Metal Injection Moulding of High Nb-Containing TiAl Alloy and Its Oxidation Behaviour at 900 °C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Powder Loading and Rheological Behaviour of the Feedstocks
3.2. Binder Decomposition Behavior
3.3. Phase Analysis and Microstructure
3.4. Mechanical Properties
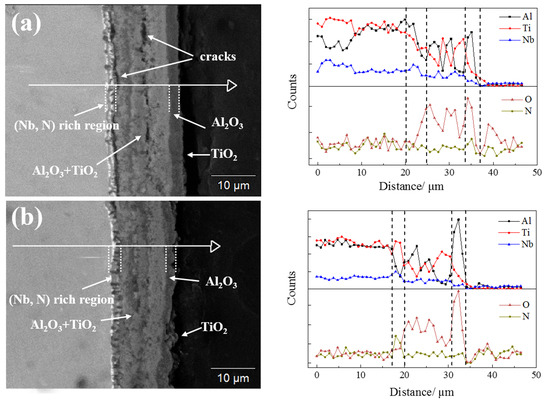
3.5. Oxidation Behaviour
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Using the improved binder, a feedstock with powder loading of 68 vol % was obtained. The viscosity of the feedstock accords with the pseudo-plastic behaviour and the flow behaviour index n at 160 °C and activation energy E were 0.547 and 18.50 KJ/mol, respectively.
- (2)
- The improved binder was easier to remove during thermal debinding and the impurity contents of the debound part using an improved binder were lower than those of the traditional binder feedstock.
- (3)
- The 1480 °C-sintered sample consisted of γ/α2 lamellar microstructure with the average colony size of about 70 µm, and its porosity was about 4%. The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and plastic elongation for the sample sintered at 1480 °C for 2 h were 412 MPa and 0.33%, at room temperature, respectively. The lower levels of ultimate tensile strength and plastic elongation can be related to the higher oxygen content and higher porosity levels in the MIM alloys.
- (4)
- The fine oxide grains of the alloy can effectively relieve the thermal stress and suppress the crack formation during the oxidation process. On the other hand, the presence of a TiN layer plays a role as a barrier against the inward diffusion of oxygen and gives rise to good oxygen scale adhesion. The results mentioned above lead to a better oxidation resistance of the as-sintered alloy than that of the cast alloy counterpart.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clemens, H.; Mayer, S. Design, Processing, Microstructure, Properties, and Applications of Advanced Intermetallic TiAl Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2013, 15, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, F.; Clemens, H.; Fischer, F.D. Modeling concepts for intermetallic titanium aluminides. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 81, 55–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, G.; Qi, Z.; Wang, M.; Yu, H.; Dong, C.; Liu, C.T. Polysynthetic twinned TiAl single crystals for high-temperature applications. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothari, K.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Wereley, N.M. Advances in gamma titanium aluminides and their manufacturing techniques. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Chang, H.; Tang, B.; Kou, H.; Li, J. Deformation and dynamic recrystallization behaviour of a high Nb containing TiAl alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 552, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, F.; Paul, J.D.H.; Oehring, M. Gamma Titanium Aluminide Alloys: Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.Y.; Seo, D.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.E.; Hong, J.K.; Lee, D.B. High temperature oxidation of Ti-46Al-6Nb-0.5W-0.5Cr-0.3Si-0.1C alloy. Intermetallics 2016, 74, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, J.; Oehring, M.; Ebel, T.; Kainer, K.U.; Pyczak, F. Sintering Behavior and Microstructure Formation of Titanium Aluminide Alloys Processed by Metal Injection Molding. JOM 2017, 69, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, T.; Kanda, Y.; Kudo, K.; Tsumori, F.; Miura, H. High temperature mechanical properties of TiAl intermetallic alloy parts fabricated by metal injection molding. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Metall. 2016, 63, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerling, R.; Aust, E.; Limberg, W.; Pfuff, M.; Schimansky, F.P. Metal injection moulding of gamma titanium aluminide alloy powder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 423, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limberg, W.; Ebel, T.; Pyczak, F.; Oehring, M.; Schimansky, F.P. Influence of the sintering atmosphere on the tensile properties of MIM-processed Ti 45Al 5Nb 0.2B 0.2C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 552, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; He, X.; Qu, X.H.; Zhao, L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high Nb containing TiAl alloy parts fabricated by metal injection molding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 526, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Cao, P. Design Strategy of Binder Systems for Ti Injection Moulding. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 520, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, M.D.; Wen, G.; Zulkifli, M.F.; Cao, P. Effect of PEG molecular weight on rheological properties of Ti-MIM feedstocks and water debinding behaviour. Powder Technol. 2015, 270, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, L.; Xiangyi, X. Isothermal Oxidation Behavior of TiAl-Nb-W-B-Y Alloys with Different Lamellar Colony Sizes. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2016, 45, 1695–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Lin, J.P.; He, Y.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. Fabrication and SPS microstructures of Ti-45Al-8.5Nb-(W, B, Y) alloying powders. Intermetallics 2008, 16, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Lin, J.; Li, J. Phase transformation mechanisms in a quenched Ti-45Al-8.5Nb-0.2W-0.2B-0.02Y alloy after subsequent annealing at 800 °C. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Khalil, K.A. Effect of powder loading on metal injection molding stainless steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 183, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rei, M.; Milke, E.C.; Gomes, R.M.; Schaeffer, L.; Souza, J.P. Low-pressure injection molding processing of a 316-L stainless steel feedstock. Mater. Lett. 2002, 52, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan-Manshadi, A.; Bermingham, M.; Dargusch, M.S.; StJohn, D.H.; Qian, M. Metal injection moulding of titanium and titanium alloys: Challenges and recent development. Powder Technol. 2017, 319, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baril, E.; Lefebvre, L.P.; Thomas, Y. Interstitial elements in titanium powder metallurgy: Sources and control. Powder Metall. 2011, 54, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; He, X.B.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Qu, X.H.; Guo, Z.X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a spark plasma sintered Ti-45Al-8.5Nb-0.2W-0.2B-0.1Y alloy. Intermetallics 2009, 17, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obasi, G.C.; Ferri, O.M.; Ebel, T.; Bormann, R. Influence of processing parameters on mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V alloy fabricated by MIM. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3929–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Lin, J.P.; Wang, Y.L.; Gao, J.F.; Lin, Z.; Chen, G.L. Microstructure and tensile properties of as-cast Ti-45Al-(8-9)Nb-(W, B, Y) alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 414, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Xu, X.; Shen, Z.; Ye, T.; Xu, S.; Lin, J. Microstructure and properties of forged plasma arc melted pilot ingot of Ti-45Al-8.5Nb-(W, B, Y) alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 677, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.P.; Zhao, L.L.; Li, G.Y.; Zhang, L.Q.; Song, X.P.; Ye, F.; Chen, G.L. Effect of Nb on oxidation behavior of high Nb containing TiAl alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.L.; Li, G.Y.; Zhang, L.Q.; Lin, J.P.; Song, X.P.; Ye, F.; Chen, G.L. Influence of Y addition on the long time oxidation behaviors of high Nb containing TiAl alloys at 900 °C. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1586–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.B. High Temperature Oxidation of TiAl-1.5 wt % Mn-(0, 5, 10) wt % Y2O3 Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2006, 522, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.G.; Kim, K.Y. Effect of a Yttrium Coating on the Oxidation Behavior of Ni3Al (II). Oxid. Met. 1998, 49, 403–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitoraj, M.; Godlewska, E.; Heintz, O.; Geoffroy, N.; Fontana, S.; Chevalier, S. Scale composition and oxidation mechanism of the Ti-46Al-8Nb alloy in air at 700 and 800 °C. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Rahmel, A.; Schorr, M.; Schütze, M. Mechanism of isothermal oxidation of the intel-metallic TiAl and of TiAl alloys. Oxid. Met. 1992, 38, 425–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Constituent | PW | LDPE | PP | SA | LPW | PEG-10,000 | Naphthalene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melting point (°C) | 58 | 125 | 142 | 66 | −24 | 65 | 80.5 |
| Degradation temperature (°C) | 200–320 | 170–330 | 250–500 | 170–440 | 170–320 | 160–240 | 180–200 |
| Binder weight (F1) (wt %) | balance | 5–10 | 4 | 5 | 5–9 | 3 | 6–10 |
| Binder weight (F2) (wt %) | 63 | 20 | 12 | 5 | - | - | - |
| Temperature (°C) | F1 | F2 |
|---|---|---|
| 140 | 0.5334 | 0.562 |
| 150 | 0.536 | 0.5725 |
| 160 | 0.547 | 0.5972 |
| Impurity | Raw Powder (wt %) | Debound Parts | |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (wt %) | F2 (wt %) | ||
| C | 0.012 ± 0.002 | 0.040 ± 0.003 | 0.055 ± 0.005 |
| O | 0.080 ± 0.01 | 0.130 ± 0.01 | 0.180 ± 0.02 |
| N | 0.021 ± 0.002 | 0.032 ± 0.004 | 0.031 ± 0.005 |
| Phases | Ti (at %) | Al (at %) | Nb (at %) | W (at %) | B (at %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β phase | 53.28 | 32.73 | 13.46 | 0.53 | - |
| Boride | 19.65 | 11.46 | 5.18 | 0.16 | 63.55 |
| Lamellar colony | 45.51 | 45.74 | 8.75 | - | - |
| Sintering Temperature | UTS (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1440 °C | 272 ± 5 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 7 ± 0.3 |
| 1460 °C | 361 ± 3 | 0.26 ± 0.08 | 4.6 ± 0.4 |
| 1480 °C | 412 ± 6 | 0.33 ± 0.06 | 4 ± 0.2 |
| 1500 °C | 383 ± 7 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 3.8 ± 0.3 |
| As-cast alloy [24] | 668 | 0.49 | ~0 |
| Wrought alloy [25] | 897 | 2.2 | ~0 |
| MIM-ed Ti-45Al-5Nb-0.2B-0.2C (at %) [11] | 630 | 0.2 | <1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Yang, F.; Xu, W.; Wang, Z.; Qu, X. Metal Injection Moulding of High Nb-Containing TiAl Alloy and Its Oxidation Behaviour at 900 °C. Metals 2018, 8, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030163
Liu C, Lu X, Yang F, Xu W, Wang Z, Qu X. Metal Injection Moulding of High Nb-Containing TiAl Alloy and Its Oxidation Behaviour at 900 °C. Metals. 2018; 8(3):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030163
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chengcheng, Xin Lu, Fei Yang, Wei Xu, Zhe Wang, and Xuanhui Qu. 2018. "Metal Injection Moulding of High Nb-Containing TiAl Alloy and Its Oxidation Behaviour at 900 °C" Metals 8, no. 3: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030163
APA StyleLiu, C., Lu, X., Yang, F., Xu, W., Wang, Z., & Qu, X. (2018). Metal Injection Moulding of High Nb-Containing TiAl Alloy and Its Oxidation Behaviour at 900 °C. Metals, 8(3), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8030163