Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure: A Review
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Aspects of Dry Anaerobic Digestion
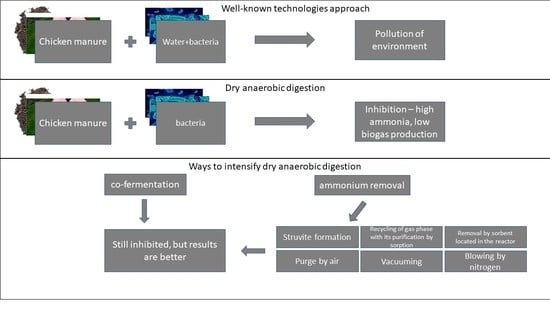
2.1. Dry and Wet Anaerobic Digestion
2.2. Advantages of the Dry Anaerobic Digestion
2.3. Inhibition of AD by Ammonia
Mechanism of Inhibition by Ammonia
2.4. Influence of Water Activity on Dry AD
2.5. Inhibition of Dry AD
2.6. The Efficiency of Dry AD
2.7. Technologies of Dry AD
3. Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure
4. Ways to Intensify Dry AD of Chicken Manure
4.1. Dry Anaerobic co-Fermentation of Chicken Manure
4.2. Dry AD under Ammonium Removal
4.3. Adaptation during Dry AD
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nichols, C.E. Overview of Anaerobic Digestion Technologies in Europe. Biocycle 2004, 45, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yakushko, S.I. Vyibor Tehnologicheskih Rezhimov v Ustanovkah Dlya Proizvodstva Biogaza (Selection of technological modes in plants for biogas production). VIsnik SumDU 2006, 89, 102–108. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Abouelenien, F.; Fujiwara, W.; Namba, Y.; Kosseva, M.; Nishio, N.; Nakashimada, Y. Improved Methane Fermentation of Chicken Manure via Ammonia Removal by Biogas Recycle. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6368–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosey, F.; Jago, D. The Determination of Dissolved Sulphide Using a Sulphide-Selective Electrode. Water Res. Centre Tech. Rep. TR 1977, 53, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Kukić, S.; Bračun, B.; Kralik, D.; Burns, R.T.; Rupčić, S.; Jovičić, D. Comparison between Biogas Production from Manure of Laying Heners and Broilers. Poljoprivreda 2010, 16, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Garófallo, R.; Ii, G.; Ribeiro, S.; Alexandre, C.I.; Mendes, R.; Ii, F. Biodigestão Anaeróbia de Dejetos de Poedeiras Coletados Após Diferentes Períodos de Acúmulo Anaerobic Biodigestion of Laying Hens Manure Collected after Different Periods of Accumulation. Ciência Rural 2012, 42, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Kothari, R.; Pandey, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Tyagi, V.V.; Tyagi, S.K. Different Aspects of Dry Anaerobic Digestion for Bio-Energy: An Overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 174–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Zhu, J. Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion for Methane Production from Organic Waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, C.; Liu, G.; He, Y.; Liu, X. Biogas Production from Co-Digestion of Corn Stover and Chicken Manure under Anaerobic Wet, Hemi-Solid, and Solid State Conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Pérez, M.; Romero, L.I. Effect of Substrate Concentration on Dry Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste (OFMSW). Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6075–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, F.; De La Rubia, M.A.; Fernández-Cegrí, V.; Borja, R. Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Organic Substrates in Batch Mode: An Overview Relating to Methane Yields and Experimental Procedures. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissens, G.; Vandevivere, P.; De Baere, L.; Biey, E.M.; Verstraete, W. Solid Waste Digestors: Process Performance and Practice for Municipal Solid Waste Digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 44, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapport, J.; Zhang, R.; Jenkins, B.; Williams, R. Current Anaerobic Digestion Technologies Used for Treatment of Municipal Organic Solid Waste; California Environmental Protection Agency: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Oleszkiewicz, J.A.; Poggi-Varaldo, H.M. High-Solids Anaerobic Digestion of Mixed Municipal and Industrial Waste. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoto, E.N. Anaerobic Digetion of Organic Solid Waste for Energy Production; KIT Scientific Publishing: Karlsruhe, Baden-Württemberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Salyuk, A.I.; Zhadan, S.A.; Shapovalov, Y.B.; Tarasenko, R.A.; Shapovalov, Y.B. Vliyanie Vodopotrebleniya Na Effektivnost Metanovogo Brozheniya Kurinogo Pometa (Influence of water consumption on the efficiency of methane fermentation of chicken manure). Int. Sci. J. Altern. Energy Ecol. 2015, 15, 53–58. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov, Y.B.; Salyuk, A.I.; Kotinskiy, A.V.; Tarasenko, R.A. The Reaserch of Dry Chicken Manure Methanogenesis Stability. Environ. Probl. 2019, 4, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baeten, D. In-Reactor Anaerobic Digestion of Municipal Solid Waste Solids. In Science and Engineering of Compost—Design, Environmenal, Microbiological and Utilisation Aspects; Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 1993; pp. 111–130. [Google Scholar]
- Luning, L.; Van Zundert, E.H.M.; Brinkmann, A.J.F. Comparison of Dry and Wet Digestion for Solid Waste. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guendouz, J.; Buffière, P.; Cacho, J.; Carrère, M.; Delgenes, J.P. Dry Anaerobic Digestion in Batch Mode: Design and Operation of a Laboratory-Scale, Completely Mixed Reactor. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, W.; Lehto, M.; Teye, F. Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Residues On-Farm -A Feasibility Study; MTT Agrifood Research Finland Distribution: Jokioinen, Finland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mata-Alvarez, J. Biomethanization of the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Wastes; IWA Publishing: Barcelona, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, C. Anaerobic Digestion of Poultry Manure: Implementation of Ammonia Control to Optimize Biogas Yield; The University of Guelph: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abbassi-Guendouz, A.; Brockmann, D.; Trably, E.; Dumas, C.; Delgenès, J.P.; Steyer, J.P.; Escudié, R. Total Solids Content Drives High Solid Anaerobic Digestion via Mass Transfer Limitation. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedwitschka, H.; Ibanez, D.G.; Schäfer, F.; Jenson, E.; Nelles, M. Material Characterization and Substrate Suitability Assessment of Chicken Manure for Dry Batch Anaerobic Digestion Processes. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauser, A.; Deublein, D. Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vavilin, V.A.; Shchelkanov, M.Y.; Rytov, S.V. Effect of Mass Transfer on Concentration Wave Propagation during Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Waste. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2405–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, Z.-W.; Tang, L.; Li, Y. A Mass Diffusion-Based Interpretation of the Effect of Total Solids Content on Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion of Cellulosic Biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C. Wet and Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Biowaste and of Co- Substrates; Karlsruhe Institute of Technology: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bujoczek, G.; Oleszkiewicz, J.; Sparling, R.; Cenkowski, S. High Solid Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2000, 76, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.H.; Angelidaki, I.; Ahring, B. Improving Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Swine Manure. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Jacobi, H.F.; Strach, K.; Xu, C.; Zhou, H.; Liebetrau, J. Mono-Fermentation of Chicken Manure: Ammonia Inhibition and Recirculation of the Digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ni, P.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Dach, J.; Dong, R. Integrated Approach to Sustain Biogas Production in Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure under Recycled Utilization of Liquid Digestate: Dynamics of Ammonium Accumulation and Mitigation Control. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 205, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belostotskiy, D.; Jacobi, H.; Strach, K.; Liebetrau, J. Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure as a Single Substrate by Control of Ammonia Concentration. In Proceedings of the 13th World Congress on Anaerobic Digestio composting, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 25–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal, R.; Massé, D.I.; Singh, G. A Critical Review on Inhibition of Anaerobic Digestion Process by Excess Ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and Potential of the Anaerobic Digestion of Waste-Activated Sludge. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.; Dabert, P.; Barrington, S.; Burton, C. Livestock Waste Treatment Systems for Environmental Quality, Food Safety, and Sustainability. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5527–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnürer, A.; Nordberg, Å. Ammonia, a Selective Agent for Methane Production by Syntrophic Acetate Oxidation at Mesophilic Temperature. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.R.; Hawkes, F.R. The Anaerobic Digestion of Poultry Manure: Variation of Gas Yield with Influent Concentration and Ammonium-Nitrogen Levels. Agric. Wastes 1985, 14, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, I.W.; Lettinga, G. Anaerobic Digestion at Extreme Ammonia Concentrations. Biol. Wastes 1988, 25, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moestedt, J.; Müller, B.; Westerholm, M.; Schnürer, A. Ammonia Threshold for Inhibition of Anaerobic Digestion of Thin Stillage and the Importance of Organic Loading Rate. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakashev, D.; Batstone, D.J.; Angelidaki, I. Influence of Environmental Conditions on Methanogenic Compositions in Anaerobic Biogas Reactors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, W.; Hojo, T.; Niu, Q.; Li, Y.-Y.; Qiang, H. Mesophilic Methane Fermentation of Chicken Manure at a Wide Range of Ammonia Concentration: Stability, Inhibition and Recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, P.L.; Mckinney, R.E. Salt Toxity in Anaerobic Digestion. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1961, 33, 399–415. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, A.G. Ammonia Inhibition of Methanogenesis from Cattle Wastes. Agric. Wastes 1986, 17, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, C.; Zeng, A.P.; Deckwer, W.D. Growth Inhibition by Ammonia and Use of a PH-Controlled Feeding Strategy for the Effective Cultivation of Mycobacterium Chlorophenolicum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 44, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallert, C.; Bauer, S.; Winter, J. Effect of Ammonia on the Anaerobic Degradation of Protein by a Mesophilic and Thermophilic Biowaste Population. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, B.P.; Leahy, J.J.; Heniahan, A.M.; O’Dwyer, T.F.; Sutton, D.; Leahy, M.J. Advances in Poultry Litter Disposal Technology—A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Yuan, T.; Lei, Z.; Cai, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Effective Ammonia Recovery from Swine Excreta through Dry Anaerobic Digestion Followed by Ammonia Stripping at High Total Solids Content. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 90, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, R.; Huber, P.; Meyrath, J. Ammonia Toxicity in Liquid Piggery Manure Digestion. Biotechnol. Lett. 1981, 3, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, A.G.F.; Speece, R.E.; Yang, C.H.J.; Kocher, W.M.; Parkin, G.F. Response Fermentation Industrial of Methane to Systems Toxicants. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1983, 55, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández Rodríguez, J.; Pérez, M.; Romero, L.I. Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste: Optimisation of the Semicontinuous Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 193–194, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rodríguez, J.; Pérez, M.; Romero, L.I. Comparison of Mesophilic and Thermophilic Dry Anaerobic Digestion of OFMSW: Kinetic Analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 232, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera, A.C.; Vymazal, J.; Maucieri, C. Greenhouse Gases Formation and Emission, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantrania, A.R. High-Solids Anaerobic Fermentation of Poultry Manure; Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Corry, J.E. The Water Relations and Heat Resistance of Microorganisms. Prog. Ind. Microbiol. 1972, 12, 73–108. [Google Scholar]
- García-Bernet, D.; Buffière, P.; Latrille, E.; Steyer, J.P.; Escudié, R. Water Distribution in Biowastes and Digestates of Dry Anaerobic Digestion Technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buan, N.R. Methanogens: Pushing the Boundaries of Biology. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2018, 2, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, W.J. Water Relations of Food Spoilage Microorganisms. Adv. Food Res. 1957, 7, 83–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockland, L.B.; Beuchal, L.R. Water Activity: Theory and Applications to Food. J. Hepatol. 2005, 20, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, C.W. Semi-Solid Anaerobic Fermentation of Cellulose to Ethanol; Cornell University: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal, R.; Massé, D.I. Start-up of Dry Anaerobic Digestion System for Processing Solid Poultry Litter Using Adapted Liquid Inoculum. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 102, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, W.; De Baere, L. Dry Anaerobic Conversion of Municipal Solid Waste by Means of the Dranco Process. Water Sci. Technol. 1992, 25, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.P.; Li, X.J.; Wang, K.S.; Yuan, H.R. Improving Biodegradability and Biogas Production of Corn Stover through Sodium Hydroxide Solid State Pretreatment. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 2761–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, G.F.; Owen, W.F. Fundamentals of Anaerobic Digestion of Wastewater Sludges. J. Environ. Eng. 2008, 112, 867–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster-Carneiro, T.; Perez, M.; Romero, L.I.; Sales, D. Dry-Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Fraction of the Municipal Solid Waste: Focusing on the Inoculum Sources. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3195–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelenien, F.; Namba, Y.; Nishio, N.; Nakashimada, Y. Dry Co-Digestion of Poultry Manure with Agriculture Wastes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 178, 932–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laclos, H.F.; Desbois, S.; Saint-Joly, C. Anaerobic Digestion of Municipal Solid Organic Waste: Valorga Full-Scale Plant in Tilburg, the Netherlands. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbassi-Guendouz, A. Link Between Operating Parameters, Microorganisms and Performances of Dry Anaerobic Digestion; University of Montpellier II, Sciences et Techniques du Languedoc: Montpellier, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- De Baere, L. Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Waste: State-of-the-Art. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, P.; Battistoni, P.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Cecchi, F. Performance of Thermophilic Semi-Dry Anaerobic Digestion Process Changing the Feed Biodegradability. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiland, P. One- and Two-Step Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Agroindustrial Residues. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safley, L.M.; Westerman, P.W. Psychrophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Animal Manure: Proposed Design Methodology. Biol. Wastes 1990, 34, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S. Anaerobic Digestion of Biodegradable Organics in Municipal Solid Wastes; Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baere, L.D. The DRANCO Process: A Dry Continuous System for Solid Organic Waste and Energy Crops. In Proceedings of theInternational Symposium on Anaerobic Dry Fermentation, Berlin, Germany, 20–22 February 2008; pp. 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Vandevivere, P.; De Baere, L.; Verstraete, W.; De Baere, L.; Verstraete, W. Types of Anaerobic Digesters for Solid Wastes. In Biomethanization of the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Wastes; Mata-Alvarez, J., Ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2003; pp. 111–140. [Google Scholar]
- Den Boer, E. Mechanical-Biological Treatment of Municipal Waste in Poland Dominating Technologies and Their Efficiency in Diverting Waste from Landfills. Waste Manag. 2015, 5, 349–361. [Google Scholar]
- Edelmann, W.; Engeli, H. More than 12 Years of Experience with Commercial Anaerobic Digestion of the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Wastes in Switzerland. In Proceedings of the ADSW 2005 Conference Proceedings, Copenhagen, Denmark, 31 August–2 September 2005; Volume 1, pp. 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Appressi, L. Biogas and Bio-Hydrogen: Production and Uses. A Review. Available online: https://amslaurea.unibo.it/9071/1/Research_B_-_Appressi.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Guide to Biogas from Production to Use. Fachagentur Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e.V. (FNR). 2012. Available online: https://mediathek.fnr.de/broschuren/fremdsprachige-publikationen/english-books/guide-to-biogas-from-production-to-use.html (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Chavez-Vazquez, M.; Bagley, D.M. Evaluation of the Performance of Different Anaerobic Digestion Technologies for Solid Waste Treatment. In Proceedings of the CSCE/EWRI of ASCE Environmental Engineering Conference, Niagara, ON, Canada, 5 June 2002; pp. 2–15. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.B.; Spiegel, L. UC Davis Technology Assessment for Advanced Biomass Power Generation; California Energy Commission: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ten Brummeler, E. Full Scale Experience with the BIOCEL Process. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Brummeler, E. Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Waste in the Biocel Process with a Full Scale Unit. In Proceedings of the Intertional Symposium on Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Waste, Venice, Italy, 14–17 April 1992; pp. 557–560. [Google Scholar]
- Ouedraogo, A. Pilot Scale Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion of the Biodegradable Organic Fraction of Bamako District Municipal Solid Waste. In Proceedings of the II International Symposium Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Waste, Barcelona, Spain, 15–18 June 1999; pp. 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cecchi, F.; Battistoni, P.; Pavan, P.; Bolzonella, D.; Innocenti, L. Digestione Anaerobica Della Frazione Organica Dei Rifiuti Solidi; Agenzia per la Protezione Dell’ambiente e per i Servizi Tecnici: Rome, Italy, 2005; p. 178. [Google Scholar]
- Salyuk, A.I.; Zhadan, S.O.; Shapovalov, Y.B. Metanove Brodinnya Kuryachoho Poslidu u Termofil"nomu Rezhymi (Methane Fermentation of Chicken Manure in Thermophilic Mode). In Novi Ideyi V Xarchovij Nauci—Novi Produkty Xarchovij Promyslovosti; NUFT: Kiev, Ukraine, 2014; p. 708. [Google Scholar]
- Salyuk, A.I.; Zhadan, S.O.; Shapovalov, Y.B. Termofil’ne Metanove Brodinnya Kuryachoho Poslidu (Thermophilic Methane Fermentation of Chicken Manure). In Mizhnarodna Naukova konferenciya, Prysvyachena 130-Richchyu Nacional’noho Universytetu Xarchovyx Texnolohij; National University of Food Technologies: Kiev, Ukraine, 2014; p. 708. [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov, Y.B.; Salyuk, A.I.; Kotinskiy, A.V. DoslIdzhennya StabIlnostI Metanogenezu Kuryachogo PoslIdu u Tverdofaznih Umovah (Investigation of the stability of chicken manure methanogenesis in solid phase conditions). Naukovi Pratsi Natsionalnogo Univ. Harchovih Tehnol. 2018, 24, 57–64. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar]
- Abouelenien, F.; Nakashimada, Y.; Nishio, N. Dry Mesophilic Fermentation of Chicken Manure for Production of Methane by Repeated Batch Culture. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2009, 107, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelenien, F.; Kitamura, Y.; Nishio, N.; Nakashimada, Y. Dry Anaerobic Ammonia-Methane Production from Chicken Manure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, C.; Crolla, A.; Kinsley, C.; McBean, E. Anaerobic Digestion of Poultry Manure: Process Optimization Employing Struvite Precipitation and Novel Digestion Technologies. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2017, 36, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markou, G. Improved Anaerobic Digestion Performance and Biogas Production from Poultry Litter after Lowering Its Nitrogen Content. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 196, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šinkora, M.; Havlíček, M. Monitoring of Dry Anaerobic Fermentation in Experimental Facility with Use of Biofilm Reactor. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2011, 59, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, H.K.; Smith, M.C.; Kondrad, S.L.; White, J.W. Evaluation of Biogas Production Potential by Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Switchgrass-Animal Manure Mixtures. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.J.; Ban, L.T.; Liu, H.F.; Hao, J.C.; Zhang, W.Y. Study on Biogas Production by Dry Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Animal Manure and Straw. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 236, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, T. Anaerobic Dry Fermentation of Dried Chicken Manure and Kitchen Waste; University of Jyväskylä: Jyväskylä, Finland, 2014; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Callaghan, F.J.; Wase, D.A.J.; Thayanithy, K.; Forster, C.F. Co-Digestion of Waste Organic Solids: Batch Studies. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 67, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapovalov, Y.B.; Zhadan, S.O. KofermentatsIya Kuryachogo PoslIdu z VIdhodami Virobnitstva BIodizelyu (Co-fermentation of chicken manure with waste from biodiesel production). In III-th Mizhnarodniy Naukovo-Praktichniy Seminar Rozvitok Bioenergetichnogo Potentsialu V Silskomu Gospodarstvi; National University of Life and Environmental Sciences of Ukraine: Kiev, Ukraine, 2018; pp. 90–93. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar]
- Foucault, L.J. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Chicken Processing Wastewater and Crude Glycerol from Biodiesel. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A & M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Patinvoh, R.J.; Kalantar Mehrjerdi, A.; Sárvári Horváth, I.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Dry Fermentation of Manure with Straw in Continuous Plug Flow Reactor: Reactor Development and Process Stability at Different Loading Rates. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noike, T.; Endo, G.; Chang, J.-E.; Yaguchi, J.-I.; Matsumoto, J.-I. Characteristics of Carbohydrate Degradation and the Rate-limiting Step in Anaerobic Digestion. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1985, 27, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, Z.; Shapovalov, Y.B.; Stabnikov, V.; Zhadan, S.O.; Salyuk, A.I.; Saleem, S.; Ivanov, V. Large-Scale Application of Iron-Containing Mineral Resources in Environmental Engineering. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Sustainable Mineral Resource Development & Utilization, Novokuznetsk, Russia, 4–7 June 2019; Mehran University of Engineering and Technology: Jamshoro, Pakistan, 2019; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Stabnikov, V.; Ivanov, V. The Effect of Various Iron Hydroxide Concentrations on the Anaerobic Fermentation of Sulfate-Containing Model Wastewater. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabnikov, V.P.; Ivanov, V.; Reshetnyak, L.R.; Toy, S.T. Influence of Iron Hydroxide on Anaerobic Treatment of Sulfate-Containing Wastewater. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2004, 26, 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, V.; Stabnikov, V.; Stabnikova, O.; Salyuk, A.; Shapovalov, E.; Ahmed, Z.; Tay, J.H. Iron-Containing Clay and Hematite Iron Ore in Slurry-Phase Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2019, 6, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of Anaerobic Digestion Process: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibulin, R.E. Issledovanie i Razrabotka Intensivnoy Biotehnologi Anaerobnoy Pererabotki Kurinogo Pometa; Avtoreferat Dissretatsii (Research and Development of Intensive Biotechnology for Anaerobic Processing of Chicken Manure); Kazanskiy Gosudarstvennyiy Tehnologicheskiy Universitet: Kazan, Russia, 1995. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Salyuk, A.I.; Zhadan, S.A.; Shapovalov, Y.B.; Tarasenko, R.A. Metanovaya Fermentatsiya Kurinogo Pometa Pri Ponizhennoy Kontsentratsii Ingibitorov (Anerobic digestion of chicken manure at low concentrations of inhibitors). Mezhdunarodnyiy Nauchnyiy Zhurnal Altern. Energ. I Ekol. 2017, 04-06, 89–98. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhadan, S.O.; Shapovalov, Y.B.; Tarasenko, R.A.; Salyuk, A.I. Metanogenez Kuryachogo PoslIdu Pri PonizhenIy KontsentratsIYi IngIbItorIv (Anerobic digestion of chicken manure at low concentrations of inhibitors). In BIologIchnI DoslIdzhennya; Individual Entrpiser «Ruta»: Zhitomir, Ukraine, 2016; pp. 48–49. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/17W9vrrxCiZ8Si8P59bTT5WM68UdDeU2Y/view?usp=sharing (accessed on 30 September 2020). (In Ukrainian)
- Zhadan, S.O.; Shapovalov, Y.B.; Salyuk, A.I.; Shapovalov, V.B. SposIb Oderzhannya Tverdogo MIneralnogo Dobriva Pri MetanovIy Fermentatsiyi (The Method of Obtaining Solid Mineral Fertilizer by Methane Fermentation). Accepted Date: 10.03.2017, Ukrpatent No. 114655. 2016. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1VDIGImJVc8t5wJpExrgaKux7jOyd0QIA/view?usp=sharing (accessed on 30 September 2020). (In Ukrainian).
- Zhadan, S.O.; Shapovalov, Y.B.; Salyuk, A.I.; Shapovalov, V.B. SposIb Otrimannya BIogazu Ta Dobriva z VIdhodIv z Visokim VmIstom Azotu (The Method of Obtaining Biogas and Fertilizers from Waste with High Nitrogen Content). Accepted date: 10.03.2016, 2016 Ukrpatent 105080. 2016. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1VDIGImJVc8t5wJpExrgaKux7jOyd0QIA/view?usp=sharing (accessed on 30 September 2020). (In Ukrainian).
- Zhadan, S.O.; Shapovalov, Y.B.; Salyuk, A.I.; Shapovalov, V.B. BIogazoviy Reaktor Dlya Pererobki VIdhodIv z Visokim VmIstom Azotu(Biogas Reactor for Processing Waste with High Nitrogen Content). Accepted Date: 25.03.2016. 2016. Ukrpatent 105418. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1XQdfYSJlO3aQf2jsuuZyqM2zgj3id-2t/view?usp=sharing (accessed on 30 September 2020). (In Ukrainian).
- Shapovalov, Y.B.; Zhadan, S.O.; Salyuk, A.I.; Shapovalov, V.B. Anaerobniy Fermenter Dlya UtilIzatsIYi NItrogevmIsnih VIdhodIv(Anaerobic Digester for Utilization of Nitrogen-Containing Waste). Accepted Date: 10.08.2018. 2018. Ukrpatent No. 127615. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/17TBqfSVPCvRbefRLogY_BB_g0j6Fn1hN/view?usp=sharing (accessed on 30 September 2020). (In Ukrainian).
- Shapovalov, Y.B.; Salyuk, A.I. The Liquid Phase Recirculation under Methanogenic Fermentation of Chicken Manure. Environ. Probl. 2018, 3, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov, Y.B.; Zhadan, S.O.; Salyuk, A.I. Regulyuvannya KontsentratsIYi AmonIynogo NItrogenu Pri MetanovIy FermentatsIYi Kuryachogo PoslIdu v Umovah RetsirkulyatsIYi RIdkoYi Fazi (Regulation of ammonium nitrogen concentration during methane fermentation of chicken manure under liquid phase recirculation conditions). In VIdnovlyuvana ta Vodneva Energetika—2018; Polytechnic University: Kiev, Ukraine, 2018; pp. 180–183. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov, Y.B.; Zhadan, S.O.; Salyuk, A.I.; Kotinskiy, A.V. Regulyuvannya KontsentratsIYi AmonIynogo Azotu Pri MetanovIy FermentatsIYi Kuryachogo PoslIdu v Umovah RetsirkulyatsIYi RIdkoYi Fazi(Regulation of ammonium nitrogen concentration during methane fermentation of chicken manure under liquid phase recirculation conditions). Naukovi Pratsi Natsionalnogo Univ. Harchovih Tehnol. 2018, 24, 65–72. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Parameters | Mean Value | A Range of Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| g/kg | TS, % | g/kg | |
| Water | 657 | – | 369–770 |
| C | 289 | 84.26 | 224–328 |
| Total N | 46 | 13.41 | 18.2–72 |
| Organic N | 38 | 11.08 | – |
| Ammonium | 14.4 | 4.20 | 0.21–29.9 |
| NO3-N | 0.4 | 0.12 | 0.03–1.5 |
| Total P | 20.7 | 6.03 | 13.5–34 |
| K | 20.9 | 6.09 | 12.5–32.5 |
| Cl | 24.5 | 7.14 | 6–60 |
| Ca | 38.9 | 11.34 | 36.2–59.6 |
| Mg | 4.7 | 1.37 | 1.8–6.6 |
| Na | 4.2 | 1.22 | 2–7.4 |
| Mn | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0.26–0.38 |
| Fe | 0.32 | 0.009 | 0.08–0.56 |
| Cu | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.04–0.07 |
| Zn | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.29–0.39 |
| As | 0.03 | 0.01 | – |
| Technology Type | Biogas Production, mL/g Wet Mass | Temperature Conditions | HRT, Days | TS Content, % | Specific Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relatively Stirred | |||||
| Dranco | 103–147 (100–200) | Thermophili, mesophilic | 15–30 | 20–50 | No very specific advantages/disadvantages |
| Kompogas | 110–130 | Thermophilic | 15–20 | 25–32 | No very specific advantages/disadvantages |
| STRABAG | Near to 103.44 | Thermophili, mesophilic | no data | 15–45 | No very specific advantages/disadvantages |
| Valorga | 80–160 | Thermophili, mesophilic | 18–25 | 25–32 | -/Clogging of injectors |
| Unstirred | |||||
| Biocel | Twice lower than continuous [86] | Mesophilic | 15–21 | 25–40 | Cheaper, simpler/occupies large areas, the problem of channel formation and clogging, the danger of explosion |
| № | TS Content, % | Temperature, °C | Methane Yield, mL/g VS | Ammonium Content, g/L | VFA Content, g/L | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Researches | ||||||
| 1 | 16–28 | 35, 50 | 2–208 | 0.14–9.3 | 0.06–12.6 | Zhadan |
| 2 | 22.5 | 37 | 5 | 7 | no data | Abouelenien |
| 3 | 20 | 35 | 140 | 10,2 | no data | Farrow |
| 4 | 20 | 35 | 217 | 3.5 | no data | Farrow |
| 5 | 20 | 35 | 136.9 | 2.1 | 6.1 | Abouelenien |
| 6 | 20 | 55 | 129 | 3.99 | 17.6 | Abouelenien |
| 7 | 25 | 35 | 8.2 | 16 | 72 ** | Abouelenien |
| 8 | 25 | 45 | 6.2 | 16 | 72 ** | Abouelenien |
| 9 | 25 | 55, 65 | 0 | 16 | 48 ** | Abouelenien |
| 10 | 15 | 35 | 117 | 8 | 6.5 | Markou |
| 11 | 20 | 35 | 51 | 10 | 16 | Markou |
| 12 | 20 | 35 | 470 * | 2.46 | no data | Farrow |
| 13 | 23 | 38 | 247 | 1.35–2 | no data | Šinkora |
| 14 | 30 | 20 | 162 | no data | no data | Rajagopal |
| Continuous Researches | ||||||
| Not found | ||||||
| № | Co-Substrate | The Ratio of Chicken Manure to the Co-Substrate | TS Content, % | Temperature, °C | Methane Yield, mL/g VS | Methane Content, % | The of Ammonium Content, g/L | The VFA Content, g/L | Intensification of Methane Yield, % | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Researches | ||||||||||
| 1 | Switchgrass | 1:2 | 16 | 55 | 2 | no data | 15 | 9.4 | no data | Ahn |
| 2 | Straw | 2.5:1 | 20 | 35 | 4.34 | no data | 0.935 | no data | no data | Shi |
| 3 | Corn | 2.5:1 | 35 | 35 | 42.95 | 59 | 20 | no data | no data | Jantrania |
| 4 | Glycerol (biodiesel) | 9:1, 8:2, 7:3 | 26, 22.18% | 35, 55 | 6.34 | 13.3 | - | no data | no data | Shapovalov |
| 5 | Agriculture wastes | 14:11 | 20 | 35 | 406 | no data | 1.39 | 0.47 | no data | Abouelenien |
| 6 | Agriculture wastes | 14:11 | 20 | 55 | 323.4 | no data | 2.28 | 0.76 | 150 | Abouelenien |
| 7 | Cattle manure | 2:7 | 15 | 35 | 70 | no data | 8.8 | no data | 195 | Callaghan |
| 8 | Maize silage | 5:1 / 6.9:1 | 20 | 35 | 246 | 52 | - | no data | no data | Farrow |
| Continuous Researches | ||||||||||
| 9 | Kitchen waste | 1:4 | 26.5 | 35 | 230 | no data | Process significantly inhibited | no data | no data | Kukkonen |
| 10 | Kitchen waste | 1:31.5 | 18.24 | 35 | 388 | no data | 1.3 | no data | no data | Kukkonen |
| 11 | Straw | no data | 22.29 | 37 | 163 | 65.1 | 2 | no data | Patinvoh | |
| Method | The Efficiency of Ammonium Removal, % | Improvement of Efficiency of Methane Yield, % | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purge by air | 62–73 | up to 124 | Markou |
| Struvite formation | 73 | 135 | Farrow |
| Stripping by nitrogen | 74.7 | no data | Abouelenien |
| Vacuuming | 80 | no data | Abouelenien |
| Recirculation of the gas phase | 55 | 40–73 | Abouelenien |
| Addition of minerals | no data | 185 | Habibulin |
| Removal from the gas phase in the reactor by the sorbent | 33 * | 5 * | Salyuk |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shapovalov, Y.; Zhadan, S.; Bochmann, G.; Salyuk, A.; Nykyforov, V. Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7825. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217825
Shapovalov Y, Zhadan S, Bochmann G, Salyuk A, Nykyforov V. Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure: A Review. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(21):7825. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217825
Chicago/Turabian StyleShapovalov, Yevhenii, Sergey Zhadan, Günther Bochmann, Anatoly Salyuk, and Volodymyr Nykyforov. 2020. "Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure: A Review" Applied Sciences 10, no. 21: 7825. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217825
APA StyleShapovalov, Y., Zhadan, S., Bochmann, G., Salyuk, A., & Nykyforov, V. (2020). Dry Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure: A Review. Applied Sciences, 10(21), 7825. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217825