Wastewater-Based Epidemiology as a Tool to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Circulation at the Community Level: Findings from a One-Year Wastewater Investigation Conducted in Sicily, Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
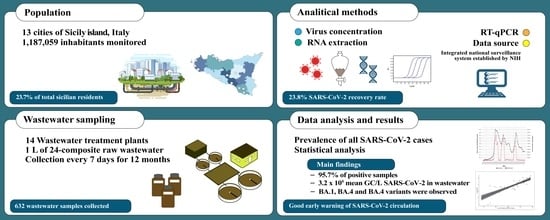
2.1. Study Design and Sample Collections
2.2. Laboratory Methods
2.2.1. Virus Concentration
2.2.2. RNA Extraction
2.2.3. RT-qPCR
2.2.4. Flash Surveying the SARS-CoV-2 Variants
2.2.5. Clinical Data Sources
2.2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Marques, E.; Da Silva, E.E.; Dos Santos, V.M.; Kew, O.M.; Martins, M.T. Application of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to poliomyelitis surveillance through the analyses of sewage samples. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1993, 9, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kettani, S.; Azzouzi, E.; Boukachabine, K.; El Yamani, M.; Maata, A.; Rajaoui, M. Intestinal parasitosis and use of untreated wastewater for agriculture in Settat, Morocco. East Mediterr. Health J. 2008, 14, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harder, R.; Heimersson, S.; Svanström, M.; Peters, G.M. Including pathogen risk in life cycle assessment of wastewater management. 1. Estimating the burden of disease associated with pathogens. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9438–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diemert, S.; Yan, T. Clinically Unreported Salmonellosis Outbreak Detected via Comparative Genomic Analysis of Municipal Wastewater Salmonella Isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00139-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Benedetto, M.A.; Di Piazza, F.; Maida, C.M.; Oliveri, R. Occurrence of Giardia and Cryptosporidium in wastewater, surface water and ground water samples in Palermo (Sicily). Ann. Di Ig. 2005, 17, 367–375. [Google Scholar]
- La Rosa, G.; Iaconelli, M.; Mancini, P.; Bonanno Ferraro, G.; Veneri, C.; Bonadonna, L.; Lucentini, L.; Suffredini, E. First detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewaters in Italy. Sci. Total. Enviro. 2020, 736, 139652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.; Curtis, K.; Bivins, A.; Bibby, K.; Weir, M.H.; Yetka, K.; Thompson, H.; Keeling, D.; Mitchell, J.; Gonzalez, D. COVID-19 surveillance in Southeastern Virginia using wastewater-based epidemiology. Water. Res. 2020, 186, 116296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.W.; Ibrahim, Y.; Daou, M.; Kannout, H.; Jan, N.; Lopes, A.; Alsafar, H.; Yousef, A.F. Detection and quantification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater and treated effluents: Surveillance of COVID-19 epidemic in the United Arab Emirates. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Zhang, K.; Du, W.; Ali, W.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H. The potential of wastewater-based epidemiology as surveillance and early warning of infectious disease outbreaks. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health. 2020, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, G.; Iaconelli, M.; Veneri, C.; Mancini, P.; Bonanno Ferraro, G.; Brandtner, D.; Lucentini, L.; Bonadonna, L.; Rossi, M.; Grigioni, M.; et al. The rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in Italy reflected early through wastewater surveillance. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maida, C.M.; Amodio, E.; Mazzucco, W.; La Rosa, G.; Lucentini, L.; Suffredini, E.; Palermo, M.; Andolina, G.; Iaia, F.R.; Merlo, F.; et al. SARI Collaboration Group. Wastewater-based epidemiology for early warning of SARS-CoV-2 circulation: A pilot study conducted in Sicily, Italy. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health. 2022, 242, 113948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Angel, N.; Edson, J.; Bibby, K.; Bivins, A.; O’Brien, J.W.; Choi, P.M.; Kitajima, M.; Simpson, S.L.; Li, J.; et al. First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: A proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherchan, S.P.; Shahin, S.; Ward, L.M.; Tandukar, S.; Aw, T.G.; Schmitz, B.; Ahmed, W.; Kitajima, M. First detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater in North America: A study in Louisiana, USA. Sci Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haramoto, E.; Malla, B.; Thakali, O.; Kitajima, M. First environmental surveillance for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater and river water in Japan. Sci Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Expert Consultation on Public Health Needs Related to Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/339487/WHO-EURO-2021-1965-41716-57097-eng.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- European Commission. Commission Recommendation (EU) 2021/472 of 17 March 2021 on a Common Approach to Establish Systematic Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants in Wastewater in the EU. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/05b46cb0-8855-11eb-ac4c-01aa75ed71a1/language-en/format-PDF (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Weidhaas, J.; Aanderud, Z.T.; Roper, D.K.; VanDerslice, J.; Brown Gaddis, E.; Ostermiller, J.; Hoffman, K.; Jamal, R.; Heck, P.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater with COVID-19 disease burden in sewer sheds. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyllestad, S.; Myrmel, M.; Baz Lomba, J.A.; Jordhøy, F.; Schipper, S.K.; Amato, E. Effectiveness of environmental surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 as an early warning system during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 1223–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillary, L.S.; Farkas, K.; Maher, K.H.; Lucaci, A.; Thorpe, J.; Distaso, M.A.; Gaze, W.H.; Paterson, S.; Burke, T.; Connor, T.R.; et al. Monitoring SARS-CoV-2 in municipal wastewater to evaluate the success of lockdown measures for controlling COVID-19 in the UK. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierkegaard, P.; McLister, A.; Buckle, P. Rapid point-of-care testing for COVID-19: Quality of supportive information for lateral flow serology assays. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e047163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Baluja, M.Q.; Graham, D.W.; Corbishley, A.; Mcdonald, J.E.; Malham, S.K.; Hillary, L.S.; Connor, T.R.; Gaze, W.H.; Moura, I.B.; et al. Shedding of SARS-CoV-2 in faeces and urine and its potential role in person-to-person transmission and the environment-based spread of COVID-19. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Hossen, F.; Rahman, A.; Sultana, K.F.; Hasan, M.N.; Haque, A.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Oyervides-Muñoz, M.A.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Ahmed, T.; et al. An opinion on Wastewater-Based Epidemiological Monitoring (WBEM) with Clinical Diagnostic Test (CDT) for detecting high-prevalence areas of community COVID-19 Infections. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 31, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, P.M.; Tscharke, B.J.; Donner, E.; O’Brien, J.W.; Grant, S.C.; Kaserzon, S.L.; Mackie, R.; O’Malley, E.; Crosbie, N.D.; Thomas, K.V.; et al. Wastewater-based epidemiology biomarkers: Past, present and future. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C. Watcher in the wastewater. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, M.B.; Keshaviah, A.; Bento, A.I.; Conroy-Ben, O.; Driven, E.M.; Ensor, K.B.; Halden, R.U.; Hopkins, L.P.; Kuhn, K.G.; Moe, C.L.; et al. Wastewater surveillance of pathogens can inform public health responses. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1992–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Integrate Surveillance System. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/coronavirus/sars-cov-2-sorveglianza (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Press Release N°41/2020 —“Wastewater and Coronavirus, the ‘Sentinel’ Network of Epidemiological Surveillance is Underway”. Available online: https://www.iss.it/cov19-acque-reflue/-/asset_publisher/dJSrLJgOqlTV/content/cs-n°41-2020-acque-reflue-e-coronavirus-al-via-la-rete-sentinella-di-sorveglianza-epidemiologica-?_com_liferay_asset_publisher_web_portlet_AssetPublisherPortlet_INSTANCE_dJSrLJgOqlTV_assetEntryId=5428743&_com_liferay_asset_publisher_web_portlet_AssetPublisherPortlet_INSTANCE_dJSrLJgOqlTV_redirect=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.iss.it%2Fcov19-acque-reflue%3Fp_p_id=com_liferay_asset_publisher_web_portlet_AssetPublisherPortlet_INSTANCE_dJSrLJgOqlTV%26p_p_lifecycle=0%26p_p_state=normal%26p_p_mode=view%26_com_liferay_asset_publisher_web_portlet_AssetPublisherPortlet_INSTANCE_dJSrLJgOqlTV_assetEntryId=5428743%26_com_liferay_asset_publisher_web_portlet_AssetPublisherPortlet_INSTANCE_dJSrLJgOqlTV_cur=2%26_com_liferay_asset_publisher_web_portlet_AssetPublisherPortlet_INSTANCE_dJSrLJgOqlTV_delta=20%26p_r_p_resetCur=false (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Italian Legislative Decrete no. 24/2022. Urgent Provisions for Overcoming the Measures to Contrast the Spread of the COVID-19 Epidemic, as a Result of the Cessation of the State of Emergency. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2022/03/24/22G00034/sg (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Italian National Statistics Institute (ISTAT). Estimated Resident Population—Years 2001–2019. Available online: http://dati.istat.it/Index.aspx?QueryId=12409&lang=en (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Surveillance Protocol of SARS-CoV-2 in Municipal Wastewater (SARI)—Rev.3. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/5758725#.Y8-y9y9aZnt (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, A.; Gu, X.; Lee, W.L.; Armas, F.; Kauffman, K.; Hanage, W.; Matus, M.; Ghaeli, N.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Titers in Wastewater Are Higher than Expected from Clinically Confirmed Cases. mSystems 2020, 5, e00614-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, G.; Mancini, P.; Bonanno Ferraro, G.; Veneri, C.; Iaconelli, M.; Lucentini, L.; Bonadonna, L.; Brusaferro, S.; Brandtner, D.; Fasanella, A.; et al. Rapid screening for SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in clinical and environmental samples using nested RT-PCR assays targeting key mutations of the spike protein. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Ad hoc survey on B.1.1.159 (Omicron) Variant on SARS-CoV-2 in Urban Wastewater in Italy (Study Period: 5 December–25 December 2021). Available online: https://www.iss.it/documents/20126/0/Report_Flash_survey_omicron_dicembre2021+-+rev+03.01.22+ore+15.pdf/fe204e2c-2fdb-cd0b-f9e4-aa6e2a8edcc3?t=1641235787698 (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Flash Survey on SARS-CoV-2 in Urban Wastewater in Italy, 6th Report (Study Period: 7 February–11 February 2022). Available online: https://www.iss.it/documents/20126/0/Flash+survey_FEBBRAIO+2022_Report_10-03-2022+%282%29.pdf/a4e09270-7aef-61d8-00f9-e25d13306be6?t=1647012625685 (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Flash survey on SARS-CoV-2 in Urban Wastewater in Italy, 10th Report (Study Period: 6 June–10 June 2022). Available online: https://www.iss.it/documents/20126/0/Flash+survey_Giugno_2022_Report_12-07-2022.pdf/4ed6a021-0c27-aa76-5705-20756f7b17e6?t=1657716314850 (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- D’Aoust, P.M.; Graber, T.E.; Mercier, E.; Montpetit, D.; Alexandrov, I.; Neault, N.; Baig, A.T.; Mayne, J.; Zhang, X.; Alain, T.; et al. Catching a resurgence: Increase in SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA identified in wastewater 48 h before COVID-19 clinical tests and 96 h before hospitalizations. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Ellenberg, R.M.; Graham, K.E.; Wigginton, K.R. Survivability, Partitioning, and Recovery of Enveloped Viruses in Untreated Municipal Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5077–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboa, S.; Mauricio-Iglesias, M.; Rodriguez, S.; Martínez-Lamas, L.; Vasallo, F.J.; Regueiro, B.; Lema, J.M. The fate of SARS-CoV-2 in WWTPS points out the sludge line as a suitable spot for detection of COVID-19. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattino, G.; Castiglioni, S.; Cereda, D.; Della Valle, P.G.; Pellegrinelli, L.; Bertolini, G.; Pariani, E. Association Between SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Wastewater and Reported Cases, Hospitalizations, and Vaccinations in Milan, March 2020 to November 2021. JAMA 2022, 327, 1922–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schill, R.; Nelson, K.L.; Harris-Lovett, S.; Kantor, R.S. The dynamic relationship between COVID-19 cases and SARS-CoV-2 wastewater concentrations across time and space: Considerations for model training data sets. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, J.A.; Trigo-Tasende, N.; Rumbo-Feal, S.; Conde-Pérez, K.; López-Oriona, A.; Barbeito, I.; Vaamonde, M.; Tarrío-Saavedra, J.; Reif, R.; Ladra, S.; et al. Modeling the number of people infected with SARS-CoV-2 from wastewater viral load in Northwest Spain. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2022, 811, 152334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schussman, M.K.; McLellan, S.L. Effect of Time and Temperature on SARS-CoV-2 in Municipal Wastewater Conveyance Systems. Water 2022, 14, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. National Wastewater Surveillance System (NWSS)—A Public Health Tool to Understand COVID-19 Spread in A Community. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/surveillance/wastewater-surveillance/wastewater-surveillance.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https&per;3A&per;2F&per;2Fwww.cdc.gov&per;2Fcoronavirus&per;2F2019-ncov&per;2Fcases-updates&per;2Fwastewater-surveillance.html (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- European Commission. SARS-CoV-2 Surveillance Employing Sewage Towards A Sentinel System. Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC125065 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- World Health Organization. Environmental Surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 to Complement Public Health Surveillance—Interim Guidance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-HEP-ECH-WSH-2022.1 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. COVID-19: Surveillance, Impact of Infections and Vaccine Efficacy. National Update: 28 Giugno 2022. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/coronavirus/bollettino/Bollettino-sorveglianza-integrata-COVID-19_28-giugno-2022.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Ahmed, W.; Tscharke, B.; Bertsch, P.M.; Bibby, K.; Bivins, A.; Choi, P.; Clarke, L.; Dwyer, J.; Edson, J.; Nguyen, T.M.H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 RNA monitoring in wastewater as a potential early warning system for COVID-19 transmission in the community: A temporal case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roka, E.; Khayer, B.; Kis, Z.; Kovacs, L.B.; Schuler, E.; Magyar, N.; Malnasi, T.; Oravecz, O.; Palyi, B.; Pandics, T.; et al. Ahead of the second wave: Early warning for COVID-19 by wastewater surveillance in Hungary. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.; Tian, J.; Liu, J.; Mao, Y. Environmental contamination by SARS-CoV-2 in a designated hospital for coronavirus disease 2019. Am. J. Infect. Control 2020, 48, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, D.; Dinero, R.; Asiago-Reddy, E.; Green, H.; Lane, S.; Shaw, A.; Zeng, T.; Kmush, B. A review of infectious disease surveillance to inform public health action against the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. SocArXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, M.N.K.; Geraghty, E.M. Geographical tracking and mapping of coronavirus disease COVID-19/severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) epidemic and associated events around the world: How 21st century GIS technologies are supporting the global fight against outbreaks and epidemics. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2020, 19, 8. [Google Scholar]



| Wastewater Treatment Plant | Average Inflow (m3/die ± SD) | Served Population (N) |
|---|---|---|
| Agrigento | 7593.0 ± 1238.6 | 55,000 |
| Bagheria | 9988.7 ± 1795.7 | 75,000 |
| Caltanissetta | 13,217.5 ± 2329.4 | 76,700 |
| Enna | 3807.7 ± 1170.2 | 34,000 |
| Gela | 1465.6 ± 475.9 | 12,000 |
| Marsala | 7500 ± n.d. | 40,000 |
| Mazara del Vallo | 3630 ± n.d. | 17,000 |
| Messina | 2488.9 ± 450.0 | 227,000 |
| Modica | 8061.8 ± 1940.3 | 50,000 |
| Palermo WWTP1 | 83,205.2 ± 2292.1 | 53,886 |
| Palermo WWTP2 | 19,438.7 ± 1575.0 | 314,973 |
| Ragusa | 11,171.6 ± 1725.7 | 58,000 |
| Trapani | 16,893.4 ± 2372.8 | 118,500 |
| Vittoria | 11,197.1 ± 2218.0 | 55,000 |
| Total | 1,187,059 | |
| t0 Prevalence | t7 Prevalence | t14 Prevalence | Severe Clinical Outcomes | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Periods (Months) | R | r2 | p-Value | R | r2 | p-Value | R | r2 | p-Value | R | r2 | p-Value | |
| GC/L * | 0–6 | 0.90 | 0.82 | <0.001 | 0.89 | 0.79 | <0.001 | 0.87 | 0.76 | <0.001 | 0.93 | 0.61 | <0.001 |
| 7–12 | 0.77 | 0.59 | <0.001 | 0.79 | 0.62 | <0.001 | 0.69 | 0.47 | <0.001 | 0.75 | 0.53 | <0.001 | |
| 0–12 | 0.85 | 0.72 | <0.001 | 0.87 | 0.76 | <0.001 | 0.86 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 0.90 | 0.51 | <0.001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maida, C.M.; Tramuto, F.; Giammanco, G.M.; Palermo, R.; Priano, W.; De Grazia, S.; Purpari, G.; La Rosa, G.; Suffredini, E.; Lucentini, L.; et al. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology as a Tool to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Circulation at the Community Level: Findings from a One-Year Wastewater Investigation Conducted in Sicily, Italy. Pathogens 2023, 12, 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060748
Maida CM, Tramuto F, Giammanco GM, Palermo R, Priano W, De Grazia S, Purpari G, La Rosa G, Suffredini E, Lucentini L, et al. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology as a Tool to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Circulation at the Community Level: Findings from a One-Year Wastewater Investigation Conducted in Sicily, Italy. Pathogens. 2023; 12(6):748. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060748
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaida, Carmelo Massimo, Fabio Tramuto, Giovanni Maurizio Giammanco, Roberta Palermo, Walter Priano, Simona De Grazia, Giuseppa Purpari, Giuseppina La Rosa, Elisabetta Suffredini, Luca Lucentini, and et al. 2023. "Wastewater-Based Epidemiology as a Tool to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Circulation at the Community Level: Findings from a One-Year Wastewater Investigation Conducted in Sicily, Italy" Pathogens 12, no. 6: 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060748
APA StyleMaida, C. M., Tramuto, F., Giammanco, G. M., Palermo, R., Priano, W., De Grazia, S., Purpari, G., La Rosa, G., Suffredini, E., Lucentini, L., Palermo, M., Pollina Addario, W., Graziano, G., Immordino, P., Vitale, F., SARI Collaboration Group, & Mazzucco, W. (2023). Wastewater-Based Epidemiology as a Tool to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Circulation at the Community Level: Findings from a One-Year Wastewater Investigation Conducted in Sicily, Italy. Pathogens, 12(6), 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12060748