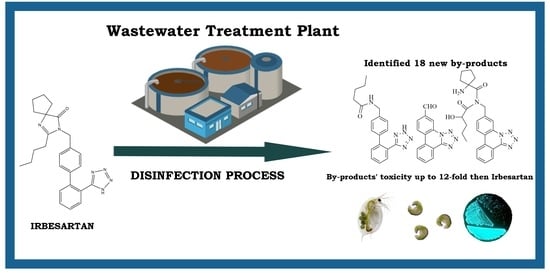
Newly Discovered Irbesartan Disinfection Byproducts via Chlorination: Investigating Potential Environmental Toxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drug and Reagents
2.2. Apparatus and Equipment
2.3. Preparative Chlorination Procedure and Product Isolation
2.4. Ecotoxicity Assays
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chlorination Experiments
3.2. Structural Elucidation
3.2.1. Structural Elucidation of DBP7
3.2.2. Structural Elucidation of DBP8
3.2.3. Structural Elucidation of DBP9
3.2.4. Structural Elucidation of DBP10
3.2.5. Structural Elucidation of DBP11
3.2.6. Structural Elucidation of DBP12
3.2.7. Structural Elucidation of DBP13
3.2.8. Structural Elucidation of DBP14
3.2.9. Structural Elucidation of DBP15
3.2.10. Structural Elucidation of DBP16
3.2.11. Structural Elucidation of DBP17
3.2.12. Structural Elucidation of DBP18
3.3. Proposed Mechanism for the Formation of Disinfection Byproducts
3.4. Ecotoxicity Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monteiro, S.C.; Boxall, A.B. Occurrence and fate of human pharmaceuticals in the environment. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 202, 53–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, A.; Meric, S.; Fatta, D. Occurrence patterns of pharmaceuticals in water and wastewater environments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenker, A.; Cicero, M.R.; Prestinaci, F.; Bottoni, P.; Carere, M. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification potential of pharmaceuticals with a focus to the aquatic environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabicova, K.; Grabic, R.; Fedorova, G.; Fick, J.; Cerveny, D.; Kolarova, J.; Turek, J.; Zlabek, V.; Randak, T. Bioaccumulation of psychoactive pharmaceuticals in fish in an effluent dominated stream. Water Res. 2017, 124, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles, L.F.; Mullen, R.A.; Huang, I.J.; Wilson, C.; Khunjar, W.; Sirotkin, H.I.; McElroy, A.E.; Aga, D.S. Assessing pharmaceutical removal and reduction in toxicity provided by advanced wastewater treatment systems. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrelli, A.; Della Greca, M.; Parolisi, A.; Iesce, M.R.; Cermola, F.; Isidori, M.; Temussi, F.; Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Passananti, M.; et al. Chemical fate and genotoxic risk associated with hypochlorite treatment of nicotine. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luongo, G.; Guida, M.; Siciliano, A.; Libralato, G.; Saviano, L.; Amoresano, A.; Previtera, L.; Di Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A. Oxidation of diclofenac in water by sodium hypochlorite: Identification of new degradation by-products and their ecotoxicological evaluation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 194, 113762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrull, J.; Colom, A.; Fabregas, J.; Borrull, F.; Pocurull, E. Presence, behaviour and removal of selected organic micropollutants through drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troger, R.; Klöckner, P.; Ahrens, L.; Wiberg, K. Micropollutants in drinking water from source to tap-Method development and application of a multiresidue screening method. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1404–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarrón, S.; Gernjak, W.; Valero, F.; Barceló, A.; Petrovic, M.; Rodríguez-Roda, I. Evaluation of emerging contaminants in a drinking water treatment plant using electrodialysis reversal technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 309, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, E.; Petrie, B.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Wolfaardt, G.M. The fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs), endocrine disrupting contaminants (EDCs), metabolites and illicit drugs in a WWTW and environmental waters. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, A.; Asner, R.; Schüssler, W.; Kopf, W.; Weiß, K.; Sengl, M.; Letzel, M. Behaviour of sartans (antihypertensive drugs) in wastewater treatment plants, their occurrence and risk for the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 10830–10839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boix, C.; Ibáñez, M.; Sancho, J.V.; Parsons, J.R.; de Voogt, P.; Hernández, F. Biotransformation of pharmaceuticals in surface water and during waste water treatment: Identification and occurrence of transformation products. J. Hazard. Mat. 2016, 302, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Olivas, F.J.; Aristegui, I.; Estan, L.; Rodicio, J.L.; Moreno, A.; Gil, V.; Ferrón, G.; Velasco, O. The KARTAN study: A postmarketing assessment of irbesartan in patients with hypertension. Clin. Ther. 2004, 26, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladhari, A.; La Mura, G.; Di Marino, C.; Di Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A. Sartans: What they are for, how they degrade, where they are found and how they transform. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 20, 100409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanucci, V.; Siciliano, A.; Guida, M.; Libralato, G.; Saviano, L.; Luongo, G.; Previtera, L.; Di Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A. Disinfection by-products and ecotoxic risk associated with hypochlorite treatment of irbesartan. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 135625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekadu, S.; Alemayehu, E.; Dewil, R.; Van der Bruggen, B. Pharmaceuticals in freshwater aquatic environments: A comparison of the african and european challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 654, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, J.; Lindberg, R.H.; Kaj, L.; Brorström-Lundén, E. Results from the swedish national screening Programme Subreport 3, Pharmaceuticals. Swed. Environ. Res. Inst. 2011, 1–22. Available online: http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:ivl:diva-2649 (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Margot, J.; Kienle, C.; Magnet, A.; Weil, M.; Rossi, L.; De Alencastro, L.F.; Abbeglen, C.; Thonney, D.; Chevre, N.; Sharer, M.; et al. Treatment of micropollutants in municipal wastewater: Ozone or powdered activated carbon? Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461, 480–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chusaksri, S.; Sutthivaiyakit, S.; Sedlak, D.L.; Sutthivaiyakit, P. Reactions of phenylurea compounds with aqueous chlorine: Implications for herbicide transformation during drinking water disinfection. J. Hazard. Mat. 2012, 209, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedner, M.; Mac Crehan, W.A. Transformation of acetaminophen by chlorination produces the toxicants 1,4-benzoquinone and N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 6341; Water Quality–Determination of the Inhibition of the Mobility of Daphnia Magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea)–Acute Toxicity Test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 8692; Water Quality—Fresh Water Algal Growth Inhibition Test with Unicellular Green Algae. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 11348-3; Water Quality-Determination of the Inhibitory Effect of Water Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio Fischeri (Luminescent bacteria Test)-Part 3: Method Using Freeze-Dried Bacteria. ISO: London, UK, 2007.
- Romanucci, V.; Siciliano, A.; Galdiero, E.; Guida, M.; Luongo, G.; Liguori, R.; Di Fabio, G.; Previtera, L.; Zarrelli, A. Disinfection byproducts and ecotoxic risk associated with hypochlorite treatment of tramadol. Molecules 2019, 24, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Liang, C.; Svendsen, S.B.; Kisielius, V.; Bester, K. Sartan blood pressure regulators in classical and biofilm wastewater treatment–Concentrations and metabolism. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpinteiro, I.; Castro, G.; Rodríguez, I.; Cela, R. Free chlorine reactions of angiotensin II receptor antagonists: Kinetics study, transformation products elucidation and in-silico ecotoxicity assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutha, V.V.S.R.N.A.K.; Guduru, S.; Kaliyaperumal, M.; Rumalla, C.S.; Maddi, S.R.; Korupolu, R.B.; Gajbhiye, S.B. Disinfection study of irbesartan: Isolation and structural elucidation of novel degradants. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 157, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.P.; Sahu, A.; Singh, S. Identification and characterization of disinfection products of irbesartan using LC–MS/TOF, MSn, on-line H/D exchange and LC–NMR. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, G.; Previtera, L.; Ladhari, A.; Di Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A. Peracetic acid vs. sodium hypochlorite: Degradation and transformation of drugs in wastewater. Molecules 2020, 25, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousaert, N.; Toto, P.; Willand, N.; Deprez, B. Efficient, protection-free Suzuki–Miyaura synthesis of ortho-biphenyltetrazoles. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 6529–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.P.; Dandala, R.; Handa, V.K.; Rao, I.V.S.; Rani, A.; Shivashankar, S.; Naidu, A. A novel approach for the conversion of primary amides into tetrazoles by using tributyltin chloride and sodium azide in the presence of DMF. Synlett 2007, 8, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Chen, B.; Jiang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cai, Z. Toxicity of 17 disinfection by-products to different trophic levels of aquatic organisms: Ecological risks and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10534–10541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasse, C.; von Gunten, U.; Sedlak, D.L. Chlorination of phenols revisited: Unexpected formation of α,β-unsaturated C4-dicarbonyl ring cleavage products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grbović, G.; Malev, O.; Dolenc, D.; Klobučar, R.S.; Cvetković, Ž.; Cvetković, B.; Trebše, P. Synthesis, characterisation and aquatic ecotoxicity of the UV filter hexyl 2-(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxybenzoyl) benzoate (DHHB) and its chlorinated by-products. Environ. Chem. 2015, 13, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, P.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K.; Huang, X. Phytoplankton in an urban river replenished by reclaimed water: Features, influential factors and simulation. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 11, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.; Bednarska, A.J.; Kramarz, P.E.; Loureiro, S.; Scheil, V.; Kudłek, J.; Holmstrup, M. Interactions between toxic chemicals and natural environmental factors. A meta-analysis and case studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3763–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siciliano, A.; Medici, A.; Guida, M.; Libralato, G.; Saviano, L.; Previtera, L.; Di Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A. Newly Discovered Irbesartan Disinfection Byproducts via Chlorination: Investigating Potential Environmental Toxicity. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148170
Siciliano A, Medici A, Guida M, Libralato G, Saviano L, Previtera L, Di Fabio G, Zarrelli A. Newly Discovered Irbesartan Disinfection Byproducts via Chlorination: Investigating Potential Environmental Toxicity. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(14):8170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148170
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiciliano, Antonietta, Antonio Medici, Marco Guida, Giovanni Libralato, Lorenzo Saviano, Lucio Previtera, Giovanni Di Fabio, and Armando Zarrelli. 2023. "Newly Discovered Irbesartan Disinfection Byproducts via Chlorination: Investigating Potential Environmental Toxicity" Applied Sciences 13, no. 14: 8170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148170
APA StyleSiciliano, A., Medici, A., Guida, M., Libralato, G., Saviano, L., Previtera, L., Di Fabio, G., & Zarrelli, A. (2023). Newly Discovered Irbesartan Disinfection Byproducts via Chlorination: Investigating Potential Environmental Toxicity. Applied Sciences, 13(14), 8170. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148170