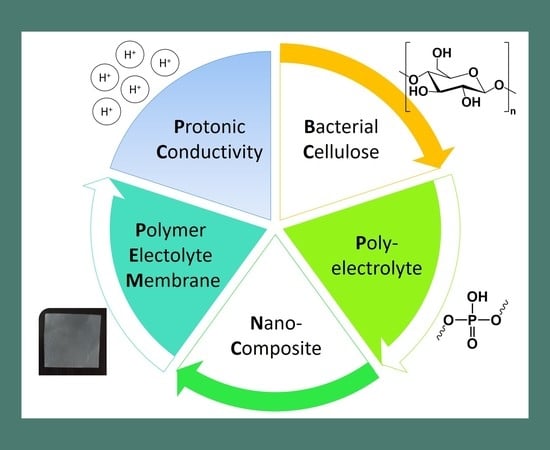
Poly(bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate)/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocomposites: Preparation, Characterization and Application as Polymer Electrolyte Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of P(bisMEP)/BC Nanocomposite Membranes
2.3. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural and Morphological Characterization
3.2. Thermal Stability
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. Water-Uptake and Ion Exchange Capacity
3.5. Protonic Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Junter, G.-A.; Lebrun, L. Cellulose-based virus-retentive filters: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 455–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargarzadeh, H.; Mariano, M.; Gopakumar, D.; Ahmad, I.; Thomas, S.; Dufresne, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, N. Advances in cellulose nanomaterials. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2151–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, J. Self-assembled cellulose materials for biomedicine: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, A.R.P.; Vilela, C.; Neto, C.P.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R. Bacterial Cellulose-Based Nanocomposites: Roadmap for Innovative Materials. In Nanocellulose Polymer Composites; Thakur, V.K., Ed.; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 17–64. [Google Scholar]
- Vilela, C.; Pinto, R.J.B.; Figueiredo, A.R.P.; Neto, C.P.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R. Development and applications of cellulose nanofibers based polymer composites. In Advanced Composite Materials: Properties and Applications; Bafekrpour, E., Ed.; De Gruyter Open: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Dufresne, A. Cellulose nanomaterials as green nanoreinforcements for polymer nanocomposites. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2018, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abitbol, T.; Rivkin, A.; Cao, Y.; Nevo, Y.; Abraham, E.; Ben-Shalom, T.; Lapidot, S.; Shoseyov, O. Nanocellulose, a tiny fiber with huge applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 39, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, C.; Engström, J.; Valente, B.F.A.; Jawerth, M.; Carlmark, A.; Freire, C.S.R. Exploiting poly(ε-caprolactone) and cellulose nanofibrils modified with latex nanoparticles for the development of biodegradable nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Chen, L.; Sisler, J.; Tam, K.C. Cellulose Nanocrystal (CNC)—Inorganic Hybrid Systems: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 864–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiniati, I.; Hrymak, A.N.; Margaritis, A. Recent developments in the production and applications of bacterial cellulose fibers and nanocrystals. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 510–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniri, M.; Moghaddam, A.B.; Azizi, S.; Rahim, R.A.; Ariff, A.B.; Saad, W.Z.; Navaderi, M.; Mohamad, R. Production and Status of Bacterial Cellulose in Biomedical Engineering. Nanomaterials 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greca, L.G.; Lehtonen, J.; Tardy, B.L.; Guo, J.; Rojas, O.J. Biofabrication of multifunctional nanocellulosic 3D structures: A facile and customizable route. Mater. Horiz. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.R.; O’Neill, H.M.; Malyvanh, V.P.; Lee, I.; Woodward, J. Palladium-bacterial cellulose membranes for fuel cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, D.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Yu, J.; Hao, Q.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Zou, Z.; Gu, J. In situ deposition of platinum nanoparticles on bacterial cellulose membranes and evaluation of PEM fuel cell performance. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 6300–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, S.; Yang, B.; Tang, T. Preparation of a carboxymethylated bacterial cellulose/polyaniline composite gel membrane and its characterization. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68599–68605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, W.; Guo, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, S. Sulfonated bacterial cellulose/polyaniline composite membrane for use as gel polymer electrolyte. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 145, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalsky, S.; Bardeau, J.F.; Makhno, S.; Babkina, N.; Tarasyuk, O.; Cherniavska, T.; Orlovska, I.; Kozyrovska, N.; Brovko, O. New proton conducting membrane based on bacterial cellulose/polyaniline nanocomposite film impregnated with guanidinium-based ionic liquid. Polymer 2018, 142, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Qiao, J.; Hong, F. Application of phosphoric acid and phytic acid-doped bacterial cellulose as novel proton-conducting membranes to PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 9182–9192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Liang, S.S.; Chen, S.W.; Lai, J.T. Sorption and transport properties of 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid-grafted bacterial cellulose membranes for fuel cell application. J. Power Sources 2013, 232, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadim, T.D.O.; Figueiredo, A.G.P.R.; Rosero-Navarro, N.C.; Vilela, C.; Gamelas, J.A.F.; Barros-Timmons, A.; Neto, C.P.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R.; Figueiredo, F.M.L. Nanostructured bacterial cellulose-poly(4-styrene sulfonic acid) composite membranes with high storage modulus and protonic conductivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7864–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, C.; Gadim, T.D.O.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R.; Figueiredo, F.M.L. Nanocellulose/poly (methacryloyloxyethyl phosphate) composites as proton separator materials. Cellulose 2016, 23, 3677–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadim, T.D.O.; Vilela, C.; Loureiro, F.J.A.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R.; Figueiredo, F.M.L. Nafion® and nanocellulose: A partnership for greener polymer electrolyte membranes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 93, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadim, T.D.O.; Loureiro, F.J.A.; Vilela, C.; Rosero-Navarro, N.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R.; Figueiredo, F.M.L. Protonic conductivity and fuel cell tests of nanocomposite membranes based on bacterial cellulose. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 233, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, C.; Sousa, N.; Pinto, R.J.B.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Figueiredo, F.M.L.; Freire, C.S.R. Exploiting poly(ionic liquids) and nanocellulose for the development of bio-based anion-exchange membranes. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 100, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zarrin, H.; Chen, Z.; Hong, F. Bacterial nanocellulose/Nafion composite membranes for low temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2015, 273, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf, O.Z.; Orhan, M.F. An overview of fuel cell technology: Fundamentals and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 32, 810–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Wu, L.; He, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ge, L.; Bakangura, E.; Xu, T. Ion exchange membranes: New developments and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 522, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovatti, E.; Serafim, L.S.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Neto, C.P. Gluconacetobacter sacchari: An efficient bacterial cellulose cell-factory. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.; Rager, T.; Noda, A.; Kreuer, K.D.; Maier, J. About the choice of the protogenic group in PEM separator materials for intermediate temperature, low humidity operation: A critical comparison of sulfonic acid, phosphonic acid and imidazole functionalized model compounds. Fuel Cells 2005, 5, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tolley, H.D.; Lee, M.L. Polymeric cation-exchange monolithic columns containing phosphoric acid functional groups for capillary liquid chromatography of peptides and proteins. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 3844–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavan, V.; Agarwal, C.; Shinde, R.N. Phosphate barrier on pore-filled cation-exchange membrane for blocking complexing ions in presence of non-complexing ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 443, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Jeong, Y.K. Synthesis and flame-retardancy of UV-curable methacryloyloxy ethyl phosphates. Fibers Polym. 2008, 9, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, E.; Manzani, D.; Messaddeq, Y.; Ribeiro, S.J.L. Bacterial Cellulose from Glucanacetobacter xylinus: Preparation, Properties and Applications. In Monomers, Polymers and Composites from Renewable Resources; Belgacem, M.N., Gandini, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 369–383. [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy, L.J. The Infrared Spectra of Complex Molecules, 3rd ed.; Chapman and Hall, Ltd.: London, UK, 1975; ISBN 0412138506. [Google Scholar]
- Lacerda, P.S.S.; Barros-Timmons, A.M.M.V.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Neto, C.P. Nanostructured Composites Obtained by ATRP Sleeving of Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers with Acrylate Polymers. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, A.D. Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 2014, 21, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Sugiyama, J.; Chanzy, H.; Langan, P. Crystal structure and hydrogen bonding system in cellulose iα from synchrotron x-ray and neutron fiber diffraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14300–14306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadsetan, M.; Giuliani, M.; Wanivenhaus, F.; Brett Runge, M.; Charlesworth, J.E.; Yaszemski, M.J. Incorporation of phosphate group modulates bone cell attachment and differentiation on oligo(polyethylene glycol) fumarate hydrogel. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Z.; Wen, L.; Cen, K. Mechanism study on cellulose pyrolysis using thermogravimetric analysis coupled with infrared spectroscopy. Front. Energy Power Eng. China 2007, 1, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Jana, S.C. Highly conductive epoxy/graphite composites for bipolar plates in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 172, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, F.; Xu, X.; Kuang, Y.; Fu, K.; Hitz, E.; Hu, L. Super-strong, super-stiff macrofibers with aligned, long bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuPontTM Nafion® PFSA Membranes. Available online: https://www.chemours.com/Nafion/en_US/assets/downloads/nafion-extrusion-cast-membranes-product-information.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2018).
- Tanpichai, S.; Quero, F.; Nogi, M.; Yano, H.; Young, R.J.; Lindström, T.; Sampson, W.W.; Eichhorn, S.J. Effective Young’s modulus of bacterial and microfibrillated cellulose fibrils in fibrous networks. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peura, M.; Grotkopp, I.; Lemke, H.; Vikkula, A.; Laine, J.; Müller, M.; Serimaa, R. Negative poisson ratio of crystalline cellulose in kraft cooked Norway spruce. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervy, M.; Santmarti, A.; Lahtinen, P.; Tammelin, T.; Lee, K.Y. Sample geometry dependency on the measured tensile properties of cellulose nanopapers. Mater. Des. 2017, 121, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero-Navarro, N.C.; Domingues, E.M.; Sousa, N.; Ferreira, P.; Figueiredo, F.M. Protonic conductivity and viscoelastic behaviour of Nafion® membranes with periodic mesoporous organosilica fillers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 5338–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero-Navarro, N.C.; Domingues, E.M.; Sousa, N.; Ferreira, P.; Figueiredo, F.M.L. Meso-structured organosilicas as fillers for Nafion® membranes. Solid State Ion. 2014, 262, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Membranes | Nominal Composition a | Measured Composition b | Thickness/µm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WbisMEP/WBC | WP(bisMEP)/WBC | WBC/Wtotal | WP(bisMEP)/Wtotal | ||
| BC | – | – | 1.0 | – | 42 ± 11 |
| P(bisMEP)/BC_1 | 3 | 0.26 | 0.79 | 0.21 | 64 ± 11 |
| P(bisMEP)/BC_2 | 5 | 1.0 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 132 ± 12 |
| Sample * | Tdi/°C | Tdmax1/°C | Tdmax2/°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| P(bisMEP) | 230 | 289 | – |
| BC | 266 | 347 | – |
| P(bisMEP)/BC_1 | 205 | 234 | 300 |
| P(bisMEP)/BC_2 | 195 | 235 | 303 |
| Membrane * | Young’s Modulus/GPa | Tensile Strength/MPa | Elongation at Break/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 10.2 ± 2.21 | 222 ± 47.0 | 4.1 ± 0.93 |
| P(bisMEP)/BC_1 | 6.22 ± 0.95 | 47.8 ± 9.4 | 0.68 ± 0.30 |
| P(bisMEP)/BC_2 | 2.68 ± 0.41 | 23.5 ± 3.3 | 1.1 ± 0.24 |
| Sample * | WU/% | IEC/mmol g−1 |
|---|---|---|
| BC | 121 ± 11 | – |
| P(bisMEP) | – | 3.5 ± 0.02 |
| P(bisMEP)/BC_1 | 79 ± 6 | 1.1 ± 0.12 |
| P(bisMEP)/BC_2 | 155 ± 8 | 3.0 ± 0.05 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vilela, C.; Martins, A.P.C.; Sousa, N.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Figueiredo, F.M.L.; Freire, C.S.R. Poly(bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate)/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocomposites: Preparation, Characterization and Application as Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071145
Vilela C, Martins APC, Sousa N, Silvestre AJD, Figueiredo FML, Freire CSR. Poly(bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate)/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocomposites: Preparation, Characterization and Application as Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(7):1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071145
Chicago/Turabian StyleVilela, Carla, Ana P. C. Martins, Nuno Sousa, Armando J. D. Silvestre, Filipe M. L. Figueiredo, and Carmen S. R. Freire. 2018. "Poly(bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate)/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocomposites: Preparation, Characterization and Application as Polymer Electrolyte Membranes" Applied Sciences 8, no. 7: 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071145
APA StyleVilela, C., Martins, A. P. C., Sousa, N., Silvestre, A. J. D., Figueiredo, F. M. L., & Freire, C. S. R. (2018). Poly(bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate)/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocomposites: Preparation, Characterization and Application as Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Applied Sciences, 8(7), 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071145