Pathogenic Bacteria in Free-Living Birds, and Its Public Health Significance
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
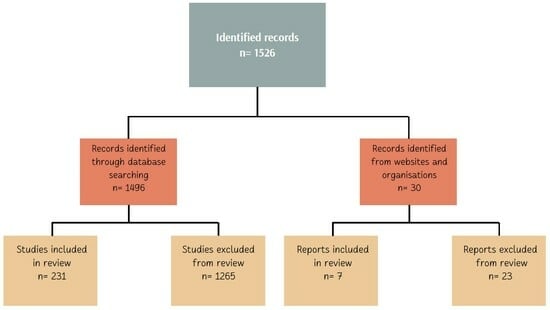
2. Materials and Methods
3. Bacterial Pathogens in Wild Birds
4. Virulence Profiles and Genetic Diversity of Bacteria Isolated from Free-Living Birds
5. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Bacteria Isolated from Free-Living Birds
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gogu-Bogdan, M.; Cobzaru, I.; Páll, E.; Niculae, M.; Spinu, M. Wild birds as potential vectors for pathogen dissemination on migration routes in the Danube Delta Wetlands. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 890–897. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiodras, S.; Kelesidis, T.; Kelesidis, I.; Bauchinger, U.; Falagas, M.E. Human infections associated with wild birds. J. Infect. 2008, 56, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.P.; Minichino, A.; Gargiulo, A.; Varriale, L.; Borrelli, L.; Pace, A.; Santaniello, A.; Pompameo, M.; Fioretti, A.; Dipineto, L. Prevalence and Phenotypic Antimicrobial Resistance among ESKAPE Bacteria and Enterobacterales Strains in Wild Birds. J. Antibiot. 2022, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.; Mascetti, A.; Fisichella, V.; Fulco, E.; Orlandella, B.M.; Lo Piccolo, F. Antibiotic Resistance Assessment in Bacteria Isolated in Migratory Passeriformes Transiting through the Metaponto Territory (Basilicata, Italy). Avian Res. 2017, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.S.; Elshafiee, E.A.; Khalefa, H.S.; Kadry, M.; Hamza, D.A. Evidence of Colistin Resistance Genes (Mcr-1 and Mcr-2) in Wild Birds and Its Public Health Implication in Egypt. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacopello, C.; Foti, M.; Mascetti, A. Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Enterobacteriaceae in European Wild Bird Species Admitted in a Wildlife Rescue. Centre. Vet. Ital. 2016, 52, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pancerasa, M.; Ambrosini, R.; Saino, N.; Casagrandi, R. Barn swallows long-distance migration occurs between significantly temperature-correlated areas. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, D.W.; Gandoy, F.A.; Areta, J.I.; Iliff, M.J.; Rakhimberdiev, E.; Kardynal, K.J.; Hobson, K.A. Long-Distance Range Expansion and Rapid Adjustment of Migration in a Newly Established Population of Barn Swallows Breeding in Argentina. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Corl, A.; Wolfenden, A.; Lublin, A.; Ishaq, S.; Turjeman, S.; Getz, W.; Nathan, R.; Bowie, R.; Kamath, P. High-Throughput Sequencing for Examining Salmonella Prevalence and Pathogen—Microbiota Relationships in Barn Swallows. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 683183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, G.; Wang, Y.; Lü, L.; Jiang, C.; Ahmad, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, D. Bats and birds as viral reservoirs: A physiological and ecological perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnedahl, J.; Järhult, J.D. Antibiotic Resistance in Wild Birds. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najdenski, H.; Dimova, T.; Zaharieva, M.M.; Nikolov, B.; Petrova-Dinkova, G.; Dalakchieva, S.; Popov, K.; Hristova-Nikolova, I.; Zehtindjiev, P.; Peev, S.; et al. Migratory birds along the Mediterranean—Black Sea Flyway as carriers of zoonotic pathogens. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvala, M.; Woivalin, E.; Kivistö, R.; Laukkanen-Ninios, R.; Laaksonen, S.; Stephan, R.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M. Hunted game birds—Carriers of foodborne pathogens. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, S.A.; Lehrer, E.; Magle, S.B. Wild birds as sentinels for multiple zoonotic pathogens along an urban to rural gradient in greater Chicago, Illinois. Zoonoses Public Health 2012, 59, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.H.; Latham, S.M.; Woolhouse, M.E. Risk factors for human disease emergence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 29, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The European Union One Health 2021 Zoonoses Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/7666 (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Golz, J.C.; Epping, L.; Knüver, M.T.; Borowiak, M.; Hartkopf, F.; Deneke, C.; Malorny, B.; Semmler, T.; Stingl, K. Whole genome sequencing reveals extended natural transformation in Campylobacter impacting diagnostics and the pathogens adaptive potential. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansarifar, E.; Riahi, S.M.; Tasara, T. Campylobacter prevalence from food, animals, human and environmental samples in Iran: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.A.; Gulhan, T. Campylobacter in Wild Birds: Is It an Animal and Public. Health Concern? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 812591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, J.S.; Atwill, E.R.; Hunter, A. Prevalence of Campylobacter and Salmonella at a squab (young pigeon) processing plant. Poult. Sci. 2001, 80, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashin, I.; Stoyanchev, T. Presence of Campylobacter spp. in meat and internal organs of Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix). Trakia J. Sci. 2005, 3, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kilonzo-Nthenge, A.; Nahashon, S.N.; Chen, F.; Adefope, N. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of pathogenic bacteria in chicken and guinea fowl. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.; Ghaderpour, A.; Radmehr, B.; Swee Chuan Wei, K.; Chai, L.C.; Ismail, S. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter species isolates in ducks and geese. Food Control. 2014, 50, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colles, F.M.; Ali, J.S.; Sheppard, S.K.; McCarthy, N.D.; Maiden, M.C. Campylobacter populations in wild and domesticated Mallard ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2011, 3, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, J.I.; Cho, S.; Ryu, S.; Jeon, B. Comparative Analysis of Aerotolerance, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Gene Prevalence in Campylobacter jejuni Isolates from Retail Raw Chicken and Duck Meat in South Korea. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysok, B.; Wojtacka, J.; Wiszniewska-Łaszczych, A.; Szteyn, J. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Properties of Campylobacter Spp. Originating from Domestic Geese in Poland. Animals 2020, 10, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, P.S.; Xavier, C.; Santovenia, M.; Pruckler, J.; Stroika, S.; Joyce, K.; Gardner, T.; Fields, P.I.; McLaughlin, J.; Tauxe, R.V.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing confirms wild birds as the source of a Campylobacter outbreak associated with the consumption of raw peas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4540–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahpour, N.; Zendehbad, B.; Alipour, A.; Khayatzadeh, J. Wild-bird feces as a source of Campylobacter jejuni infection in children’s playgrounds in Iran. Food Control 2015, 50, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, J.P.; Smith, R.M.; Palmer, S.R. Bird attack on milk bottles: Possible mode of transmission of Campylobacter jejuni to man. Lancet 1990, 336, 1425–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, J.; Sufi, F.; McNulty, C.; Park, P. Outbreak of campylobacter enteritis in a residential school associated with bird pecked bottle tops. Commun. Dis. Rep. CDR Rev. 1997, 7, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sanad, Y.M.; Closs, G.J.; Kumar, A.; LeJeune, J.T.; Rajashekara, G. Molecular epidemiology and public health relevance of Campylobacter isolated from dairy cattle and European starlings in Ohio, USA. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovanen, S.; Rossi, M.; Pohja-Mykrä, M.; Nieminen, T.; Raunio-Saarnisto, M.; Sauvala, M.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Hänninen, M.L.; Kivistö, R. Population Genetics and Characterization of Campylobacter jejuni Isolates from Western Jackdaws and Game Birds in Finland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02365-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osek, J.; Lachtara, B.; Wieczorek, K. Listeria monocytogenes—How This Pathogen Survives in Food-Production Environments? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 866462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, R.; Gorris, L.; Hayman, M.J.; Whiting, R. A Review of Listeria monocytogenes: An Update on Outbreaks, Virulence, Dose-response, Ecology, and Risk Assessments. Food Control. 2017, 75, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, S.; Kiviniemi, K.; Autio, T.; Korkeala, H. Listeria monocytogenes is common in wild birds in Helsinki region and genotypes are frequently similar with those found along the food chain. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauders, B.D.; Overdevest, J.; Fortes, E.; Windham, K.; Schukken, Y.; Lembo, A.; Wiedmann, M. Diversity of Listeria species in urban and natural environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4420–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milillo, S.R.; Friedly, E.C.; Saldivar, J.C.; Muthaiyan, A.; O’Bryan, C.; Crandall, P.G.; Johnson, M.G.; Ricke, S.C. A review of the ecology, genomics, and stress response of Listeria innocua and Listeria monocytogenes. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, R.; Garner, M.M.; Hopkins, S.G.; Shah, D.H. Outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes in an urban poultry flock. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saif, Y.M. Diseases of Poultry, 11th ed.; Iowa State Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2005; pp. 968–969. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Sato, M.; Hirai, K. Incidence of Listeria monocytogenes in Wild Animals in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2000, 62, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouttefroy, A.; Lemaître, J.P.; Rousset, A. Prevalence of Listeria sp. in droppings from urban rooks (Corvus frugilegus). J. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 82, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.; Potel, J.; Schäfer-Schmidt, R.; Prell, A.; Datzmann, C. Untersuchungen zum Vorkommen von Listeria monocytogenes in Kotproben von Haus- und Heimtieren. Zentralbl Hyg. Umweltmed. 1995, 198, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, J.; Seeliger, H.P. Incidence of Listeria monocytogenes in nature. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 30, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoder, D.; Guldimann, C.; Märtlbauer, E. Asymptomatic Carriage of Listeria monocytogenes by Animals and Humans and Its Impact on the Food Chain. Foods 2022, 11, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee against Birds Slaughter (CABS). Shooting Bag Figures for Waterfowl and Coots, Cranes, and Rails. In 533 Committee Against Bird Slaughter; 2010. Available online: https://laczanasptaki.pl/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/CABS-Hunting-in-Europe-2017.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Kiu, R.; Hall, L.J. An update on the human and animal enteric pathogen Clostridium perfringens. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, Z.V.; Macías-Rodríguez, M.E.; Arratia-Quijada, J.; Gonzalez-Torres, Y.S.; Nuño, K.; Villarruel-López, A. Clostridium perfringens as Foodborne Pathogen in Broiler Production: Pathophysiology and Potential Strategies for Controlling Necrotic Enteritis. Animals 2020, 10, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, H. Prevalence and multilocus sequence typing of Clostridium perfringens isolated from 4 duck farms in Shandong province, China. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5105–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, M.; Mohamed, E.; Awadallah, M.; Merwad, A.; Selim, M. Clostridium perfringens in duck farms, retail outlets and in contact workers in Egypt incidence and toxin genotyping. Egypt. J. Food Safety 2018, 5, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaoka, Y.; Yanai, T.; Hirayama, H.; Une, Y.; Saito, E.; Sakai, H.; Goryo, M.; Fukushi, H.; Masegi, T. Fatal necrotic enteritis associated with Clostridium perfringens in wild crows (Corvus macrorhynchos). Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildfell, R.J.; Eltzroth, E.K.; Songer, J.G. Enteritis as a Cause of Mortality in the Western Bluebird (Sialia mexicana). Avian Dis. 2001, 45, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmyar, J.; Kalidari, G.A.; Tolooe, A.; Rad, M.; Movassaghi, A.R. Genotyping of Clostridium perfringens isolated from healthy and diseased ostriches (Struthio camelus). Iran. J. Microbiol. 2014, 6, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hagen, C.A.; Bildfell, R.J. An observation of Clostridium perfringens in Greater Sage-Grouse. J. Wildl. Dis. 2007, 43, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chary, R.; Lucas, A. Entérotoxémie à Clostridium perfringens type A chez des faisans d’élevage. Commentaires étiologiques. Bull. Acad. Vet. Fr. 1970, 43, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Stuve, G.; Hofshagen, M.; Holt, G. Necrotizing lesions in the intestine, gizzard, and liver in captive capercaillies (Tetrao urogallus) associated with Clostridium perfringens. J. Wildl. Dis. 1992, 28, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, S.E.; Stern, N.J.; Line, E.; Bailey, J.S.; Cox, N.A.; Fedorka-Cray, P. Determination of the incidence of Salmonella spp., Campylobacter jejuni, and Clostridium perfringens in wild birds near broiler chicken houses by sampling intestinal droppings. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathima, S.; Hakeem, W.G.A.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Selvaraj, R.K. Necrotic Enteritis in Broiler Chickens: A Review on the Pathogen, Pathogenesis, and Prevention. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, K.; Suzuki, N.; Nagai, A.; Nakamoto, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kamatsuka, T.; Kimura, K.; Kikuchi, H.; Uetsuka, K. Prevalence of Clostridium perfringens in wild resident birds (Corvus spp., Sturnus cineraceus, Passer montanus) in Ibaraki prefecture. Jpn. J. Anim. Hyg. 2022, 48, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chaguza, C.; Smith, J.T.; Bruce, S.A.; Gibson, R.; Martin, I.W.; Andam, C.P. Prophage-encoded immune evasion factors are critical for Staphylococcus aureus host infection, switching, and adaptation. Cell Genom. 2022, 2, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, C.B. Staphylococcosis. Diseases of Poultry; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Iowa, IA, USA, 2013; pp. 971–976. [Google Scholar]
- Le, H.; Dalsgaard, A.; Skytt, A.P.; Nguyen, H.; Ta, Y.; Nguyen, T. Large-Scale Staphylococcus aureus Foodborne Disease Poisoning Outbreak among Primary School Children. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning from a military unit lunch party—United States, 2012. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Tao, X.; Xia, X.; Yang, B.; Xi, M.; Meng, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, B. Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in retail raw chicken in China. Food Control. 2013, 29, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, K.I.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Elhadidy, M.; Tamura, T. Molecular Characterization and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Retail Chicken. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 1879–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.; Silva, N.; Igrejas, G.; Silva, F.; Sargo, R.; Alegria, N.; Benito, D.; Gómez, P.; Lozano, C.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance determinants in Staphylococcus spp. recovered from birds of prey in Portugal. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Lopes, A.F.; Soeiro, V.; Caniça, M.; Manageiro, V.; Pereira, J.E.; Maltez, L.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Nocturnal Birds of Prey as Carriers of Staphylococcus aureus and Other Staphylococci: Diversity, Antimicrobial Resistance and Clonal Lineages. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, A.; Baldomà, L.; Molina-López, R.A.; Martin, M.; Darwich, L. Microbiological diagnosis and antimicrobial sensitivity profiles in diseased free-living raptors. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardyn, S.E.; Kauffman, L.K.; Smith, T.C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in central Iowa wildlife. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapaliya, D.; Dalman, M.; Kadariya, J.; Little, K.; Mansell, V.; Taha, M.Y.; Grenier, D.; Smith, T.C. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus in Goose Feces from State Parks in Northeast Ohio. Ecohealth. 2017, 14, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Gómez, P.; Alonso, C.A.; Camacho, M.C.; de la Puente, J.; Fernández-Fernández, R.; Ramiro, Y.; Quevedo, M.A.; Blanco, J.M.; Zarazaga, M.; et al. Detection of MRSA of Lineages CC130-mecC and CC398-mecA and Staphylococcus delphini-lnu(A) in Magpies and Cinereous Vultures in Spain. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, P.; Lozano, C.; Camacho, M.C.; Lima-Barbero, J.F.; Hernández, J.M.; Zarazaga, M.; Höfle, Ú.; Torres, C. Detection of MRSA ST3061-t843-mecC and ST398-t011-mecA in white stork nestlings exposed to human residues. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad-Alla, M.E.; Abdien, H.M.; Dessouki, A.A. Prevalence of bacteria and parasites in White Ibis in Egypt. Vet. Ital. 2010, 46, 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Topić, N.; Cenov, A.; Jozić, S.; Glad, M.; Mance, D.; Lušić, D.; Kapetanović, D.; Mance, D.; Vukić Lušić, D. Staphylococcus aureus-An Additional Parameter of Bathing Water Quality for Crowded Urban Beaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021, 18, 5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, J.; Clayton, Y.M. Bacterial and fungal flora of seagull droppingsd in Jersey. J. Clin. Pathol. 1971, 24, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, I.N.; Fernández-Fernández, R.; Juárez-Fernández, G.; Martínez-Álvarez, S.; Eguizábal, P.; Zarazaga, M.; Lozano, C.; Torres, C. Wild Animals Are Reservoirs and Sentinels of Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA Clones: A Problem with “One Health” Concern. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.H.; Khor, W.C.; Quek, J.Y. Occurrence and antimicrobial resistance traits of Escherichia coli from wild birds and rodents in Singapore. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020, 17, 5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, C.A.; Cardozo, M.V.; Beraldo, L.G.; Oliveira, E.S.; Maluta, R.P.; Barboza, K.B.; Werther, K.; Ávila, F.A. Wild birds and urban pigeons as reservoirs for diarrheagenic Escherichia coli with zoonotic potential. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; Cauich-Sánchez, P.I.; Trejo, A.; Gutiérrez, A.; Díaz, S.P.; Díaz, C.M.; Cravioto, A.; Eslava, C. Characterization of Diarrheagenic Strains of Escherichia coli Isolated from Cattle Raised in Three Regions of Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertelloni, F.; Lunardo, E.; Rocchigiani, G. Occurrence of Escherichia coli virulence genes in Faeces of wild birds from Central Italy. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2019, 12, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Sanches, L.A.; Gomes, M.D.S.; Teixeira, R.H.F.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Oliveira, M.G.X.; Vieira, M.A.M.; Gomes, T.A.T.; Knobl, T. Captive wild birds as reservoirs of enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) and Shiga-toxin producing E. coli (STEC). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Pohjanvirta, T.; Pelkonen, S. Prevalence and characteristics of intimin-and shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli from gulls, pigeons and broilers in Finland. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2002, 64, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.A.; Samanta, I.; Bhat, M.A.; Nishikawa, Y. Investigation of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in avian species in India. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 39, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Nicoli, J.; Nascimento, T.; Diniz, C. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains recovered from urban pigeons (Columba livia) in Brazil and their antimicrobial susceptibility patterns. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, M.; Rivera, I.; Jara, L.M.; Ulloa-Stanojlovic, F.M.; Shiva, C. 2 Isolation and molecular identification of potentially pathogenic Escherichia coli and Campylobacter jejuni in feral pigeons from an urban area in the city of Lima, Peru. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2015, 57, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koochakzadeh, A.; Askari Badouei, M.; Zahraei Salehi, T.; Aghasharif, S.; Soltani, M.; Ehsan, M. Prevalence of shiga toxin-producing and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in wild and pet birds in Iran. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 2015, 17, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.; Bennett, M.; Coffey, P.; Elliott, J.; Jones, T.; Jones, R.; Lahuerta-Marin, A.; McNiffe, K.; Norman, D.; Williams, N. Risk factors for the occurrence of Escherichia coli virulence genes eae, stx1 and stx2 in wild bird populations. Epidemiol. Infect. 2009, 137, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.Y.; Kang, M.S.; Hwang, H.T.; An, B.K.; Kwon, J.H.; Kwon, Y.K. Epidemiological investigation of eaeA-positive Escherichia coli and Escherichia albertii strains isolated from healthy wild birds. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacristán, C.; Esperón, F.; Herrera-León, S.; Iglesias, I.; Neves, E.; Nogal, V.; Muñoz, M.; de la Torre, A. Virulence genes, antibiotic resistance and integrons in Escherichia coli strains isolated from synanthropic birds from Spain. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, S.; Pewsner, M.; Hüssy, D.; Hächler, H.; Ryser Degiorgis, M.P.; von Hirschheydt, J.; Origgi, F.C. Epidemic of salmonellosis in passerine birds in Switzerland with spillover to domestic cats. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.; Azriel, S.; Auster, O.; Gal, A.; Zitronblat, C.; Mikhlin, S.; Scharte, F.; Hensel, M.; Rahav, G.; Gal-Mor, O. Pathoadaptation of the passerine-associated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium lineage to the avian host. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, A.E.; Lawson, B.; de Pinna, E.; Wigley, P.; Parkhill, J.; Thomson, N.R.; Page, A.J.; Holmes, M.A.; Paterson, G.K. Genomic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium from Wild Passerines in England and Wales. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6728–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderlund, R.; Jernberg, C.; Trönnberg, L.; Pääjärvi, A.; Ågren, E.; Lahti, E. Linked seasonal outbreaks of Salmonella Typhimurium among passerine birds, domestic cats and humans, Sweden, 2009 to 2016. Euro Surveill. 2019, 24, 1900074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.J.I.; Islam, M.; Sikder, T.; Rubaya, R.; Halder, J.; Alam, J. Multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. isolated from pigeons. Vet. World. 2020, 13, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasmans, F.; Van Immerseel, F.; Hermans, K.; Heyndrickx, M.; Collard, J.M.; Ducatelle, R.; Haesebrouck, F. Assessment of virulence of pigeon isolates of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar typhimurium variant copenhagen for humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2000–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhogoju, S.; Nahashon, S.; Wang, X.; Darris, C.; Kilonzo-Nthenge, A. A comparative analysis of the microbial profile of Guinea fowl and chicken using a metagenomic approach. PLoS ONE. 2018, 13, e0191029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizard, I. Salmonellosis in wild birds Sem. Avian Exot. Pet. Med. 2004, 13, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.J.; Saito, E.K. Avian wildlife mortality events due to Salmonellosis in the United States, 1985–2004. J. Wild. Dis. 2008, 44, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Salmonella Outbreak Linked to Wild Songbirds. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/typhimurium-04-21/index.html (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Lawson, B.; de Pinna, E.; Horton, R.A.; Macgregor, S.K.; John, S.K. Epidemiological Evidence That Garden Birds Are a Source of Human Salmonellosis in England and Wales. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.J.; Ogbunugafor, C.B. When Vibrios Take Flight: A Meta-Analysis of Pathogenic Vibrio Species in Wild and Domestic Birds. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1404, 295–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Páll, E.; Niculae, M.; Brudașcă, G.F.; Ravilov, R.K.; Șandru, C.D.; Cerbu, C.; Olah, D.; Zăblău, S.; Potârniche, A.V.; Spinu, M.; et al. Assessment and Antibiotic Resistance Profiling in Vibrio Species Isolated from Wild Birds Captured in Danube Delta Biosphere Reserve, Romania. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.D.; Lemos, L.S.; Roges, E.M.; de Moura, J.F.; Tavares, D.C.; Matias, C.A.R.; Rodrigues, D.P.; Siciliano, S. A comprehensive survey of Aeromonas sp. and Vibrio sp. in seabirds from southeastern Brazil: Outcomes for public health. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Hao, J.; Yang, Q. Long-distance transmission of pathogenic Vibrio species by migratory waterbirds: A potential threat to the public health. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Zhu, L.W.; Jing, J.; Guan, J.Y.; Lu, G.J.; Xie, L.H.; Ji, X.; Chu, D.; Sun, Y.; Chen, P.; et al. Pan-Genome Analysis of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio metschnikovii Strains Isolated from Migratory Birds at Dali Nouer Lake in Chifeng, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 638820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carniel, E. The Yersinia high-pathogenicity island: An iron-uptake island. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Barac, A.; Bienert, A.; Demir, A.; Drüke, N.; Jäckel, C.; Matthies, N.; Jun, J.W.; Skurnik, M.; Ulrich, J.; et al. Birds Kept in the German Zoo “Tierpark Berlin” Are a Common Source for Polyvalent Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Phages. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 634289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niskanen, T.; Waldenström, J.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Olsen, B.; Korkeala, H. virF-positive Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica found in migratory birds in Sweden. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4670–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domanska-Blicharz, K.; Opolska, J.; Lisowska, A.; Szczotka-Bochniarz, A. Bacterial and Viral Rodent-borne Infections on Poultry Farms. An. Attempt at a Systematic Review. J. Vet. Res. 2023, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dorrestein, G.M. Passerines. In Handbook of Avian Medicine; Saunders Ltd.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 169–208. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, S.; Hayashidani, H.; Sotohira, Y.; Une, Y. Yersiniosis caused by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis in captive toucans (Ramphastidae) and a Japanese squirrel (Sciurus lis) in zoological gardens in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shopland, S.; Barbon, A.R.; Cotton, S.; Whitford, H.; Barrows, M. Retrospective review of mortality in captive pink pigeons (nesoenas mayeri) housed in european collections: 1977–2018. J. Zoo. Wildl. Med. 2020, 51, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, I. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection in captive black grouse (Tetrao lyrurus) and willow ptarmigan (Lagopus l. lagopus). Acta Vet. Scand. 1982, 23, 622–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galosi, L.; Farneti, S.; Rossi, G.; Cork, S.C.; Ferraro, S.; Magi, G.E.; Petrini, S.; Valiani, A.; Cuteri, V.; Attili, A.R. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, serogroup o:1a, infection in two amazon parrots (Amazona aestiva and Amazona oratrix) with hepatic hemosiderosis. J. Zoo. Wildl. Med. 2015, 46, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoute, S.T.; Cooper, G.L.; Bickford, A.A.; Carnaccini, S.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Sentíes-Cué, C.G. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis in Eurasian Collared Doves (Streptopelia decaocto) and Retrospective Study of Avian Yersiniosis at the California Animal Health and Food Safety Laboratory System (1990–2015). Avian Dis. 2016, 60, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cork, S.C.; Collins-Emerson, J.M.; Alley, M.R.; Fenwick, S.G. Visceral lesions caused by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, serotype II, in different species of bird. Avian Pathol. 1999, 28, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpellini, R.; Giunti, M.; Bulgarelli, C.; Mondo, E.; Esposito, E.; Assirelli, G.; Piva, S. Case report: First isolation of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis from the blood of a cat. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 10, 1261925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasch, A.J.; Dinter, J.; Goeser, T.; Plum, G.; Seifert, H. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis bloodstream infection and septic arthritis: Case report and review of the literature. Infection 2012, 40, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M. The third international consensus definitions for Sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Seki, R.; Tsubokura, M.; Takeda, N.; Shubin, F.N. Geographical heterogeneity between far eastern and Western countries in prevalence of the virulence plasmid, the Superantigen Yersinia pseudotuberculosis-derived mitogen, and the high-Pathogenicity Island among Yersinia pseudotuberculosis strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3541–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amphlett, A. Far East Scarlet-Like Fever: A Review of the Epidemiology, Symptomatology, and Role of Superantigenic Toxin: Yersinia pseudotuberculosis-Derived Mitogen, A. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 3, ofv202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fàbrega, A.; Vila, J. Yersinia enterocolitica: Pathogenesis, virulence and antimicrobial resistance. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2012, 30, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (EFSA). EU summary report on zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks 2015. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4634–4865. [Google Scholar]
- Bottone, E.J. Yersinia enterocolitica: The charisma continues. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odyniec, M.; Stenzel, T.; Ławreszuk, D.; Bancerz-Kisiel, A. Bioserotypes, Virulence Markers, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Yersinia enterocolitica Strains Isolated from Free-Living Birds. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8936591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.; Rinaldo, D.; Guercio, A. Pathogenic microorganisms carried by migratory birds passing through the territory of the island of Ustica, Sicily (Italy). Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Ito, K.; Kubokura, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Kaneko, K.; Ogawa, M. Occurrence of Yersinia enterocolitica in wild-living birds and Japanese serows. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, H.; Gomyoda, M. Intestinal carriage of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by wild birds and mammals in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 1152–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, J.H. Microbial Virulence Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Dhasmana, N.; Dubey, N.; Kumar, N.; Gangwal, A.; Gupta, M.; Singh, Y. Bacterial Virulence Factors: Secreted for Survival. Indian J. Microbiol. 2017, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreling, V.; Falcone, F.H.; Kehrenberg, C.; Hensel, A. Campylobacter sp.: Pathogenicity factors and prevention methods—New molecular targets for innovative antivirulence drugs? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10409–10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanalizadgan, M.; Bakhshi, B.; Kazemnejad Lili, A.; Najar-Peerayeh, S.; Nikmanesh, B. A molecular survey of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli virulence and diversity. Iran. Biomed. J. 2014, 18, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krause-Gruszczynska, M.; Rohde, M.; Hartig, R.; Genth, H.; Schmidt, G.; Keo, T.; König, W.; Miller, W.G.; Konkel, M.E.; Backert, S. Role of the small Rho GTPases Rac1 and Cdc42 in host cell invasion of Campylobacter jejuni. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2431–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Luo, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, B.; Chang, H.; Ji, J.; Sen, K.; et al. Emergence of Genetic Diversity and Multi-Drug Resistant Campylobacter jejuni from Wild Birds in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyaka, A.; Kusumoto, A.; Chaisowwong, W.; Okouchi, Y.; Fukumoto, S.; Yoshimura, A.; Kawamoto, K. Virulence characterization of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from resident wild birds in Tokachi area, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Kang, M.; Jang, H.K. Genetic characterization and epidemiological implications of Campylobacter isolates from wild birds in South Korea. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirado, P.; Paytubi, S.; Miró, E.; Iglesias-Torrens, Y.; Navarro, F.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Stephan-Otto Attolini, C.; Balsalobre, C.; Madrid, C. Differential Distribution of the wlaN and cgtB Genes, Associated with Guillain-Barré Syndrome, in Campylobacter jejuni Isolates from Humans, Broiler Chickens, and Wild Birds. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deirdre, M. Prendergast and others, Genomic diversity, virulence and source of Campylobacter jejuni contamination in Irish poultry slaughterhouses by whole genome sequencing. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 3150–3160. [Google Scholar]
- Andrzejewska, M.; Śpica, D.; Skowron, K.; Indykiewicz, P.; Klawe, J.J. Genetic relatedness, virulence, and drug susceptibility of Campylobacter isolated from water and wild birds. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1005085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Arguello, Y.M.; Perdoncini, G.; Rodrigues, L.B.; Ruschel Dos Santos, L.; Apellanis Borges, K.; Quedi Furian, T.; Pippi Salle, C.T.; de Souza Moraes, H.L.; Pereira Gomes, M.J.; Pinheiro do Nascimento, V. Identification of pathogenic genes in Campylobacter jejuni isolated from broiler carcasses and broiler slaughterhouses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Adawy, H.; Hotzel, H.; García-Soto, S.; Tomaso, H.; Hafez, H.M.; Schwarz, S.; Neubauer, H.; Linde, J. Genomic insight into Campylobacter jejuni isolated from commercial turkey flocks in Germany using whole-genome sequencing analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1092179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljazzar, A.; Abd El-Hamid, M.I.; El-Malt, R.M.S.; El-Gharreb, W.R.; Abdel-Raheem, S.M.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Ibrahim, D. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Campylobacter Species with Particular Focus on the Growth Promoting, Immunostimulant and Anti-Campylobacter jejuni Activities of Eugenol and Trans-Cinnamaldehyde Mixture in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2022, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béjaoui, A.; Gharbi, M.; Bitri, S.; Nasraoui, D.; Ben Aziza, W.; Ghedira, K.; Rfaik, M.; Marzougui, L.; Ghram, A.; Maaroufi, A. Virulence Profiling, Multidrug Resistance and Molecular Mechanisms of Campylobacter Strains from Chicken Carcasses in Tunisia. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levison, L.S.; Thomsen, R.W.; Andersen, H. Increased mortality following Guillain–Barré syndrome: A population-based cohort study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, J.L.; Berche, P.; Mounier, J.; Richard, S.; Sansonetti, P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 2822–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.; Maroushek, N.; Czuprynski, C.J. Multiplication of Listeria monocytogenes in a murine hepatocyte cell line. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 3068–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireton, K.; Payrastre, B.; Cossart, P. The Listeria monocytogenes protein InlB is an agonist of mammalian phosphoinositide 3-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17025–17032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werbrouck, H.; Grijspeerdt, K.; Botteldoorn, N.; Van Pamel, E.; Rijpens, N.; Van Damme, J.; Uyttendaele, M.; Herman, L.; Van Coillie, E. Differential inlA and inlB expression and interaction with human intestinal and liver cells by Listeria monocytogenes strains of different origins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3862–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro-Cerda, J.; Cossart, P. Listeria monocytogenes membrane trafficking and lifestyle: The exception or the rule? Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 22, 657–676. [Google Scholar]
- Kocks, C.; Gouin, E.; Tabouret, M.; Berche, P.; Ohayon, H.; Cossart, P. Listeria monocytogenes-induced actin assembly requires the actA gene product, a surface protein. Cell 1992, 68, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Orsi, R.H.; Chen, R.; Gunderson, M.; Roof, S.; Wiedmann, M.; Childs-Sanford, S.E.; Cummings, K.J. Characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from wildlife in central New York. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Z. Detection of hlyA Gene of Listeria Monocytogenes with Electrochemical DNA Biosensor. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai, China, 16–18 May 2008; pp. 375–378. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Liang, X.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Y. Outbreak of Listeria Monocytogenes in Pheasants. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 2905–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzal, F.A.; Freedman, J.C.; Shrestha, A.; Theoret, J.R.; Garcia, J.; Awad, M.M.; Adams, V.; Moore, R.J.; Rood, J.I.; McClane, B.A. Towards an understanding of the role of Clostridium perfringens toxins in human and animal disease. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rood, J.I.; Adams, V.; Lacey, J. Clostridium perfringens and Clostridial Diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Adams, V.; Bannam, T.L.; Miyamoto, K.; Garcia, J.P.; Uzal, F.A.; Rood, J.I. Toxin plasmids of Clostridium perfringens. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. 2018, 82, 208–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, S. Prevalence and molecular characteristics of Clostridium perfringens isolated from wild birds in China. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 928–931. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, T. Staphylococcus. Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch. at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; Chapter 12. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK8448/ (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Cunha, M.L.R.S.; Calsolari, R.A.O.; Araújo, J.P., Jr. Detection of enterotoxin and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 genes in Staphylococcus, with emphasis on coagulase-negative staphylococci. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 51, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulikowska, M.; Marek, A.; Jarosz, Ł.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Urban-Chmiel, R. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes in Staphylococci Isolated from Aviary Capercaillies and Free-living Birds in South-eastern Poland. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 15, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Seijas, C.; Mascarós, P.; Lizana, V.; Martí-Marco, A.; Arnau-Bonachera, A.; Chillida-Martínez, E.; Cardells, J.; Selva, L.; Viana, D.; Corpa, J.M. Genomic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus in Wildlife. Animals 2023, 13, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, A.; Mazumder, A. Occurrence of diarrheagenic virulence genes and genetic diversity in Escherichia coli isolates from fecal material of various avian hosts in British Columbia, Canada. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleem, A.; Sabry, M.A.; Abdel-Moein, K.A. Migratory birds as a potential overseas transmitter of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2021, 9, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, J.H.; Nayak, J.B.; Brahmbhatt, M.N.; Makwana, P.P. Virulence genes detection of Salmonella serovars isolated from pork and slaughterhouse environment in Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Vet. World. 2015, 8, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombade, S.; Navneet, K. Pathogenicity Island in Salmonella. In Salmonella Spp.—A Global Challenge; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/75674 (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Nikiema, M.E.M.; Kakou-ngazoa, S.; Ky/Ba, A. Characterization of virulence factors of Salmonella isolated from human stools and street food in urban areas of Burkina Faso. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, J.A.; Steele-Mortimer, O. Salmonella--the ultimate insider. Salmonella virulence factors that modulate intracellular survival. Cell Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahori, A.; Umeda, K.; Ohnishi, T.; Kawanishi, M. Molecular characteristics of Salmonella isolates from wild birds in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Matias, C.A.; Pereira, I.A.; de Araújo Mdos, S.; Santos, A.F.; Lopes, R.P.; Christakis, S.; Rodrigues Ddos, P.; Siciliano, S. Characteristics of Salmonella spp. Isolated from Wild Birds Confiscated in Illegal Trade Markets, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 3416864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Fenske, G.J.; Antony, L. Whole genome sequencing-based detection of antimicrobial resistance and virulence in non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica isolated from wildlife. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Orth, K. Virulence determinants for Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Ono, T.; Rokuda, M.; Jang, M.H.; Okada, K.; Iida, T.; Honda, T. Functional characterization of two type III secretion systems of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 6659–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaper, J.B.; Morris, J.G., Jr.; Levine, M.M. Cholera. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 8, 48–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, T.; Iida, T. The pathogenicity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and the role of the thermostable direct hemolysin and related hemolysins. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 1993, 4, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, S. Prevalence, molecular characterization, and antibiotic susceptibility of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus strains isolated from cultured silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus) in China. BioMed. Res. Int. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Yang, C.; Chen, P.; Zhu, L.; Wen, H.; Liu, M.; Guan, J.; Lu, G.; Jing, J.; Sun, S.; et al. Vibrio parahaemolyticus from Migratory Birds in China Carries an Extra Copy of tRNA-Gly and Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance Gene qnrD. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02170-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangnapoh, C.; Tamboon, E.; Supha, N.; Toyting, J.; Chitrak, A.; Kitkumthorn, N.; Ekchariyawat, P.; Iida, T.; Suthienkul, O. Multilocus Sequence Typing and Virulence Potential of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Strains Isolated from Aquatic Bird Feces. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00886-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottone, E.J. Yersinia enterocolitica: Revisitation of enduring human pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2015, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terentjeva, M.; Ķibilds, J.; Meistere, I.; Gradovska, S.; Alksne, L.; Streikiša, M.; Ošmjana, J.; Valciņa, O. Virulence Determinants and Genetic Diversity of Yersinia Species Isolated from Retail Meat. Pathogens 2022, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Pieczywek, M.; Łada, P.; Szweda, W. The most important virulence markers of Yersinia enterocolitica and their role during infection. Genes 2018, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksic, S.; Bockenmühl, J.; Wuthe, H.H. Epidemiology of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis in Germany, 1983–1993. Contrib. Microbiol. Immunol. 1995, 13, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Press, N.; Fyfe, M.; Bowie, W.; Kelly, M. Clinical and microbiological follow-up of an outbreak of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis serotype 1b. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bancerz-Kisiel, A.; Szczerba-Turek, A.; Platt-Samoraj, A.; Szweda, W. Distribution of the ymoA and ystA genes and enterotoxins Yst production by Yersinia enterocolitica strains isolated from humans and pigs. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 15, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Flach, C.F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Mohamed, D.S.; Ahmed, E.F.; Hashem, Z.S. Prevalence of Virulence Genes and Their Association with Antimicrobial Resistance Among Pathogenic E. coli Isolated from Egyptian Patients with Different Clinical Infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Rodríguez, C.; Alt, K.; Grobbel, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; Irrgang, A.; Szabo, I.; Stingl, K.; Schuh, E.; Wiehle, L.; Pfefferkorn, B. Wildlife as Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance in Germany? Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 627821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guenther, S.; Grobbel, M.; Heidemanns, K.; Schlegel, M.; Ulrich, R.G.; Ewers, C.; Wieler, L.H. First insights into antimicrobial resistance among faecal Escherichia coli isolates from small wild mammals in rural areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3519–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.E.; Williams, N.J.; Bennett, M. Disperse abroad in the land: The role of wildlife in the dissemination of antimicrobial resistance. Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20160137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.S.; Urdahl, A.M.; Madslien, K.; Sunde, M.; Nesse, L.L.; Slettemeås, J.S.; Norström, M. What does the fox say? Monitoring antimicrobial resistance in the environment using wild red foxes as an indicator. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasyl, D.; Zając, M.; Lalak, A.; Skarżyńska, M.; Samcik, I.; Kwit, R.; Jabłoński, A.; Bocian, Ł.; Woźniakowski, G.; Hoszowski, A.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolated from Wild Animals in Poland. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, G.; Lemus, J.A.; Grande, J. Microbial pollution in wildlife: Linking agricultural manuring and bacterial antibiotic resistance in red-billed choughs. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skurnik, D.; Ruimy, R.; Andremont, A.; Amorin, C.; Rouquet, P.; Picard, B.; Denamur, E. Effect of human vicinity on antimicrobial resistance and integrons in animal faecal Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, H.K.; Donato, J.; Wang, H.H.; Cloud-Hansen, K.A.; Davies, J.; Handelsman, J. Call of the wild: Antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neogi, S.B.; Islam, M.M.; Islam, S.K.S. Risk of multi-drug resistant Campylobacter spp. and residual antimicrobials at poultry farms and live bird markets in Bangladesh. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.; Oh, J.; Jeong, O.; Moon, O.; Kang, M.; Jung, B.; An, B.; Youn, S.; Kim, H.; Jang, I.; et al. Prevalence of Campylobacter species in wild birds of South Korea. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensale, M.; Cuomo, A.; Dipineto, L.; Santaniello, A.; Calabria, M.; Menna, L.F.; Fioretti, A. Survey of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in different taxa and ecological guilds of migratory birds. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 5, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnohi, M.Y.; Saleha, A.A.; Jalila, A.; Khairani-Bejo, S.; Puan, C.L.; Jalo, M.I.; Fauziah, N. Wild Birds as A Probable Source of Colonization of Campylobacter in Poultry. In Proceedings of the WPSA [Malaysia Branch] and WVPA [Malaysia Branch] Scientific Conference, Serdang, Malaysia, 30 November–1 December 2013; pp. 130–131. [Google Scholar]
- Tawakol, M.M.; Nabil, N.M.; Samir, A. The potential role of migratory birds in the transmission of pathogenic Campylobacter species to broiler chickens in broiler poultry farms and live bird markets. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Sahin, O.; Grover, M.; Zhang, Q. New and alternative strategies for the prevention, control, and treatment of antibiotic-resistant Campylobacter. Transl. Res. 2020, 223, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, G.; D’Amico, F.; Dinardo, F.R.; Bozzo, G.; Napoletano, V.; Camarda, A.; Bove, A.; Lombardi, R.; D’Onghia, F.P.; Circella, E. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in Wild Birds from a Wildlife Rescue Centre. Animals 2022, 12, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indykiewicz, P.; Andrzejewska, M.; Minias, P.; Śpica, D.; Kowalski, J. Prevalence and Antibiotic Resistance of Campylobacter spp. in Urban. and Rural. Black-Headed Gulls Chroicocephalus ridibundus. Ecohealth 2021, 18, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serwecińska, L. Antimicrobials and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A Risk to the Environment and to Public Health. Water 2020, 12, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, M.; Mairpady Shambat, S.; Brugger, S.D.; Zinkernagel, A.S. Antibiotic resistance and persistence-Implications for human health and treatment perspectives. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e51034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-Sastre, L.; Arroyo, C.; Fox, E.M.; McMahon, B.J.; Bai, L.; Li, F.; Fanning, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Listeria Species. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morvan, A.; Moubareck, C.; Leclercq, A.; Hervé-Bazin, M.; Bremont, S.; Lecuit, M.; Courvalin, P.; Le Monnier, A. Antimicrobial resistance of Listeria monocytogenes strains isolated from humans in France. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2728–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulet, V.; Marchetti, P. Listeriosis in 225 non-pregnant patients in 1992: Clinical aspects and outcome in relation to predisposing conditions. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 28, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, J.M.; Peterkin, P.I. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 476–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylonakis, E.; Hohmann, E.L.; Calderwood, S.B. Central nervous system infection with Listeria monocytogenes. 33 years’ experience at a general hospital and review of 776 episodes from the literature. Medicine 1998, 77, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaimat, A.N.; Al-Holy, M.A.; Shahbaz, H.M.; Al-Nabulsi, A.A.; Abu Ghoush, M.H.; Osaili, T.M.; Ayyash, M.M.; Holley, R.A. Emergence of Antibiotic Resistance in Listeria monocytogenes Isolated from Food Products: A Comprehensive Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temple, M.E.; Nahata, M.C. Treatment of listeriosis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2000, 34, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagtap, U.V.; Kolhe, R.; Deshpande, P.D.; Kurkure, N.; Dhandore, C.V.; Muglikar, D.; Jadhav, S.; Nighot, N.K.; Barbuddhe, S. Isolation of Listeria monocytogenes from Peridomestic Birds and Captive Wild Animals. Curr. Sci. 2017, 113, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, H.M.; Ahmed, A. Screening of crows and waterfowls for Salmonella and Listeria monocytogenes infection. Int. J. One Health 2019, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çokal, Y.; Günaydın, E.; Goncagül, G. The investigation of the presence of Listeria species in poultry farms and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Listeria monocytogenes strains. J. İstanbul Vet. Sci. 2022, 6, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.X.; Zheng, H.R.; Wang, Y.Y.; Bai, L.L.; Du, X.L.; Wu, Y.; Lu, J.X. Molecular characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of Clostridium perfringens from different regions in China, from 2013 to 2021. Front Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1195083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzman, J.D.; Reller, L.B.; Wang, W.L. Susceptibility of Clostridium perfringens isolated from human infections to twenty antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1977, 11, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareen, A.R.; Zahra, R. Community acquired methicillin resistant Staphylococci (CA-MRS) in fecal matter of wild birds—A ‘one health’ point of concern. J. Infect. Public. Health. 2023, 16, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutkowska, J.; Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Kucharczyk, M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and glycopeptide-resistant enterococci in fecal samples of birds from South-Eastern Poland. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N.; Cascella, M. Beta-Lactam Antibiotics; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mattes, B.R.; Consiglio, S.; de Almeida, B.Z.; Guido, M.C.; Orsi, R.B.; da Silva, R.M.; Costa, A.; Ferreira, A.J.P.; Knöbl, T. Influência da biossegurança na colonização instestinal por Escherichia coli em psitacídeos. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2005, 72, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobrak, M.Y.; Abo-Amer, A.E. Role of wild birds as carriers of multi-drug resistant Escherichia coli and Escherichia vulneris. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 45, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, B.; Sandegren, L.; Melhus, A.; Drobni, M.; Hernandez, J.; Waldenström, J.; Alam, M.; Olsen, B. Antimicrobial drug-resistant Escherichia coli in wild birds and free-range poultry, Bangladesh. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2055–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowaczek, A.; Dec, M.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Urban-Chmiel, R.; Marek, A.; Różański, P. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Wild Birds in Poland. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liang, B.; Jiang, B.W.; Zhu, L.W.; Wang, T.C.; Li, Y.G.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.J.; Ji, X.; Sun, Y. Migratory wild birds carrying multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli as potential transmitters of antimicrobial resistance in China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.I.; Abu, J.; Zakaria, Z.; Khan, A.R.; Abdul Aziz, S.; Bitrus, A.A.; Habib, I. Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogenic Escherichia coli Isolated from Wild Birds, Chicken, and the Environment in Malaysia. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbab, S.; Ullah, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. Antimicrobial drug resistance against Escherichia coli and its harmful effect on animal health. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salleh, M.Z.; Nik Zuraina, N.M.N.; Hajissa, K.; Ilias, M.I.; Deris, Z.Z. Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in Asia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Maldonado, B.; Vega, S.; Mencía-Gutiérrez, A.; Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L.; de Frutos, C.; González, F.; Revuelta, L.; Marin, C. Urban birds: An important source of antimicrobial resistant Salmonella strains in Central Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 72, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2017. EFSA J. 2019, 17, 5598. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, W.V. Multiresistente Bakterien: Antibiotikaverordnung und Reserveantibiotika. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2018, 143, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinu, M.; Gurzau, A.E.; Niculae, M.; Brudasca, G.F.; Sandru, C.D.; Krieb, C.; Páll, E. Reciprocal relationships in antibiotic resistance of Salmonella spp. carried by wild birds and fish in the danube delta. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 79, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahan Yapicier, O.; Hesna Kandir, E.; Öztürk, D. Antimicrobial Resistance of E. coli and Salmonella Isolated from Wild Birds in a Rehabilitation Center in Turkey. Arch. Razi Inst. 2022, 77, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Botti, V.; Navillod, F.V.; Domenis, L.; Orusa, R.; Pepe, E.; Robetto, S.; Guidetti, C. Salmonella spp. and antibiotic-resistant strains in wild mammals and birds in north-western Italy from 2002 to 2010. Vet. Ital. 2013, 49, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Garg, S.; Mitra, R.; Basu, A.; Rajendran, K.; Dutta, D.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Shimada, T.; Takeda, T.; Takeda, Y.; et al. Temporal shifts in traits of Vibrio cholerae strains isolated from hospitalized patients in Calcutta: A 3-year (1993 to 1995) analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2537–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Verma, J.; Kumar, P.; Ghosh, A.; Ramamurthy, T. Antibiotic resistance in Vibrio cholerae: Understanding the ecology of resistance genes and mechanisms. Vaccin. 2020, 38, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Yuan, M.; Tao, Q.; Xu, T.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Discovery of Novel Resistance Mechanisms of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Biofilm against Aminoglycoside Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Jeggo, M. The One Health Approach-Why Is. It So Important? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 88. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobuszewska, A.; Wysok, B. Pathogenic Bacteria in Free-Living Birds, and Its Public Health Significance. Animals 2024, 14, 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060968
Kobuszewska A, Wysok B. Pathogenic Bacteria in Free-Living Birds, and Its Public Health Significance. Animals. 2024; 14(6):968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060968
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobuszewska, Aleksandra, and Beata Wysok. 2024. "Pathogenic Bacteria in Free-Living Birds, and Its Public Health Significance" Animals 14, no. 6: 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060968
APA StyleKobuszewska, A., & Wysok, B. (2024). Pathogenic Bacteria in Free-Living Birds, and Its Public Health Significance. Animals, 14(6), 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060968