Deposits in Gas-fired Rotary Kiln for Limonite Magnetization-Reduction Roasting: Characteristics and Formation Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Chemical Analysis on Raw Materials
2.1.2. Locations in the Kiln Where Deposits Were Collected
2.2. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. In-Line Observation of Deposits
3.2. Appearance of Deposits
3.3. Chemical Composition of Deposits
3.4. Microstructural Characterization and Phase Evaluation
3.5. Mechanism for Deposit Formation
3.5.1. Generation of Wüstite (FeO)
3.5.2. Solid Phase Reaction Process of Al2O3-SiO2-CaO-FeO System
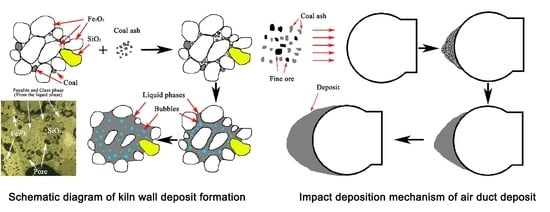
3.5.3. Analysis of the Deposit Formation Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, F.; Cao, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhong, H. Novel and green metallurgical technique of comprehensive utilization of refractory limonite ores. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-S.; Strezovb, V.; Lucas, J.A.; Wibberley, L.J. Thermal investigations of direct iron ore reduction with coal. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 410, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y. Recovering limonite from Australia iron ores by flocculation-high intensity magnetic separation. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2005, 12, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Q. Recovery of Huangmei limonite by flash magnetic roasting technique. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing, Hoboken, NJ, USA, 17 March 2012; pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Rath, S.S.; Dhawan, N.; Rao, D.S.; Das, B.; Mishra, B.K. Beneficiation studies of a difficult to treat iron ore using conventional and microwave roasting. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.; Youssef, M.A. Optimization of magnetizing reduction and magnetic separation of iron ores by experimental design. ISIJ Int. 1996, 36, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.A.; Morsi, M.B. Reduction roast and magnetic separation of oxidized iron ores for the production of blast furnace feed. Can. Metall. Q. 2013, 37, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, H.; Bai, J.; Li, L. Innovative methodology for comprehensive utilization of iron ore tailings: Part 1. The recovery of iron from iron ore tailings using magnetic separation after magnetizing roasting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, S.S.; Sahoo, H.; Dhawan, N.; Rao, D.S.; Das, B.; Mishra, B.K. Optimal recovery of iron values from a low grade iron ore using reduction roasting and magnetic separation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, H.; Qi, Y. Magnetic roasting of limonite of low grade. J. Iron Steel Res. 2015, 27, 8–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ponomar, V.P.; Dudchenko, N.O.; Brik, A.B. Synthesis of magnetite powder from the mixture consisting of siderite and hematite iron ores. Miner. Eng. 2018, 122, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, H. Status quo and development prospect of magnetizing roasting via fluidized bed for low grade iron ore. CIESC J. 2014, 65, 2437–2442. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Chai, T.; Yu, W.; Xu, Z. Multi-objective evaluation-based hybrid intelligent control optimization for shaft furnace roasting process. Control Eng. Pract. 2012, 20, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Yu, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, X. Test research on the flash magnetization roasting technology for complex and refractory iron ore. Metal Mine 2009, 402, 73–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, T. Recovery of low grade haematite via fluidised bed magnetising roasting: Investigation of magnetic properties and liberation characteristics. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2013, 39, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, Y.; Hong, Z.; Peng, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q. Development and application of packaged technology for flash(fluidization) magnetizing roasting of refractory weakly magnetic iron ore. Mining Metall. Eng. 2017, 37, 40–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Innovative utilization of refractory iron ore via suspension magnetization roasting: A pilot-scale study. Powder Technol. 2019, 352, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Mao, Y.; Xue, S. Study on deposit formation and prevention control of large industrial magnetized roasting rotary kiln. Nonferrous Met. (Mineral Processing Section) 2013, s1, 236–239. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Fan, J.; He, Y.; Jiang, T.; Chen, F.; Zheng, F.; Yang, L. Initial stage of deposit formation process in a coal fired grate-rotary kiln for iron ore pellet production. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 175, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Fan, J.; Jiang, T.; Chen, F.; Zheng, F.; Yang, L. Deposits in a coal fired grate-kiln plant for hematite pellet production: Characterization and primary formation mechanisms. Powder Technol. 2018, 333, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-F.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Jiang, T.; Chen, F.; Zheng, F.-Q. Deposit formation mechanisms in a pulverized coal fired grate for hematite pellet production. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 161, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Li, Q.; Xu, B. Effect of coal ash on ring behavior of iron-ore pellet powder in kiln. Powder Technol. 2018, 323, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; He, G.; Gan, M.; Li, G.; Fan, X.; Yuan, L. Forming mechanism of rings in rotary-Kiln for forming mechanism of rings in rotary-kiln for oxidized pellet. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2009, 16, 292–297. [Google Scholar]
- Stjernberg, J.; Jonsson, C.Y.C.; Wiinikka, H.; Lindblom, B.; Boström, D.; Öhman, M. Deposit formation in a grate–kiln plant for iron-ore pellet production. Part 2: Characterization of deposits. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 6171–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G. Chemical analysis method standards and proficiency testing of laboratory for iron ore. Metall. Anal. 2015, 35, 37–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Ji, H.; Dai, B.; Zhang, L. Xinjiang lignite ash slagging and flowability under the weak reducing environment at 1300 °C—A new method to quantify slag flow velocity and its correlation with slag properties. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 171, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhou, T.; Chen, Y.; Hou, N.; Piao, G.; Kobayashi, N.; Itaya, Y.; Mori, S. The effect of iron-bearing mineral melting behavior on ash deposition during coal combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 2853–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, L.L.; DeSollart, R.W. A mechanistic description of ash deposition during pulverized coal combustion predictions compared with observations. Fuel 1993, 72, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, L.L. Ash deposition during biomass and coal combustion a mechanistic approach. Biomass Bioenerg. 1993, 4, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K. (Ed.) Advanced Pulverized Coal Injection Technology and Blast Furnace Operation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, R. Microstructure of Sinter and Pellet; Central South University Press: Changsha, China, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Wang, C.; Yang, W.; Yin, F.; Chen, Y. Screening and reduction roasting of limonitic laterite and ammonia-carbonate leaching of nickel–cobalt to produce a high-grade iron concentrate. Miner. Eng. 2013, 50, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Theory and Technology of Sintered Pellets; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, T.; Helble, J.J.; Bool, L.E.; Sarofim, A.F. Iron transformations during combustion of Pittsburgh No. 8 coal. Fuel 2009, 88, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Chen, F.; He, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zheng, F. Combustion reaction of pulverized coal on the deposit formation in the kiln for iron ore pellet production. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 6123–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, R.; Maier, J. On the tammann-rule. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2005, 631, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahotre, N.B.; Kadolkar, P.; Shah, S. Refractory ceramic coatings: Processes, systems and wettability/adhesion. Surf. Interface Anal. 2001, 31, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stjernberg, J.; Ion, J.C.; Antti, M.-L.; Nordin, L.-O.; Lindblom, B.; Odén, M. Extended studies of degradation mechanisms in the refractory lining of a rotary kiln for iron ore pellet production. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.P.; Huggins, F.E.; Dunmyre, G.R. Investigation of the high-temperature behaviour of coal ash in reducing and oxidizing atmospheres. Fuel 1981, 60, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Total Fe | FeO | Fe2O3 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | MnO | K2O | Na2O | S | Ig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35.85 | 10.2 | 39.92 | 18.89 | 3.79 | 2.22 | 2.42 | 1.86 | 1.02 | 0.092 | 0.26 | 15.8 |
| Moisture/% | Ash/% | Volatile Matter/% | Fixed Carbon/% | Qgr/(MJ·Kg−1) | Coking Properties (1–8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.3 | 10.28 | 30.02 | 57.32 | 28.63 | 2 |
| SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55.42 | 9.81 | 20.18 | 2.68 | 2.8 | 3.56 | 0.42 |
| Deposit Sample | Comp. FeO | TFe | FeO | Fe2O3 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | MnO | K2O | Na2O | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | max | 42.51 | 44.89 | 8.66 | 29.57 | 6.52 | 2.51 | 2.69 | 2.28 | 2.05 | 0.15 | 0.31 |
| min | 39.78 | 40.16 | 9.93 | 30.32 | 7.64 | 2.82 | 2.02 | 2.09 | 1.93 | 0.22 | 0.27 | |
| S2 | max | 40.67 | 41.35 | 9.54 | 30.18 | 7.29 | 2.91 | 2.25 | 1.81 | 2.08 | 0.21 | 0.27 |
| min | 38.80 | 38.32 | 11.81 | 31.02 | 8.00 | 2.70 | 2.02 | 2.05 | 2.20 | 0.24 | 0.13 | |
| S3 | - | 34.53 | 37.22 | 6.82 | 33.42 | 9.28 | 4.41 | 2.40 | 1.77 | 2.20 | 0.32 | 0.18 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, X.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X.; He, L.; Song, Y. Deposits in Gas-fired Rotary Kiln for Limonite Magnetization-Reduction Roasting: Characteristics and Formation Mechanism. Metals 2019, 9, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070764
Fu X, Chen Z, Xu X, He L, Song Y. Deposits in Gas-fired Rotary Kiln for Limonite Magnetization-Reduction Roasting: Characteristics and Formation Mechanism. Metals. 2019; 9(7):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070764
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Xianghui, Zezong Chen, Xiangyang Xu, Lihua He, and Yunfeng Song. 2019. "Deposits in Gas-fired Rotary Kiln for Limonite Magnetization-Reduction Roasting: Characteristics and Formation Mechanism" Metals 9, no. 7: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070764
APA StyleFu, X., Chen, Z., Xu, X., He, L., & Song, Y. (2019). Deposits in Gas-fired Rotary Kiln for Limonite Magnetization-Reduction Roasting: Characteristics and Formation Mechanism. Metals, 9(7), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9070764