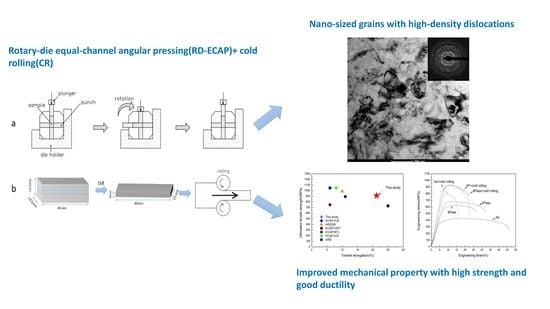
Fabrication of an Ultra-Fine Grained Pure Titanium with High Strength and Good Ductility via ECAP plus Cold Rolling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Microstructure of As-Received and ECAP CP-Ti (Equal-Channel Angular Pressed Commercially Pure Titanium)
3.2. Microstructure of ECAP + CR (Cold Rolling) CP-Ti
3.3. Mechanical Properties of CP-Ti at Different Processing Stages
3.4. Correlation between Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of CP-Ti
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The grain size of CP-Ti is effectively refined after the combination of RD-ECAP and CR. It decreases from 80 μm of as-received state to around 500 nm and 310 nm after 4 passes and 8 passes RD-ECAP, and further decreases to about 120 nm and 90 nm after subsequent CR processing.
- (2)
- XRD analysis shows that no phase transformation happens during ECAP + CR processing, and α-Ti is the only phase in these SPD CP-Ti. Moreover, calculated results by Williamson-Hall analysis of XRD and TEM observations demonstrate that the dislocation density increases remarkably after combination of ECAP and CR.
- (3)
- Room temperature tensile tests showed that CP-Ti after ECAP + CR exhibited the best combination of strength and ductility, with ultimate tensile strength and fracture strain reached 920 MPa and 20%, respectively. The high strength of this UFG CP-Ti originated mainly from refined grains and high density of dislocations, while the good ductility could be attributed to the increased activation of grain boundary sliding and improved homogeneity of UFG microstructure.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leyens, C.; Peters, M. Titanium and titanium alloys: Fundamentals and applications. In Titanium and Titanium Alloys; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 401, pp. 23–67. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, J.R.; Bomberger, H.B.; Froes, F.H. Corrosion behavior and use of titanium and its alloys. JOM 1984, 36, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanosh, K.P.; Balakrishnan, A.; Francis, L.; Kim, T.N. Vickers and knoop micro-hardness behavior of coarse- and ultrafine-grained titanium. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Langdon, T.G. Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 881–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.T.; Gao, N.; Gee, M.G.; Wood, R.J.K.; Langdon, T.G. Effect of grain size on the micro-tribological behavior of pure titanium processed by high-pressure torsion. Wear 2012, 280–281, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Xu, D.K.; Wu, R.Z.; Chen, X.B.; Peng, Q.M.; Jin, L.; Xin, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.H.; et al. What is going on in magnesium alloys? J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Z.J.; Yan, K.; Yan, J.L.; Bai, J.; Jiang, J.H.; Ma, A.B. Effect of multi-pass equal channel angular pressing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a heterogeneous Mg88Y8Zn4 alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Yoo, S.J.; Jin, W.A.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.J. Ultrafine grained titanium sheets with high strength and high corrosion resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 8479–8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Korznikov, A.V.; Mulyukov, R.R. Structure and properties of ultrafine-grained materials produced by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1993, 168, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Estrin, Y.; Horita, Z.; Langdon, T.G.; Zechetbauer, M.J.; Zhu, Y.T. Producing bulk ultrafine-grain materials by severe plastic deformation. JOM 2006, 58, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolyarov, V.V.; Zhu, Y.T.; Lowe, T.C.; Lslamgaliev, R.K.; Valiev, R.Z. A two step SPD processing of ultrafine-grained titanium. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 11, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ju, J.; Lu, F.M.; Yan, J.L.; Bai, J.; Jiang, J.H.; Ma, A.B. Dynamic precipitation behavior and mechanical property of an Mg94Y4Zn2 alloy prepared by multi-pass successive equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 682, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, D.; Inoue, S.; Tsuji, N. Microstructure and mechanical properties of commercial purity titanium severely deformed by ARB process. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolyarov, V.V.; Zhu, Y.T.; Alexandrov, I.V.; Lowe, T.C.; Valiev, R.Z. Grain refinement and properties of pure Ti processed by warm ECAP and cold rolling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 343, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Zhu, S.S.; Zhang, C.H. Analysis of the grain refinement mechanism for commercial pure titanium by ECAP and SMAT. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 937, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodposhti, P.S.; Farahbakhsh, N.; Sarkar, A.; Murty, K.L. Microstructural approach to equal channel angular processing of commercially pure titanium—A review. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fu, W.; Yang, X.; Langdon, T.G. Microstructure and properties of pure titanium processed by equal-channel angular pressing at room temperature. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, C.S.; Khan, A.S. The microstructural evolution and thermo-mechanical behavior of UFG Ti processed via equal channel angular pressing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 219, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Langdon, T.G. The processing of pure titanium through multiple passes of ECAP at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 6335–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Kim, J.; Shin, D.H.; Lee, C.S.; Hwang, S.K. Effects of equal channel angular pressing temperature on deformation structures of pure ti. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 342, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Arima, H.; Kim, J.C.; Ando, T. Rotary-die equal-channel angular pressing of an Al-7 mass% Si-0.35 mass% Mg alloy. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ju, J.; Bai, J.; Sun, J.P.; Song, D.; Yan, J.L.; Jiang, J.H.; Ma, A.B. Preparation, microstructure evolutions, and mechanical property of an ultra-fine grained Mg-10Gd-4Y-1.5Zn-0.5Zr alloy. Metals 2017, 7, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.X.; Ma, A.B.; Jiang, J.H.; Yuan, Y.C.; Li, H.Y. Deformation structure and mechanical properties of pure titanium produced by rotary-die equal-channel angular pressing. Metals 2017, 7, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Mcdonald, D.T.; Zhu, S.M.; Palanisamy, S.; Dargusch, M.S.; Xia, K. Analysis of microstructure and strengthening in pure titanium recycled from machining chips by equal channel angular pressing using electron backscatter diffraction. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 538, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Fu, W. Deformed microstructures and mechanical properties of CP-Ti processed by multi-pass ECAP at room temperature. Rare Metall. Mater. Eng. 2009, 38, 955–957. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.; Kim, J.; Shin, D.H.; Park, K.T. Effects of grain size and pressing speed on the deformation mode of commercially pure Ti during equal channel angular pressing. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2003, 34, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolyarov, V.V.; Zhu, Y.T.; Lowe, T.C.; Valiev, R.Z. Microstructure and properties of pure Ti processed by ECAP and cold extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 303, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K. Stabilizing nanostructures in metals using grain and twin boundary architectures. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradgholi, J.; Monshi, A.; Farmanesh, K. An investigation in to the mechanical properties of CP Ti/TiO2 nanocomposite manufactured by the accumulative roll bonding (ARB) process. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, K. Grain size effect of commercial pure titanium foils on mechanical properties, fracture behaviors and constitutive models. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Figueiredo, R.B.; Alhajeri, S.N.; Wang, J.T.; Gao, N.; Langdon, T.G. Structure and mechanical properties of commercial purity titanium processed by ECAP at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 7708–7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah-Alhosseini, A.; Keshavarz, M.K.; Mazaheri, Y.; Ansari, A.R.; Karimi, M. Strengthening mechanisms of nano-grained commercial pure titanium processed by accumulative roll bonding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 693, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcek, G.; Yapici, G.G.; Karaman, I.; Maier, H.J. Effect of commercial purity levels on the mechanical properties of ultrafine-grained titanium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 2303–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, S.; Tan, H.; Lin, X.; Huang, W.D. Influence of α/β interface phase on the tensile properties of laser cladding deposited Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Mcdonald, D.T.; Xu, W.; Palanisamy, S.; Dargusch, M.S.; Xia, K. A modified Hall-Petch relationship in ultrafine-grained titanium recycled from chips by equal channel angular pressing. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Bringa, E.M.; Meyers, M.A. Inverse Hall-Petch relationship in nanocrystalline tantalum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 580, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, W.; Balogh, L.; Ungár, T.; Choo, H.; Feng, Z. Grain structure and dislocation density measurements in a friction-stir welded aluminum alloy using X-ray peak profile analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 498, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, T.; Borbely, A. The effect of dislocation contrast on X-ray line broadening: A new approach to line profile analysis. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 3173–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Hall, W.H. X-ray line broadening from field aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Smallman, R.E., III. Dislocation densities in some annealed and cold worked metals from measurement on the X-ray debye-scherrer spectrum. Philos. Mag. 1956, 1, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafler, E.; Zehetbauer, M.; Ungàr, T. Measurement of screw and edge dislocation density by means of X-ray Bragg profile analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 319, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderov, D.V.; Polyakov, A.V.; Semenova, I.P.; Raab, G.I.; Churakova, A.A.; Gimaltdinova, E.I.; Sabirov, I.; Segurado, J.; Sitdikov, V.D.; Alexandrov, I.V.; et al. Evolution of microstructure, macrotexture and mechanical properties of commercially pure Ti during ECAP-conform processing and drawing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 562, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmametov, A.R.; Ivanisenko, Y.; Mazilkin, A.A.; Straumal, B.B.; Gornakova, A.S.; Fabrichnaya, O.B.; Kriegel, M.J.; Rafaja, D.; Hahn, H. The α → ω and β → ω phase transformations in Ti-Fe alloys under high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2018, 144, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmametov, A.; Ivanisenko, Y.; Straumal, B.; Mazilkin, A.A.; Gornakova, A.S.; Kriegel, M.J.; Fabrichnaya, O.B.; Rafaja, D.; Hahn, H. Transformations of α’ martensite in Ti-Fe alloys under high pressure torsion. Scr. Mater. 2017, 136, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, W.J. Annealing effects on the corrosion resistance of ultrafine-grained pure titanium. Corros. Sci. 2014, 89, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Element | C | Fe | O | N | H | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.015 | 0.059 | 0.062 | 0.013 | 0.002 | balence |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Jiang, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Gu, Y.; Tang, R.; Zhao, X.; Ma, A. Fabrication of an Ultra-Fine Grained Pure Titanium with High Strength and Good Ductility via ECAP plus Cold Rolling. Metals 2017, 7, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120563
Wu H, Jiang J, Liu H, Sun J, Gu Y, Tang R, Zhao X, Ma A. Fabrication of an Ultra-Fine Grained Pure Titanium with High Strength and Good Ductility via ECAP plus Cold Rolling. Metals. 2017; 7(12):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120563
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Haoran, Jinghua Jiang, Huan Liu, Jiapeng Sun, Yanxia Gu, Ren Tang, Xincan Zhao, and Aibin Ma. 2017. "Fabrication of an Ultra-Fine Grained Pure Titanium with High Strength and Good Ductility via ECAP plus Cold Rolling" Metals 7, no. 12: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120563
APA StyleWu, H., Jiang, J., Liu, H., Sun, J., Gu, Y., Tang, R., Zhao, X., & Ma, A. (2017). Fabrication of an Ultra-Fine Grained Pure Titanium with High Strength and Good Ductility via ECAP plus Cold Rolling. Metals, 7(12), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120563