Glycyrol Alone or in Combination with Gefitinib Is Effective against Gefitinib-Resistant HCC827GR Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.3. Crystal Violet Staining
2.4. Apoptosis Evaluation
2.5. Calculation of Combination Index
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Animals and Treatments
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Exposure to Glycyrol Leads to Reduced Viability of HCC827 GR Cells In Vitro
3.2. Glycyrol Inhibits Tumor Growth in HCC827GR Xenograft Model
3.3. Glycyrol Sensitizes HCC827GR Cells to Gefitinib
3.4. Both the Benzofuranyl Group at c-3/4 and the Isopentenyl Group at c-6 Are Indispensable for Glycyrol to Exert the Sensitization Effect
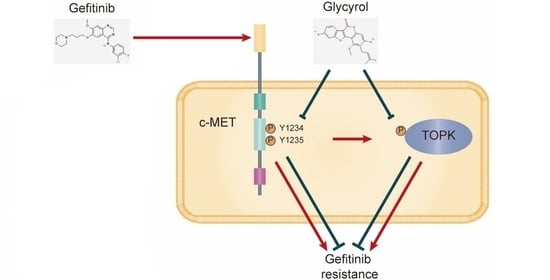
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schram, A.M.; Chang, M.T.; Jonsson, P.; Drilon, A. Fusions in solid tumours: Diagnostic strategies, targeted therapy, and acquired resistance. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.R.; Jänne, P.A. The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.G.; Shih, J.Y. Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asl, M.N.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Review of pharmacological effects of Glycyrrhiza sp. and its bioactive compounds. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; Liu, C.F.; Ji, S.; Lin, X.H.; Guo, D.A.; Ye, M. Simultaneous determination of five minor coumarins and flavonoids in Glycyrrhiza uralensis by solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Ji, S.; Song, W.; Kuang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Tang, S.; Cui, Z.; Qiao, X.; Yu, S.; Ye, M. Glycybridins A–K, Bioactive Phenolic Compounds from Glycyrrhiza glabra. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Ye, L.; Yin, S.; Zhao, C.; Yan, M.; Liu, X.; Cui, J.; Hu, H. Glycyrol exerts potent therapeutic effect on lung cancer via directly inactivating T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 147, 104366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, F.; Lu, H.; Xu, S.; Zou, L.; Tian, Q.; Fu, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, L.; Yuan, P.; et al. Targeting the COX2/MET/TOPK signaling axis induces apoptosis in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Oh, Y.T.; Zhang, G.; Yao, W.; Yue, P.; Li, Y.; Kanteti, R.; Riehm, J.; Salgia, R.; Owonikoko, T.K.; et al. Met gene amplification and protein hyperactivation is a mechanism of resistance to both first and third generation EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 2016, 380, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, J.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Choi, E.K.; Yoon, S.J.; Park, B.M.; Park, E.; Bae, J.H.; Choi, C.M.; et al. MET and AXL inhibitor NPS-1034 exerts efficacy against lung cancer cells resistant to EGFR kinase inhibitors because of MET or AXL activation. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Yuan, Q. Current mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and updated therapy strategies in human nonsmall cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res Ther. 2016, 12, C131–C137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westover, D.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Cho, B.C.; Lovly, C.M.; Paz-Ares, L. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first- and second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 1), i10–i19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ohba, M.; Ohmori, T. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase-Targeted Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagano, T.; Tachihara, M.; Nishimura, Y. Mechanism of Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and a Potential Treatment Strategy. Cells 2018, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Lu, S.; Fan, L.; Hu, H. Glycyrol Alone or in Combination with Gefitinib Is Effective against Gefitinib-Resistant HCC827GR Lung Cancer Cells. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10526. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210526
Zhao S, Lu S, Fan L, Hu H. Glycyrol Alone or in Combination with Gefitinib Is Effective against Gefitinib-Resistant HCC827GR Lung Cancer Cells. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(22):10526. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210526
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Shuang, Shangyun Lu, Lihong Fan, and Hongbo Hu. 2021. "Glycyrol Alone or in Combination with Gefitinib Is Effective against Gefitinib-Resistant HCC827GR Lung Cancer Cells" Applied Sciences 11, no. 22: 10526. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210526
APA StyleZhao, S., Lu, S., Fan, L., & Hu, H. (2021). Glycyrol Alone or in Combination with Gefitinib Is Effective against Gefitinib-Resistant HCC827GR Lung Cancer Cells. Applied Sciences, 11(22), 10526. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210526