Evidence of the Extrahepatic Replication of Hepatitis E Virus in Human Endometrial Stromal Cells
Abstract
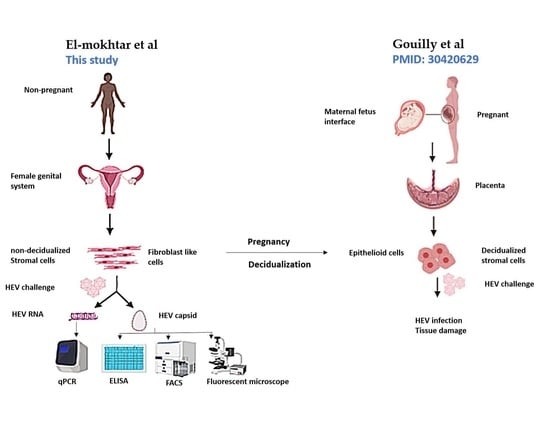
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Characterization of PHESCs
2.2. HEV RNA Kinetic in PHESCs Challenged with HEV Preparations
2.3. HEV Capsid Protein Was Assembled in PHESCs and the Virus Completes the Life Cycle in the Cells
2.4. HEV-1 Upregulated the Inflammatory Transcriptome of PHESCs and Impaired Interferon (IFN) Type III Expression
2.5. Ribavirin (RBV) Abolished HEV Replication in PHESCs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Characterization of PHESCs from Non-Pregnant Women
4.2. HEV Inoculums
4.3. Infection of PHESCs with HEV Preparations
4.4. Quantification of HEV RNA by qRT-PCR
4.5. Detection of HEV ORF2 Ag in the Infected PHESCs by Immunofluorescence and Flow Cytometry
4.6. Monitoring of Extracellular HEV Capsid Protein by ELISA
4.7. Test the Effect of HEV Infection on the Transcriptome of PHESCs
4.8. Testing the Effect of Ribavirin (RBV) on HEV Replication in PHESCs
4.9. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sayed, I.M.; Vercauteren, K.; Abdelwahab, S.F.; Meuleman, P. The emergence of hepatitis E virus in Europe. Future Virol. 2015, 10, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayed, I.M.; Vercouter, A.S.; Abdelwahab, S.F.; Vercauteren, K.; Meuleman, P. Is hepatitis E virus an emerging problem in industrialized countries? Hepatology 2015, 62, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rein, D.B.; Stevens, G.A.; Theaker, J.; Wittenborn, J.S.; Wiersma, S.T. The global burden of hepatitis E virus genotypes 1 and 2 in 2005. Hepatology 2012, 55, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Simmonds, P.; Izopet, J.; Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Ulrich, R.G.; Johne, R.; Koenig, M.; Jameel, S.; Harrison, T.J.; Meng, X.J.; et al. Proposed reference sequences for hepatitis E virus subtypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Simmonds, P.; Jameel, S.; Emerson, S.U.; Harrison, T.J.; Meng, X.J.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.; Purdy, M.A. Consensus proposals for classification of the family Hepeviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Halbur, P.G.; Lehman, J.R.; Webb, D.M.; Tsareva, T.S.; Haynes, J.S.; Thacker, B.J.; Emerson, S.U. A novel virus in swine is closely related to the human hepatitis E virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9860–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavio, N.; Meng, X.J.; Doceul, V. Zoonotic origin of hepatitis E. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 10, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, S.P. The Current Host Range of Hepatitis E Viruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, A.K.; Joseph, M.; Wong, E.Y.; Tang, Y.; Sivakumar, S.; Xie, J.; Bai, R.; et al. New hepatitis E virus genotype in camels, the Middle East. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Tan, B.H.; Teo, E.C.; Lim, S.G.; Dan, Y.Y.; Wee, A.; Aw, P.P.; Zhu, Y.; Hibberd, M.L.; Tan, C.K.; et al. Chronic Infection With Camelid Hepatitis E Virus in a Liver Transplant Recipient Who Regularly Consumes Camel Meat and Milk. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavio, N.; Doceul, V.; Bagdassarian, E.; Johne, R. Recent knowledge on hepatitis E virus in Suidae reservoirs and transmission routes to human. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domanović, D.; Tedder, R.; Blümel, J.; Zaaijer, H.; Gallian, P.; Niederhauser, C.; Sauleda Oliveras, S.; O’Riordan, J.; Boland, F.; Harritshøj, L.; et al. Hepatitis E and blood donation safety in selected European countries: A shift to screening? Euro Surveill. 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Sato, H.; Sato, Y.; Jirintai; Nagashima, S.; Okamoto, H. Analysis of the full-length genome of a hepatitis E virus isolate obtained from a wild boar in Japan that is classifiable into a novel genotype. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, A.; Kar, P.; Agarwal, S.; Ramji, S.; Husain, S.A.; Prasad, S.; Sharma, S. Risk factors for vertical transmission of hepatitis E virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charre, C.; Ramière, C.; Dumortier, J.; Abravanel, F.; Lhomme, S.; Gincul, R.; Scholtès, C. Chronic genotype 3 hepatitis E in pregnant woman receiving infliximab and azathioprine. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 941–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabatabai, J.; Wenzel, J.J.; Soboletzki, M.; Flux, C.; Navid, M.H.; Schnitzler, P. First case report of an acute hepatitis E subgenotype 3c infection during pregnancy in Germany. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, P.D.; Das, B.C.; Hazam, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Medhi, S.; Kar, P. Evidence of extrahepatic replication of hepatitis E virus in human placenta. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, P.D.; Das, B.C.; Kumar, A.; Gondal, R.; Kumar, D.; Kar, P. High viral load and deregulation of the progesterone receptor signaling pathway: Association with hepatitis E-related poor pregnancy outcome. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaneethan, U.; Al Mohajer, M.; Shata, M.T. Hepatitis E and pregnancy: Understanding the pathogenesis. Liver Int. 2008, 28, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayed, I.M.; Elkhawaga, A.A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A. In vivo models for studying Hepatitis E virus infection; Updates and applications. Virus Res. 2019, 274, 197765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischke, S.; Hartl, J.; Pas, S.D.; Lohse, A.W.; Jacobs, B.C.; Van der Eijk, A.A. Hepatitis E virus: Infection beyond the liver? J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Situ, J.; Wang, W.; Long, F.; Yang, W.; Yang, C.; Wei, D.; Yu, W.; Huang, F. Hepatitis E viral infection causes testicular damage in mice. Virology 2020, 541, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Long, F.; Yu, W.; Situ, J.; Fu, L.; He, Z.; Dong, H.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; et al. High prevalence of hepatitis E virus in semen of infertile male and causes testis damage. Gut 2018, 67, 1199–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Liu, T.; She, R.; Wu, Q.; Tian, J.; Shi, R.; Hao, W.; Ren, X.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. Replication of hepatitis E virus in the ovary and promotion of oocyte apoptosis in rabbits infected with HEV-4. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 4475–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Long, F.; He, Q.; Huang, F. Successful establishment of hepatitis E virus infection in pregnant BALB/c mice. Viruses 2019, 11, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, C.L.; Kelly, R.W.; Critchley, H.O. Decidualization of the human endometrial stromal cell: An enigmatic transformation. Reprod. BioMed. Online 2003, 7, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, I.; Ghezzi, S.; Ulisse, A.; Rubio, A.; Turrini, F.; Garavaglia, E.; Candiani, M.; Castilletti, C.; Ippolito, G.; Poli, G.; et al. Human endometrial stromal cells are highly permissive to productive infection by zika virus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neidleman, J.A.; Chen, J.C.; Kohgadai, N.; Muller, J.A.; Laustsen, A.; Thavachelvam, K.; Jang, K.S. Mucosal stromal fibroblasts markedly enhance HIV infection of CD4+ T cells. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouilly, J.; Chen, Q.; Siewiera, J.; Cartron, G.; Levy, C.; Dubois, M.; Al-Daccak, R.; Izopet, J.; Jabrane-Ferrat, N.; El Costa, H. Genotype specific pathogenicity of hepatitis E virus at the human maternal-fetal interface. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altayyeb, A.; Othman, E.; Khashbah, M.; Esmaeel, A.; El-Mokhtar, M.; Lambalk, C.; Mijatovic, V.; Abdelgawad, M. Characterization of mechanical signature of eutopic endometrial stromal cells of endometriosis patients. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 27, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischke, S.; Behrendt, P.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H. HEV-associated cryoglobulinaemia and extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis E. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 678–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, M.H.; Shi, R.; She, R.; Yang, Y. Molecular and structural changes related to hepatitis E virus antigen and its expression in testis inducing apoptosis in Mongolian gerbil model. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, J.; Sheng, Y.; Lu, Q.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, E.M. Prevalence of hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection in various pig farms from Shaanxi Province, China: First detection of HEV RNA in pig semen. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horvatits, T.; Varwig-Janssen, D.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, J.; Lubke, R.; Reucher, S.; Frerk, S.; Addo, M.M.; Schneider, S.W.; Lohse, A.W.; Luetgehetmann, M.; et al. No link between male infertility and HEV genotype 3 infection. Gut 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Tsuzuki, T.; Murata, H. Decidualization of the human endometrium. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2018, 17, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drave, S.A.; Debing, Y.; Walter, S.; Todt, D.; Engelmann, M.; Friesland, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Neyts, J.; Behrendt, P.; Steinmann, E. Extra-hepatic replication and infection of hepatitis E virus in neuronal-derived cells. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knegendorf, L.; Drave, S.A.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Debing, Y.; Brown, R.J.P.; Vondran, F.W.R. Hepatitis E virus replication and interferon responses in human placental cells. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayed, I.M.; Foquet, L.; Verhoye, L.; Abravanel, F.; Farhoudi, A.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Izopet, J.; Meuleman, P. Transmission of hepatitis E virus infection to human-liver chimeric FRG mice using patient plasma. Antivir. Res. 2017, 141, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, I.M.; Verhoye, L.; Cocquerel, L.; Abravanel, F.; Foquet, L.; Montpellier, C.; Debing, Y.; Farhoudi, A.; Wychowski, C.; Dubuisson, J.; et al. Study of hepatitis E virus infection of genotype 1 and 3 in mice with humanised liver. Gut 2017, 66, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, I.M.; Verhoye, L.; Montpellier, C.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Cocquerel, L.; Meuleman, P. Study of hepatitis E virus ORF2 antigen kinetics in human-liver chimeric mice and its impact on HEV diagnosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, I.M.; Elkhawaga, A.A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A. Circulation of hepatitis E virus (HEV) and/or HEV-like agent in non-mixed dairy farms could represent a potential source of infection for Egyptian people. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 317, 108479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, I.M.; Meuleman, P. Murine tissues of human liver chimeric mice are not susceptible to hepatitis E virus genotypes 1 and 3. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 919–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Donor # | Age | Screening Tests 1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 27 | HAV: rapid tests for anti-HAV IgM |
| 2 | 32 | HBV: HBsAg and anti-HBV core IgM |
| 3 | 34 | HCV: anti-HCV IgG. |
| 4 | 35 | HEV: Anti HEV IgM, anti HEV IgG, HEV Ag and |
| 5 | 33 | HEV RNA |
| Gene | Primer Sequence 5′-3′ | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| 18srRNA | Forward GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT Reverse CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG | 151 |
| IL-6 | Forward TCAATATTAGAGTCTCAACCCCCA Reverse TTCTCTTTCGTTCCCGGTGG | 90 |
| IL-8 | Forward ATGACTTCCAAGCTGGCCGTGGCT Reverse TCTCAGCCCTCTTCAAAAACTTCTC | 292 |
| IL-15 | Forward: CTGACGTCACATGGAGCACA Reverse: CTGCACTGAAACAGCCCAAA | 283 |
| IL- β1 |
Forward CCACAGACCTTCCAGGAGAATG Reverse GTGCAGTTCAGTGATCGTACAGG | 131 |
| MCP-1 (CCL2) |
Forward AGTCTCTGCCGCCCTTCT Reverse GTGACTGGGGCATTGATTG | 93 |
| TNF-α |
Forward CGCTCCCCAAGAAGACAG Reverse AGAGGCTGAGGAACAAGCAC | 60 |
| Cxcl-9 |
Forward AGTGCAAGGAACCCCAGTAG Reverse AGGGCTTGGGGCAAATTGTT | 112 |
| Cxcl-10 | Forward: CCACGTGTTGAGATCATTGCT Reverse: TGCATCGATTTTGCTCCCCT | 152 |
| Cxcl-11 |
Forward:
GAGTGTGAAGGGCATGGCTA
Reverse: ACATGGGGAAGCCTTGAACA | 71 |
| IFN-α |
Forward:
CCTGATGAATGCGGACTCCA
Reverse: TAGCAGGGGTGAGAGTCTTTG | 265 |
| IFN-β |
Forward: CGCCGCATTGACCATCTA.
Reverse: GACATTAGCCAGGAGGTTCTC. | 112 |
| IFN-ɤ | Forward GAGTGTGGAGACCATCAAGGAAG Reverse TGCTTTGCGTTGGACATTCAAGTC | 124 |
| IFN-λ1 | Forward: GCAGGTTCAAATCTCTGTCACC Reverse AAGACAGGAGAGCTGCAACTC | 109 |
| IFN-λ2/3 | Forward: CAGCTGCAGGTGAGGGA Reverse GCGGTGGCCTCCAGAACCTT | 77 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Othman, E.R.; Khashbah, M.Y.; Ismael, A.; Ghaliony, M.A.; Seddik, M.I.; Sayed, I.M. Evidence of the Extrahepatic Replication of Hepatitis E Virus in Human Endometrial Stromal Cells. Pathogens 2020, 9, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9040295
El-Mokhtar MA, Othman ER, Khashbah MY, Ismael A, Ghaliony MA, Seddik MI, Sayed IM. Evidence of the Extrahepatic Replication of Hepatitis E Virus in Human Endometrial Stromal Cells. Pathogens. 2020; 9(4):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9040295
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Mokhtar, Mohamed A., Essam R. Othman, Maha Y. Khashbah, Ali Ismael, Mohamed AA Ghaliony, Mohamed Ismail Seddik, and Ibrahim M. Sayed. 2020. "Evidence of the Extrahepatic Replication of Hepatitis E Virus in Human Endometrial Stromal Cells" Pathogens 9, no. 4: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9040295
APA StyleEl-Mokhtar, M. A., Othman, E. R., Khashbah, M. Y., Ismael, A., Ghaliony, M. A., Seddik, M. I., & Sayed, I. M. (2020). Evidence of the Extrahepatic Replication of Hepatitis E Virus in Human Endometrial Stromal Cells. Pathogens, 9(4), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9040295