Spatial Connections between Microplastics and Heavy Metal Pollution within Floodplain Soils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Geospatial Sampling
2.2. Laboratory Analysis
2.2.1. Metal Analysis
2.2.2. Microplastic Analysis
2.3. Statsitics and Data Evaluation
2.4. Limitations
3. Results
3.1. Floodplain Soil Properties
3.2. Spatial Relationships between Plastic and Metal Concentrations
3.2.1. Total Plastic Concentration
3.2.2. Heavy Metal Concentrations
3.2.3. Correlations between Plastics and Heavy Metals
3.3. Heavy Metals in Macroplastics and Coarse Microplastics
4. Discussion
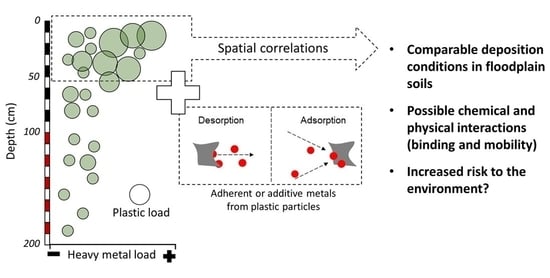
4.1. Spatial Correlations
4.2. Pollution Sources and Interactions
4.3. Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
- Quantitative spatial assessment of plastic and heavy metal contaminations in different floodplains and river systems.
- Consideration of heavy metals in different chemical bonds and analysis of adsorbed and additive metals in order to draw conclusions about the sources and interactions.
- Examination of contaminants in both soil water (pore water) and groundwater in order to better understand their mobility and possible associated risks.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Sampling Site | Soil Profile | Ptot (p kg–1) a | Heavy Metal Concentrations (mg kg–1) | Pollution Indices | ||||||||||||
| V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | Ef b | PLI c | CSI d | RI e | ||||
| ELM | ELM-1 | 4.00 | 18.40 | 38.01 | 14.40 | 49.41 | 33.23 | 105.25 | 7.93 | 0.51 | 44.63 | 2.72 | 1.74 | 1.18 | 325.5 | |
| ELM-2 | 1.31 | 23.12 | 37.36 | 14.74 | 41.81 | 21.71 | 61.66 | 9.74 | 0.23 | 21.72 | 1.81 | 1.32 | 0.95 | 187.4 | ||
| ROT | ROT-1 | 1.49 | 10.43 | 19.27 | 6.97 | 20.49 | 13.50 | 50.24 | 4.81 | 0.25 | 20.05 | 3.45 | 0.95 | 0.67 | 262.5 | |
| ROT-2 | 0.54 | 11.60 | 20.12 | 7.69 | 19.87 | 8.88 | 29.73 | 4.48 | 0.12 | 12.64 | 1.86 | 0.68 | 0.59 | 92.6 | ||
| STD | STD-1 | 2.04 | 16.70 | 29.75 | 11.15 | 29.40 | 14.72 | 44.32 | 6.01 | 0.20 | 15.74 | 1.80 | 0.90 | 0.74 | 134.0 | |
| STD-2 | 0.51 | 14.94 | 26.42 | 9.27 | 27.94 | 14.05 | 43.53 | 6.18 | 0.16 | 16.40 | 1.70 | 0.89 | 0.71 | 129.6 | ||
| STD-3 | 1.83 | 18.05 | 33.26 | 10.65 | 31.44 | 17.66 | 58.37 | 7.20 | 0.35 | 25.44 | 2.28 | 1.17 | 0.81 | 216.7 | ||
| STD-4 | 0.96 | 16.83 | 31.65 | 9.70 | 29.42 | 14.71 | 44.92 | 6.70 | 0.17 | 20.79 | 1.74 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 127.3 | ||
| LIM | LIM-1 | 5.26 | 14.15 | 28.73 | 13.43 | 35.10 | 17.71 | 72.81 | 6.36 | 0.48 | 31.89 | 3.18 | 1.39 | 0.93 | 325.0 | |
| LIM-2 | 0.91 | 14.49 | 26.67 | 10.35 | 27.68 | 13.90 | 51.09 | 5.66 | 0.30 | 25.37 | 2.32 | 1.05 | 0.18 | 186.7 | ||
| LIM-3 | 0.64 | 15.55 | 27.82 | 9.39 | 25.44 | 13.73 | 40.72 | 6.15 | 0.18 | 22.07 | 1.79 | 0.91 | 0.17 | 124.1 | ||
| LIM-4 | 0.81 | 11.48 | 19.26 | 5.92 | 15.77 | 6.80 | 24.92 | 4.21 | 0.10 | 13.46 | 1.77 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 64.1 | ||
| SHW f | - | 60.0 | - | 29.0 | 38.9 | - | 0.7 | 0.4 | 27.0 | Specific limit values g | >5.0 | >1.0 | 1.0–2.0 | 180–360 | ||
| GBH h | 38.3 | 25.0 | 8.8 | 24.0 | 13.3 | 58.5 | 8.0 | 0.1 | 27.0 | Interpre-tation of limit value | moderate enrich-ment | deteriorate-ion of soil quality | low to moderate severity | Strong ecological risk | ||
| LPL i | - | 60.0 | - | 50.0 | 40.0 | 150.0 | - | 1.0 | 70.0 | |||||||
| Samples (n) exceed LPL or limit values (total n = 118) | 2 | 9 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 45 | 1 | 40 | ||||||
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Healthy Soils are the Basis for Healthy Food Production. Fact Sheet; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Blume, H.-P.; Brümmer, G.W.; Fleige, H.; Horn, R.; Kandeler, E.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Kretzschmar, R.; Stahr, K.; Wilke, B.-M. Scheffer/Schachtschabel Soil Science, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783642309410. [Google Scholar]
- Willgoose, G. Principles of Soilscape and Landscape Evolution; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dudka, S.; Adriano, D.C. Environmental impacts of metal ore mining and processing: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 1997, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.M.; Zalasiewicz, J. Assessing the Anthropocene with geochemical methods. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2014, 395, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. The plastic in microplastics: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karbalaei, S.; Hanachi, P.; Walker, T.R.; Cole, M. Occurence, sources, human health impacts and mitigation of microplastic pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36046–36063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Machado, A.A.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C.; Hempel, S.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics as an emerging threat to terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braun, M.; Mail, M.; Heyse, R.; Amelung, W. Plastic in compost: Prevalence and potential input into agricultural and horticultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta Lwanga, E.; Mendoza Vega, J.; Ku Quej, V.; Chi, J.d.L.A.; Sanchez Del Cid, L.; Chi, C.; Escalona Segura, G.; Gertsen, H.; Salánki, T.; van der Ploeg, M.; et al. Field evidence for transfer of plastic debris along a terrestrial food chain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, F.; Bartholomeus, H.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Gertsen, H.; Geissen, V. Predicting soil microplastic concentration using vis-NIR spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lu, S.; Song, Y.; Lei, L.; Hu, J.; Lv, W.; Zhou, W.; Cao, C.; Shi, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Microplastic and mesoplastic pollution in farmland soils in suburbs of Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.S.; Liu, Y.F. The distribution of microplastics in soil aggregate fractions in southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.S.; Zhang, F.X.; Li, X.T. Effects of polyester microfibers on soil physical properties: Perception from a field and a pot experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piehl, S.; Leibner, A.; Löder, M.G.J.; Dris, R.; Bogner, C.; Laforsch, C. Identification and quantification of macro- and microplastics on an agricultural farmland. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheurer, M.; Bigalke, M. Microplastics in Swiss Floodplain Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3591–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechthaler, S.; Esser, V.; Schüttrumpf, H.; Stauch, G. Why analysing microplastics in floodplains matters: Application in a sedimentary context. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2021, 71, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.J.; Opp, C. Spatial patterns of mesoplastics and coarse microplastics in floodplain soils as resulting from land use and fluvial processes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüffer, T.; Metzelder, F.; Sigmund, G.; Slawek, S.; Schmidt, T.C.; Hofmann, T. Polyethylene microplastics influence the transport of organic contaminants in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Ziersch, L.; Hempel, S. Microplastic transport in soil by earthworms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; van der Ploeg, M.; Lwanga, E.H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Leaching of microplastics by preferential flow in earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) burrows. Environ. Chem. 2019, 16, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Ingraffia, R.; Souza Machado, A.A.de. Microplastic Incorporation into Soil in Agroecosystems. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rillig, M.C.; Lehmann, A.; Souza Machado, A.A.de.; Yang, G. Microplastic effects on plants. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Liu, F.; Cryder, Z.; Huang, D.; Lu, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z.; Brookes, P.C.; Tang, C.; et al. Microplastics in the soil environment: Occurrence, risks, interactions and fate—A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 26, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Lei, L. Microplastics in soils: Analytical methods, pollution characteristics and ecological risks. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.R.; Nizzetto, L. Fate and occurrence of micro(nano)plastics in soils: Knowledge gaps and possible risks. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.A.; Turner, A.; Thompson, R.C. Adsorption of trace metals to plastic resin pellets in the marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 160, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, B.; Bendell, L.I. Macro and micro plastics sorb and desorb metals and act as a point source of trace metals to coastal ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennecke, D.; Duarte, B.; Paiva, F.; Cacador, I.; Canning-Clode, J. Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 178, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Tan, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, Q.; Cai, L. Microplastics in the surface sediments from the Beijiang River littoral zone: Composition, abundance, surface textures and interaction with heavy metals. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, H.K.; Laforsch, C.; Wiesheu, A.C.; Schmid, J.; Anger, P.M.; Niessner, R.; Ivleva, N.P. Pigments and plastic in limnetic ecosystems: A qualitative and quantitative study on microparticles of different size classes. Water Res. 2016, 98, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Velis, C.A.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verla, A.W.; Enyoh, C.E.; Verla, E.N.; Nwarnorh, K.O. Microplastic–toxic chemical interaction: A review study on quantified levels, mechanism and implication. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cizdziel, J.V. Effect of prothioconazole on the degradation of microplastics derived from mulching plastic film: Apparent change and interaction with heavy metals in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, P.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Metal type and aggregate microenvironment govern the response sequence of speciation transformation of different heavy metals to microplastics in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Hou, J.; Dang, Q.; Cui, D.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Decrease in bioavailability of soil heavy metals caused by the presence of microplastics varies across aggregate levels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blettler, M.C.M.; Ulla, M.A.; Rabuffetti, A.P.; Garello, N. Plastic pollution in freshwater ecosystems: Macro-, meso-, and microplastic debris in a floodplain lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, J.S. Rivers and Floodplains: Forms, Processes, and Sedimentary Record, 1st ed.; Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Siegfried, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Kroeze, C. Export of microplastics from land to sea. A modelling approach. Water Res. 2017, 127, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechthaler, S.; Waldschläger, K.; Stauch, G.; Schüttrumpf, H. The Way of Macroplastic through the Environment. Environments 2020, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Yu, M. Wetland-a hub for microplastic transmission in the global ecosystem. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 142, 153–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Wu, C.; Elser, J.J.; Mei, Z.; Hao, Y. Occurrence and fate of microplastic debris in middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River—From inland to the sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 659, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.J.; Opp, C.; Prume, J.A.; Koch, M.; Andersen, T.J.; Chifflard, P. Deposition and in-situ translocation of microplastics in floodplain soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 152039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.J.; Weihrauch, C.; Opp, C.; Chifflard, P. Investigating microplastic dynamics in soils: Orientation for sampling strategies and sample pre-procession. Land Degrad. Devel. 2020, 32, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regional Council Giessen. Hochwasserrisikomanagementplan für das Hessische Einzugsgebiet der Lahn (Flood Risk Management Plan); Regional Council Giessen: Giessen, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.W. Trace metal concentrations along tributary streams of historically mined areas, Lower Lahn and Dill River basins, central Germany. Catena 2019, 174, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.W. Recent changes in heavy metal contamination at near-channel positions of the Lahn River, central Germany. Geomorphology 2012, 139–140, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.W. Trace metal storage in recent floodplain sediments along the Dill River, central Germany. Geomorphology 2015, 235, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ad-hoc AG Boden. Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung, 5th ed.; Schweizerbart: Stuttgart, Germany, 2005; ISBN 3510959205. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Guidelines for Soil Description, 4th ed.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group. World reference base for soil resources 2014, update 2015. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. In World Soil Resources Reports; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Durner, W.; Iden, S.C.; von Unold, G. The integral suspension pressure method (ISP) for precise particle-size analysis by gravitational sedimentation. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voica, C.; Dehelean, A.; Iordache, A.; Geana, I. Method validation for determination of metals in soils by ICP-MS. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2012, 64, 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R. A Beginner’s Guide to ICP-MS. Spectroscopy 2001, 16–17, 22–36. [Google Scholar]
- Catrouillet, C.; Davranche, M.; Khatib, I.; Fauny, C.; Wahl, A.; Gigault, J. Metals in microplastics: Determining which are additive, adsorbed, and bioavailable. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2021, 23, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konde, S.; Ornik, J.; Prume, J.A.; Taiber, J.; Koch, M. Exploring the potential of photoluminescence spectroscopy in combination with Nile Red staining for microplastic detection. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 159, 111475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, T.; Jessop, R.; Wellner, N.; Haupt, K.; Mayes, A.G. A rapid-screening approach to detect and quantify microplastics based in fluorescent tagging with Nile Red. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep44501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination—A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedrich, K.; Lügger, K. Hintergrundwerte von Spurenstoffen in Hessischen Böden; Hessian Agency of Nature Conservation, Environment and Geology (HLNUG): Wiesbaden, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pejman, A.; Nabi Bidhendi, G.; Ardestani, M.; Saeedi, M.; Baghvand, A. A new index for assessing heavy metals contamination in sediments: A case study. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; Macdonald, D.D.; Smith, S.L.; Calder, F.D. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bund-/Länderarbeitsgemeinschaft Bodenschutz. Hintergrundwerte Für Anorganische und Organische Stoffe in Böden, 3rd ed.; Bund-/Länderarbeitsgemeinschaft Bodenschutz: Magdeburg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bundes-Bodenschutz- und Altlastenverordnung: BbodSchV; Bundesgesetzblatt: Bonn, Germany, 1999; pp. 1554–1582, Teil I (36).
- Rittweger, H. The ‘‘Black Floodplain Soil’’ in the Amöneburger Becken, Germany: A lower Holocene marker horizon and indicator of an upper Atlantic to Subboreal dry period in Central Europe? Catena 2000, 41, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, F.; Meza, P.; Eguiluz, R.; Casado, F.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Geissen, V. Evidence of microplastic accumulation in agricultural soils from sewage sludge disposal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryirs, K.A.; Brierley, G.J. Geomorphic Analysis of River Systems: An Approach to Reading the Landscape; Wiley: Chichester, UK; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781420093681. [Google Scholar]
- Manta, D.S.; Angelone, M.; Bellanca, A.; Neri, R.; Sprovieri, M. Heavy metals in urban soils: A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 300, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, J.; Zils, V.; Berresheim, L. Joint recording of contamination status, multi-element dynamics, and source identification on a sub-catchment scale: The example Lahn River (Germany). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, J.; Opp, C.; Zitzer, N.; Laufenberg, G. Impacts of river impoundment on dissolved heavy metals in floodplain soils of the Lahn River (Germany). Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschede, M.; Warr, L.N. The Geology of Germany: A Process-Oriented Approach; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 9783319761039. [Google Scholar]
- Zalasiewicz, J.; Waters, C.N.; Ivar do Sul, J.A.; Corcoran, P.L.; Barnosky, A.D.; Cearreta, A.; Edgeworth, M.; Gałuszka, A.; Jeandel, C.; Leinfelder, R.; et al. The geological cycle of plastics and their use as a stratigraphic indicator of the Anthropocene. Anthropocene 2016, 13, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plastics Europe. Plastics-the facts 2018: An analysis of European plastic production, demand and waste data. Plast. Eur. 2018, 52, 9874–9888. [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts, J.; Krause, S.; Lynch, I.; Sambrook Smith, G. Abundance, Distribution, and Drivers of Microplastic Contamination in Urban River Environments. Water 2018, 10, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Happ, M.; Duffy, J.; Wilson, G.J.; Pask, S.D.; Buding, H.; Ostrowicki, A. Rubber, 8. Synthesis by Polymer Modification. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2000; ISBN 3527306730. [Google Scholar]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calmano, W.; Hong, J.; Förstner, U. Binding and mobilization of heavy metals in contaminated sediments affected by pH and redox potential. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masson-Delmotte, V. Global Warming of 1.5 °C: An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15/ (accessed on 13 November 2021).






| Row | Column | Entire Soil Profile | Upper Soil (0–50 cm) | Subsoil (50–200 cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cor | p | Cor | p | Cor | p | ||
| Ptota | V | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.04 | −0.04 | 0.79 |
| Cr | 0.36 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.80 | |
| Fe | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.33 | 0.01 | −0.04 | 0.78 | |
| Co | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.00 | −0.01 | 0.93 | |
| Ni | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.47 | 0.00 | −0.08 | 0.59 | |
| Cu | 0.32 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 0.00 | −0.11 | 0.42 | |
| Zn | 0.37 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 0.00 | −0.11 | 0.46 | |
| As | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.06 | −0.14 | 0.31 | |
| Cd | 0.39 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 0.00 | −0.12 | 0.39 | |
| Pb | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.41 | 0.00 | −0.12 | 0.39 | |
| Ef b | 0.35 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.00 | −0.04 | 0.78 | |
| PLI c | 0.35 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 0.00 | −0.06 | 0.66 | |
| CSI d | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.49 | 0.00 | −0.03 | 0.84 | |
| RI e | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.43 | 0.00 | −0.10 | 0.46 | |
| clay | −0.01 | 0.92 | −0.09 | 0.49 | −0.07 | 0.64 | |
| silt | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.21 | −0.02 | 0.89 | |
| sand | −0.10 | 0.30 | −0.09 | 0.50 | 0.04 | 0.79 | |
| pH | −0.05 | 0.63 | −0.02 | 0.91 | 0.06 | 0.68 | |
| OM f | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.36 | 0.00 | −0.01 | 0.96 | |
| bulk density | −0.05 | 0.61 | −0.17 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.35 | |
| root density | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.02 | −0.03 | 0.85 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weber, C.J.; Hahn, J.; Opp, C. Spatial Connections between Microplastics and Heavy Metal Pollution within Floodplain Soils. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020595
Weber CJ, Hahn J, Opp C. Spatial Connections between Microplastics and Heavy Metal Pollution within Floodplain Soils. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(2):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020595
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeber, Collin J., Jens Hahn, and Christian Opp. 2022. "Spatial Connections between Microplastics and Heavy Metal Pollution within Floodplain Soils" Applied Sciences 12, no. 2: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020595
APA StyleWeber, C. J., Hahn, J., & Opp, C. (2022). Spatial Connections between Microplastics and Heavy Metal Pollution within Floodplain Soils. Applied Sciences, 12(2), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12020595