Germanium and Indium Recovery from Zinc Metallurgy by-Products—Dross Leaching in Sulphuric and Oxalic Acids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
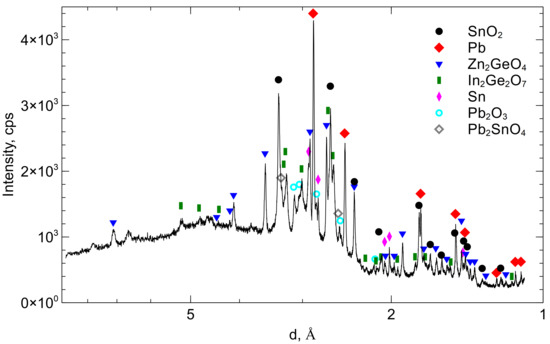
3.1. Dross Analysis
3.2. Leaching—Sulphuric Acid
3.3. Leaching—Sulphuric Acid + Oxidant
3.4. Leaching—Oxalic Acid
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- the highest leaching yield of germanium in H2SO4(aq) was 85%. It was achieved for T = 80 °C, t = 3 h, CH₂SO₄ = 10%, S/L = 1/10.
- (2)
- germanium leachability in sulphuric acid strongly depends on acid concentration and S/L ratio—there was a maximum observed for CH₂SO₄ = 10% and S/L = 1/10.
- (3)
- indium leaching yield in sulphuric acid strongly depends on temperature—for 2 h process In leachability increased from 37% at 40 °C to ca. 82% at 80 °C.
- (4)
- the addition of an oxidant to sulphuric acid during leaching increased copper leachability—by up to 69% when sodium hypochlorite was used. However, it did not have a positive impact on Ge, In, and Sn leaching yields.
- (5)
- leaching in H2C2O4 allowed us to achieve an 80% leaching yield of germanium. Leaching yields of indium and tin for S/L ≥ 1/10 were below 20%.
- (6)
- high germanium leachability may be achieved in both sulphuric and oxalic acids. However, when a high leaching yield of indium is also desired, sulphuric acid at >80 °C should be used.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holl, R.; Kling, M.; Schroll, E. Metallogenesis of germanium—A review. Ore Geol. Rev. 2007, 30, 145–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.S.; Chang, B.C.; Chiu, K.L. Recovery of germanium from waste Optical Fibers by hydrometallurgical method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5215–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, C.; Peiro, L.T.; Villalba, G. Global Substance Flow Analysis of Gallium, Germanium, and Indium: Quantification of Extraction, Uses, and Dissipative Losses within their Anthropogenic Cycles. J. Ind. Ecol. 2015, 19, 890–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertz, B.; Verhelle, J.; Schurmans, M. The Primary and Secondary Production of Germanium: A Life-Cycle Assessment of Different Process Alternatives. JOM 2015, 67, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries 2018; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018.
- Dai, S.F.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Jiang, J.H.; Hower, J.C.; Song, X.L.; Jiang, Y.F.; Wang, X.B.; Gornostaeva, T.; Li, X.; et al. Composition and modes of occurrence of minerals and elements in coal combustion products derived from high-Ge coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 121, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, O.; Querol, X.; Lopez-Soler, A.; Chimenos, J.M.; Fernandez, A.I.; Burgos, S.; Pena, F.G. Ge extraction from gasification fly ash. Fuel 2005, 84, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, D.; Wieronska, F.; Strugala, A.; Kosowska, K. Germanium content in Polish hard coals. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on the Sustainable Energy and Environment Development (SEED), Krakow, Poland, 17–19 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kul, A.; Topkaya, Y. Recovery of germanium and other valuable metals from zinc plant residues. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 92, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, S.; Aghazadeh, S.; Noaparast, M.; Gharabaghi, M.; Taheri, B. Germanium separation and purification by leaching and precipitation. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayram, T.S.; Anderson, C.G. The development and implementation of industrial hydrometallurgical gallium and germanium recovery. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2008, 108, 261–271. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, Y.H.; Wilson, B.P.; Lundstrom, M. Recovery and separation of gallium(III) and germanium(IV) from zinc refinery residues: Part I: Leaching and iron(III) removal. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, Q.H.; Zeng, L. Extraction of gallium and germanium from zinc refinery residues by pressure acid leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, Y.H.; Wilson, B.P.; Lundstrom, M. Extraction of Ga and Ge from zinc refinery residues in H2C2O4 solutions containing H2O2. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 163, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, F.; Fernandez-Pereira, C.; Olivares, J.; Coca, P. Hydrometallurgical Recovery of Germanium from Coal Gasification Fly Ash: Pilot Plant Scale Evaluation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 3573–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.Q.; Wang, J.K.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, F.; Jiang, J.B. Behavior of tannins in germanium recovery by tannin process. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 93, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, J.; Anderson, C.G. Tannins in Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy. Metals 2015, 5, 1520–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arroyo, F.; Font, O.; Fernandez-Pereira, C.; Querol, X.; Juan, R.; Ruiz, C.; Coca, P. Germanium recovery from gasification fly ash: Evaluation of end-products obtained by precipitation methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Chen, Y.W.; Guo, H.; Liu, H.Q.; Xue, Y.D.; Zhang, W.F.; Sun, Y.C. Review of Germanium recovery technologies from coal. In Applied Mechanics and Materials; Trans Tech Publications: Durnten-Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 423, pp. 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtolo, D.C.; Friedrich, S.; Friedrich, B. High Purity Germanium, a Review on Principle Theories and Technical Production Methodologies. J. Cryst. Process Technol. 2017, 7, 78624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, H.K.; Irannajad, M.; Fortuny, A.; Sastre, A.M. Recovery of germanium from leach solutions of fly ash using solvent extraction with various extractants. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 175, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, Y.H.; Wilson, B.P.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zeng, L.; Lundstrom, M. Recovery and separation of gallium(III) and germanium(IV) from zinc refinery residues: Part II: Solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 171, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusen, S.; Zhu, Z.W.; Chairuangsri, T.; Cheng, C.Y. Recovery of germanium from synthetic leach solution of zinc refinery residues by synergistic solvent extraction using LIX 63 and Ionquest 801. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 151, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, H.; Morisada, S.; Ohto, K.; Kawakita, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Fukuda, D. Germanium recovery by catechol complexation and subsequent flow through membrane and bead-packed bed column. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1468–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virolainen, S.; Heinonen, J.I.; Paatero, E. Selective recovery of germanium with N-methylglucamine functional resin from sulfate solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 104, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo Torralvo, F.; Fernandez-Pereira, C. Recovery of germanium from real fly ash leachates by ion-exchange extraction. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozoe, A.; Ohto, K.; Kawakita, H. Germanium Recovery using Catechol Complexation and Permeation through an Anion-Exchange Membrane. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.G.; Xu, Z.M. An environmentally-friendly vacuum reduction metallurgical process to recover germanium from coal fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 312, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.G.; Xu, Z.M. Application of vacuum reduction and chlorinated distillation to enrich and prepare pure germanium from coal fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfantazi, A.M.; Moskalyk, R.R. Processing of indium: A review. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, S. Indium, germanium and gallium in volcanic- and sediment-hosted base-metal sulphide deposits. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Strategic and Critical Materials Proceedings, Victoria, BC, Canada, 13–14 November 2015; pp. 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, T.T.; Mudd, G.M.; Jowitt, S.M. Indium: Key issues in assessing mineral resources and long-term supply from recycling. Appl. Earth Sci. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusen, S.; Chairuangsri, T.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, C.Y. Recovery of indium and gallium from synthetic leach solution of zinc refinery residues using synergistic solvent extraction with LIX 63 and Versatic 10 acid. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 160, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, C.; Deng, Z.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Li, M. Reductive leaching of indium-bearing zinc residue in sulfuric acid using sphalerite concentrate as reductant. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 161, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielarz, A.; Prajsnar, R.; Szołomicki, Z.; Becker, K.; Pietrek, W. A case study on indium recovery from by-product lead alloy. In Proceedings of the Pb-Zn, Duesseldorf, Germany, 14–17 June 2015; pp. 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Sawai, H.; Rahman, I.M.M.; Tsukagoshi, Y.; Wakabayashi, T.; Maki, T.; Mizutani, S.; Hasegawa, H. Selective recovery of indium from lead-smelting dust. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 277, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Jin, B.J.; Ma, B.Z.; Feng, X.Y. Separation of indium from lead smelting hazardous dust via leaching and solvent extraction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2182–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.B.; Liang, D.Q.; Zhong, Q.D. Precipitation of indium using sodium tripolyphosphate. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 106, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Deng, Z.G.; Li, C.X.; Wei, C.; Li, M.T.; Fan, G.; Rong, H. Direct solvent extraction of indium from a zinc residue reductive leach solution by D2EHPA. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 156, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Panda, S.; Sukla, L.B. Recent advances in indium metallurgy: A review. Miner. Process Extr. Metall. Rev. 2018, 39, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions on the 2017 List of Critical Raw Materials for the EU; COM(217) 490 Final; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Harbuck, D.D. Gallium and Germanium Recovery From Domestic Sources; Report of Investigations 9419; US Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1992.
- Pugh, W. Germanium. Part IV. The solubility of germanium dioxide in acids and alkalis. J. Chem. Soc. 1929, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, T.; Nosrati, S.; Belanger, F. Solubility of Germanium Dioxide in Commonly Used Acids—Effect of Acid Strength, Temperature, and Water Activity. In Extraction; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 2481–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein, M.F.W.; Rahway, N.J.; Udin, H. Process for Purifying Indium-Containing Material. U.S. Patent US2,526,354, 17 October 1950. [Google Scholar]






| Element | Sn | Pb | Cu | Ge | Zn | In |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [wt. %] | 28.7 | 18.0 | 10.6 | 8.90 | 8.12 | 2.74 |
| Conditions | c [g/dm3] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid | Oxidant | T [°C] | t [h] | Pb | Sn | Zn | Ge | Cu | In |
| 10% H2SO4 | - | 80 | 2 | 0.015 | 2.8 | 8.1 | 6.4 | 0.002 | 3.4 |
| 10% H2SO4 | - | 25 | 2 | 0.013 | 1.9 | 7.7 | 6.0 | 0.006 | 1.5 |
| 10% H2SO4 | 9.0 g/dm3 H2O2 | 25 | 2 | 0.006 | 0.9 | 7.8 | 4.8 | 0.54 | 1.6 |
| 10% H2SO4 | 20 g/dm3 act. Cl (NaClO) | 25 | 2 | 0.12 | 4.1 | 6.3 | 4.8 | 3.4 | 1.5 |
| 10% H2SO4 | 15.0 g/dm3 MnO2 | 90 | 2 | 0.011 | 0.05 | 7.7 | 4.8 | 2.4 | 2.8 |
| 10% H2C2O4 | - | 90 | 2.5 | 0.025 | 1.5 | 0.033 | 6.1 | 0.006 | 0.37 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drzazga, M.; Prajsnar, R.; Chmielarz, A.; Benke, G.; Leszczyńska-Sejda, K.; Ciszewski, M.; Bilewska, K.; Krawiec, G. Germanium and Indium Recovery from Zinc Metallurgy by-Products—Dross Leaching in Sulphuric and Oxalic Acids. Metals 2018, 8, 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121041
Drzazga M, Prajsnar R, Chmielarz A, Benke G, Leszczyńska-Sejda K, Ciszewski M, Bilewska K, Krawiec G. Germanium and Indium Recovery from Zinc Metallurgy by-Products—Dross Leaching in Sulphuric and Oxalic Acids. Metals. 2018; 8(12):1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121041
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrzazga, Michał, Ryszard Prajsnar, Andrzej Chmielarz, Grzegorz Benke, Katarzyna Leszczyńska-Sejda, Mateusz Ciszewski, Katarzyna Bilewska, and Grzegorz Krawiec. 2018. "Germanium and Indium Recovery from Zinc Metallurgy by-Products—Dross Leaching in Sulphuric and Oxalic Acids" Metals 8, no. 12: 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121041
APA StyleDrzazga, M., Prajsnar, R., Chmielarz, A., Benke, G., Leszczyńska-Sejda, K., Ciszewski, M., Bilewska, K., & Krawiec, G. (2018). Germanium and Indium Recovery from Zinc Metallurgy by-Products—Dross Leaching in Sulphuric and Oxalic Acids. Metals, 8(12), 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8121041