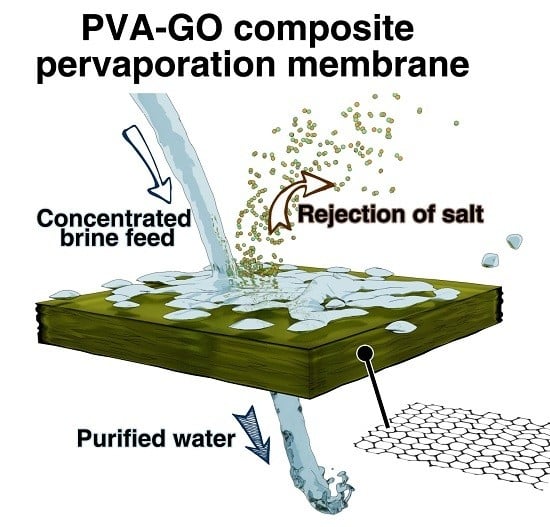
Suppressing Salt Transport through Composite Pervaporation Membranes for Brine Desalination
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Composite Membrane Preparation
2.3. Pervaporation Desalination
2.4. Membrane Characterization
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.2. Membrane Hydrophobicity/Hydrophilicity Characterization
2.4.3. Equilibrium Water Content (EWC)
2.4.4. Salt Desorption Test
2.4.5. Pore size Characterization
2.4.6. Pressurized Dead-End Filtration Test
2.4.7. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.4.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.4.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3. Results
3.1. Investigation on Cross-linking of PVA by Glutaraldehyde
3.1.1. Pervaporation Performance Using Single Salt Brine
3.1.2. Transport Mechanism of Salt
3.2. Incorporation of GO into PVA Matrix
3.2.1. Characterizations
3.2.2. Pervaporation Performance Using Single Salt Brine
3.3. Anti-Fouling Performance
3.4. Effect of Permeate Pressure on Pervaporation Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lattemann, S.; Höpner, T. Environmental impact and impact assessment of seawater desalination. Desalination 2008, 220, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariah, L.; Buckley, C.A.; Brouckaert, C.J.; Curcio, E.; Drioli, E.; Jaganyi, D.; Ramjugernath, D. Membrane distillation of concentrated brines—Role of water activities in the evaluation of driving force. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mericq, J.-P.; Laborie, S.; Cabassud, C. Vacuum membrane distillation of seawater reverse osmosis brines. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5260–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayet, M.; Matsuura, T. Pervaporation and vacuum membrane distillation processes: Modeling and experiments. AIChE J. 2004, 50, 1697–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Huang, R.Y. Pervaporation with chitosan membranes. I. Separation of water from ethylene glycol by a chitosan/polysulfone composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 116, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.D.; Oliveira, T.; Livingston, A.G.; Li, K. Membranes for the dehydration of solvents by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 5–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Kissick, K.; Ghorpade, A.; Hannah, R.; Bhattacharyya, D. Pervaporation of alcohol–water and dimethylformamide–water mixtures using hydrophilic zeolite NaA membranes: Mechanisms and experimental results. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 179, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones-Bolaños, E.; Zhou, H.; Soundararajan, R.; Otten, L. Water and solute transport in pervaporation hydrophilic membranes to reclaim contaminated water for micro-irrigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 252, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, N.; Bolto, B.; Hoang, M.; Xie, Z. Desalination by pervaporation: A review. Desalination 2016, 387, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolto, B.; Tran, T.; Hoang, M.; Xie, Z. Crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praptowidodo, V.S. Influence of swelling on water transport through pva-based membrane. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 739, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Hoang, M.; Duong, T.; Ng, D.; Dao, B.; Gray, S. Sol–gel derived poly (vinyl alcohol)/maleic acid/silica hybrid membrane for desalination by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Ng, D.; Hoang, M.; Duong, T.; Gray, S. Separation of aqueous salt solution by pervaporation through hybrid organic–inorganic membrane: Effect of operating conditions. Desalination 2011, 273, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-D.; Ren, P.-G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Ji, X.; Li, Z.-M. High barrier graphene oxide nanosheet/poly (vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite films. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 409, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Thomas, N.L. A review of the water barrier properties of polymer/clay and polymer/graphene nanocomposites. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Kundalwal, S.I.; Kumar, S. Gas barrier performance of graphene/polymer nanocomposites. Carbon 2016, 98, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, B.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.F. Enhanced hydrophilicity and salt rejection study of graphene oxide-polysulfone mixed matrix membrane. Desalination 2013, 313, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinadini, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Rahimi, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Zangeneh, H. Preparation of a novel antifouling mixed matrix pes membrane by embedding graphene oxide nanoplates. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhu, G.; Deng, B. Graphene oxide (GO) enhanced polyamide (PA) thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane for water purification. Desalination 2016, 379, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, S.; Mahmood, A.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, K.-H. Graphene oxide modified polyamide nanofiltration membrane with improved flux and antifouling properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Improving the antifouling property of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane by incorporation of isocyanate-treated graphene oxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 9084–9092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Development of novel SiO2–GO nanohybrid/polysulfone membrane with enhanced performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 451, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, F. Effect of graphene oxide concentration on the morphologies and antifouling properties of pvdf ultrafiltration membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, M.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Desalination across a graphene oxide membrane via direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2016, 378, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Deng, B. Polymer-matrix nanocomposite membranes for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Hou, J.; Chen, V.; Xu, Z.-K. Surface and interface engineering for organic–inorganic composite membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 9716–9729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, G.; Huang, K.; Jin, W.; Lee, K.-R.; Xu, N. Membranes with fast and selective gas-transport channels of laminar graphene oxide for efficient CO2 capture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 578–582. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Hou, J.; Sutrisna, P.D.; Chen, V. Shear-aligned graphene oxide laminate/pebax ultrathin composite hollow fiber membranes using a facile dip-coating approach. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 7732–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Zhan, W.; Qi, G.; Nan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lin, S.; Cao, B.; Pan, K. High performance graphene oxide/polyacrylonitrile composite pervaporation membranes for desalination applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, L. Desalination of dye solution utilizing PVA/PVDF hollow fiber composite membrane modified with TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 471, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hashaikeh, R.; Arafat, H.A. Development of eco-efficient micro-porous membranes via electrospinning and annealing of poly (lactic acid). J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Han, N.W. Effects of the degree of crosslinking on properties of poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes. Polym. J. 1993, 25, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, P.; Luo, Y. Dehydration of caprolactam–water mixtures through cross-linked pva composite pervaporation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 306, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhri, S.G.; Rajai, B.H.; Singh, P.S. Preparation of ultra-thin poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes supported on polysulfone hollow fiber and their application for production of pure water from seawater. Desalination 2015, 367, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Pan, K.; Li, L.; Giannelis, E.P.; Cao, B. High performance hydrophilic pervaporation composite membranes for water desalination. Desalination 2014, 347, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Huang, X.; Jawor, A.; Hoek, E.M. Transport, structural, and interfacial properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)–polysulfone composite nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 353, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroña, G.N.B.; Choi, M.; Jung, B. High permeate flux of PVA/PSf thin film composite nanofiltration membrane with aluminosilicate single-walled nanotubes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 386, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.H.; Chen, J.T.; Chang, C.H.; Liao, K.S.; Tung, K.L.; Price, W.E.; Yamauchi, Y.; Wu, K.C.W. A drying-free, water-based process for fabricating mixed-matrix membranes with outstanding pervaporation performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12793–12796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.; Sagle, A.C.; Freeman, B.D.; Mardel, J.I.; Hill, A.J. Characterization of sodium chloride and water transport in crosslinked poly (ethylene oxide) hydrogels. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 358, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z. Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Pervaporation Membranes for Desalination; Victoria University: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kusumocahyo, S.P.; Sano, K.; Sudoh, M.; Kensaka, M. Water permselectivity in the pervaporation of acetic acid–water mixture using crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2000, 18, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Lin, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, J.; Tsuru, T. Development of ethenylene-bridged organosilica membranes for desalination applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Ren, J.; Qiu, Y.; Li, H.; Hua, K.; Li, X.; Deng, M. Effect of graphene oxide on the behavior of poly (amide-6-b-ethylene oxide)/graphene oxide mixed-matrix membranes in the permeation process. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, B.; Lvov, Y.; Van der Bruggen, B. Oriented clay nanotube membrane assembled on microporous polymeric substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34914–34923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Prakash, J.; Pujari, P. Effects of the molecular level dispersion of graphene oxide on the free volume characteristics of poly (vinyl alcohol) and its impact on the thermal and mechanical properties of their nanocomposites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 29201–29209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loryuenyong, V.; Saewong, C.; Aranchaiya, C.; Buasri, A. The improvement in mechanical and barrier properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide packaging films. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2015, 28, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Dong, G.; Ye, Y.; Chen, V. Enzymatic degradation of bisphenol-a with immobilized laccase on tio 2 sol–gel coated pvdf membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Guo, T.; Chen, Y. Molecular-level dispersion of graphene into poly (vinyl alcohol) and effective reinforcement of their nanocomposites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2297–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Highly permeable polymer membranes containing directed channels for water purification. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Carbone, P.; Wang, F.-C.; Kravets, V.G.; Su, Y.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Wu, H.; Geim, A.K.; Nair, R.R. Precise and ultrafast molecular sieving through graphene oxide membranes. Science 2014, 343, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Kim, E.-S.; Yang, J.; Deng, B. Fabrication of a novel thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane containing MCM-41 silica nanoparticles (NPs) for water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-S.; Deng, B. Fabrication of polyamide thin-film nano-composite (PA-TFN) membrane with hydrophilized ordered mesoporous carbon (H-OMC) for water purifications. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Yoon, K.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High flux filtration medium based on nanofibrous substrate with hydrophilic nanocomposite coating. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7684–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Ji, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, G. Poly (vinyl alcohol)–graphene oxide nanohybrid “pore-filling” membrane for pervaporation of toluene/n-heptane mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Ye, Y.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. Fouling and crystallisation behaviour of superhydrophobic nano-composite pvdf membranes in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Ye, Y.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. Crystallization behavior of salts during membrane distillation with hydrophobic and superhydrophobic capillary membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 473, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Pressurized Filtration Test Results | Unit | Commercial PVDF | MR0.025 | MR0.1 | MR0.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure water flux | L/m2h | >15,000 | 240 ± 56 | 5.5 ± 0.27 | 1.4 ± 0.4 |
| Permeability | L/m2 h·bar | >1000 | 16 ± 3.5 | 0.37 ± 0.018 | 0.093 ± 0.027 |
| Average membrane resistance | m−1 | <3.9 × 1011 | ~2.5 × 1013 | ~1.1 × 1015 | 4.3 × 1015 |
| Flux using 30 g/L NaCl as the feed | L/m2h | / | 129 ± 16.5 | 3.74 ± 0.23 | 0.54 ± 0.1 |
| Salt rejection using 30 g/L NaCl as the feed | % | / | ~0 | ~9 | ~33 |
| Flux using 100 mg/L Dextran as the feed | L/m2h | / | 142 ± 21 | 4.69 ± 0.42 | 0.99 ± 0.18 |
| Rejection using 100 mg/L Dextran as the feed | % | / | ~0 | 53.9% | 83.4 |
| Composite Membrane | Surface Roughness (nm) | EWC (%) in Water | EWC (%) in 100 g/L NaCl | NaCl Diffusivity (10−6 cm2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR0.025 | 281.5 ± 7.78 | 184.5 ± 35.3 | 129.7 ± 16.8 | 2.02 ± 0.97 |
| MR0.1 | 140 ± 31.1 | 60.4 ± 5.2 | 56.6 ± 2.5 | 1.42 ± 0.36 |
| MR0.2 | 106.4 ± 13.58 | 49.6 ± 7.0 | 38.1 ± 6.3 | 0.64 ± 0.13 |
| Freestanding Films | Tg (°C) | EWC in Milli-Q Water (%) | EWC in 100 g/L NaCl (%) | NaCl Diffusivity (10−6 cm2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA only | 48 | 49.6 ± 7 | 38.1 ± 6.3 | 0.64 ± 0.13 |
| PVA0.1GO | 59 | 25.35 ± 1.41 | 28.06 ± 1.07 | 0.712 ± 0.001 |
| PVA0.2GO | 60 | 38.15 ± 2.05 | 34.98 ± 1.66 | 0.549 ± 0.066 |
| PVA0.3GO | 60 | 35.35 ± 4.37 | 30.68 ± 0.54 | 0.526 ± 0.005 |
| Operation Time (h) | Conductivity (µS/cm) | Na+ (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 19.2 | 3.7 | 0.55 | 0.00 |
| 66.5 | 78.8 | 13.6 | 0.03 |
| 116.4 | 205 | 37.1 | 0.18 |
| 164.25 | 493 | 127 | 1.07 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Hou, J.; Ye, Y.; Mansouri, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, V. Suppressing Salt Transport through Composite Pervaporation Membranes for Brine Desalination. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080856
Li L, Hou J, Ye Y, Mansouri J, Zhang Y, Chen V. Suppressing Salt Transport through Composite Pervaporation Membranes for Brine Desalination. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(8):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080856
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lin, Jingwei Hou, Yun Ye, Jaleh Mansouri, Yatao Zhang, and Vicki Chen. 2017. "Suppressing Salt Transport through Composite Pervaporation Membranes for Brine Desalination" Applied Sciences 7, no. 8: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080856
APA StyleLi, L., Hou, J., Ye, Y., Mansouri, J., Zhang, Y., & Chen, V. (2017). Suppressing Salt Transport through Composite Pervaporation Membranes for Brine Desalination. Applied Sciences, 7(8), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080856