A Survey on Machine Reading Comprehension—Tasks, Evaluation Metrics and Benchmark Datasets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Overview
1.2. History
1.3. Motivation
1.4. Outline
2. Tasks
2.1. Definition of Typical MRC Tasks
2.2. Discussion on MRC Tasks
2.2.1. Multi-Modal MRC vs. Textual MRC
2.2.2. Machine Reading Comprehension vs. Question Answering
2.2.3. Machine Reading Comprehension vs. Other NLP Tasks
2.3. Classification of MRC Tasks
2.3.1. Existing Classification Methods of MRC Tasks
- Cloze style
- Multiple-choice
- Span prediction
- Free-form answer
2.3.2. Limitations of Existing Classification Method
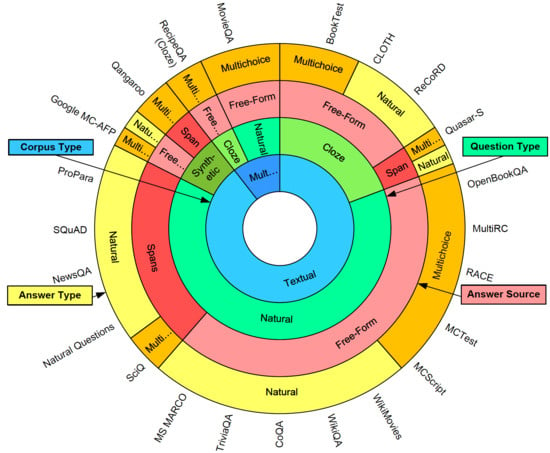
2.3.3. A New Classification Method
2.4. Definition of Each Category in the New Classification Method
2.4.1. Type of Corpus
- Multi-modal
- Textual
2.4.2. Type of Questions
- Cloze style
- Natural form
- Synthetic style
2.4.3. Type of Answers
- Multiple-choice answer
- Natural form of answers
2.4.4. Source of Answers
- Span answer
- Free-form answer
2.5. Statistics of MRC Tasks
Form of Task vs. Content of Task
3. Evaluation Metrics
3.1. Overview of Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Accuracy
3.3. Exact Match
3.4. Precision
3.4.1. Token-Level Precision
3.4.2. Question-Level Precision
3.5. Recall
3.5.1. Token-Level Recall
3.5.2. Question-Level Recall
3.6. F1
3.6.1. Token-Level F1
3.6.2. Question-Level F1
3.7. ROUGE
3.8. BLEU
3.9. Meteor
3.10. HEQ
3.11. Statistics of Evaluation Metrics
4. Benchmark Dataset
4.1. The Size of Datasets
4.2. The Generation Method of Datasets
4.3. The Source of Corpus
4.4. The Type of Context
4.5. The Availability of Datasets, Leaderboards and Baselines
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Prerequisite Skills
4.8. Citation Analysis
4.9. Characteristics of Datasets
4.9.1. Overview
4.9.2. MRC with Unanswerable Questions
4.9.3. Multi-Hop Reading Comprehension
4.9.4. Multi-Modal Reading Comprehension
4.9.5. Reading Comprehension Require Commonsense or World Knowledge
4.9.6. Complex Reasoning MRC
4.9.7. Conversational Reading Comprehension
4.9.8. Domain-Specific Datasets
4.9.9. MRC with Paraphrased Paragraph
4.9.10. Large-Scale MRC Dataset
4.9.11. MRC Dataset for Open-Domain QA
4.10. Descriptions of Each Mrc Dataset
4.10.1. WikiQA
4.10.2. SQuAD 2.0
4.10.3. Natural Questions
4.10.4. MS MARCO
4.10.5. DuoRC
4.10.6. Who-Did-What
4.10.7. ARC
4.10.8. MCScript
4.10.9. OpenBookQA
4.10.10. ReCoRD
4.10.11. CommonSenseQA
4.10.12. WikiReading
4.10.13. WikiMovies
4.10.14. MovieQA
4.10.15. COMICS
4.10.16. TQA
4.10.17. RecipeQA
4.10.18. HotpotQA
4.10.19. NarrativeQA
4.10.20. Qangaroo
4.10.21. MultiRC
4.10.22. CNN/Daily Mail
4.10.23. BookTest
4.10.24. MCTest
4.10.25. CuratedTREC
4.10.26. Quasar
4.10.27. SearchQA
4.10.28. SciQ
4.10.29. CliCR
4.10.30. PaperQA (Hong et al., 2018)
4.10.31. PaperQA (Park et al., 2018)
4.10.32. ReviewQA
4.10.33. SciTail
4.10.34. DROP
4.10.35. Facebook CBT
4.10.36. Google MC-AFP
4.10.37. LAMBADA
4.10.38. NewsQA
4.10.39. SQuAD 1.1
4.10.40. RACE
4.10.41. TriviaQA
4.10.42. CLOTH
4.10.43. ProPara
4.10.44. DREAM
4.10.45. CoQA
4.10.46. QuAC
4.10.47. ShARC
5. Open Issues
5.1. What Needs to Be Improved?
5.1.1. Multi-Modal MRC
5.1.2. Commonsense and World Knowledge
5.1.3. Complex Reasoning
5.1.4. Robustness
5.1.5. Interpretability
5.1.6. Evaluation of the Quality of MRC Datasets?
5.2. Have We Understood Understanding?
“In an attempt to summarize the preceding review, we propose the following general definition for the process and outcome of understanding: The acquisition, organization, and appropriate use of knowledge to produce a response directed towards a goal, when that action is taken with awareness of its perceived purpose.”
“From roughly the 1970s through the 1990s, the dominant theory of conceptual knowledge was the Amodal Symbolic Model. It emerged from earlier developments in logic, formal linguistics, and computer science, and its central claim was that concepts, including word meanings, consist entirely of abstract symbols that are represented and processed in an autonomous semantic system that is completely separate from the modality specific systems for perception and action [115,116,117].Since 1990s, the Grounded Cognition Model has been attracting increasing interest. The key idea is that semantic knowledge does not reside in an abstract realm that is totally segregated from perception and action, but instead overlaps with those capacities to some degree. To return to the banana example mentioned above, understanding this object noun is assumed to involve activating modality-specific records in long-term memory that capture generalizations about how bananas look, how they taste, how they feel in one’s hands, how they are manipulated, and so forth. This theory maintains that conceptual processing amounts to recapitulating modality-specific states, albeit in a manner that draws mainly on high-level rather than low-level components of the perceptual and motor systems [103].”
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, T.; Hazarika, D.; Poria, S.; Cambria, E. Recent trends in deep learning based natural language processing. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2018, 13, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, J.; Cui, Y.; Hu, J. DeepPatent: Patent classification with convolutional neural networks and word embedding. Scientometrics 2018, 117, 721–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, J. Tourism Review Sentiment Classification Using a Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network with an Attention Mechanism and Topic-Enriched Word Vectors. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boerma, I.E.; Mol, S.E.; Jolles, J. Reading pictures for story comprehension requires mental imagery skills. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugawara, S.; Stenetorp, P.; Inui, K.; Aizawa, A. Assessing the Benchmarking Capacity of Machine Reading Comprehension Datasets. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.09241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, A.; Li, S.; Wang, Y. Machine reading comprehension: A literature review. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.01686. [Google Scholar]
- Baradaran, R.; Ghiasi, R.; Amirkhani, H. A Survey on Machine Reading Comprehension Systems. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.01582. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Rawat, B.P.S. Conversational Machine Comprehension: A Literature Review. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.00671. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Galley, M.; Li, L. Neural Approaches to Conversational AI. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Tutorial Abstracts, Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; pp. 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehnert, W.G. The Process of Question Answering. Ph.D. Thesis, Yale Univ New Haven Conn Dept Of Computer Science, New Haven, CT, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman, L.; Light, M.; Breck, E.; Burger, J.D. Deep Read: A Reading Comprehension System. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, College Park, MD, USA, 20–26 June 1999; pp. 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riloff, E.; Thelen, M. A Rule-Based Question Answering System for Reading Comprehension Tests. In Proceedings of the ANLP-NAACL 2000 Workshop: Reading Comprehension Tests as Evaluation for Computer-Based Language Understanding Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2000; pp. 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charniak, E.; Altun, Y.; de Salvo Braz, R.; Garrett, B.; Kosmala, M.; Moscovich, T.; Pang, L.; Pyo, C.; Sun, Y.; Wy, W.; et al. Reading Comprehension Programs in a Statistical-Language-Processing Class. In Proceedings of the ANLP-NAACL 2000 Workshop: Reading Comprehension Tests as Evaluation for Computer-Based Language Understanding Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 29 April–4 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D. Neural Reading Comprehension and Beyond. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, M.; Burges, C.J.; Renshaw, E. MCTest: A Challenge Dataset for the Open-Domain Machine Comprehension of Text. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–21 October 2013; pp. 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Bansal, M.; Gimpel, K.; McAllester, D. Machine comprehension with syntax, frames, and semantics. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 2: Short Papers), Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 700–706. [Google Scholar]
- Sachan, M.; Dubey, K.; Xing, E.; Richardson, M. Learning answer-entailing structures for machine comprehension. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 239–249. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan, K.; Barzilay, R. Machine comprehension with discourse relations. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 1253–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Zhang, J.; Lopyrev, K.; Liang, P. Squad: 100,000+ questions for machine comprehension of text. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.05250. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, M.; Kembhavi, A.; Farhadi, A.; Hajishirzi, H. Bidirectional attention flow for machine comprehension. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.01603. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, M.E.; Neumann, M.; Iyyer, M.; Gardner, M.; Clark, C.; Lee, K.; Zettlemoyer, L. Deep contextualized word representations. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.05365. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.; Salakhutdinov, R.R.; Le, Q.V. Xlnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 5754–5764. [Google Scholar]
- Grail, Q.; Perez, J. ReviewQA: A relational aspect-based opinion reading dataset. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.12196. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, B.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y. A Survey on Neural Machine Reading Comprehension. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.03824. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. Neural machine reading comprehension: Methods and trends. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3698. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, F.; Bordes, A.; Chopra, S.; Weston, J. The Goldilocks Principle: Reading Children’s Books with Explicit Memory Representations. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2016, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Weston, J.; Bordes, A.; Chopra, S.; Mikolov, T. Towards AI-Complete Question Answering: A Set of Prerequisite Toy Tasks. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2016, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, R.; Liang, P. Adversarial Examples for Evaluating Reading Comprehension Systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 9–11 September 2017; pp. 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembhavi, A.; Seo, M.; Schwenk, D.; Choi, J.; Farhadi, A.; Hajishirzi, H. Are you smarter than a sixth grader? textbook question answering for multimodal machine comprehension. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4999–5007. [Google Scholar]
- Tapaswi, M.; Zhu, Y.; Stiefelhagen, R.; Torralba, A.; Urtasun, R.; Fidler, S. Movieqa: Understanding stories in movies through question-answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4631–4640. [Google Scholar]
- Iyyer, M.; Manjunatha, V.; Guha, A.; Vyas, Y.; Boyd-Graber, J.; Daume, H.; Davis, L.S. The amazing mysteries of the gutter: Drawing inferences between panels in comic book narratives. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7186–7195. [Google Scholar]
- Yagcioglu, S.; Erdem, A.; Erdem, E.; Ikizler-Cinbis, N. RecipeQA: A Challenge Dataset for Multimodal Comprehension of Cooking Recipes. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Fisch, A.; Weston, J.; Bordes, A. Reading Wikipedia to Answer Open-Domain Questions. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 July–4 August 2017; pp. 1870–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M. Research on Machine Reading Comprehension and Textual Question Answering. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Defense Technology of China, Changsha, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwende, L. Answering and Questioning for Machine Reading. In Proceedings of the AAAI 2007 Spring Symposium, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 26–28 March 2007; p. 91. [Google Scholar]
- Saeidi, M.; Bartolo, M.; Lewis, P.; Singh, S.; Rocktäschel, T.; Sheldon, M.; Bouchard, G.; Riedel, S. Interpretation of Natural Language Rules in Conversational Machine Reading. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Rosenberg, M.; Song, X.; Gao, J.; Tiwary, S.; Majumder, R.; Deng, L. MS MARCO: A Human Generated MAchine Reading COmprehension Dataset. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.09268. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Duh, K.; Gao, J. Stochastic Answer Networks for Machine Reading Comprehension. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1611.09268. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Li, W.; Fang, Y.; Kim, A.; Duh, K.; Gao, J. Stochastic Answer Networks for SQuAD 2.0. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.09194. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Duh, K.; Gao, J. Stochastic Answer Networks for Natural Language Inference. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.07888. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, M. Document-Level Multi-Aspect Sentiment Classification as Machine Comprehension. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 9–11 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Asai, A.; Eriguchi, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Tsuruoka, Y. Multilingual Extractive Reading Comprehension by Runtime Machine Translation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.03275. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Duan, S.; Wang, R. SG-Net: Syntax-Guided Machine Reading Comprehension. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2020), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Minaee, S.; Kalchbrenner, N.; Cambria, E.; Nikzad, N.; Chenaghlu, M.; Gao, J. Deep Learning Based Text Classification: A Comprehensive Review. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.03705. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, S.; Chen, D.; Manning, C.D. Coqa: A conversational question answering challenge. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2019, 7, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, T.; Wang, H.; Bansal, M.; Gimpel, K.; McAllester, D. Who did What: A Large-Scale Person-Centered Cloze Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–5 November 2016; pp. 2230–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welbl, J.; Stenetorp, P.; Riedel, S. Constructing datasets for multi-hop reading comprehension across documents. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2018, 6, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dua, D.; Wang, Y.; Dasigi, P.; Stanovsky, G.; Singh, S.; Gardner, M. DROP: A Reading Comprehension Benchmark Requiring Discrete Reasoning Over Paragraphs. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.00161. [Google Scholar]
- Baudiš, P.; Šedivỳ, J. Modeling of the question answering task in the yodaqa system. In International Conference of the Cross-Language Evaluation Forum for European Languages; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yih, W.T.; Meek, C. Wikiqa: A challenge dataset for open-domain question answering. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; pp. 2013–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.H.; Fisch, A.; Dodge, J.; Karimi, A.H.; Bordes, A.; Weston, J. Key-Value Memory Networks for Directly Reading Documents (EMNLP16). arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.03126. [Google Scholar]
- Trischler, A.; Wang, T.; Yuan, X.; Harris, J.; Sordoni, A.; Bachman, P.; Suleman, K. NewsQA: A Machine Comprehension Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Representation Learning for NLP, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 July–4 August 2017; pp. 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleda, G.; Paperno, D.; Kruszewski, G.; Lazaridou, A.; Pham, Q.N.; Bernardi, R.; Pezzelle, S.; Baroni, M.; Fernandez, R. The LAMBADA dataset: Word prediction requiring a broad discourse context. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Berlin, Germany, 7–12 August 2016; pp. 1525–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett, D.; Lacoste, A.; Jones, L.; Polosukhin, I.; Fandrianto, A.; Han, J.; Kelcey, M.; Berthelot, D. WikiReading: A Novel Large-scale Language Understanding Task over Wikipedia. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Berlin, Germany, 7–12 August 2016; pp. 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajgar, O.; Kadlec, R.; Kleindienst, J. Embracing data abundance: Booktest dataset for reading comprehension. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.00956. [Google Scholar]
- Soricut, R.; Ding, N. Building Large Machine Reading-Comprehension Datasets using Paragraph Vectors. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.04342. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, M.; Choi, E.; Weld, D.; Zettlemoyer, L. TriviaQA: A Large Scale Distantly Supervised Challenge Dataset for Reading Comprehension. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 July–4 August 2017; pp. 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.; Xie, Q.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Hovy, E. RACE: Large-scale ReAding Comprehension Dataset From Examinations. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 9–11 September 2017; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhingra, B.; Mazaitis, K.; Cohen, W.W. Quasar: Datasets for Question Answering by Search and Reading. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.03904. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, M.; Sagun, L.; Higgins, M.; Guney, V.U.; Cirik, V.; Cho, K. Searchqa: A new q&a dataset augmented with context from a search engine. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.05179. [Google Scholar]
- Kočiskỳ, T.; Schwarz, J.; Blunsom, P.; Dyer, C.; Hermann, K.M.; Melis, G.; Grefenstette, E. The narrativeqa reading comprehension challenge. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2018, 6, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welbl, J.; Liu, N.F.; Gardner, M. Crowdsourcing Multiple Choice Science Questions. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Noisy User-generated Text, Copenhagen, Denmark, 7 September 2017; pp. 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; He, H.; Iyyer, M.; Yatskar, M.; Yih, W.T.; Choi, Y.; Liang, P.; Zettlemoyer, L. QuAC: Question Answering in Context. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 2174–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Jia, R.; Liang, P. Know What You Don’t Know: Unanswerable Questions for SQuAD. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2018; pp. 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Qi, P.; Zhang, S.; Bengio, Y.; Cohen, W.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Manning, C.D. HotpotQA: A Dataset for Diverse, Explainable Multi-hop Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; pp. 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, A.; Aralikatte, R.; Khapra, M.M.; Sankaranarayanan, K. DuoRC: Towards Complex Language Understanding with Paraphrased Reading Comprehension. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; pp. 1683–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Q.; Lai, G.; Dai, Z.; Hovy, E. Large-scale Cloze Test Dataset Created by Teachers. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; pp. 2344–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Duh, K.; Van Durme, B. Record: Bridging the gap between human and machine commonsense reading comprehension. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.12885. [Google Scholar]
- Šuster, S.; Daelemans, W. CliCR: A Dataset of Clinical Case Reports for Machine Reading Comprehension. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers), New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2018; pp. 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, P.; Cowhey, I.; Etzioni, O.; Khot, T.; Sabharwal, A.; Schoenick, C.; Tafjord, O. Think you have Solved Question Answering? Try ARC, the AI2 Reasoning Challenge. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.05457. [Google Scholar]
- Mihaylov, T.; Clark, P.; Khot, T.; Sabharwal, A. Can a Suit of Armor Conduct Electricity? A New Dataset for Open Book Question Answering. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.02789. [Google Scholar]
- Khot, T.; Sabharwal, A.; Clark, P. Scitail: A textual entailment dataset from science question answering. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khashabi, D.; Chaturvedi, S.; Roth, M.; Upadhyay, S.; Roth, D. Looking Beyond the Surface: A Challenge Set for Reading Comprehension over Multiple Sentences. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers), New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2018; pp. 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Choi, Y.; Kim, D.; Yu, M.; Kim, S.; Kang, J. Can Machines Learn to Comprehend Scientific Literature? IEEE Access 2019, 7, 16246–16256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z. Learning to Read Academic Papers. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-18), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann, S.; Modi, A.; Roth, M.; Thater, S.; Pinkal, M. MCScript: A Novel Dataset for Assessing Machine Comprehension Using Script Knowledge. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–12 May 2018; European Language Resources Association (ELRA): Miyazaki, Japan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dalvi, B.; Huang, L.; Tandon, N.; Yih, W.T.; Clark, P. Tracking State Changes in Procedural Text: A Challenge Dataset and Models for Process Paragraph Comprehension. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers), New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2018; pp. 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwiatkowski, T.; Palomaki, J.; Redfield, O.; Collins, M.; Parikh, A.; Alberti, C.; Epstein, D.; Polosukhin, I.; Devlin, J.; Lee, K.; et al. Natural questions: A benchmark for question answering research. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2019, 7, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Yu, D.; Chen, J.; Yu, D.; Choi, Y.; Cardie, C. Dream: A challenge data set and models for dialogue-based reading comprehension. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2019, 7, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talmor, A.; Herzig, J.; Lourie, N.; Berant, J. CommonsenseQA: A Question Answering Challenge Targeting Commonsense Knowledge. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2019; pp. 4149–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y. ROUGE: A Package for Automatic Evaluation of Summaries; Text Summarization Branches Out; Association for Computational Linguistics: Barcelona, Spain, 2004; pp. 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. Bleu: A Method for Automatic Evaluation of Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; Association for Computational Linguistics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, S.; Lavie, A. METEOR: An Automatic Metric for MT Evaluation with Improved Correlation with Human Judgments. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Summarization, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 25–30 June 2005; Association for Computational Linguistics: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2005; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Denkowski, M.; Lavie, A. METEOR-NEXT and the METEOR Paraphrase Tables: Improved Evaluation Support for Five Target Languages. In Proceedings of the Joint Fifth Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation and MetricsMATR, Uppsala, Sweden, 15–16 July 2010; Association for Computational Linguistics: Uppsala, Sweden, 2010; pp. 339–342. [Google Scholar]
- Denkowski, M.; Lavie, A. Meteor 1.3: Automatic Metric for Reliable Optimization and Evaluation of Machine Translation Systems. In Proceedings of the Sixth Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation, Edinburgh, UK, 30–31 July 2011; Association for Computational Linguistics: Edinburgh, UK, 2011; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rijsbergen, C.J. Information Retrieval; Butterworth: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, M.C.; King, I.; Leung, K.S. A survey of crowdsourcing systems. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Third International Conference on Privacy, Security, Risk and Trust and 2011 IEEE Third International Conference on Social Computing, Boston, MA, USA, 9–11 October 2011; pp. 766–773. [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara, S.; Aizawa, A. An analysis of prerequisite skills for reading comprehension. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Uphill Battles in Language Processing: Scaling Early Achievements to Robust Methods, Austin, TX, USA, 5 November 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara, S.; Kido, Y.; Yokono, H.; Aizawa, A. Evaluation metrics for machine reading comprehension: Prerequisite skills and readability. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 July–4 August 2017; pp. 806–817. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Xia, J.; Wu, C.; Bi, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Si, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Chen, H. A deep cascade model for multi-document reading comprehension. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 7354–7361. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, J.; He, W.; Lyu, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Multi-Passage Machine Reading Comprehension with Cross-Passage Answer Verification. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; pp. 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowman, S.R.; Angeli, G.; Potts, C.; Manning, C.D. A large annotated corpus for learning natural language inference. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Speer, R.; Chin, J.; Havasi, C. Conceptnet 5.5: An open multilingual graph of general knowledge. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Antol, S.; Agrawal, A.; Lu, J.; Mitchell, M.; Batra, D.; Lawrence Zitnick, C.; Parikh, D. Vqa: Visual question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2425–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, M. Project Gutenberg. 1971. Available online: https://www.gutenberg.org (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- NIST. The Text REtrieval Conference (TREC). Available online: https://trec.nist.gov/ (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- Raison, M.; Mazaré, P.E.; Das, R.; Bordes, A. Weaver: Deep co-encoding of questions and documents for machine reading. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.10490. [Google Scholar]
- Sampath, R.; Ma, P. QA with Wiki: Improving Information Retrieval and Machine Comprehension. Available online: https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs224n/reports/custom/15737727.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- Callan, J.; Hoy, M.; Yoo, C.; Zhao, L. The ClueWeb09 Dataset. 2009. Available online: https://lemurproject.org/clueweb09/ (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- Graff, D.; Kong, J.; Chen, K.; Maeda, K. English gigaword. Linguist. Data Consortium Phila 2003, 4, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Kemmerer, D. Cognitive Neuroscience of Language; Psychology Press: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Barsalou, L.W. Grounded cognition. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 59, 617–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pecher, D.; Zwaan, R.A. Grounding Cognition: The Role of Perception and Action in Memory, Language, and Thinking; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Semin, G.R.; Smith, E.R. Embodied Grounding: Social, Cognitive, Affective, and Neuroscientific Approaches; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, R.W., Jr. Embodiment and Cognitive Science; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Barsalou, L.W. Perceptual symbol systems. Behav. Brain Sci. 1999, 22, 577–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L. Embodied Cognition; Routledge: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Storks, S.; Gao, Q.; Chai, J.Y. Commonsense reasoning for natural language understanding: A survey of benchmarks, resources, and approaches. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.01172. [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid, J.P.; Fishburne, R.P., Jr.; Rogers, R.L.; Chissom, B.S. Derivation of New Readability Formulas (Automated Readability Index, Fog Count and Flesch Reading Ease Formula) for Navy Enlisted Personnel; Butterworth: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Benzahra, M.; Yvon, F. Measuring Text Readability with Machine Comprehension: A Pilot Study. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hough, A.R.; Gluck, K. The understanding problem in cognitive science. In Proceedings of the Seventh Annual Conference on Advances in Cognitive Systems, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2–5 August 2019; pp. 55–74. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, P.C., Jr. Toward Human-Level Knowledge Representation with a Natural Language of Thought; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fodor, J.A. The Language of Thought; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1975; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.E. Theories of semantic memory. Handbook Learn. Cogn. Process. 1978, 6, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Pylyshyn, Z.W. Computation and Cognition; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Men, W.; Gao, J.; Caramazza, A.; Bi, Y. Two Forms of Knowledge Representations in the Human Brain. Neuron 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
























| Year | MRC Tasks | Corpus Type | Question Type | Answer Source | Answer Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | MCTest [15] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2015 | CNN/Daily Mail [19] | Textual | Cloze | Spans | Natural |
| 2015 | CuratedTREC [51] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2015 | WikiQA [52] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2016 | WikiMovies [53] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2016 | SQuAD 1.1 [19] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Natural |
| 2016 | Who-did-What [48] | Textual | Cloze | Spans | Natural |
| 2016 | MS MARCO [39] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2016 | NewsQA [54] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Natural |
| 2016 | LAMBADA [55] | Textual | Cloze | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2016 | WikiReading [56] | Textual | Synthetic | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2016 | Facebook CBT [28] | Textual | Cloze | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2016 | BookTest [57] | Textual | Cloze | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2016 | Google MC-AFP [58] | Textual | Synthetic | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2016 | MovieQA [32] | Multi-modal | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Web [59] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Wiki [59] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2017 | RACE [60] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2017 | Quasar-S [61] | Textual | Cloze | Spans | Multi-choice |
| 2017 | Quasar-T [61] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Natural |
| 2017 | SearchQA [62] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2017 | NarrativeQA [63] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2017 | SciQ [64] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Multi-choice |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-MedHop [49] | Textual | Synthetic | Spans | Multi-choice |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-WikiHop [49] | Textual | Synthetic | Spans | Multi-choice |
| 2017 | TQA [31] | Multi-modal | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2017 | COMICS-Coherence [33] | Multi-modal | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2017 | COMICS-Cloze [33] | Multi-modal | Cloze | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | QuAC [65] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2018 | CoQA [47] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2018 | SQuAD 2.0 [66] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Natural |
| 2018 | HotpotQA-Distractor [67] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Natural |
| 2018 | HotpotQA-Fullwiki [67] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Natural |
| 2018 | DuoRC-Self [68] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2018 | DuoRC-Paraphrase [68] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2018 | CLOTH [69] | Textual | Cloze | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2018 | ReCoRD [70] | Textual | Cloze | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2018 | CliCR [71] | Textual | Cloze | Free-Form | Natural |
| 2018 | ReviewQA [25] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | ARC-Challenge Set [72] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | ARC-Easy Set [72] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | OpenBookQA [73] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | SciTail [74] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | MultiRC [75] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | RecipeQA-Cloze [34] | Multi-modal | Cloze | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | RecipeQA-Coherence [34] | Multi-modal | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | PaperQA-Title [76] | Textual | Cloze | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | PaperQA-Last [76] | Textual | Cloze | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | PaperQA(Hong et al.) [77] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Natural |
| 2018 | MCScript [78] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2018 | ProPara [79] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Natural |
| 2019 | Natural Questions-Short [80] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Natural |
| 2019 | Natural Questions-Long [80] | Textual | Natural | Spans | Natural |
| 2019 | DREAM [81] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2019 | ShARC [38] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2019 | CommonSenseQA [82] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Multi-choice |
| 2019 | DROP [50] | Textual | Natural | Free-Form | Natural |
| Year | MRC Tasks | Metric 1 | Metric 2 | Metric 3 | Metric 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | MCTest [15] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2015 | CNN/Daily Mail [19] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2015 | CuratedTREC [51] | Exact Match | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2015 | WikiQA [52] | Question-level Precision | Question-level Recall | Question-level F1 | N/A |
| 2016 | BookTest [57] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2016 | Facebook CBT [28] | Accuracy on Named Entities | Accuracy on Common Nouns | Accuracy on Verbs | Accuracy on Prepositions |
| 2016 | Google MC-AFP [58] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2016 | LAMBADA [55] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2016 | MovieQA [32] | Accuracy of Video Clips | Accuracy of Plots and Subtitles | N/A | N/A |
| 2016 | MS MARCO [39] | Rouge-L | BLEU-1 | N/A | N/A |
| 2016 | NewsQA [54] | Exact Match | Token-level F1 | N/A | N/A |
| 2016 | SQuAD 1.1 [19] | Token-level F1 | Exact Match | N/A | N/A |
| 2016 | Who-did-What [48] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2016 | WikiMovies [53] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2016 | WikiReading [56] | Question level F1 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | COMICS-Cl [33] | Accuracy of Text Cloze | Accuracy of Visual Cloze | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | COMICS-Co [33] | Accuracy of Coherence | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | NarrativeQA [63] | ROUGE-L | BLEU-1 | BLEU-4 | Meteor |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-M [49] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-W [49] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | Quasar-S [61] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | Quasar-T [61] | Exact Match | Token-level F1 | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | RACE [60] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | SciQ [64] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | SearchQA [62] | F1 score (for n-gram) | Accuracy | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | TQA [31] | Accuracy of All | Accuracy of Diagram | N/A | N/A |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Wiki [59] | Exact Match | Question-level F1 | Verified-EM | Verified-F1 |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Web [59] | Exact Match | Document-level F1 | Verified-EM | Verified-F1 |
| 2018 | ARC-C [72] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | ARC-E [72] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | CliCR [71] | Exact Match | Token-level F1 | BLEU-2 | BLEU-4 |
| 2018 | CLOTH [69] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | CoQA [47] | Token-level F1 | F1 out of domain | F1 in domain | N/A |
| 2018 | DuoRC-P [68] | Accuracy | Token-level F1 | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | DuoRC-S [68] | Accuracy | Token-level F1 | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | HotpotQA-D [67] | EM of Answer | F1 of Answer (Token-level) | EM of Supportings | F1 of Supportings |
| 2018 | HotpotQA-F [67] | EM of Answer | F1 of Answer (Token-level) | EM of Supportings | F1 of Supportings |
| 2018 | MCScript [78] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | MultiRC [75] | F1m | Exact Match | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | OpenBookQA [73] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | PaperQA(Hong et al.) [77] | F1 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | PaperQA-LS [76] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | PaperQA-T [76] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | ProPara [79] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | QuAC [65] | Token-level F1 | HEQ-Q | HEQ-D | N/A |
| 2018 | RecipeQA-Cl [34] | Accuracy of Textual Cloze | Accuracy of Visual Cloze | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | RecipeQA-Co [34] | Accuracy-VO | Accuracy-VC | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | ReCoRD [70] | Exact Match | Token-level F1 | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | ReviewQA [25] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | SciTail [74] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2018 | SQuAD 2.0 [66] | Token-level F1 | EM | N/A | N/A |
| 2019 | CommonSenseQA [82] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2019 | DREAM [81] | Accuracy | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 2019 | DROP [50] | EM | Token-level F1 | N/A | N/A |
| 2019 | Natural Questions-Long [80] | Precision | Recall | N/A | N/A |
| 2019 | Natural Questions-Short [80] | Precision | Recall | F1 | N/A |
| 2019 | ShARC [38] | Micro Accuracy | Macro Accuracy | BLEU-1 | BLEU-4 |
| Metrics | Accuracy | F1 | EM | BLEU | Recall | Precision | ROUGE-L | HEQ-D | Meteor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Usage | 61.40% | 36.84% | 22.81% | 7.02% | 5.26% | 5.26% | 3.51% | 1.75% | 1.75% |
| Year | Datasets | Question Size | #Training Questions | #Dev Questions | #Test Questions | Percentage of Training Set |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | WikiReading [56] | 18.87M | 16.03M | 1.89M | 0.95M | 84.95% |
| 2016 | BookTest [57] | 14,160,825 | 14,140,825 | 10,000 | 10,000 | 99.86% |
| 2016 | Google MC-AFP [58] | 1,742,618 | 1,727,423 | 7602 | 7593 | 99.13% |
| 2015 | Daily Mail [19] | 997,467 | 879,450 | 64,835 | 53,182 | 88.17% |
| 2016 | Facebook CBT [28] | 687K | 669,343 | 8000 | 10,000 | 97.38% |
| 2018 | ReviewQA [25] | 587,492 | 528,665 | N/A | 58,827 | 89.99% |
| 2015 | CNN [19] | 387,420 | 380,298 | 3924 | 3198 | 98.16% |
| 2019 | Natural Questions [80] | 323,045 | 307,373 | 7830 | 7842 | 95.15% |
| 2016 | Who-did-What [48] | 147,786 | 127,786 | 10,000 | 10,000 | 86.47% |
| 2018 | SQuAD 2.0 [66] | 151,054 | 130,319 | 11,873 | 8862 | 86.27% |
| 2017 | SearchQA [62] | 140,461 | 99,820 | 13,393 | 27,248 | 71.07% |
| 2018 | CoQA [47] | 127K | 110K | 7K | 10K | 86.61% |
| 2018 | ReCoRD [70] | 120,730 | 100,730 | 10,000 | 10,000 | 83.43% |
| 2016 | NewsQA [54] | 119K | 107K | 6K | 6K | 89.92% |
| 2018 | HotpotQA [67] | 105,374 | 90,564 | 7405 | 7405 | 85.95% |
| 2018 | CliCR [71] | 104,919 | 91,344 | 6391 | 7184 | 87.06% |
| 2018 | DuoRC-P [68] | 100,316 | 70K | 15K | 15K | 70.00% |
| 2016 | SQuAD 1.1 [19] | 107,702 | 87,599 | 10,570 | 9533 | 81.33% |
| 2016 | WikiMovies [53] | 116K | 96K | 10K | 10K | 82.76% |
| 2018 | CLOTH [69] | 99,433 | 76,850 | 11,067 | 11,516 | 77.29% |
| 2018 | QuAC [65] | 98,275 | 83,568 | 7354 | 7353 | 85.03% |
| 2017 | RACE [60] | 97,687 | 87,866 | 4887 | 4934 | 89.95% |
| 2019 | DROP [50] | 96,567 | 77,409 | 9536 | 9622 | 80.16% |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Web [59] | 95,956 | 76,496 | 9951 | 9509 | 79.72% |
| 2018 | PaperQA-T [76] | 84,803 | 77,298 | 3752 | 3753 | 91.15% |
| 2018 | DuoRC-S [68] | 84K | 60K | 12K | 12K | 70.00% |
| 2018 | PaperQA-L [76] | 80,118 | 71,804 | 4179 | 4135 | 89.62% |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Wiki [59] | 77,582 | 61,888 | 7993 | 7701 | 79.77% |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-W [49] | 51,318 | 43,738 | 5129 | 2451 | 85.23% |
| 2017 | NarrativeQA [63] | 46,765 | 32,747 | 3461 | 10,557 | 70.02% |
| 2017 | Quasar-T [61] | 43,013 | 37,012 | 3000 | 3000 | 86.05% |
| 2017 | Quasar-S [61] | 37,362 | 31,049 | 3174 | 3139 | 83.10% |
| 2018 | RecipeQA [34] | 36K | 29,657 | 3562 | 3567 | 80.62% |
| 2017 | TQA [31] | 26,260 | 15,154 | 5309 | 5797 | 57.71% |
| 2016 | MovieQA [32] | 21,406 | 14,166 | 2844 | 4396 | 66.18% |
| 2018 | MCScript [78] | 13,939 | 9731 | 1411 | 2797 | 69.81% |
| 2017 | SciQ [64] | 13,679 | 11,679 | 1000 | 1000 | 85.38% |
| 2019 | CommonSenseQA [82] | 12,102 | 9741 | 1221 | 1140 | 80.49% |
| 2019 | DREAM [81] | 10,197 | 6116 | 2040 | 2041 | 59.98% |
| 2018 | OpenBookQA [73] | 5957 | 4957 | 500 | 500 | 83.21% |
| 2018 | ARC-Easy Set [72] | 5197 | 2251 | 570 | 2376 | 43.31% |
| 2015 | WikiQA [52] | 3047 | 2118 | 296 | 633 | 69.51% |
| 2018 | ARC-Challenge Set [72] | 2590 | 1119 | 299 | 1172 | 43.20% |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-M [49] | 2508 | 1620 | 342 | 546 | 64.59% |
| 2013 | MCTest-mc500 [15] | 2000 | 1200 | 200 | 600 | 60.00% |
| 2018 | SciTail [74] | 1834 | 1542 | 121 | 171 | 84.08% |
| 2019 | ShARC [38] | 948 | 628 | 69 | 251 | 66.24% |
| 2013 | MCTest-mc160 [15] | 640 | 280 | 120 | 240 | 43.75% |
| 2018 | ProPara [79] | 488 | 391 | 54 | 43 | 80.12% |
| Year | Datasets | Corpus Size | #Train Corpus | #Dev Corpus | #Test Corpus | Unit of Corpus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | WikiReading [56] | 4.7M | N/A | N/A | N/A | Article |
| 2016 | SQuAD 1.1 [19] | 536 | 442 | 48 | 46 | Article |
| 2018 | SQuAD 2.0 [66] | 505 | 442 | 35 | 28 | Article |
| 2016 | BookTest [57] | 14,062 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Book |
| 2017 | COMICS [33] | 3948 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Book |
| 2016 | Facebook CBT [28] | 108 | 98 | 5 | 5 | Book |
| 2019 | DREAM [81] | 6444 | 3869 | 1288 | 1287 | Dialogue |
| 2016 | NewsQA [54] | 1,010,916 | 909,824 | 50,546 | 50,546 | Document |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Web [59] | 662,659 | 528,979 | 68,621 | 65,059 | Document |
| 2015 | Daily Mail [19] | 219,506 | 196,961 | 12,148 | 10,397 | Document |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Wiki [59] | 138,538 | 110,648 | 14,229 | 13,661 | Document |
| 2018 | ReviewQA [25] | 100,000 | 90,000 | N/A | 10,000 | Document |
| 2015 | CNN [19] | 92,579 | 90,266 | 1220 | 1093 | Document |
| 2017 | NarrativeQA [63] | 1572 | 1102 | 115 | 355 | Document |
| 2017 | TQA [31] | 1076 | 666 | 200 | 210 | Lesson |
| 2016 | MovieQA [32] | 548 | 362 | 77 | 109 | Movie |
| 2016 | Google MC-AFP [58] | 1,742,618 | 1,727,423 | 7602 | 7593 | Passage |
| 2016 | Who-did-What [48] | 147,786 | 127,786 | 10,000 | 10,000 | Passage |
| 2017 | SearchQA [62] | 140,461 | 99,820 | 13,393 | 27,248 | Passage |
| 2018 | ReCoRD [70] | 80,121 | 65,709 | 7133 | 7279 | Passage |
| 2017 | Quasar-T [61] | 43,012 | 37,012 | 3000 | 3000 | Passage |
| 2017 | Quasar-S [61] | 37,362 | 31,049 | 3174 | 3139 | Passage |
| 2017 | RACE [60] | 27,933 | 25,137 | 1389 | 1407 | Passage |
| 2018 | SciTail [74] | 27,026 | 23,596 | 1304 | 2126 | Passage |
| 2016 | LAMBADA [55] | 12,684 | 2662 | 4869 | 5153 | Passage |
| 2018 | CoQA [47] | 8399 | 7199 | 500 | 700 | Passage |
| 2018 | CLOTH [69] | 7131 | 5513 | 805 | 813 | Passage |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-W [49] | 51,318 | 43,738 | 5129 | 2451 | Passage |
| 2019 | DROP [50] | 6735 | 5565 | 582 | 588 | Passage |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-M [49] | 2508 | 1620 | 342 | 546 | Passage |
| 2018 | RecipeQA [34] | 19,779 | 15,847 | 1963 | 1969 | Recipe |
| 2015 | WikiQA [52] | 29,258 | 20,360 | 2733 | 6165 | Sentence |
| 2013 | MCTest-mc500 [15] | 500 | 300 | 50 | 150 | Story |
| 2013 | MCTest-mc160 [15] | 160 | 70 | 30 | 60 | Story |
| 2018 | QuAC [65] | 8845 | 6843 | 1000 | 1002 | Unique section |
| 2019 | ShARC [38] | 32,436 | 21,890 | 2270 | 8276 | Utterance |
| 2019 | Natural Questions [80] | 323,045 | 307,373 | 7830 | 7842 | Wikipedia Page |
| Year | Datasets | Generation Method | Source of Corpus | Type of Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | MCTest-mc160 [15] | Crowd-sourcing | Factoid stories | Paragraph |
| 2013 | MCTest-mc500 [15] | Crowd-sourcing | Factoid stories | Paragraph |
| 2015 | CNN [19] | Automated | News | Document |
| 2015 | CuratedTREC [51] | Crowd-sourcing | Factoid stories | Paragraph |
| 2015 | Daily Mail [19] | Automated | News | Document |
| 2015 | WikiQA [52] | Crowd-sourcing | Wikipedia | Paragraph |
| 2016 | BookTest [57] | Automated | Factoid stories | Paragraph |
| 2016 | Facebook CBT [28] | Automated | Factoid stories | Paragraph |
| 2016 | Google MC-AFP | Automated | The Gigaword corpus | Paragraph |
| 2016 | LAMBADA [55] | Crowd-sourcing | Book Corpus | Paragraph |
| 2016 | MovieQA [32] | Crowd-sourcing | Movie | Paragraph with Images and Videos |
| 2016 | MS MARCO | Automated | The Bing | Paragraph |
| 2016 | NewsQA [54] | Crowd-sourcing | News | Document |
| 2016 | SQuAD 1.1 [19] | Crowd-sourcing | Wikipedia | Paragraph |
| 2016 | Who-did-What [48] | Automated | News | Document |
| 2016 | WikiMovies [53] | Automated | Movie | Document |
| 2016 | WikiReading [56] | Automated | Wikipedia | Document |
| 2017 | COMICS [33] | Automated | Comics | Paragraph with Images |
| 2017 | NarrativeQA [63] | Crowd-sourcing | Movie | Document |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-M [49] | Crowd-sourcing | Wikipedia | Paragraph |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-W [49] | Crowd-sourcing | Scientic paper | Paragraph |
| 2017 | Quasar-S [61] | Crowd-sourcing | Stack Overflow | Paragraph |
| 2017 | Quasar-T [61] | Crowd-sourcing | Stack Overflow | Paragraph |
| 2017 | RACE [60] | Expert | English Exam | Document |
| 2017 | SciQ [64] | Crowd-sourcing | School science curricula | Paragraph |
| 2017 | SearchQA [62] | Crowd-sourcing | J! Archive and Google | Paragraph & URL |
| 2017 | TQA [31] | Expert | School science curricula | Paragraph with Images |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Wiki [59] | Automated | The Bing | Paragraph |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Web [59] | Automated | The Bing | Paragraph |
| 2018 | ARC-Challenge Set [72] | Expert | School science curricula | Paragraph |
| 2018 | ARC-Easy Set [72] | Expert | School science curricula | Paragraph |
| 2018 | CliCR [71] | Automated | BMJ Case Reports | Paragraph |
| 2018 | CLOTH [69] | Expert | English Exam | Document |
| 2018 | CoQA [47] | Crowd-sourcing | Jeopardy | Paragraph |
| 2018 | DuoRC-Paraphrase [68] | Crowd-sourcing | Movie | Paragraph |
| 2018 | DuoRC-Self [68] | Crowd-sourcing | Movie | Paragraph |
| 2018 | HotpotQA-D [67] | Crowd-sourcing | Wikipedia | Multi-paragraph |
| 2018 | HotpotQA-F [67] | Crowd-sourcing | Wikipedia | Multi-paragraph |
| 2018 | MCScript [78] | Crowd-sourcing | Narrative texts | Paragraph |
| 2018 | MultiRC [75] | Crowd-sourcing | News and other web pages | Multi-sentence |
| 2018 | OpenBookQA [73] | Crowd-sourcing | School science curricula | Paragraph |
| 2018 | PaperQA(Hong et al.) [77] | Crowd-sourcing | Scientic paper | Paragraph |
| 2018 | PaperQA-L [76] | Automated | Scientic paper | Paragraph |
| 2018 | PaperQA-T [76] | Automated | Scientic paper | Paragraph |
| 2018 | ProPara [79] | Crowd-sourcing | Process Paragraph | Paragraph |
| 2018 | QuAC [65] | Crowd-sourcing | Wikipedia | Document |
| 2018 | RecipeQA [34] | Automated | Recipes | Paragraph with Images |
| 2018 | ReCoRD [70] | Crowd-sourcing | News | Paragraph |
| 2018 | ReviewQA [25] | Crowd-sourcing | Hotel Comments | Paragraph |
| 2018 | SciTail [74] | Crowd-sourcing | School science curricula | Paragraph |
| 2018 | SQuAD 2.0 [66] | Crowd-sourcing | Wikipedia | Paragraph |
| 2019 | CommonSenseQA [82] | Crowd-sourcing | Narrative texts | Paragraph |
| 2019 | DREAM [81] | Crowd-sourcing | English Exam | Dialogues |
| 2019 | DROP [50] | Crowd-sourcing | Wikipedia | Paragraph |
| 2019 | Natural Questions-L [80] | Crowd-sourcing | Wikipedia | Paragraph |
| 2019 | Natural Questions-S [80] | Crowd-sourcing | Wikipedia | Paragraph |
| 2019 | ShARC [38] | Crowd-sourcing | Government Websites | Paragraph |
| Year | Datasets | Dataset Availability | Leaderboard Availability | Baseline Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | CommonSenseQA [82] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2018 | MCScript [78] | √ | √ | × |
| 2018 | OpenBookQA [73] | √ | √ | × |
| 2018 | ReCoRD [70] | √ | √ | × |
| 2018 | ARC-Challenge Set [72] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2018 | ARC-Easy Set [72] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2018 | CLOTH [69] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2016 | Facebook CBT [28] | √ | × | √ |
| 2016 | NewsQA [54] | √ | × | × |
| 2018 | ProPara [79] | √ | √ | × |
| 2017 | RACE [60] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2016 | SQuAD 1.1 [19] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Wiki [59] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2017 | TriviaQA-Web [59] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2019 | DROP [50] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2017 | NarrativeQA [63] | √ | × | √ |
| 2019 | ShARC [38] | √ | √ | × |
| 2018 | CoQA [47] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2019 | DREAM [81] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2018 | QuAC [65] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2013 | MCTest-mc160 [15] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2013 | MCTest-mc500 [15] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2015 | WikiQA [52] | √ | × | × |
| 2018 | CliCR [71] | √ | × | √ |
| 2018 | PaperQA (Hong et al.) [77] | √ | × | × |
| 2018 | PaperQA-L [76] | × | × | × |
| 2018 | PaperQA-T [76] | × | × | × |
| 2018 | ReviewQA [25] | √ | × | × |
| 2017 | SciQ [64] | √ | × | × |
| 2016 | WikiMovies [53] | √ | × | √ |
| 2016 | BookTest [57] | √ | × | × |
| 2015 | CNN [19] | √ | × | √ |
| 2015 | Daily Mail [19] | √ | × | √ |
| 2016 | Who-did-What [48] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2016 | WikiReading [56] | √ | × | √ |
| 2016 | Google MC-AFP [58] | √ | × | × |
| 2016 | LAMBADA [55] | √ | × | √ |
| 2018 | SciTail [74] | √ | √ | × |
| 2018 | DuoRC-Paraphrase [68] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2018 | DuoRC-Self [68] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2015 | CuratedTREC [51] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2017 | Quasar-S [61] | √ | × | √ |
| 2017 | Quasar-T [61] | √ | × | √ |
| 2017 | SearchQA [62] | √ | × | × |
| 2019 | Natural Questions-L [80] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2019 | Natural Questions-S [80] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2018 | SQuAD 2.0 [66] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2016 | MS MARCO [39] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-MEDHOP [49] | √ | √ | × |
| 2017 | Qangaroo-WIKIHOP [49] | √ | √ | × |
| 2018 | MultiRC [75] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2018 | HotpotQA-Distractor [67] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2018 | HotpotQA-Fullwiki [67] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2017 | COMICS [33] | √ | × | √ |
| 2016 | MovieQA [32] | √ | √ | √ |
| 2018 | RecipeQA [34] | √ | √ | × |
| 2017 | TQA [31] | √ | √ | × |
| Prerequisite Skills | Descriptions or Examples | Frequency SQuAD | Frequency MCTest |
|---|---|---|---|
| List/Enumeration | Tracking, retaining, and list/enumeration of entities or states | 5.00% | 11.70% |
| Mathematical operations | Four basic operations and geometric comprehension | 0.00% | 4.20% |
| Coreference resolution | Detection and resolution of coreferences | 6.20% | 57.50% |
| Logical reasoning | Induction, deduction, conditional statement, and quantifier | 1.20% | 0.00% |
| Analogy | Trope in figures of speech, e.g., metaphor | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Spatiotemporal relations | Spatial and/or temporal relations of events | 2.50% | 28.30% |
| Causal relations | Why, because, the reason, etc. | 6.20% | 18.30% |
| Commonsense reasoning | Taxonomic/qualitative knowledge, action and event change | 86.20% | 49.20% |
| Complex sentences | Coordination or subordination of clauses | 20.00% | 15.80% |
| Special sentence structure | Scheme in figures of speech, constructions, and punctuation marks | 25.00% | 10.00% |
| Year | Datasets | Average Monthly Citations | Total Citations | Months after Publication | Date of Publication | Date of Statistics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | SQuAD 1.1 [19] | 33.35 | 1234 | 37 | 2016-10-10 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2015 | CNN/Daily Mail [19] | 25.21 | 1210 | 48 | 2015-11-19 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | SQuAD 2.0 [66] | 14.65 | 249 | 17 | 2018-06-11 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2019 | Natural Questions [80] | 9.00 | 45 | 5 | 2019-07-01 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2017 | TriviaQA [59] | 7.97 | 239 | 30 | 2017-05-13 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | CoQA [47] | 7.93 | 119 | 15 | 2018-08-21 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2016 | WikiMovies [53] | 7.73 | 286 | 37 | 2016-10-10 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2016 | CBT [28] | 6.92 | 332 | 48 | 2015-11-07 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2016 | MS MARCO [39] | 6.65 | 246 | 37 | 2016-10-31 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2015 | WikiQA [52] | 6.43 | 328 | 51 | 2015-09-01 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | HotpotQA [67] | 5.71 | 80 | 14 | 2018-09-25 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2016 | NewsQA [54] | 5.21 | 172 | 33 | 2017-02-07 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2016 | MovieQA [32] | 5.00 | 235 | 47 | 2015-12-09 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2017 | RACE [60] | 4.87 | 151 | 31 | 2017-04-15 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | QuAC [65] | 4.73 | 71 | 15 | 2018-08-27 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2013 | MCTest [15] | 4.69 | 347 | 74 | 2013-10-01 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2017 | Qangaroo [49] | 4.59 | 78 | 17 | 2018-06-11 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | SciTail [74] | 4.16 | 79 | 19 | 2018-04-27 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2017 | NarrativeQA [63] | 3.74 | 86 | 23 | 2017-12-19 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2019 | DROP [50] | 3.00 | 27 | 9 | 2019-03-01 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | ARC | 2.90 | 58 | 20 | 2018-03-14 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2017 | SearchQA [62] | 2.81 | 87 | 31 | 2017-04-18 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | OpenBookQA [73] | 2.64 | 37 | 14 | 2018-09-08 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2016 | WikiReading [56] | 2.41 | 77 | 32 | 2017-03-15 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2019 | CommonSenseQA [82] | 2.33 | 28 | 12 | 2018-11-02 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2017 | Quasar [61] | 1.82 | 51 | 28 | 2017-07-12 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2016 | Who-did-What [48] | 1.69 | 66 | 39 | 2016-08-18 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | MultiRC [75] | 1.67 | 30 | 18 | 2018-06-01 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2017 | TQA [31] | 1.55 | 45 | 29 | 2017-07-01 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2019 | DREAM [81] | 1.50 | 15 | 10 | 2019-01-31 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | ReCoRD [70] | 1.39 | 18 | 13 | 2018-10-30 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2016 | LAMBADA [55] | 1.29 | 53 | 41 | 2016-6-20 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2019 | ShARC [38] | 1.27 | 19 | 15 | 2018-08-28 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | MCScript [78] | 1.10 | 22 | 20 | 2018-03-14 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2015 | CuratedTREC [51] | 0.98 | 47 | 48 | 2015-11-20 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | RecipeQA [34] | 0.93 | 13 | 14 | 2018-09-04 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2017 | COMICS [33] | 0.86 | 31 | 36 | 2016-11-16 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | ProPara [79] | 0.83 | 15 | 18 | 2018-05-17 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2017 | SciQ [64] | 0.79 | 22 | 28 | 2017-07-19 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2016 | BookTest [57] | 0.73 | 27 | 37 | 2016-10-04 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | DuoRC [68] | 0.63 | 12 | 19 | 2018-04-21 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | CliCR [71] | 0.55 | 11 | 20 | 2018-03-26 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | CLOTH [69] | 0.42 | 10 | 24 | 2017-11-09 | 2019-12-01 |
| 2018 | ReviewQA [25] | 0.08 | 1 | 13 | 2018-10-29 | 2019-12-01 |
| Year | Datasets | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | WikiQA [52] | With Unanswerable Questions |
| 2018 | SQuAD 2.0 [66] | With Unanswerable Questions |
| 2019 | Natural Question [80] | With Unanswerable Questions |
| 2016 | MS MARCO [39] | With Unanswerable Questions; Multi-hop MRC |
| 2018 | DuoRC [68] | With Paraphrased Paragraph; Require Commonsense (World knowledge); Complex Reasoning; With Unanswerable Questions |
| 2016 | Who-did-What [48] | With Paraphrased Paragraph; Complex Reasoning |
| 2018 | ARC [72] | Require Commonsense (World knowledge); Complex Reasoning |
| 2018 | MCScript [78] | Require Commonsense (World knowledge) |
| 2018 | OpenBookQA [73] | Require Commonsense (World knowledge) |
| 2018 | ReCoRD [70] | Require Commonsense (World knowledge) |
| 2019 | CommonSenseQA [82] | Require Commonsense (World knowledge) |
| 2016 | WikiReading [56] | Require Commonsense (External knowledge); Large Scale Dataset |
| 2016 | WikiMovies [53] | Require Commonsense (External knowledge); Domain-specific |
| 2016 | MovieQA [32] | Multi-Modal MRC |
| 2017 | COMICS [33] | Multi-Modal MRC |
| 2017 | TQA [31] | Multi-Modal MRC |
| 2018 | RecipeQA [34] | Multi-Modal MRC |
| 2018 | HotpotQA [67] | Multi-hop MRC; Complex Reasoning |
| 2017 | NarrativeQA [63] | Multi-hop MRC; Complex Reasoning |
| 2017 | Qangaroo [49] | Multi-hop MRC |
| 2018 | MultiRC [75] | Multi-hop MRC |
| 2015 | CNN/Daily Mail [19] | Large-scale Dataset |
| 2016 | BookTest [57] | Large-scale Dataset |
| 2013 | MCTest [15] | For Open-domain QA |
| 2015 | CuratedTREC [51] | For Open-domain QA |
| 2017 | Quasar [61] | For Open-domain QA |
| 2017 | SearchQA [62] | For Open-domain QA |
| 2017 | SciQ [64] | Domain-specific |
| 2018 | CliCR [71] | Domain-specific |
| 2018 | PaperQA(Hong et al.) [77] | Domain-specific |
| 2018 | PaperQA(Park et al.) [76] | Domain-specific |
| 2018 | ReviewQA [25] | Domain-specific |
| 2018 | SciTail [74] | Domain-specific |
| 2019 | DROP [50] | Complex Reasoning |
| 2016 | Facebook CBT [28] | Complex Reasoning |
| 2016 | Google MC-AFP | Complex Reasoning |
| 2016 | LAMBADA [55] | Complex Reasoning |
| 2016 | NewsQA [54] | Complex Reasoning |
| 2016 | SQuAD 1.1 [19] | Complex Reasoning |
| 2017 | RACE [60] | Complex Reasoning |
| 2017 | TriviaQA [59] | Complex Reasoning |
| 2018 | CLOTH [69] | Complex Reasoning |
| 2018 | ProPara [79] | Complex Reasoning |
| 2019 | DREAM [81] | Conversational MRC; Require Commonsense (World knowledge) |
| 2018 | CoQA [47] | Conversational MRC; With Unanswerable Questions |
| 2018 | QuAC [65] | Conversational MRC; With Unanswerable Questions |
| 2019 | ShARC [38] | Conversational MRC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, C.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Hu, J.; Hu, J. A Survey on Machine Reading Comprehension—Tasks, Evaluation Metrics and Benchmark Datasets. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7640. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217640
Zeng C, Li S, Li Q, Hu J, Hu J. A Survey on Machine Reading Comprehension—Tasks, Evaluation Metrics and Benchmark Datasets. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(21):7640. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217640
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Changchang, Shaobo Li, Qin Li, Jie Hu, and Jianjun Hu. 2020. "A Survey on Machine Reading Comprehension—Tasks, Evaluation Metrics and Benchmark Datasets" Applied Sciences 10, no. 21: 7640. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217640
APA StyleZeng, C., Li, S., Li, Q., Hu, J., & Hu, J. (2020). A Survey on Machine Reading Comprehension—Tasks, Evaluation Metrics and Benchmark Datasets. Applied Sciences, 10(21), 7640. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217640