Biological Effects of Paullinia cupana (Guarana) in Combination with Whole-Body Vibration Exercise in Wistar Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
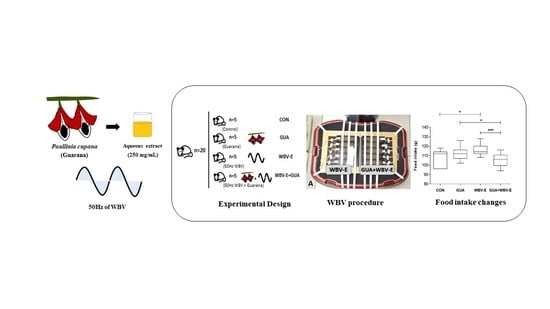
2.1. Rats Conditions and Ethical Consideration
2.2. Guarana Extract
2.3. Experimental Steps
2.4. Administration of the Radiopharmaceutical Na99mTcO4
2.5. Blood Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Body Mass Analysis
2.7. Food Intake Measurement
2.8. Stool Consistency Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alviano, D.S.; Alviano, C.S. Plant extracts: Search for new alternatives to treat microbial diseases. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 10, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, U.A.; Rahman, H.; Niaz, Z.; Qasim, M.; Khan, J.; Tayyaba Rehman, B. Antibacterial activity of some medicinal plants against selected human pathogenic bacteria. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 3, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henman, A.R. Guaraná (Paullinia cupana var. sorbilis): Ecological and social perspectives on an economic plant of the central Amazon basin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1982, 6, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimpl, F.C.; da Silva, J.F.; Gonçalves, J.F.; Mazzafera, P. Guarana: Revisiting a highly caffeinated plant from the Amazon. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, E.; Cadoná, F.C.; Machado, A.K.; Azzolin, V.; Holmrich, S.; Assmann, C.; Ledur, P.; Ribeiro, E.E.; Souza Filho, O.C.; Mânica-Cattani, M.F.; et al. Effect of Paullinia cupana on MCF-7 breast cancer cell response to chemotherapeutic drugs. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, L.V.D.N.; Cordeiro, M.F.; Sampaio, M.C.P.D.; de Mello, G.S.V.; da Costa, V.D.C.M.; Marques, L.L.M.; Klein, T.; de Mello, J.C.P.; Cavalcanti, I.M.F.; Pitta, I.R.; et al. Evaluation of antibacterial, antineoplastic, and immunomodulatory activity of Paullinia cupana seeds crude extract and ethyl-acetate fraction. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 1203274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulku, E.; Zinkovsky, D.; Patel, P.; Javia, V.; Lahoti, T.; Khodos, I.; Stohs, S.J.; Ray, S.D. A novel dietary supplement containing multiple phytochemicals and vitamins elevates hepatorenal and cardiac antioxidant enzymes in the absence of significant serum chemistry and genomic changes. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longevity 2010, 3, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krewer Cda, C.; Ribeiro, E.E.; Ribeiro, E.A.; Moresco, R.N.; da Rocha, M.I.; Montagner, G.F.; Machado, M.M.; Viegas, K.; Brito, E.; da Cruz, I.B. Habitual intake of guaraná and metabolic morbidities: An epidemiological study of an elderly Amazonian population. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.; Fogh, J. Weight loss and delayed gastric emptying following a South American herbal preparation in overweight patients. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2001, 14, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Audi, E.A.; de Mello, J.C.P. Efeito antidepressivo do extrato da droga vegetal guaraná (Paullinia cupana var. sorbilis (Martius) Ducke). Fundação Universidade Estadual de Maringá BR Patent# PI00066389 Cl. Int. A61P 2000, 25, A61K. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel, M.P.; Mello, J.C.P.; Audi, E.A. Evaluation of neurotransmitters involved in the anxiolytic and panicolytic effect of the aqueous fraction of Paullinia cupana (Guaraná) in elevated T maze. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2013, 23, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.X.; Zheng, S.; Qin, S.; Zhong, Z.M.; Wu, X.H.; Huang, Z.P.; Li, W.; Ding, R.T.; Yu, H.; Chen, J.T. Effect of low-magnitude whole-body vibration combined with alendronate in ovariectomized rats: A random controlled osteoporosis prevention study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuermer, E.K.; Komrakova, M.; Sehmisch, S.; Tezval, M.; Dullin, C.; Schaefer, N.; Hallecker, J.; Stuermer, K.M. Whole body vibration during fracture healing intensifies the effects of estradiol and raloxifene in estrogen-deficient rats. Bone 2014, 64, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghii, M.R.; Darvishi, P.; Ebrahimpour, Y.; Ghanizadeh, G.; Mofid, M.; Hedayati, M.; Asgari, A.R. Effect of combination therapy of fatty acids, calcium, vitamin D and boron with regular physical activity on cardiovascular risk factors in rat. J. Oleo Sci. 2012, 61, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frederico, E.H.F.F.; Cardoso, A.L.B.D.; Guimarães, C.A.S.; Almeida, L.P.; Neves, R.F.; Sá-Caputo, D.C.; Moreira-Marconi, E.; Dionello, C.F.; Morel, D.S.; Paineiras-Domingos, L.L.; et al. Whole body vibration exercise combined with an extract of Coriandrum sativum modify some biochemical/physiological parameters in rats. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coza, A.; Nigg, B.M.; Dunn, J.F. Effects of vibrations on gastrocnemius medialis tissue oxygenation. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, F.; Sievanen, H.; Boonen, S.; Cardinale, M.; Degens, H.; Felsenberg, D.; Roth, J.; Schoenau, E.; Verschueren, S.; Rittweger, J. Reporting whole-body vibration intervention studies: Recommendations of the International Society of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2010, 10, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Rittweger, J. Vibration as an exercise modality: How it may work, and what its potential might be. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 877–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.Y.; Mougios, V.; Skraparlis, A.; Kabasakalis, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Irisin in response to acute and chronic whole-body vibration exercise in humans. Metabolism 2014, 63, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, K.; Takamatsu, K. Hormone and lipolytic responses to whole body vibration in young men. Jpn. J. Physiol. 2005, 55, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Giminiani, R.; Fabiani, L.; Baldini, G.; Cardelli, G.; Giovannelli, A.; Tihanyi, J. Hormonal and neuromuscular responses to mechanical vibration applied to upper extremity muscles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erceg, D.N.; Anderson, L.J.; Nickles, C.M.; Lane, C.J.; Weigensberg, M.J.; Schroeder, E.T. Changes in bone biomarkers, BMC, and insulin resistance following a 10-week whole body vibration exercise program in overweight Latino boys. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verschueren, S.M.; Roelants, M.; Delecluse, C.; Swinnen, C.; Vanderschueren, D.; Boonen, S. Effect of 6-month whole body vibration training on hip density, muscle strength, and postural control in postmenopausal women: A randomized controlled pilot study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 19, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.Y.; Son, W.M.; Kwon, O.S. Effects of whole body vibration training on body composition, skeletal muscle strength, and cardiovascular health. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2015, 11, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.Y.; Hsu, P.S.; Lai, C.L.; Liao, W.C.; Lee, M.C.; Wang, C.H. Effect of two frequencies of whole-body vibration training on balance and flexibility of the elderly: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regterschot, G.R.H.; Van Heuvelen, M.J.G.; Zeinstra, E.B.; Fuermaier, A.B.M.; Tucha, L.; Koerts, J.; Tucha, O.; Van Der Zee, E.A. Whole body vibration improves cognition in healthy young adults. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hladik, W.B., III; Nigg, K.K.; Rhodes, B.A. Drug-induced changes in the biologic distribution of radiopharmaceuticals. In Seminars in Nuclear Medicine; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1982; Volume 12, pp. 184–218. [Google Scholar]
- Góes, V.C.; Neves, R.H.; Arnóbio, A.; Bernardo-Filho, M.; Machado-Silva, J.R. Streptozotocin (STZ) and schistosomiasis mansoni change the biodistribution of radiopharmaceutical sodium 99mTc-pertechnetate in mice. Nuclear Med. Biol. 2016, 43, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawi, M.H.; Omran, S.; Wageeh, S.; Isa, M.; Okasha, S.; Mohsen, N.A.; El-Karaksy, H.M. 99mTechnetium-macroaggregated albumin perfusion lung scan versus contrast enhanced echocardiography in the diagnosis of the hepatopulmonary syndrome in children with chronic liver disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 22, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selivanova, S.V.; Lavallée, É.; Senta, H.; Caouette, L.; Mcewan, A.J.; Guérin, B.; Turcotte, É. Clinical Trial with Sodium 99mTc-Pertechnetate Produced by a Medium-Energy Cyclotron: Biodistribution and Safety Assessment in Patients with Abnormal Thyroid Function. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holanda, C.M.D.C.X.; Barbosa, D.A.; Demeda, V.F.; Bandeira, F.T.M.; Medeiros, H.C.S.D.; Pereira, K.R.S.G.; Medeiros, A.C. Influence of Annona muricata (soursop) on biodistribution of radiopharmaceuticals in rats. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira 2014, 29, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederico, E.H.F.F.; Carmo, F.S.; Arnóbio, A.; Guedes, S.S.V.; Sá-Caputo, D.C.; Bernardo, L.C.; Bernardo-Filho, M. Does the whole body vibration alter the effect of a Coriandrum sativum extract on the biodistribution of the radiopharmaceutical technetium-99m sodium pertechnetate and some biomarkers in Wistar rats? Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 3529. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, A.L.B.D.; Frederico, É.H.F.F.; Guimarães, C.A.S.; Almeida, L.P.; de Figueiredo Neves, R.; de Sá-Caputo, D.; Moreira-Marconi, E.; Dionello, C.F.; Morel, D.S.; Paineiras-Domingos, L.L.; et al. Chenopodium ambrosioides associated with whole body vibration exercises alters the feed intake in Wistar rats. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20170846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lima, N.; Teixeira, L.; Gambero, A.; Ribeiro, M. Guarana (Paullinia cupana) stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis in mice fed high-fat diet. Nutrients 2018, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Celik, F.; Gocmez, C.; Bozkurt, M.; Kaplan, I.; Kamasak, K.; Akil, E.; Uzar, E. Neuroprotective effects of carvacrol and pomegranate against methotrexate-induced toxicity in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 17, 2988–2993. [Google Scholar]
- Otero-Losada, M.; González, J.; Müller, A.; Ottaviano, G.; Cao, G.; Azzato, F.; Milei, J. Exercise ameliorates endocrine pancreas damage induced by chronic cola drinking in rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, M.; Tomczak, E. The need to report effect size estimates revisited. An overview of some recommended measures of effect size. Trends Sport Sci. 2014, 21, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.O.; Pinto, N.S.; Monteiro, M.O.; Santos-Filho, S.D.; Carmo, F.S.; Diniz, C.L.; Marin, P.J.; Bernardo-Filho, M. Influence of Whole-body vibration on biodistribution of the radiopharmaceutical [99mTc] methylene diphosphonate in Wistar rats. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2013, 89, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Mau-Moeller, A.; Weippert, M.; Fuhrmann, J.; Wegner, K.; Skripitz, R.; Bruhn, S. Caffeine-induced increase in voluntary activation and strength of the quadriceps muscle during isometric, concentric and eccentric contractions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; El-Kareem, M.A.; Yahia, A.B. Influence of low grade exercise on skeletal scintigraphy using Tc-99m methylene diphosphonate. Nuclear Med. Rev. Cent. East. Eur. 2015, 18, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardinier, J.D.; Mohamed, F.; Kohn, D.H. PTH signaling during exercise contributes to bone adaptation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacheco-Costa, R.; Davis, H.M.; Atkinson, E.G.; Katchburian, E.; Plotkin, L.I.; Reginato, R.D. Osteocytic connexin 43 is not required for the increase in bone mass induced by intermittent PTH administration in male mice. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2016, 16, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.; Ward, K.; Lee, E.; Razaghi, H.; Horne, C.; Bishop, N.J. Acute bone response to whole body vibration in healthy pre-pubertal boys. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2015, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dorneles, I.M.P.; Fucks, M.B.; Fontela, P.C.; Frizzo, M.N.; Winkelmann, E.R. Guarana (Paullinia cupana) presents a safe and effective anti-fatigue profile in patients with chronic kidney disease: A randomized, double-blind, three-arm, controlled clinical trial. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 51, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Gotardo, E.; Brianti, M.; Piraee, M.; Gambero, A.; Ribeiro, M. Effects of yerba maté, a plant extract formulation (“YGD”) and resveratrol in 3T3-L1 adipogenesis. Molecules 2014, 19, 16909–16924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kerrick, W.G. The off rate of Ca(2+) from troponin C is regulated by force-generating cross bridges in skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 2409–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, E.P. Runner’s diarrhea: What is it, what causes it, and how can it be prevented? Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 33, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Song, C. Determining the posture and vibration frequency that maximize pelvic floor muscle activity during whole-body vibration. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2016, 22, 4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Boo, J.; Hendriksen, C. Reduction strategies in animal research: A review of scientific approaches at the intra-experimental, supra-experimental and extra-experimental levels. Atla-Nottingham 2005, 33, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ORGANS | CON | GUA | WBV-E | GUA+WBV-E | p | ε2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroid | 7.82 ± 2.75 | 7.76 ± 2.30 | 7.81 ± 1.25 | 7.91 ± 0.54 | 0.8142 | 0.0631 |
| Stomach | 5.16 ± 1.54 | 5.69 ± 2.05 | 5.93 ± 1.46 | 8.55 ± 1.43 | 0.1134 | 0.3727 |
| Bowel | 1.15 ± 0.28 | 1.65 ± 0.21 | 1.22 ± 0.22 | 1.39 ± 0.27 | 0.1120 | 0.4280 |
| Kidney | 1.57 ± 0.11 | 1.60 ± 0.23 | 1.66 ± 0.38 | 1.60 ± 0.14 | 0.5756 | 0.1103 |
| Liver | 1.86 ± 0.45 | 2.45 ± 0.63 | 2.33 ± 0.42 | 2.42 ± 0.43 | 0.4078 | 0.1525 |
| Pancreas | 1.30 ± 0.16 | 0.85 ± 0.34 | 1.31 ± 0.25 | 1.29 ± 0.40 | 0.2268 | 0.2554 |
| Brain | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.8185 | 0.0546 |
| Bone | 0.41 ± 0.19 | 0.69 ± 0.20 | 0.51 ± 0.10 | 0.66 ± 0.18 | 0.1718 | 0.2632 |
| Lung | 1.85 ± 0.64 | 1.95 ± 0.29 | 1.81 ± 0.53 | 2.01 ± 1.38 | 0.9529 | 0.0177 |
| Heart | 1.01 ± 0.73 | 0.92 ± 0.42 | 1.02 ± 0.18 | 1.14 ± 0.39 | 0.7160 | 0.0797 |
| Spleen | 1.00 ± 0.09 | 1.17 ± 0.18 | 1.15 ± 0.26 | 1.06 ± 0.10 | 0.5052 | 0.1299 |
| Muscle | 0.27 ± 0.11 | 0.43 ± 0.07 * | 0.28 ± 0.06 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.0298 | 0.4979 |
| Penis | 1.63 ± 0.26 | 1.79 ± 0.36 | 1.69 ± 0.21 | 1.73 ± 0.39 | 0.7487 | 0.0641 |
| Prostate | 0.53 ± 0.14 | 0.90 ± 0.23 | 0.77 ± 0.29 | 0.93 ± 0.21 | 0.0983 | 0.3311 |
| Seminal vesicle | 0.54 ± 0.21 | 0.54 ± 0.16 | 0.44 ± 0.14 | 0.54 ± 0.19 | 0.7489 | 0.0641 |
| Bladder | 1.28 ± 0.15 | 1.68 ± 0.46 | 1.32 ± 0.34 | 1.30 ± 0.55 | 0.4659 | 0.1963 |
| Testis | 0.55 ± 0.17 | 0.51 ± 0.19 | 0.48 ± 0.04 | 0.56 ± 0.16 | 0.6125 | 0.0953 |
| Blood | 2.58 ± 0.61 | 2.52 ± 0.35 | 2.79 ± 1.66 | 2.95 ± 0.88 | 0.7817 | 0.0721 |
| Biomarkers | CON | GUA | WBV-E | GUA+WBV-E | p | ε2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin (g/L) | 34.7 ± 1.0 | 34.2 ± 1.3 | 36.2 ± 2.5 | 37.4 ± 2.3 | 0.1138 | 0.3308 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 2.38 ± 0.07 | 2.36 ± 0.02 | 2.52 ± 0.20 * | 2.48 ± 0.08 * | 0.0449 | 0.4475 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 39.78 ± 8.84 | 37.13 ± 3.54 | 40.66 ± 7.96 | 37.13 ± 3.54 | 0.83241 | 0.0484 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.07 ± 0.15 | 1.21 ± 0.21 | 1.07 ± 0.23 | 1.16 ± 0.13 | 0.5365 | 0.1209 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 6.22 ± 0.45 | 5.69 ± 0.44 | 5.76 ± 0.18 | 5.85 ± 0.94 | 0.4270 | 0.1853 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.09 ± 0.07 | 1.16 ± 0.15 | 1.07 ± 0.17 | 1.13 ± 0.11 | 0.7040 | 0.0781 |
| Magnesium (mmol/L) | 1.10 ± 0.14 | 1.00 ± 0.06 | 1.27 ± 0.36 | 1.17 ± 0.11 | 0.0661 | 0.3995 |
| Direct Bilirubin (µmol/L) | 0.34 ± 0.17 | 0.51 ± 0.17 | 0.34 ± 0.17 | 0.34 ± 0.17 | 0.2657 | 0.2330 |
| Total Bilirubin (µmol/L) | 0.86 ± 0.51 | 0.68 ± 0.51 | 0.51 ± 0.17 | 0.68 ± 0.34 | 0.9386 | 0.0291 |
| Total Protein (g/L) | 57.7 ± 2.5 | 59.0 ± 1.9 | 62.2 ± 4.0 | 61.8 ± 3.8 | 0.1185 | 0.3257 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 0.47 ± 0.26 | 0.52 ± 0.16 | 0.42 ± 0.14 | 0.38 ± 0.11 | 0.6177 | 0.0993 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 7.84 ± 1.01 | 7.07 ± 0.32 | 7.47 ± 0.42 | 7.57 ± 0.53 | 0.3153 | 0.1968 |
| Enzymes | CON | GUA | WBV-E | GUA+WBV-E | p | ε2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amylase (µKat/L) | 0.79 ± 0.08 | 0.77 ± 0.14 | 00.75 ± 0.10 | 0.80 ± 0.06 | 0.8384 | 0.0470 |
| AST (µKat/L) | 2.20 ± 0.25 | 2.45 ± 0.21 | 2.30 ± 0.49 | 2.38 ± 0.30 | 0.5325 | 0.1465 |
| ALT (µKat/L) | 1.02 ± 0.12 | 1.13 ± 0.21 | 1.12 ± 0.10 | 1.21 ± 0.10 | 0.3990 | 0.1640 |
| ALP (µKat/L) | 2.20 ± 0.30 | 1.92 ± 0.29 | 2.16 ± 0.27 | 2.30 ± 0.21 | 0.3064 | 0.2007 |
| Lipase (µKat/L) | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.6838 | 0.0830 |
| CK (µKat/L) | 31.97 ± 1.03 | 31.56 ± 6.74 | 26.73 ± 4.74 | 28.58 ± 7.41 | 0.6170 | 0.0411 |
| WEEK | CON | GUA | WBV-E | GUA+WBV-E | p | ε2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100.00 ± 8.89 | 100.00 ± 8.21 | 100.00 ± 11.7 | 100.00 ± 2.10 | 0.4828 | 0.1294 |
| 1 | 103.90 ± 7.20 | 103.27 ± 7.67 | 105.29 ± 9.54 | 105.12 ± 3.80 | 0.3452 | 0.1746 |
| 2 | 109.00 ± 5.29 | 107.00 ± 7.24 | 113.40 ± 6.38 | 108.92 ± 3.42 | 0.0839 | 0.3501 |
| 3 | 112.31 ± 5.78 | 111.99 ± 7.04 | 116.77 ± 5.33 | 113.55 ± 3.63 | 0.1014 | 0.3273 |
| 4 | 115.31 ± 6.34 | 115.42 ± 7.82 | 120.38 ± 4.41 | 116.94 ± 4.29 | 0.1101 | 0.3174 |
| 5 | 118.61 ± 6.04 | 119.15 ± 4.94 | 123.27 ± 4.45 | 121.57 ± 3.88 | 0.0736 | 0.3657 |
| Day | CON | GUA | WBV-E | GUA+WBV-E | p | ε2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–10 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 4.00 ± 0.00 *** | 3.00 ± 1.00 # | 4.00 ± 0.75 ** | 0.0005 | 0.4566 |
| 11–20 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 4.00 ± 0.00 *** | 2.00 ± 0.00 ## | 4.00 ± 0.00 **+ | <0.0001 | 0.6272 |
| 21–30 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 4.00 ± 0.00 *** | 2.00 ± 0.00 ## | 4.00 ± 1.00 **+ | <0.0001 | 0.6527 |
| 31–40 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 4.00 ± 0.75 *** | 2.00 ± 0.00 ### | 3.00 ± 1.00 ***++ | <0.0001 | 0.7726 |
| Total (1–40) | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 4.00 ± 0.25 *** | 2.00 ± 0.00 ### | 4.00 ± 1.00 ***+++ | <0.0001 | 0.6016 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardoso, A.L.B.D.; Frederico, É.H.F.F.; Guimarães, C.A.S.; Reis-Silva, A.; de Oliveira Guedes-Aguiar, E.; Francisca Santos, A.; Cristina Moura-Fernandes, M.; Felipe Ferreira-Souza, L.; Eduardo-Santos, T.; Eduardo-Santos, D.; et al. Biological Effects of Paullinia cupana (Guarana) in Combination with Whole-Body Vibration Exercise in Wistar Rats. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031104
Cardoso ALBD, Frederico ÉHFF, Guimarães CAS, Reis-Silva A, de Oliveira Guedes-Aguiar E, Francisca Santos A, Cristina Moura-Fernandes M, Felipe Ferreira-Souza L, Eduardo-Santos T, Eduardo-Santos D, et al. Biological Effects of Paullinia cupana (Guarana) in Combination with Whole-Body Vibration Exercise in Wistar Rats. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(3):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031104
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardoso, André L.B.D., Éric H.F.F. Frederico, Carlos A.S. Guimarães, Aline Reis-Silva, Eliane de Oliveira Guedes-Aguiar, Arlete Francisca Santos, Márcia Cristina Moura-Fernandes, Luiz Felipe Ferreira-Souza, Tiago Eduardo-Santos, Diego Eduardo-Santos, and et al. 2020. "Biological Effects of Paullinia cupana (Guarana) in Combination with Whole-Body Vibration Exercise in Wistar Rats" Applied Sciences 10, no. 3: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031104
APA StyleCardoso, A. L. B. D., Frederico, É. H. F. F., Guimarães, C. A. S., Reis-Silva, A., de Oliveira Guedes-Aguiar, E., Francisca Santos, A., Cristina Moura-Fernandes, M., Felipe Ferreira-Souza, L., Eduardo-Santos, T., Eduardo-Santos, D., Guimarães Mendonça, R., da Cunha de Sá-Caputo, D., Liane Paineiras-Domingos, L., Taiar, R., Asad, N. R., & Bernardo-Filho, M. (2020). Biological Effects of Paullinia cupana (Guarana) in Combination with Whole-Body Vibration Exercise in Wistar Rats. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10031104