Enhancement of the Oil Absorption Capacity of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nano Porous Fibrous Membranes Derived via a Facile Electrospinning Method
Abstract
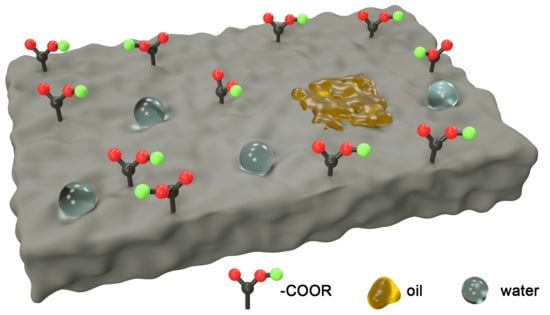
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology
3.2. Wettability
3.3. ATR-FTIR (Attenuated Total Reflection Flourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy)
3.4. Oil Absorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Short, J.W.; Rice, S.D.; Heintz, R.A.; Carls, M.G.; Moles, A. Long-term effects of crude oil on developing fish: Lessons from the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Energy Sources 2003, 25, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubansky, B.; Whitehead, A.; Miller, J.T.; Rice, C.D.; Galvez, F. Multitissue molecular, genomic, and developmental effects of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill on resident Gulf killifish (Fundulus grandis). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5074–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, B.; Caschera, D.; Federici, F.; Ingo, G.M.; Gigli, G. Superhydrophobic fabrics for oil–water separation through a diamond like carbon (DLC) coating. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 6781–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, B.; Caschera, D.; Padeletti, G.; Ingo, G.M.; Gigli, G. A brief review of surface-functionalized cotton fabrics. Surf. Innov. 2013, 1, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Tai, N.-H.; Lee, S.-B.; Kuo, W.-S. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties of graphene-based sponges fabricated using a facile dip coating method. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7908–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Sun, D.Z.; Tan, W.J.; Fan, S.H.; Wen, X.J.; Qing, G.X.; Li, S.Y.; Deng, W.-Q. Superhydrophobic conjugated microporous polymers for separation and adsorption. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2062–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, D.; Dogu, S.; Karacik, B.; Yakan, D.S.; Okay, S.O. Evaluation of butyl rubber as sorbent material for the removal of oil and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from seawater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acatay, K.; Simsek, E.; Ow-Yang, C.; Menceloglu, Y.Z. Tunable, superhydrophobically stable polymeric surfaces by electrospinning. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5210–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, Y.; Ding, B.; Shiratori, S. Fabrication of a silver-ragwort-leaf-like super-hydrophobic micro/nanoporous fibrous mat surface by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.-Z.; Wei, H.-M.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Han, G.-Z.; Pan, C.; Zhang, H.; Tian, X.-J.; Chen, Z.-M. Artificial silver ragwort surface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 201915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.; Montero, G.A.; Habibi, Y. Electrospun nanocomposites from polystyrene loaded with cellulose nanowhiskers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Hill, R.M.; Lowery, J.L.; Fridrikh, S.V.; Rutledge, G.C. Electrospun Poly(Styrene-block-dimethylsiloxane) Block Copolymer Fibers Exhibiting Superhydrophobicity. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5549–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Fei, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Hong, X. Preparation of a durable superhydrophobic membrane by electrospinning poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) mixed with epoxy–siloxane modified SiO2 nanoparticles: A possible route to superhydrophobic surfaces with low water sliding angle and high water contact angle. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 380–388. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeter, M.; Wildemann, B.; Lendlein, A. Ch. 20, Biodegradable Materials. In Regenerative Medicine: From Protocol to Patient; Steinhoff, G., Ed.; Springer Science+Business Media B.V.: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 469–492. [Google Scholar]
- Sawalha, H.; Schroen, K.; Boom, R. Biodegradable polymeric microcapsules: Preparation and properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 169, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Zhou, B.; Jiao, K.; Qian, X.; Xu, Z.; Teng, K.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Jiao, Y. Switchable hydrophobic/hydrophilic surface of electrospun poly(L-lactide) membranes obtained by CF4microwave plasma treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 327, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, W.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Preparation of chitosan/PLA blend micro/nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 658–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, W. Fabrication of polylactide/poly (ecaprolactone) blend fibers by electrospinning: Morphology and orientation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 3682–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, D. Electrospinning of nanofibers and the charge injection method. In Nanofibers and Nanotechnology in Textiles; Brown, P.J., Stevens, K., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Electrospun porous structure fibrous film with high oil adsorption capacity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.A.; Halligan, J.E.; Johnson, R.F. Oil Slick Removal Using Matrices of Polypropylene Filaments. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1972, 11, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popelka, S.; Machova, L.; Rypacek, F. Adsorption of poly (ethylene oxide)–block–polylactide copolymers on polylactide as studied by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 308, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Koelling, K.W.; Chalmers, J.J. Characterization of the Degradation of Polylactic Acid Polymer in a solid substrate environment. Biotechnol. Prog. 1998, 14, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-L.; Wu, Z.-H.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.-B. Thermal and mechanical properties of chemical crosslinked polylactide (PLA). Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhao, L.L.; Li, P.; Sun, H.X.; Li, S. Electrospun polystyrene/polyacrylonitrile fiber with high oil sorption capacity. J. Reinf. Plast. Compd. 2014, 33, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.F.; Manjrekar, T.G.; Halligan, J.E. Removal of oil from water surfaces by sorption on unstructured fibers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1973, 7, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.T.; Qiu, S.S.; Jiang, W.; Wu, D.X.; Zhang, C.Y. Evaluation of electrospun polyvinyl chloride/polystyrene fibers as sorbent materials for oil spill cleanup. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4527–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, R.; Das, R.; Gulec, S.; Liu, J.; N’guessan, H.E.; Shah, M.; Wasnik, P.S.; Yadav, S.B. Solid-Liquid Work of Adhesion. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3594–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, R.; Pepper, K.G. Interfacial tension and spreading coefficient for thin films. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3185–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Type | Viscosity/(mPa·s) |
|---|---|
| Vacuum pump oil | 27.20 |
| Peanut oil | 32.40 |
| Diesel oil | 79.10 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, J.-W.; Prasad, G.; Wang, S.-C.; Wu, J.-L.; Lu, S.-G. Enhancement of the Oil Absorption Capacity of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nano Porous Fibrous Membranes Derived via a Facile Electrospinning Method. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9051014
Liang J-W, Prasad G, Wang S-C, Wu J-L, Lu S-G. Enhancement of the Oil Absorption Capacity of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nano Porous Fibrous Membranes Derived via a Facile Electrospinning Method. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(5):1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9051014
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Jun-Wei, Gajula Prasad, Shi-Cai Wang, Jia-Lin Wu, and Sheng-Guo Lu. 2019. "Enhancement of the Oil Absorption Capacity of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nano Porous Fibrous Membranes Derived via a Facile Electrospinning Method" Applied Sciences 9, no. 5: 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9051014
APA StyleLiang, J. -W., Prasad, G., Wang, S. -C., Wu, J. -L., & Lu, S. -G. (2019). Enhancement of the Oil Absorption Capacity of Poly(Lactic Acid) Nano Porous Fibrous Membranes Derived via a Facile Electrospinning Method. Applied Sciences, 9(5), 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9051014