Fabrication of a Simultaneous Highly Transparent and Highly Hydrophobic Fibrous Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
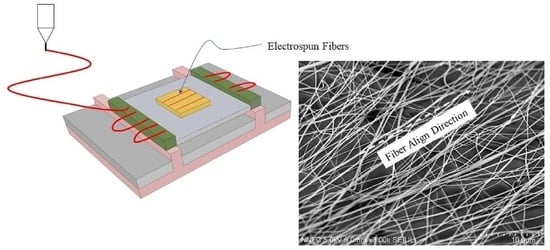
2.1. Production of Randomly Distributed Fibers
2.2. Fabrication of the Aligned Fibers
2.3. Measurements and Characteristics
2.3.1. Materials and Solution Synthesis
2.3.2. Contact-Angle Measurements
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.4. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.3.5. Optical Transmittance Measurement
3. Results
3.1. Transmission Characteristics of Randomly Distributed Fibers
3.2. Transmission Characteristics of Aligned Fiber
3.3. Hydrophobicity of the Randomly Distributed Fibers
3.4. Hydrophobic Characteristics of Aligned Fibers
4. Discussion
4.1. High Transparency of the Aligned Fiber
4.2. High Hydrophobicity of the Aligned Fibers
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, R.; Chao, G.; Jiang, H.; Hu, Y.; Pan, A. The superhydrophobic aluminum surface prepared by diferent methods. Mater. Lett. 2015, 142, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, S.J.; Muhamad-Sarih, N.; Riggs, H.J.; Thompson, R.L.; Rigby, J.; Bergius, W.N.A.; Hutchings, L.R. Electrospinning superhydrophobic fibers using surface segregating end functionalized polymer additives. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6461–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meikandan, M.; Malarmohan, K.; Velraj, R. Development of superhydrophobic surface through facile dip coating method. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2016, 11, 945–951. [Google Scholar]
- Diaa, B.M.; Jaafar, H.T. Superhydrophobic nanocomposites coating using electrospinning technique on different materials. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2017, 12, 16032–16038. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Fong, H. Electrospun polyimide nanofibers and their applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 61, 67–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Li, C.; Hota, Y.; Kim, J.; Kuwaki, O.; Shiratori, S. Conversion of an electrospun nanoibrous cellulose acetate mat from a super-hydrophilic to super-hydrophobic surface. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4332–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Ding, B.; Sone, Y.; Shiratori, S. Super-hydrophobic surfaces of layer-by-layer structured film-coated electrospun nanoibrous membranes. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 165607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, F. Surfaces and Interfaces of Biomimetic Superhydrophobic Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, B.; Mohamed, A.M.A.; Aboubakr, A.; Mariam, A.A.-M. Corrosion protection of electrospun PVDF-ZnO superhydrophobic coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 285, 946–957. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzenis, Y. Material science: Spinning continuous fibers for nanotechnology. Science 2004, 304, 1917–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Park, Y.; Park, C.H. Preparation of breathable and superhydrophobic polyurethaneelectrospun webs with silica nanoparticles. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurxat, N.; Waseem, S.K.; Yu, L.; Muhammet, C.; Ramazan, A. Hydrophobic electrospun nanofibers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1929–1946. [Google Scholar]
- Iurii, S.; Russell, E.G.; Jeff, A.J.; Kristin, A.T. Literature Review on Superhydrophobic Self-Cleaning Surfaces Produced by Electrospinning. J. Poly. Sci. 2012, 50, 824–845. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.H.; Jia, S.T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.Z. Large-area fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces for practical applications: An overview. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2010, 11, 033002–033017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Hill, R.M.; Rutledge, G.C. A review of recent results on superhydrophobic materials based on micro-and nanofibers. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2008, 22, 1799–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.J.; Jiang, L. Design and creation of superwetting/Antiwetting surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3063–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Hill, R.M.; Lowery, J.L.; Fridrikh, S.V.; Rutledge, G.C. Electrospun Poly(Styrene-block-dimethylsiloxane) Block Copolymer Fibers Exhibiting Superhydrophobicity. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5549–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmatulu, R.; Ceylan, M.; Nuraje, N. Study of Superhydrophobic Electrospun Nanocomposite Fibers for Energy Systems. Langmuir 2010, 27, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, D.-H.; Yu, Y.J.; Choi, J.S.; Park, N.M.; Yun, S.J.; Lee, I.; Kim, G.H. Transparent conducting films of silver hybrid films formed by near-field electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2016, 185, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, D.-H.; Yeon, C.; Choi, J.S.; Park, N.M.; Lee, I.; Kim, G.H.; Yun, S.J. Arbitrary alignment-angle control method of the electrospun fibers: Potential for a stretchable electrode material. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 44945–44953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youn, D.-H.; Kim, B.-J.; Yun, S.J. Synthesis and gas sensing properties of WS2 nanocrystallites assembled hierarchical WS2 fibers by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 105602–105614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotr, K.S.; Daniel, P.U.; Sara, M.; Joanna, K.-K.; Marcin, G.; Mateusz, M.M.; Andrzej, B.; Urszula, S. Roughness and Fiber Fraction Dominated Wetting of Electrospun Fiber-Based Porous Meshes. Polymers 2019, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bagrov, D.; Perunova, S.; Pavlova, E.; Klinov, D. Wetting of electrospun nylon-11 fibers and mats. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 11373–11379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, P.U.; Joanna, E.K.; Piotr, K.S.; Sara, M.; Mateusz, K.; Urszula, S. Cell Integration with Electrospun PMMA Nanofibers, Microfibers, Ribbons, and Films: A Microscopy Study. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Koysuren, O.; Koysuren, H.N. Characterization of poly(methyl methacrylate) nanofiber scaffolds by electrospinning process. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 53, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konosu, Y.; Scaffoldsumoto, H.; Tsuboi, K.; Minagawa, M.; Tanioka, A. Enhancing the Effect of the Nanofiber Network Structure on Thermoresponsive Wettability Switching. Langmuir 2011, 27, 14716–14720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busolo, T.; Ura, D.P.; Kim, S.K.; Marzec, M.M.; Bernasik, A.; Stachewicz, U.; Kar-Narayan, S. Surface potential tailoring of PMMA fibers by electrospinning for enhanced triboelectric performance. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Ura, D.P.; Metwally, S.; Gruszczyński, A.; Stachewicz, U. Biomimicking wetting properties of spider web from Linothele megatheloides with electrospun fibers. Mater. Lett. 2018, 233, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachewicz, U.; Bailey, R.J.; Zhang, H.; Stone, C.A.; Willis, C.R.; Barber, A.H. Wetting Hierarchy in Oleophobic 3D Electrospun Nanofiber Networks: ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16645–16652. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, M.; Thomas, H.; Heike, H.; Viola, V.; Daniel, E. Influence of the fiber diameter and surface roughness of electrospun vascular grafts on blood activation. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 4349–4356. [Google Scholar]
- Rasoul, M.; Javad, K.; Mojtaba, S.N.; Mohammad, A.K. Preparation and Characterization of Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Graphene hydrophobic Fibrous Films. Polymers 2015, 7, 1444–1463. [Google Scholar]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youn, D.-H.; Lee, K.-S.; Jung, S.-K.; Kang, M. Fabrication of a Simultaneous Highly Transparent and Highly Hydrophobic Fibrous Films. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5565. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125565
Youn D-H, Lee K-S, Jung S-K, Kang M. Fabrication of a Simultaneous Highly Transparent and Highly Hydrophobic Fibrous Films. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(12):5565. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125565
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoun, Doo-Hyeb, Kyu-Sung Lee, Sun-Kyu Jung, and Mangu Kang. 2021. "Fabrication of a Simultaneous Highly Transparent and Highly Hydrophobic Fibrous Films" Applied Sciences 11, no. 12: 5565. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125565
APA StyleYoun, D. -H., Lee, K. -S., Jung, S. -K., & Kang, M. (2021). Fabrication of a Simultaneous Highly Transparent and Highly Hydrophobic Fibrous Films. Applied Sciences, 11(12), 5565. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125565