Comparison of a Commercial Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with the Modified Agglutination Test (MAT) for the Detection of Antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in a Cohort of Hunting Dogs
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
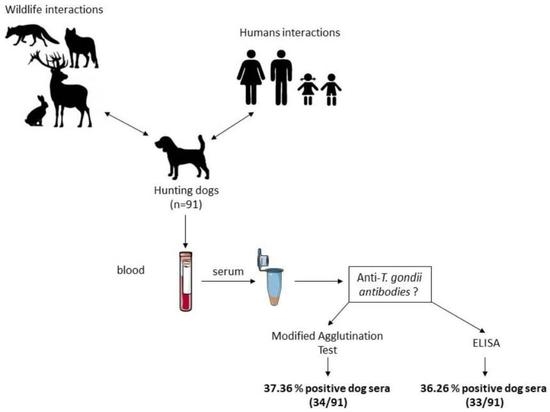
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Modified Agglutination Test (MAT)
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Darde, M.L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bigal, E.; Morick, D.; Scheinin, A.P.; Salant, H.; Berkowitz, A.; King, R.; Levy, Y.; Melero, M.; Sanchez-Vizcaino, J.M.; Goffman, O.; et al. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in three common bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus); A first description from the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 258, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, M.; Fakhri, Y.; Riahi, S.M.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Namroodi, S.; Taghipour, A.; Spotin, A.; Gamble, H.R.; Rostami, A. The global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pigs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 269, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022; 313p. [Google Scholar]
- Cenci-Goga, B.T.; Rossitto, P.V.; Sechi, P.; McCrindle, C.M.; Cullor, J.S. Toxoplasma in animals, food, and humans: An old parasite of new concern. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Opsteegh, M.; Kortbeek, T.M.; Havelaar, A.H.; van der Giessen, J.W. Intervention strategies to reduce human Toxoplasma gondii disease burden. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P.; Butler, J.M.; Blagburn, B.L. Mechanical transmission of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts by dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 73, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schares, G.; Pantchev, N.; Barutzki, D.; Heydorn, A.O.; Bauer, C.; Conraths, F.J. Oocysts of Neospora caninum, Hammondia heydorni, Toxoplasma gondii and Hammondia hammondi in faeces collected from dogs in Germany. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, J.K.; Parker, B.B. An apparent role of dogs in the transmission of Toxoplasma gondii. The probable importance of xenosmophilia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1996, 791, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, J.K.; Lindsay, D.S.; Parker, B.B.; Dobesh, M. Dogs as possible mechanical carriers of Toxoplasma, and their fur as a source of infection of young children. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2003, 7, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etheredge, G.D.; Michael, G.; Muehlenbein, M.P.; Frenkel, J.K. The roles of cats and dogs in the transmission of Toxoplasma infection in Kuna and Embera children in eastern Panama. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica = Pan Am. J. Public Health 2004, 16, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Cui, L.; Zhang, L. Comparison of a Commercial ELISA with the Modified Agglutination Test for Detection of Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies in Sera of Naturally Infected Dogs and Cats. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2012, 7, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.D.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhu, X.Q. Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis and typing of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blaga, R.; Aubert, D.; Thébault, A.; Perret, C.; Geers, R.; Thomas, M.; Alliot, A.; Djokic, V.; Ducry, T.; Ortis, N.; et al. Etude de la contamination par Toxoplasma gondii des viandes ovines, bovines et porcines—Résultats des plans de suveillance pour les années 2007. 2009 et 2013. Bull. Épidémiologique St. Anim. Aliment. 2015, 69, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Djokic, V.; Blaga, R.; Aubert, D.; Durand, B.; Perret, C.; Geers, R.; Ducry, T.; Vallee, I.; Djurkovic Djakovic, O.; Mzabi, A.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection in pork produced in France. Parasitology 2016, 143, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaga, R.; Aubert, D.; Thebault, A.; Perret, C.; Geers, R.; Thomas, M.; Alliot, A.; Djokic, V.; Ortis, N.; Halos, L.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii in beef consumed in France: Regional variation in seroprevalence and parasite isolation. Parasite 2019, 26, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villena, I.; Durand, B.; Aubert, D.; Blaga, R.; Geers, R.; Thomas, M.; Perret, C.; Alliot, A.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Thebault, A.; et al. New strategy for the survey of Toxoplasma gondii in meat for human consumption. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 183, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davoust, B.; Mediannikov, O.; Roqueplo, C.; Perret, C.; Demoncheaux, J.P.; Sambou, M.; Guillot, J.; Blaga, R. Serological survey of animal toxoplasmosis in Senegal. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2015, 108, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouatbi, M.; Amairia, S.; Amdouni, Y.; Boussaadoun, M.A.; Ayadi, O.; Al-Hosary, A.A.T.; Rekik, M.; Ben Abdallah, R.; Aoun, K.; Darghouth, M.A.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in North Africa: A review. Parasite 2019, 26, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouchetati, I.; Ouchene-Khelifi, N.A.; Ouchene, N.; Khelifi, M.; Dahmani, A.; Haif, A.; Zeroual, F.; Benakhla, A. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection among animals in Algeria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 74, 101603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, L.R.; Galisteo, A.J., Jr.; Pompeu, E.; Andrade, H.F., Jr. Toxoplasma gondii spreading in an urban area evaluated by seroprevalence in free-living cats and dogs. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2004, 9, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinparzer, R.; Reisp, K.; Grunberger, B.; Kofer, J.; Schmoll, F.; Sattler, T. Comparison of different commercial serological tests for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in serum of naturally exposed pigs. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenum, P.A.; Stray-Pedersen, B. Development of specific immunoglobulins G, M, and A following primary Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnant women. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 2907–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- OIE. Terrestrial manual; Chapter 3.10.8, Toxoplasmosis. 2018, pp. 1753–1764. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/3.10.08_TOXO.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Klun, I.; Djurkovic-Djakovic, O.; Thulliez, P. Comparison of a commercial ELISA with the modified agglutination test for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in naturally exposed sheep. Zoonoses Public Health 2007, 54, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, J.; Karamon, J.; Cencek, T.; Dutkiewicz, J. Preliminary assessment of usefulness of cELISA test for screening pig and cattle populations for presence of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2011, 18, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Thulliez, P.; Weigel, R.M.; Andrews, C.D.; Lind, P.; Powell, E.C. Sensitivity and specificity of various serologic tests for detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in naturally infected sows. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klun, I.; Uzelac, A.; Villena, I.; Mercier, A.; Bobic, B.; Nikolic, A.; Rajnpreht, I.; Opsteegh, M.; Aubert, D.; Blaga, R.; et al. The first isolation and molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from horses in Serbia. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Almeida, J.C.; Frehse, M.S.; Navarro, I.T.; Garcia, J.L.; Biondo, A.W.; Freire, R.L. Comparison of indirect fluorescent antibody test and the modified agglutination test for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in stray dogs from Southern Brazil. Acta Parasitol. 2016, 61, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| MAT (+) | MAT (−) | Total (Rate) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ELISA (+) | 26 | 7 | 33 (36.2%) |
| ELISA (−) | 8 | 50 | 58 (63.7%) |
| Total (rate) | 34 (37.4%) | 57 (62.6%) | 91 |
| MAT (Titer) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:6 | 1:12 | 1:24 | 1:48 | 1:96 | 1:192 | 1:384 | 1:768 | |
| ELISA (+) | 2 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| (%) | 7.7 | 34.62 | 23.07 | 11.54 | 11.54 | 3.85 | 3.85 | 3.85 |
| ELISA (−) | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| (%) | 62.5 | 25 | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ELISA | CI 95% | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (%) | 76.5 | 60–87.6 |
| Specificity (%) | 87.7 | 76.7–93.9 |
| Positive predictive value | 78.8 | 62.2–89.32 |
| Negative predictive value | 86.2 | 75.1–92.8 |
| Likelihood ratio | 6.23 | |
| Kappa coefficient (k) | 0.646 | 0.483–0.809 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellatreche, A.Y.; Bouzid, R.; Blaizot, A.; Aubert, D.; Blaga, R.; Ait-Oudhia, K.; Le Roux, D. Comparison of a Commercial Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with the Modified Agglutination Test (MAT) for the Detection of Antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in a Cohort of Hunting Dogs. Animals 2022, 12, 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202813
Bellatreche AY, Bouzid R, Blaizot A, Aubert D, Blaga R, Ait-Oudhia K, Le Roux D. Comparison of a Commercial Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with the Modified Agglutination Test (MAT) for the Detection of Antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in a Cohort of Hunting Dogs. Animals. 2022; 12(20):2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202813
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellatreche, Aicha Yasmine, Riad Bouzid, Amandine Blaizot, Dominique Aubert, Radu Blaga, Khatima Ait-Oudhia, and Delphine Le Roux. 2022. "Comparison of a Commercial Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with the Modified Agglutination Test (MAT) for the Detection of Antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in a Cohort of Hunting Dogs" Animals 12, no. 20: 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202813
APA StyleBellatreche, A. Y., Bouzid, R., Blaizot, A., Aubert, D., Blaga, R., Ait-Oudhia, K., & Le Roux, D. (2022). Comparison of a Commercial Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) with the Modified Agglutination Test (MAT) for the Detection of Antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in a Cohort of Hunting Dogs. Animals, 12(20), 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202813