High-Precision Pseudo-Noise Ranging Based on BOC Signal: Zero-Bias Mitigation Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System Description
2.1. Signal Reception Model
2.2. Sampling Distortion: Resolution Error
2.3. Sampling Distortion: Zero-Bias
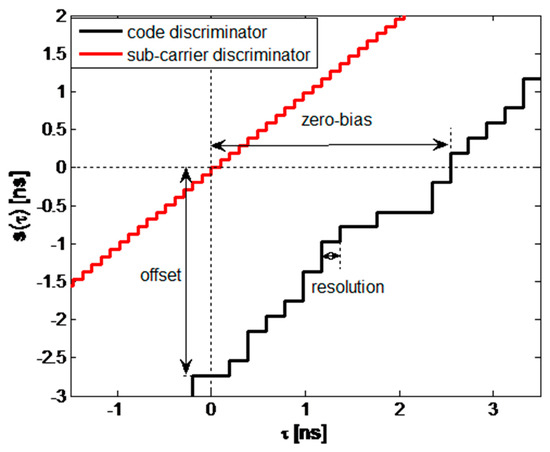
2.4. Comprehensive Analysis
3. Statistical Characteristic of Zero-Bias
3.1. Equivalent Reference Waveform Analysis
3.2. Standard Deviation of Zero-Bias
4. Zero-Bias Mitigation Method
4.1. Correlation Interval Design
4.2. Sampling Frequency Design
- (1)
- Determine specific parameters such as spreading code rate , correlator interval , and coherent integration time ;
- (2)
- Limit the range of sampling frequency to , according to the actual resource conditions;
- (3)
- Select the available noncommensurate sampling frequency , according to Formula (7);
- (4)
- Design the optimal sampling frequency to suppress zero-bias according to Equation (18).
- (5)
- For multi-system satellite navigation receivers, different spreading code rates and systems might be necessary for signal receiving [28,29,30]. In addition, in a multi-stage loop tracking design, it may be necessary to select different discrimination intervals. When multiple constraints need to be met, the above design method can still be used to select a relatively good sampling frequency.
5. Performance Simulation and Analysis
5.1. Limited Bandwidth
5.2. Doppler Frequency Shift
5.3. Thermal Noise
6. Discussion
- (1)
- When the sampling frequency of the baseband signal is limited to an equal sampling frequency, the phase resolution error of the digital discriminator is incapable to be avoided. In this case, the elimination of the influence of phase resolution error on pseudorange accuracy is inseparable from further study.
- (2)
- The article simulates the BOC (1, 1) signal, and the conclusion can be directly extended to the BOC (m, n) signal, but the applicability to the MBOC signal is still worth exploring.
- (3)
- This paper is confined to the influence of signal Doppler frequency on the statistical standard deviation of zero-bias. In the case of non-zero Doppler, the initial phase of the received signal changes continuously, and the zero-bias of the digital discriminator changes. For the phase discriminator of short-period codes, the elimination of the bias by means of the Doppler effect design algorithm is needed to be studied further.
- (4)
- When multiple signals are simultaneously transmitted in the channel, the multiple access interference has a significant impact on the high precision measurement of the pseudorange. How to quantify the impact of multiple access effects on pseudorange accuracy is still worth studying.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Betz, J.W. Binary offset carrier modulations for radio navigation. Navigation 2002, 48, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, C.J. GNSS signals—An overview. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA, 21–24 May 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Men, B. Research and progress of Beidou satellite navigation system. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2012, 55, 2899–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.; Hegarty, C. Understanding GPS: Principles and Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Zhu, X.; Li, L.; Sun, G. Band-Pass Sampling in High-Order BOC Signal Acquisition. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akos, D.M.; Pini, M. Effect of sampling frequency on GNSS receiver performance. Navigation 2006, 53, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.L. On quadrature sampling of bandpass signals. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1979, 15, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirk, K.J.; Srinivasan, M. PN code tracking using noncommensurate sampling. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2006, 54, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, C.J. Analytical model for GNSS receiver implementation losses. Navigation 2011, 58, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.T.; Shivaramaiah, N.C.; Nguyen, T.D.; Glennon, E.P.; Joon, W.C.; Dempster, A.G. Generalized theory on the effects of sampling frequency on GNSS code tracking. J. Navig. 2018, 71, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, N.; Yang, K. PN ranging based on noncommensurate sampling zero bias mitigation methods. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Yang, T. Analysis of noncommensurate sampling effects on the performance of PN code tracking loops. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Lu, M.; Feng, Z. Unambiguous sine-phased binary offset carrier modulated signal acquisition technique. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2010, 9, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Cui, X.; Lu, M.; Feng, Z.; Yang, J. Pseudo-Correlation-Function-Based Unambiguous Tracking Technique for Sine-BOC Signals. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 1782–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgart, M.S.; Blunt, P.D. Dual estimate receiver of binary offset carrier modulated signals for global navigation satellite systems. Electron. Lett. 2007, 43, 877–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lu, M. Generalized Theory of BOC Signal Unambiguous Tracking with Two Dimensional Loops. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 3056–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yao, Z.; Lu, M. Theoretical analysis of unambiguous 2-D tracking loop performance for band-limited BOC signals. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileant, A.; Million, S.; Hinedi, S.; Cheng, U. The performance of the all-digital data transition tracking loop using nonlinear analysis. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1995, 43, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirk, K.J.; Srinivasan, M. Analysis of sampling and quantization effects on the performance of PN code tracking loops. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, New York, NY, USA, 28 April–2 May 2002; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; Volume 3, pp. 1480–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, C.; Jin, Z.; Jiang, J.; Yang, W. Pseudo-noise code regeneration based on noncommensurate sampling and dynamic clock phase shifting. Electron. Lett. 2010, 46, 1126–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.T.; Shivaramaiah, N.C.; Nguyen, T.D.; Glennon, E.P.; Dempster, A.G. GNSS receiver implementations to mitigate the effects of commensurate sampling frequencies on DLL code tracking. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Z.; Jin, Z. Simple approach to determining parameters of noncommensurate sampling for optimal pseudo-noise code phase delay discrimination. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, Z.; Tang, X.; Wang, F. A Design Method of Code Correlation Reference Waveform in GNSS Based on Least-Squares Fitting. Sensors 2016, 16, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jia, W.; Ren, J.; Yao, M. Unambiguous S-curve shaping technique for multipath mitigation in cosine-boc signals. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2012, 16, 1725–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F. Double Strobe Technique for Unambiguous Tracking of TMBOC Modulated Signal in GPS. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 2204–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Tang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, G. A method of carrier phase multipath mitigation based on punctual code reference waveform. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference, Haerbin, China, 23–25 May 2018; pp. 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, D.N.; Fernando, M.G.S.; Jose, M.N.L. Gating functions for multipath mitigation in GNSS BOC signals. IEEE Trans. Aaerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borio, D.; Fantino, M.; Lo, P.L. The Impact of the Galileo Signal in Space in the Acquisition System. Signals Commun. Technol. 2006, 47, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, G.W.; Avila-Rodriguez, J.A.; Wallner, S.; Pratt, A.R.; Owen, J.; Issler, J.L.; Betz, J.W.; Hegarty, C.J.; Lenahan, L.S.; Rushanan, J.J.; et al. MBOC: The new optimized spreading modulation recommended for GALILEO L1 OS and GPS L1C. In Proceedings of the ION Position, Location, and Navigation Symposium 2006, Coronado, CA, USA, 25–27 April 2006; pp. 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Liu, W.; Sun, G. Modernization milestone: BeiDou M2-S initial signal analysis. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, J.W.; Kolodziejski, K.R. Extended theory of Early-Late code tracking for a bandlimited GPS receiver. Navigation 2000, 47, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, J.W.; Kolodziejski, K.R. Generalized theory of code tracking with an early-late discriminator Part I: Lower bound and coherent processing. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2009, 45, 1538–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, J.W.; Kolodziejski, K.R. Generalized theory of code tracking with an early-late discriminator part II: Noncoherent processing and numerical results. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2009, 45, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Notation | Definition |
|---|---|
| Baseband signal | |
| Code signal | |
| Subcarrier signal | |
| Rectangular reference signal | |
| Composite signal | |
| , , | Initial code phase |
| , , | Initial subcarrier phase |
| , | Phase estimation |
| , , , | Sampling period, chip period and subcarrier period, coherent integration time |
| , , , , | Sampling frequency, code rate, subcarrier rate, reference frequency, noncommensurate sampling frequency |
| , , , , | Frequency coefficient |
| , | Early-late correlation interval of the phase discriminator |
| , , | Correlation values corresponding to different code phases |
| , , | Correlation values corresponding to different subcarrier phases |
| , | Phase discrimination results |
| , | Phase resolution |
| , , | Zeros-bias of disrimination |
| Average number of samples of the composite waveform | |
| , , | Number of coherent integration points of the correlator, number of composite waveforms, number of non-zero composite waveforms |
| Least common multiple operation | |
| Rounding operation | |
| The maximum deviation of zero-bias | |
| The standard deviation of zero-bias |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, C.; Tang, X.; Lv, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, G. High-Precision Pseudo-Noise Ranging Based on BOC Signal: Zero-Bias Mitigation Methods. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153162
Ma C, Tang X, Lv Z, Xiao Z, Sun G. High-Precision Pseudo-Noise Ranging Based on BOC Signal: Zero-Bias Mitigation Methods. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(15):3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153162
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Chunjiang, Xiaomei Tang, Zhicheng Lv, Zhibin Xiao, and Guangfu Sun. 2019. "High-Precision Pseudo-Noise Ranging Based on BOC Signal: Zero-Bias Mitigation Methods" Applied Sciences 9, no. 15: 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153162
APA StyleMa, C., Tang, X., Lv, Z., Xiao, Z., & Sun, G. (2019). High-Precision Pseudo-Noise Ranging Based on BOC Signal: Zero-Bias Mitigation Methods. Applied Sciences, 9(15), 3162. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153162