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhao, G.Z. Reduced Graphene Oxide Decorated with ZnO Microrods for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Performance. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 31, 8637–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Qu, Z.M.; Wang, Q.G.; Sun, X.N.; Cheng, E. Reversible Nonlinear I-V Behavior of ZnO-Decorated Graphene Nanoplatelets/Epoxy Resin Composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, T.; Nie, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Huo, Y.; Xu, R.; Chen, X.; Peng, H. Flower-like CoS hierarchitectures@polyaniline organic-inorganic heterostructured composites: Preparation and enhanced microwave absorption performance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 200, 108403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhou, J.; Yao, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Wei, B.; Tan, R.; Li, Z. Multi-shell hollow porous carbon nanoparticles with excellent microwave absorption properties. Carbon 2020, 172, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Ma, T.; Shu, J.-C.; Cao, M.-S. Confinedly tailoring Fe3O4 clusters-NG to tune electromagnetic parameters and microwave absorption with broadened bandwidth. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gao, Z.; Tang, S.; Chen, C.; Duan, F.; Zhao, S.; Lin, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Qin, Y. Microwave Absorption Properties of Carbon Nanocoils Coated with Highly Controlled Magnetic Materials by Atomic Layer Deposition. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 11009–11017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.Y.; Zhou, F.K.; Chen, P.; Zhang, B.S.; Zhou, J.T. PANI/FeCo@C Composite Microspheres with Broadband Microwave Absorption Performance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 218, 109143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Kong, J. Fabrication of macroporous magnetic carbon fibers via the cooperative etching-electrospinning technology toward ultra-light microwave absorption. Carbon 2023, 208, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Ran, K.; Zheng, B.; Chen, F. Structure engineering of 3D interconnect graphene nanocapsules for microwave absorption. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 153, 110863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Che, R.; You, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Deng, J.; Qiu, L.; Peng, H. Cross-Stacking Aligned Carbon-Nanotube Films to Tune Microwave Absorption Frequencies and Increase Absorption Intensities. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 8120–8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J. Three dimensional carbon aerogel for microwave absorption from chitosan. Synth. Met. 2023, 295, 117352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Zou, Y.; Sun, L.; Xu, F.; Yu, S.; Hao, S.; Xiang, C. MoS2-decorated carbonized melamine foam/reduced graphene oxide network for constructing polyethylene-glycol-based multifunctional phase change materials toward multiple energy harvesting and microwave absorbing applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 141923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Kuang, D.; Hou, L.; Luo, H.; Deng, L.; Wang, S. Synthesis and microwave absorption performance of layered hard carbon embedded with ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 895, 162677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, R.; Kumar, A.; Nigam, A. Effect of Ni on the Dielectric Behavior and Microwave Absorption Performance of ZnO Composites. Mater. Phys. Mech. 2021, 47, 416–422. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, N.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, J. Three-Dimensional Network ZnO/BaFe12O19 Composite Thick Films and Their Microwave Absorption Properties. J. Ceram. Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Jiang, W. Synthesis of Fe3O4@ZnO/RGO nanocomposites and microwave absorption properties. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 15th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Rome, Italy, 27–30 July 2015; pp. 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Wang, H.; Huang, F.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hui, D.; Zhou, Z. Graphene-based microwave absorbing composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 137, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Zong, M.; Chen, W. Supramolecular self-assembly derived Mo2C/FeCo/NC hierarchical nanostructures with excellent wideband microwave absorption properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 221, 109325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.L.; Wang, J.; Jin, H.H.; Dong, Y.W.; Huo, S.Q.; Yang, S.; Su, X.G.; Zhang, B. Facile Synthesis of Co-Embedded Porous Spherical Carbon Composites Derived from Co3O4/ZiF-8 Compounds for Broadband Microwave Absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 195, 108206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Wang, J.; Luo, Q.; Sun, M.; Jiang, L.; Han, Q.; Liu, J.; Bi, H. Starfish-like C/CoNiO2 heterostructure derived from ZIF-67 with tunable microwave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Samples | Final Carbonization Temperature (°C) | Final Carbonization Time (min) | Absorbent Content (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CZO50-650 | 650 | 90 | 50 |
| CZO50-700 | 700 | 90 | 50 |
| CZO50-750 | 750 | 90 | 50 |
| CZO40-750 | 750 | 90 | 40 |
| CZO60-750 | 750 | 90 | 60 |
| Materials | Thickness/mm | The Minimum Reflection Loss/Db | Bandwidth (<−10 Db)/GHz | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon fibers | 2.50 | −49.4 | 10.8 | [32] |
| Graphene | 3.00 | −4.30 | 4.32 | [33] |
| CNT | 2.00 | −47.70 | 1.7 | [34] |
| 3D carbon aerogel | 2.50 | −41.00 | 5.24 | [35] |
| PEG@CMF/rGO/MoS2 | 2.10 | −32.49 | 6.16 | [36] |
| ZnO | 3.10 | −7.00 | 0 | [37] |
| ZnO/Ni | 3.00 | −12.86 | — | [38] |
| ZnO/BaFe12O19 | 4.50 | −48.60 | 2.30 | [39] |
| Fe3O4@ZnO/RGO | 4.50 | −34.00 | ~2.00 | [40] |
| ZnO/C | 1.80 | −25.64 | 2.21 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, J.; Jia, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Tunable Complex Permittivity and Strong Microwave Absorption Properties of Novel Dielectric-Conductive ZnO/C Hybrid Composite Absorbents. Metals 2023, 13, 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071220
Yan J, Jia H, Zhou L, Wang Z, Wang H. Tunable Complex Permittivity and Strong Microwave Absorption Properties of Novel Dielectric-Conductive ZnO/C Hybrid Composite Absorbents. Metals. 2023; 13(7):1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071220
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Junxiao, Hongyao Jia, Liang Zhou, Zhenjun Wang, and Hongbo Wang. 2023. "Tunable Complex Permittivity and Strong Microwave Absorption Properties of Novel Dielectric-Conductive ZnO/C Hybrid Composite Absorbents" Metals 13, no. 7: 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071220
APA StyleYan, J., Jia, H., Zhou, L., Wang, Z., & Wang, H. (2023). Tunable Complex Permittivity and Strong Microwave Absorption Properties of Novel Dielectric-Conductive ZnO/C Hybrid Composite Absorbents. Metals, 13(7), 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071220